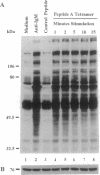
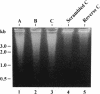
Abstract
Peptide ligands for the antigen binding site of the surface immunoglobulin receptor of a human B-cell lymphoma cell line were identified with the use of filamentous phage libraries displaying random 8- and 12-amino acid peptides. Corresponding synthetic peptides bound specifically to the antigen binding site of this immunoglobulin receptor and blocked the binding of an anti-idiotype antibody. The ligands, when conjugated to form dimers or tetramers, induced cell death by apoptosis in vitro with an IC50 between 40 and 200 nM. This effect was associated with specific stimulation of intracellular protein tyrosine phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett R. W., Cwirla S. E., Ackerman M. S., Olson A. M., Peters E. A., Dower W. J. Selective enrichment and characterization of high affinity ligands from collections of random peptides on filamentous phage. Anal Biochem. 1992 Aug 1;204(2):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Sefton B. M. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is induced in murine B lymphocytes in response to stimulation with anti-immunoglobulin. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2125–2131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll W. L., Link M. P., Cleary M. L., Bologna S., Carswell C., Amylon M. D., Smith S. D., Levy R. Idiotype as a tumor-specific marker in childhood B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):1068–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull M. G., Miller J. F., Schatz P. J. Screening for receptor ligands using large libraries of peptides linked to the C terminus of the lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1865–1869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cwirla S. E., Peters E. A., Barrett R. W., Dower W. J. Peptides on phage: a vast library of peptides for identifying ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6378–6382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L. Tyrosine phosphorylation and the mechanism of signal transduction by the B-lymphocyte antigen receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Dec 1;210(2):381–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin J. J., Panganiban L. C., Devlin P. E. Random peptide libraries: a source of specific protein binding molecules. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):404–406. doi: 10.1126/science.2143033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. F., Cho E. A., Goldman J., Carmack C. E., Besa E. C., Hardy R. R., Silberstein L. E. The role of clonal selection in the pathogenesis of an autoreactive human B cell lymphoma. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):525–537. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Law D. A., DeFranco A. L. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by the B-lymphocyte antigen receptor. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):810–813. doi: 10.1038/345810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht B. K., Epstein A. L., Berger C. S., Kaplan H. S., Hecht F. Histiocytic lymphoma cell lines: immunologic and cytogenetic studies. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1985 Jan 15;14(3-4):205–218. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(85)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwak L. W., Campbell M. J., Czerwinski D. K., Hart S., Miller R. A., Levy R. Induction of immune responses in patients with B-cell lymphoma against the surface-immunoglobulin idiotype expressed by their tumors. N Engl J Med. 1992 Oct 22;327(17):1209–1215. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199210223271705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. S., Salmon S. E., Hersh E. M., Hruby V. J., Kazmierski W. M., Knapp R. J. A new type of synthetic peptide library for identifying ligand-binding activity. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):82–84. doi: 10.1038/354082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowman H. B., Bass S. H., Simpson N., Wells J. A. Selecting high-affinity binding proteins by monovalent phage display. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 12;30(45):10832–10838. doi: 10.1021/bi00109a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Maloney D. G., Warnke R., Levy R. Treatment of B-cell lymphoma with monoclonal anti-idiotype antibody. N Engl J Med. 1982 Mar 4;306(9):517–522. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198203043060906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennell C. A., Scott D. W. Lymphoma models for B cell activation and tolerance. IV. Growth inhibition by anti-Ig of CH31 and CH33 B lymphoma cells. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1577–1581. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick M. R., Nguyen V. Q., Levy S. Anti-TAPA-1 antibodies induce protein tyrosine phosphorylation that is prevented by increasing intracellular thiol levels. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 15;151(4):1918–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Wolf I. G., Negrin R. S., Kiem H. P., Blume K. G., Weissman I. L. Use of a SCID mouse/human lymphoma model to evaluate cytokine-induced killer cells with potent antitumor cell activity. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):139–149. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. K., Smith G. P. Searching for peptide ligands with an epitope library. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):386–390. doi: 10.1126/science.1696028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweeddale M. E., Lim B., Jamal N., Robinson J., Zalcberg J., Lockwood G., Minden M. D., Messner H. A. The presence of clonogenic cells in high-grade malignant lymphoma: a prognostic factor. Blood. 1987 May;69(5):1307–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udhayakumar V., Kumar L., Subbarao B. The influence of avidity on signaling murine B lymphocytes with monoclonal anti-IgM antibodies. Effects of B cell proliferation versus growth inhibition (tolerance) of an immature B cell lymphoma. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4120–4129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuist W. M., Levy R., Maloney D. G. Lymphoma regression induced by monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibodies correlates with their ability to induce Ig signal transduction and is not prevented by tumor expression of high levels of bcl-2 protein. Blood. 1994 Feb 15;83(4):899–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A., Lee J. E., Link M. P., Smith S. D., Carroll W., Levy R., Clayberger C., Krensky A. M. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for self tumor immunoglobulin express T cell receptor delta chain. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1557–1564. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]