Abstract
Background
Lysinibacillus sphaericus (formerly named Bacillus sphaericus) is incapable of polysaccharide utilization and some isolates produce active insecticidal proteins against mosquito larvae. Its taxonomic status was changed to the genus Lysinibacillus in 2007 with some other organisms previously regarded as members of Bacillus. However, this classification is mainly based on physiology and phenotype and there is limited genomic information to support it.
Results
In this study, four genomes of L. sphaericus were sequenced and compared with those of 24 representative strains belonging to Lysinibacillus and Bacillus. The results show that Lysinibacillus strains are phylogenetically related based on the genome sequences and composition of core genes. Comparison of gene function indicates the major difference between Lysinibacillus and the two Bacillus species is related to metabolism and cell wall/membrane biogenesis. Although L. sphaericus mosquitocidal isolates are highly conserved, other Lysinibacillus strains display a large heterogeneity. It was observed that mosquitocidal toxin genes in L. sphaericus were in close proximity to genome islands (GIs) and mobile genetic elements (MGEs). Furthermore, different copies and varying genomic location of the GIs containing binA/binB was observed amongst the different isolates. In addition, a plasmid highly similar to pBsph, but lacking the GI containing binA/binB, was found in L. sphaericus SSII-1.
Conclusions
Our results confirm the taxonomy of the new genus Lysinibacillus at the genome level and suggest a new species for mosquito-toxic L. sphaericus. Based on our findings, we hypothesize that (1) Lysinibacillus strains evolved from a common ancestor and the mosquitocidal L. sphaericus toxin genes were acquired by horizontal gene transfer (HGT), and (2) capture and loss of plasmids occurs in the population, which plays an important role in the transmission of binA/binB.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12864-015-1359-x) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keyword: Lysinibacillus, Bacillus, Lysinibacillus sphaericus, Genome, Phylogeny
Background
Lysinibacillus sphaericus (formerly named Bacillus sphaericus) is a Gram-positive, aerobic, mesophilic, and spore-forming bacterium that is commonly isolated from soil. It is also an archaic organism whose spores have even been found in 25–40-million-year-old amber [1]. L. sphaericus has very distinctive phenotypic properties, including an inability to utilize polysaccharide pathways and employment of exclusive metabolic pathways for synthesis of a wide variety of organic compounds and amino acids [2]. Some strains produce active insecticidal proteins against mosquito larvae, and thus have been widely used as biocontrol agents for disease-transmitting mosquitoes [3]. The mosquitocidal properties are associated with the sporulation-specific binary toxin (Bin proteins) and vegetative-specific Mtx toxins [4], as well as a novel two-component toxin (Cry48 and Cry49 proteins) produced during sporulation [5]. Compared with another mosquito pathogen, Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis, L. sphaericus demonstrates a higher efficiency for killing mosquito larvae and a better persistence in the field [6].
The evolutionary model and systematic classification of L. sphaericus continues to be debated. On the basis of flagellar agglutination, L. sphaericus isolates can be grouped into 49 serotypes [7]. According to DNA homology between strains, five major groups (I to V) are indicated, each probably corresponding to a separate species because of the relatively low level of homology between groups [8]. However, relatively few biochemical and morphological tests are available to distinguish L. sphaericus as a different species. Recently, a multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) study has indicated that the mosquitocidal strains are highly conserved and appear near-clonal [9]. This is consistent with a previous report which observed that toxic L. sphaericus strains are all found within DNA subgroup IIA, although in association with nine serotypes (H1, H2, H3, H5, H6, H9, H25, H26, and H48).
In 2007, Bacillus sphaericus was formally renamed L. sphaericus and, together with Lysinibacillus boronitolerans and Lysinibacillus fusiformis (formerly named Bacillus fusiformis), was proposed to belong to a novel genus named Lysinibacillus gen. nov. Since then, more and more novel isolates have been assigned to Lysinibacillus. The species classification was mainly based on common features in physiology and phenotype, e.g. Gram-positive, spore-forming, rod-shaped, motile, presence of the Lys–Asp type of peptidoglycan in the cell wall, the main fatty acids as iso-C15: 0, and the predominant menaquinones as MK-7 [10], but there is little evidence to support this classification on a genomic basis. Thus, there is a need to analyze the relationship between Lysinibacillus and Bacillus on the genomic level, and to understand the evolution of mosquitocidal L. sphaericus.
Although a broad spectrum of data has been collected for L. sphaericus, there is limited genome sequence available. One complete genome sequence is available for mosquitocidal strain C3-41 (accession numbers CP000817 and CP000818) [11], and two gapped genome sequences from reference strains KCTC 3346 (or ATCC14577) and OT4b.31(both non-toxic) have also been published [12,13]. In this study we report genome sequences of four L. sphaericus strains, comprising three toxic strains (2297, LP1-G, SSII-1) and one non-toxic strain (NRS1693). We also investigate their phylogenetic relationship with genome sequences for Lysinibacillus and Bacillus strains. Our results provide the first support for the taxonomy of the reassigned new genus Lysinibacillus at the genome level and suggest a new species for mosquitocidal L. sphaericus, providing new insight into the evolution of Lysinibacillus.
Results
General features
The whole genomes of L. sphaericus 2297, LP1-G, SSII-1 and NRS1693 were sequenced and assembled into 278, 143, 138 and 546 contigs, respectively. An additional 24 genome sequences were selected for comparison to create a final dataset of 28 genomes; 10 came from Lysinibacillus (seven L. sphaericus, two L. fusiformis and one L. boronitolerans), one from Lysinibacillus-related strain Bacillus sp. NRRL B-14905 [11], and 17 from the B. cereus group and B. subtilis. The characteristics of all these genomes are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Strains and genome information used in this study
| Strain | Status | Genome size (bp) | GC content (%) | No. of contigs | No. of proteins | Genbank accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. subtilis | ||||||
| QB928 | complete | 4,146,839 | 43.60 | - | 4,031 | NC_018520 |
| BAB-1 | complete | 4,021,944 | 43.89 | - | 4,003 | NC_020832 |
| BSn5 | complete | 4,093,599 | 43.84 | - | 4,145 | NC_014976 |
| 168 | complete | 4,215,606 | 43.91 | - | 4,003 | NC_000964 |
| 6051-HGW | complete | 4,215,610 | 43.51 | - | 4,187 | NC_020507 |
| B. thuringiensis | ||||||
| BMB171 | complete | 5,330,088 | 35.17 | - | 5,352 | NC_014171 |
| Al Hakam | complete | 5,257,091 | 35.43 | - | 4,798 | NC_008600 |
| IBL 200 | draft | 6,731,790 | 34.53 | 2 | 6,693 | NZ_CM000758 |
| HD-789 | complete | 5,495,278 | 35.17 | - | 6,462 | NC_018508 |
| Bt407 | complete | 5,500,501 | 35.02 | - | 6,402 | NC_018877 |
| B. anthracis | ||||||
| Ames | complete | 5,227,293 | 35.38 | - | 5,039 | NC_003997 |
| B. cereus | ||||||
| ATCC 14579 | complete | 5,411,809 | 35.29 | - | 5,231 | NC_004722 |
| AH187 | complete | 5,269,030 | 35.51 | - | 5,783 | NC_011658 |
| E33L | complete | 5,300,915 | 35.13 | - | 5,641 | NC_006274 |
| 03BB102 | complete | 5,269,628 | 35.33 | - | 5,606 | NC_012472 |
| AH820 | complete | 5,302,683 | 35.31 | - | 5,810 | NC_011773 |
| biovar anthracis str. CI | complete | 5,196,054 | 35.25 | - | 5,558 | NC_014335 |
| L. sphaericus | ||||||
| C3-41 | complete | 4,639,821 | 37.13 | - | 4,584 (4,584)* | NC_010382 |
| 2297 | draft | 4,525,834 | 37.12 | 278 | 4,539 (4,102)* | JPDJ00000000 |
| LP1-G | draft | 4,542,839 | 37.20 | 143 | 4,630 (4,086)* | JPDL00000000 |
| SSII-1 | draft | 4,651,985 | 37.01 | 138 | 4,701 (4,202)* | JPDK00000000 |
| NRS1693 | draft | 4,640,690 | 37.55 | 546 | 4,645 (3,817)* | JPDM00000000 |
| KCTC 3346 | draft | 4,560,870 | 37.10 | 83 | 4,443 (2,791)* | AUOZ00000000 |
| OT4b.31 | draft | 4,856,302 | 37.51 | 94 | 4,575 (3,074)* | AQPX00000000 |
| L. fusiformis | ||||||
| ZB2 | draft | 4,550,616 | 37.31 | 59 | 4,494 | AMQZ00000000 |
| ZC1 | draft | 4,649,417 | 37.30 | 113 | 4,729 | ADJR00000000 |
| L. boronitoleransF1182 | draft | 4,461,358 | 37.49 | 309 | 5,270 | AJXM00000000 |
| Bacillus sp. NRRL B-14905 | draft | 4,497,271 | 37.56 | 99 | 4,470 | NZ_AAXV00000000 |
*Number of predicted genes matched with those of L. sphaericus C3-41 genome.
The total genome sizes vary from 4.0 to 6.7 Mb across species and strains. All Lysinibacillus strains have larger chromosome sizes (4.5 ~ 4.8 M) compared to B. subtilis (4.0 ~ 4.2 M) but smaller sizes compared to B. cereus group strains (5.2 ~ 6.7 M). Conversely, their G + C content (~37%) is higher than that of B. cereus group strains (~35%) but lower than that of B. subtilis (~43%).
The numbers of predicted genes in L. sphaericus genomes varied from 4,470 to 4,701, but is likely a factor of incomplete genome assemblies as well as individual strain differences. With C3-41 as a reference, the predicted gene numbers of other L. sphaericus strains varied from 2,791 to 4,202, corresponding to 62.8 to 90.4% of the total gene numbers of the individual genome. The novel strains presented in this study (2297, LP1-G, SSII-1 and NRS1693) harbor over 80% genes predicted to be homologous to genes in C3-41, whereas the corresponding numbers in the two L. sphaericus reference strains KCTC3346 and OT4b.31 were only 62.8% and 65.4% respectively.
Phylogenetic relationship
The Gegenees software package [14] was used for the comparative analysis of the gene content of the 28 genomes. The software resolves each genome into a series of overlapping fragments and then performs pairwise comparison of each fragmented genome. In this way, a distance matrix based on shared fragments is created. A heatmap of the calculated similarity matrix is shown in Figure 1. A number of genomes are well clustered, in particular the toxic isolates of L. sphaericus are highly conserved with >97% conservation between 2297, LP1-G, SSII-1 and C3-41 (green square towards the top left of the heat map in Figure 1), and clearly distinct from the non-toxic L. sphaericus isolates NRS1693, KCTC_3346 and OT4b.31 (extreme top right in the heatmap). The marine Bacillus spp. NRRL B-14905 isolate showed 79.5% similarity with the toxic isolates and 55-62% similarity with the non-toxic strains. This suggests that this marine strain has a taxonomic status that is somewhere between the toxic and non-toxic strains, but closer to the former. In addition, L. fusiformis and L. boronitolerans are related with a similarity of 84%.
Figure 1.
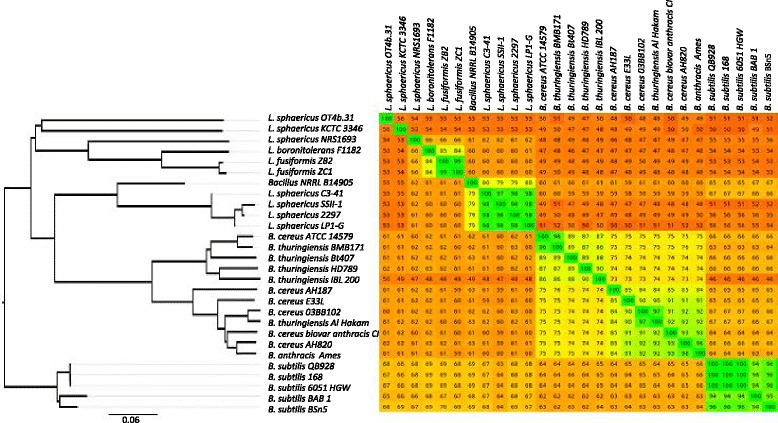
Gegenees analysis of genome composition of 28 genome sequences (10 Lysinibacillus , one from Lysinibacillus -related strain Bacillus sp. NRRL B-14905, and 17 from B. cereus group and B. subtilis, See Table 1 for full details). Right: heat map showing pairwise comparison of each genome pair based on similarity of fragments generated by sliding window. Plot colors reflect the similarity, ranging from low (red) to high (green). The heatmap is asymmetric because the contents of genomes differ in sizes and a similarity is calculated as a fraction of similar sequences in each genome. Left: SplitsTree dendrogram using the Nexus file exported from Gegenees. The toxic L. sphaericus strains form a single well defined tight cluster in both the heatmap and the dendogram (green square towards the top left of heatmap), and are distinct from other strains. The scale bar represents a 6% difference in average BLASTN score similarity.
Based on the distance matrix Nexus file exported from Gegenees, a dendrogram was produced using SplitsTree 4 (using the neighbor joining method) (Figure 1 left). The tree classifies all Lysinibacillus genomes into two main clusters. The L. sphaericus toxic isolates and the marine Bacillus spp. NRRL B-14905 are clustered and closer to B. cereus group strains, whereas the three non-toxic L. sphaericus strains are clustered with L. fusiformis and L. boronitolerans. Thus the L. sphaericus strains are diverse and scattered at the genomic level.
In addition, the genomes of Solibacillus silvestris [GenBank: NC_018065], Sporosarcina pasteurii [GenBank: AYOX00000000], and Ureibacillus thermosphaericus [GenBank: AJIK00000000], which are thought to be sphaericus-like organisms close to L. sphaericus based on 16 s rDNA and phenotypic analysis [15] were investigated. The results showed that these sphaericus-like organisms were quite divergent at the genome level and there is no obvious relationship with Lysnibacillus and Bacillus (data not shown).
Core conserved genes consensus tree
As a second estimate of the evolutionary relationship amongst the selected genomes, 55 core genes identified by BLAST analysis (e-value ≤ 1e-10, identity ≥ 0.75, coverage ≥ 0.75) (See Additional file 1: Table S1) were used to generate a consensus phylogenetic tree using the NJ method (Figure 2). Consistent with the previous results, all the 10 Lysinibacillus strains and Bacillus spp. NRRL B-14905 were grouped into one cluster, and the toxic L. sphaericus strains and L. fusiformis and L. boronitolerans each formed well supported subclusters. However, the non-toxic L. sphaericus strains fail to cluster and are scattered within the Lysinibacillus clade.
Figure 2.
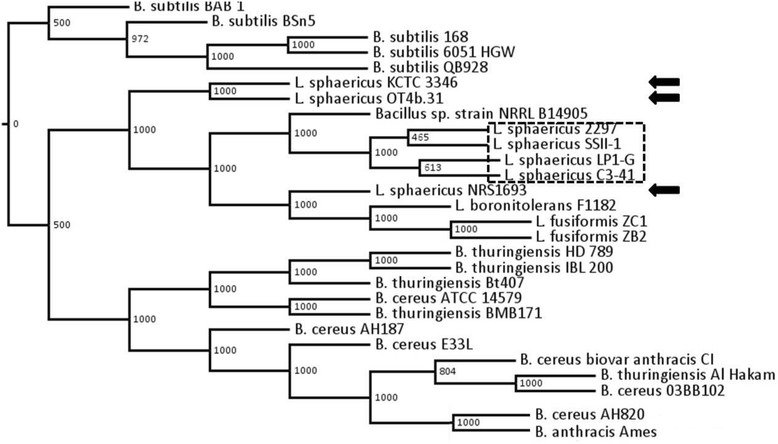
Neighbour-joining tree showing the phylogenetic relationships among 28 strains. NJ tree is based on 55 core genes present in all genomes. The genomes are grouped into three main clusters (1) 10 Lysinibacillus strains and one Bacillus spp, (2) B. subtilis and (3) B. cereus group. Within the Lysinibacillus / Bacillus spp cluster, the toxic L. sphaericus strains form a single well defined tight cluster (marked with box with dotted line) whereas the non toxic strains (marked with arrows) are less well defined. Support for clades was assessed using 1,000 bootstraps.
Gene content of pan- and core genomes
To gain further insight into the relationship between the members of Lysinibacillus and Bacillus, the pan- and core genomes, which provides a measure for the intra-species variation in gene content, were each calculated using the PanGP software package [16,17]. Since the results above indicate that the B. cereus group and B. subtilis are not closely related, their pan- and core genomes were estimated individually. The resulting plots are shown in Figure 3 and highlight the differences amongst these three groups. The largest difference between the pan- and core genome is seen in Lysinibacillus, with the largest pan-genome (12,365) and the smallest core genome (2,113), indicating the high diversity of the genome set. The B. cereus group contains 12 genomes and shows the largest gene number (4,736 ~ 6,693), but possesses a smaller pan-genome (11,069) and larger core genome (3,030) compared to Lysinibacillus. The B. subtilis genomes displays the smallest difference between pan (4,666) and core genome (3,387).
Figure 3.
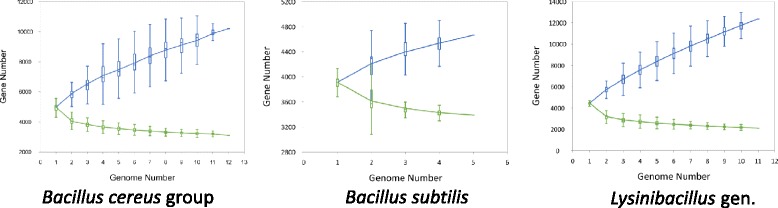
Pan- and core genome plots. (a) B. cereus group, (b) B. subtilis and (c) Lysinibacillus genomes. The blue (upper) and green (lower) curves represent pan- and core genomes respectively. Each pan- or core genome was identified using permutations of strains of each species.
In the pan-genomes, the shared genes between Lysinibacillus and the B. cereus group (1,693) is greater than the number of genes shared between Lysnibacillus and B. subtilis (1,307) or between B. cereus group and B. subtilis (1,675). For the core genome, the shared genes between B. cereus group and B. subtilis (1, 304) is much more than between Lyninibacillus and the other two Bacillus species (815 and 873, respectively) (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
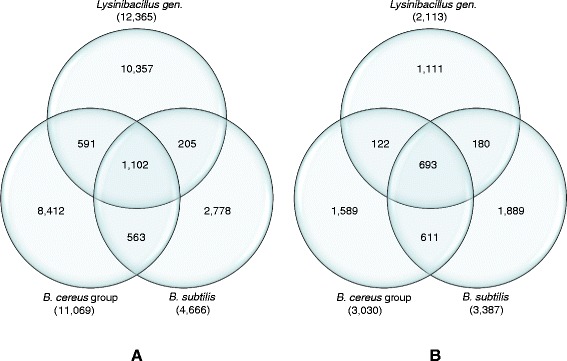
Overlap and differences of pan and core genomes amongst the full genome set. Venn diagrams show the overlap and difference between the (A) pan-genome and (B) core genome amongst Lysinibacillus, B. cereus group and B. subtilis.
Function features of the pan- and core genomes
To investigate the functional characteristics of the pan and core genomes, the COG (Clusters of Orthologous Groups) database was used to investigate the distribution of pan and core proteins mapping to each COG category for each species group. A plot of protein proportion versus COG function by species/group is shown in Figure 5. The primary differences are observed in COG categories related to metabolism. For category G (carbohydrate transport and metabolism) the pan- and core genomes sort by protein proportion in the order B. subtilis > B. cereus group > Lysinibacillus. Conversely, for category E (amino acid transport and metabolism) the order is reversed, with the largest proportion observed in Lysinibacillus, followed by the B. cereus and B. subtilis. For the remaining classifications, the distributions of category C (Energy production and conservation), F (Nucleotide transport and metabolism), H (Coenzyme transport and metabolism), and Q (Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism) both the pan- and in the core genomes of Lysinibacillus, were observed to be similar to those of the B. cereus group, but different to B. subtilis. A shift was observed within a genus or species for the core genome compared to the pan genome with a slight overrepresentation of COG categories related to metabolism, except G, Q (Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism), and P (Inorganic ion transport and metabolism). This indicates that the gene content for metabolism of amino acids, nucleotides, coenzymes, and lipids is more conserved than for carbohydrates, secondary metabolites and inorganic ions.
Figure 5.
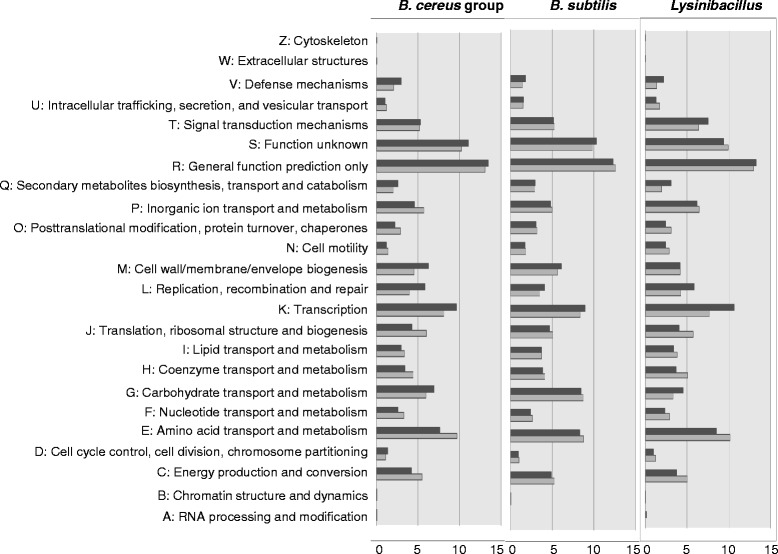
Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COG) analysis of pan- and core genomes of Lysinibacillus , B. cereus group and B. subtilis . COG grouping was determined according to NCBI annotation of identified proteins. Dark bars indicate the proportions of the orthologous genes assigned by COG category in the pan-genomes, and gray bars indicate corresponding proportions in the core genomes.
Differences in the distribution of the COG categories involved in cellular process and signaling were also observed. For instance, Lysinibacillus displays larger proportions for category T (Signal transduction mechanisms) and N (Cell motility) both in the pan- and in the core genome compared to the B. cereus group and B. subtilis. Also, Lysinibacillus harbors the smallest distribution of category M (Cell wall/membrane biogenesis) features, which is almost identical in its pan- and core genome, whereas a shift was observed in B. cereus group and in B. subtilis, with a slight overrepresentation in the pan genome compared to the core genome.
A subset of COG proteins that were unique in both the pan and core genome of Lysinibacillus were also identified (Additional file 2: Table S2) which is probably related to species-specific characteristics. For instance, six proteins were related to ethanolamine utilization, two proteins were associated with the carbon dioxide concentrating mechanism, six were involved in cobalamin (vitamin B12) biosynthesis, one was related with the cell mobility and one with chromosome segregation.
Characterization of gene contents of Lysinibacillus strains
Pairwise comparison of the genomes of all the Lysinibacillus strains indicate a strong syntenic relationship with L. sphaericus C3-41 (Additional file 3: Figure S1), indicating that Lysinibacillus strains may have shared a common “chromosome backbone” in a very ancient stage.
The unique genes in the 11 Lysinibacillus strains, varying from 34 to 711, were COG categorized (data not shown), and appear to reflect observed functional diversity for each strain. For instance, OT4b.31 displayed a large number of unique genes encoding proteins which may be related to its tolerance for heavy-metals, e.g. Co/Zn/Cd/Mg/Ni cation transporters (6 genes), metal-dependent hydrolases (3 genes), membrane proteins related to metalloendopeptidases (3 genes), Zinc metalloprotease, Mn-containing catalase, Fe-S cluster formation, and other related Oxidoreductases. KTCC 3346 contained 19 unique genes related to cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis, which may be associated with its ability to produce specific surface layer proteins [18-20]. It was also interesting that a gene homologous to the virion core protein of lumpy skin disease virus was identified in the marine strain Bacillus sp. B14905. In addition, genes encoding unique bacteriophage related proteins were identified in L. sphaericus 2297 (4), C3-41 (3), SSII-1 (4), OT4b.31 (11), and KCTC 3346 (7), indicating the presence of different bacteriophage(s) or prophage remnants. However, it should be noted that these data are not exact since, with the exception of C3-41, the genomes are not completely sequenced.
A previous study showed that many strains of L. sphaericus produce restriction endonucleases which could form a barrier to genetic manipulation [21]. The restriction enzymes and DNA methyltransferases (R-M systems) of the 11 Lysnibacillus strains were predicted by REBASE (http://rebase.neb.com). The result showed that the R-M systems in the L. sphaericus strains all belong to type II. C3-41 has the most abundant genes encoding DNA methyltransferases, with three on the chromosome and three on the plasmid pBsph, whereas 2297 and OT4b.31 only have one.
Evolution of mosquitocidal L. sphaericus
10 genomic islands (GIs) were predicted in the chromosome genome of L. sphaericus C3-41 (Table 2, Figure 6), which are mainly located in the most hypervariable regions of the genome, and carry mobile genetic elements (MGEs), such as prophages and transposons, suggesting that these regions are associated with horizontal gene transfer (HGT). It was observed that all the mosquitocidal toxin genes are within (e.g. mtx2/mtx3 and binA/binB), or close to (e.g. mtx1) the GIs; furthermore, these toxin genes are flanked by MGEs as previously described [11]. Thus, one possibility is that these mosquitocidal toxin genes were transferred to the common ancestor of L. sphaericus through HGT. GI7 (ca. 35 kb) consists of binary toxin genes binA and binB, which is the primary genetic basis of the mosquitocidal activity of L. sphaericus; this GI was present in C3-41, 2297 and LP1-G. A previous study showed that there are two copies of GI7 in L. sphaericus C3-41, present in both the chromosome and pBsph [11]. However, only one copy of GI7 was found in 2297 and LP1-G. Also, whereas C3-41 has an insert element (named ISBsph9) located downstream of binA/binB within GI7, a probable transposase pseudogene is presented in the equivalent region of 2297 and LP1-G.
Table 2.
Genome Islands (GIs) predicted in L. sphaericus C3-41
| GIs | Containing ORFs | Major Function | Functional categories |
|---|---|---|---|
| GI1 | Bsph1038 ~ Bsph1073 | Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis, Mtx2 | Fitness island |
| GI 2 | Bsph1085 ~ Bsph1110 | cell division or chromosome partitioning | Fitness island |
| GI 3 | Bsph 1936 ~ Bsph 1953 | Phage remnant | Symbiosis island |
| GI4 | Bsph2575 ~ Bsph 2615 | Multiple classes, major in information storage and processing | Fitness island |
| GI5 | Bsph2815 ~ Bsph 2824 | Mosquitocidal toxin | Pathogenicity island |
| GI6 | Bsph2913 ~ Bsph 2922 | Lipid transport and metabolism | Metabolic island |
| GI7 | Bsph3179 ~ Bsph 3195 | Mosquitocidal toxin | Pathogenicity island |
| GI8 | Bsph3265 ~ Bsph 3275 | Poorly characterized* | unknown |
| GI9 | Bsph3521 ~ Bsph 3538 | Replication, recombination and repair | Fitness island |
| GI10 | Bsph4022 ~ Bsph 4035 | Poorly characterized* | unknown |
*Many CDSs have no matches to known function protein.
Figure 6.
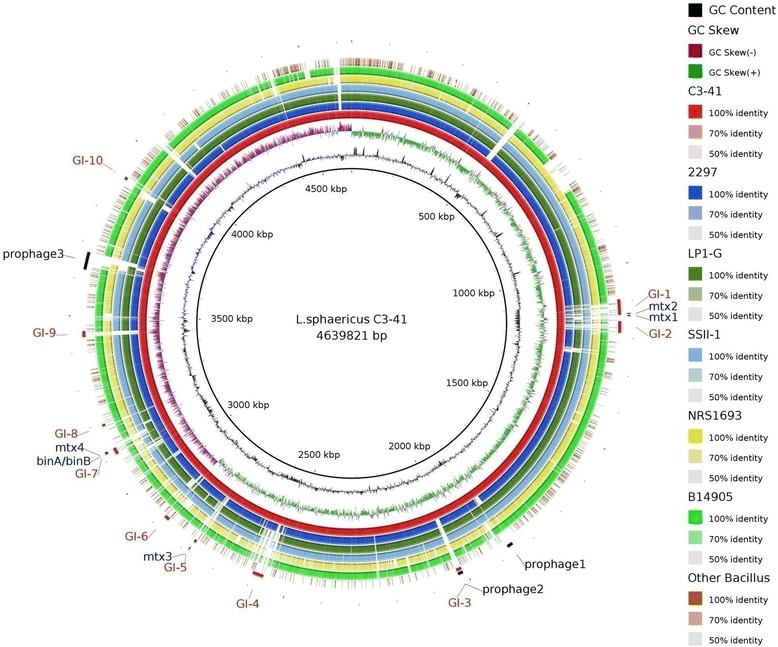
Genome Island (GI) prediction comparative analyses of L. sphaericus genomes. The C3-41 chromosome was used as reference. From the inside: circle 1, genome scale;circles 2 and 3, GC content and GC skew; circles 4–9, genome of C3-41 (red), 2297 (blue) , LP1-G (green), SSII-1 (sky blue), NRS1693 (yellow) and B14905 (emerald green), with colors from dark to light reflecting the similarity from high to low; circle 10, representative genomes for other Bacillus strains (i.e. B. anthracis strain Ames, B. cereus strain AH187, B. thuringiensis strain BMB171, and B. subtilis strain 168) used as outgroups and displaying similar mapping. The predicted GIs, prophages and toxic genes are marked on the outside of the circles.
In addition, a large contig in the genome of strain SSII-1 has a high overlap (>70%) and similarity (>95%) with pBsph, indicating that SSII-1 harbors a pBsph-like plasmid (named pBsph-2). Gene function analysis revealed that this contains some genes involved in replication, recombination and repair, but no GI7 was observed in pBSph-2. It is interesting that the large plasmid pBSph and pBSph-2 contain five genes which are predicted to encode proteins homologous to the type IV secretion system (e.g. VirD4, VirB4, and VirB6) and one gene encoding pilus assembly ATPase, all which may be involved in conjugal transfer. However, the function of the pBsph-2 is still to be characterized.
Discussion
Lysinibacillus belongs to the family Bacillaceae. Organisms in this genus were previously regarded as members of Bacillus, but their taxonomic status was changed to the genus Lysinibacillus in 2007 [10] and it remains for the classification to be confirmed on a genomic level. Moreover, as an important model bacterium for metabolism and mosquito control, the evolutionary model and systematic classification of L. sphaericus is a continual source of interest and debate. Therefore, exploring the phylogenetic relationship amongst members of the L. sphaericus genus in order to confirm the taxonomy of the reassigned new genus Lysinibacillus at the genomic level is of major importance. In this study, several novel genome sequences of L. sphaericus are reported, and their phylogenetic relationship with other genome sequences of Lysinibacillus and Bacillus strains are investigated.
The results showed that the genomes of all the studied Lysinibacillus strains and the marine strain Bacillus sp. B14905 show a high syntenic relationship with that of L. sphaericus C3-41, indicating these strains may have a common ancestor. Furthermore, the consensus trees based on the core genes and the genomic content indicated all the tested 10 Lysinibacillus organisms and B14905 are phylogenetically related and fall into a distinct and well defined cluster, confirming the taxonomy of the new Lysinibacillus genus. A previous study showed that one subspecies of B. subtilis is closely related with L. sphaericus based on 16 s rDNA analysis [22,23]. However, at the genome level, Lysinibacillus and B. subtilis are clustered separately. Moreover, it is interesting that despite being intergenus of Bacillus, the B. cereus group is not closely related to B. subtilis.
We also observed that a major difference between L. sphaericus and the two Bacillus species is the proportion of proteins encoded by the genome related to metabolism. This is in accordance with the observed species-specific metabolic characteristics; Lysinibacillus cannot utilize polysaccharides but alternatively metabolizes a wide variety of organic compounds and amino acids as an energy source [2]. This may explain our observation that, compared to B. cereus group and B. subtilis, Lysinibacillus has an abundance of genes for amino acid transport and metabolism but fewer and less variable genes related to carbohydrate transport and metabolism (probably due to functional degradation). It is interesting to note that all the Lysinibacillus strains have an ethanolamine utilization gene cluster. This could be a complementary pathway for an insect pathogen unable to use polysaccharide for surviving in the insect gut [24]. In addition, a difference was observed in the proportion of proteins with a COG classification of cell wall biosynthesis-related proteins, with members of the B. cereus group displaying a larger proportion in the pan genome than that in the core genome. This is probably because some B. cereus group strains, e. g. Bacillus mycoids and Bacillus pseudomycoids, have a different cell wall/membrane phenotype [25]. In contrast, the cell wall biosynthesis-related proteins in the pan-genome of Lysinibacillus gen. strains are almost completely complimentary to the set identified in the core genome, suggesting the strains within this genus have specific and common features in their cell wall/membrane composition [10].
Amongst L. sphaericus, the genomes of toxic isolates are highly conserved, whereas those of the non-toxic strains are clearly variant. This confirms a recent MLST study which indicated that there is considerably more heterogeneity amongst non-toxic strains than amongst toxic ones, with the toxic strains tested appearing near-clonal [9]. This is also consistent with a previous study which showed that recombination among L. sphaericus strains was relatively rare compared to the rates for most species, such as the B. cereus group, Campylobacter coli, and Listeria monocytogenes, and suggested that mutations were largely responsible for the generation of sequence diversity in L. sphaericus [9]. Due to the large heterogeneity, it is supposed that the evolutionary distance and timescale of divergence between toxic and non-toxic strains of L. sphaericus should be large. In contrast to the lesser variation within a single species in other Bacillus spp., the toxic L. sphaericus strains may be separated from non-toxic strains and we propose a new species should be introduced.
This raises the question of how L. sphaericus strains obtained mosquitocidal toxin genes and evolved into a separate population. The proximity of mosquitocidal toxin genes with the GIs and the MGEs indicates a HGT origin and the structure of GI7, a pathogenicity island containing the major mosquitocidal toxin gene binA/binB and MGEs, provides a possible clue. GI7 possesses multiple genomic locations across the various genomes: it is present in both the chromosome and plasmid of C3-41, but is only found in the chromosome of 2297 and LP1-G, and is absent in SSII-1; furthermore, it is present in pBSph but absent in the highly similar plasmid pBSph-2. In order to assess the basic transfer potential of pBSph and pBSph-2, homologs of the T4SS genes virB4, virB6, and virD4 that were identified to be in the transfer region of the conjugative plasmids, e.g. the Ti-plasmid from Agrobacterium tumefaciens, plasmid pIP501 from Enterococcus faecalis, and plasmid pAW63 from B. thuringiensis [26,27], were investigated. The result showed that each harbor five T4SS genes displaying low levels of homology to known T4SS genes, making it doubtful that they could function as the concerted secretion machinery required for conjugation. The conjugative and transfer promoting capacities of pBsph and pBsph-2 were assessed by tri-parental matings as previously described [28]. None were indicative of self-conjugative or mobilizable activities, at least under the conditions used in the assay (detection limit of 10–7 T/R) (data not shown). One interpretation of these results is that the ancestral form of the plasmid was conjugative and genetic drifts in subsequent lineages lead to the loss of transfer capability.
A previous study surveyed the presence of toxin genes and the associated mosquitocidal activities of L. sphaericus isolates. It showed that non-toxic strains contain only mtx2 or no toxin gene at all; low toxicity strains possess mtx1, mtx2 and mtx3; and moderately or highly toxic strains contain mtx3, binA/binB and/or cry48Aa/cry49Aa, in which some isolates also contains mtx1 and mtx2 [9]. In addition, mtx2 and mtx3 are homologous and have close orthologs in Bacillus sp. strain NRRL B-14905 [11]. It is also interesting that Mtx2 and Mtx3 are members of Clostridium epsilon toxin ETX/MTX2 family (pfam 03318) of pore forming toxins defined in the NCBI Conserved Domain Database [29]. Combining the results of our analysis with these other findings, we propose the following hypothesis for the evolution of mosquitocidal L. sphaericus: 1) Lysnibacillus strains share a common ancestor; 2) A mtx2 or mtx3 ortholog was initially acquired by HGT; 3) The acquisition of mtx2/mtx3 was followed by acquisition of binA/binB, cry48a/cry49a and mtx1 also by HGT at a later time; 4) The GI containing binA/binB was obtained by phage integration into the chromosome and/or plasmid; 5) The ancestral form of pBsph and pBsph-2 was conjugative, whose capture and loss probably occurred in the population, probably playing an important role for the transmission of binA/binB. However, while the data collected to date supports this hypothesis, additional L. sphaericus genomes are needed together with complementary experimental and bioinformatics analysis.
Conclusions
We present the genome sequences of four Lysinibacillus strains and investigate their phylogenetic relationship to other available Lysinibacillus strains based on analysis of genome structure and identified core genes. Our results provide the first support at the genome level for the classification of these strains into a separate genus. Our analysis also indicates that mosquitocidal L. sphaericus isolates appear distinct from other Lysinibacillus organisms at the genome level, suggesting they should be classified into a separate species. Based on our findings, we hypothesis that Lysnibacillus strains evolved from a common ancestor, and the mosquitocidal toxin genes were acquired by horizontal gene transfer (HGT) resulting in the evolution of the mosquitocidal L. sphaericus.
Methods
Genome sequencing
Genome sequencing of L. sphaericus 2297, LP1-G, SSII-1 and NRS1693 was carried out using an Illumina HiSeq 2000 system by Encode Genomics Bio-Technology Co. (Suzhou, China). Paired-end reads with average length 72 and minimum read quality of 35 were used for assembly using the Velvet-1.0.14 software package [30]. Using the genome sequence of L. sphaericus C3-41 [GenBank: CP000817 and CP000818] as reference, strains 2297, LP1-G and SSII-1 showed ~91% coverage, and their assembly produced 278, 143 and 138 contigs respectively. Strain NRS1693 showed ~74% coverage, and the assembly produced 546 contigs (Table 1).
Selection of genomes used in this study
All the 10 Lysinibacillus genomes available at the time of analysis and one Lysinibacillus-related strain Bacillus sp. NRRL B-14905 [11] were included. The selection of 20 genomes from two representative species of Bacillus, B. subtilis and B. cereus group, was based on a previous study [23], which showed that B. subtilis is classified into two subspecies and one is closely related with L. sphaericus, and that B. cereus group is located on a clade neighboring L. sphaericus/B. subtilis. Thus, the five selected genomes of B. subtilis were well representative of the two subspecies. Since the seven members (i.e. B. cereus, B. thuringiensis, B. anthracis, B. weihenstephanensis, B. mycoides, B. pseudomycoides and B. cytotoxicus) of B. cereus group share close genetic and biochemical relatedness, only 15 genomes of the three major members (i.e. B. cereus, B. thuringiensis, B. anthracis) were selected as representative of the strains and species, other closely related or derivative strains were not included. In summary, a total of 17 complete and 11 gapped genomes from Lysinibacillus, B. cereus group, and B. subtilis strains were selected for analysis in this study (Table 1).
In addition, the genomes of Solibacillus silvestris [GenBank: NC_018065], Sporosarcina pasteurii [GenBank: AYOX00000000], and Ureibacillus thermosphaericus [GenBank: AJIK00000000], which are thought to be sphaericus-like organisms close to L. sphaericus based on 16 s rDNA and phenotypic analysis and previously thought belong to Bacillus [15] were also selected to compare with Lysinibacillus strains.
Genome annotation
Genome annotation was performed using the xBASE web service (http://www.xbase.ac.uk/annotation/), which comprises the following steps: (i) Glimmer is used for gene prediction; (ii) tRNA genes are predicted using tRNAScan-SE [31]; (iii) ribosomal RNA genes are searched for with RNAmmer [32]; (iv) protein BLAST is run using the translated coding sequences as a query against the reference sequence; (v) the best result for each BLAST search is imported as the gene annotation (if under the user-supplied E-value cutoff) [33,34]. Primary parameters were set as default, which sets the minimum length of a gene to be 90 bp, while the permitted maximum overlap of two genes is 50 bp, and the BLAST e-value cutoff is1e-10.
Each annotated protein was then compared to the COG database using BLASTP to identify its member functional groups.
Fragmented alignment of multiple genomes and phylogenomic relationship
A all-against-all fragment comparison analysis was performed using Gegenees (version 1.1.5) software by fragmenting genomes and comparing all pieces with all genomes [14]. The heat-plot was based on a fragmented alignment using BLASTN with settings 500/500. The cutoff threshold for non-conserved material was 30%. A dendrogram was produced in SplitsTree version 4.12.8 (using the neighbor-joining method) made from a Nexus file exported from Gegenees [35].
Ultra-fast alignments of all Lysinibacillus genomes were finished by the MUMmer program (version 3.0) and the colinearity relationship of each draft genome with C3-41 was calculated [36,37].
Pan- and core genome analysis
The respective pan- and core genomes of 12 B. cereus group strains, 5 B. subtilis strains and 11 Lysinibacillus strains were calculated using the PanGP software package (http://pangp.big.ac.cn) [16,38], and a BLAST Matrix was constructed using a cutoff of 1e−10, and 50% identity and coverage. An R-script was used to analyze the COG protein composition in the pan- and core genomes, and the results were visualized in a bar chart [39].
Gene Islands (GIs) prediction
The GIs in the chromosome of L. sphaericus C3-41 were predicted using IslandViewer (http://www.pathogenomics.sfu.ca/islandviewer/query.php) [40]. Using the C3-41 chromosome as the reference, the draft genome sequences of 2297, LP1-G, SSII-1, NRS1693 and Bacillus sp. NRRL B-14905 were compared and mapped with BRIG (version 0.95) [41] and GBrowse (version 2.49) [42,43], with the complete genomes of B. anthracis strain Ames, B. cereus strain AH187, B. thuringiensis strain BMB171, and B. subtilis strain 168 as outgroups. Some distinct special sites, including the predicted GIs, prophages and the mosquitocidal toxin genes were presented graphically outside the circle map.
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers
All four draft L. sphaericus genomes have been deposited at GenBank. Accession numbers are listed in Table 1.
Availability of supporting data
The data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article and the additional files.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by NFSC grants (30800002 and 31272384) and a 973 grant (2009CB118902), China.
Additional files
55 core genes conserved in Lysinibacillus and Bacillus used to construct the consensus phylogenetic tree in Figure 2.
Predicted COG proteins that are both unique in the pan- and in the core genome of Lysinibacillus.
MUMmer analysis of the linear relationship between the genome sequence of Lysinibacillus strains and reference strain C3-41. The X-axis represents reference C3-41, and the Y-axis represents each strain of Lysinibacillus. The color bar on the right side reflects the similarity, ranging from high (red) to low (green). All contigs of draft genomes were sorted automatically with C3-41 by MUMmer.
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: RS, HX. Performed the experiments: XK. Analyzed the data: XK, RS, HX. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: XK, RS, HX. Wrote the paper: XK, YZ, RS, HX. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Kai Xu, Email: xukai915@qq.com.
Zhiming Yuan, Email: yzm@wh.iov.cn.
Simon Rayner, Email: simon.rayner.cn@gmail.com.
Xiaomin Hu, Email: huxm@wh.iov.cn.
References
- 1.Cano RJ, Borucki MK. Revival and identification of bacterial spores in 25- to 40-million-year-old Dominican amber. Science. 1995;268(5213):1060–4. doi: 10.1126/science.7538699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Han B, Liu HZ, Hu XM, Cai YJ, Zheng DS, Yuan ZM. Molecular characterization of a glucokinase with broad hexose specificity from Bacillus sphaericus strain C3-41. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73(11):3581–6. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02863-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Berry C. The bacterium, Lysinibacillus sphaericus, as an insect pathogen. J Invertebr Pathol. 2012;109(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2011.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wirth MC, Yang Y, Walton WE, Federici BA, Berry C. Mtx toxins synergize Bacillus sphaericus and Cry11Aa against susceptible and insecticide-resistant Culex quinquefasciatus larvae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73(19):6066–71. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00654-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jones GW, Nielsen-Leroux C, Yang Y, Yuan Z, Dumas VF, Monnerat RG, et al. A new Cry toxin with a unique two-component dependency from Bacillus sphaericus. FASEB J. 2007;21(14):4112–20. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-8913com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhang Y, Liu E, Cai C, Chen Z. Isolation of two highly toxic Bacillus sphaericus strains. Insecticidal Microorg. 1987;1:98–9. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Debarjac H, Largetthiery I, Dumanoir VC, Ripouteau H. Serological classification of Bacillus sphaericusstrains on the basis of toxicity to mosquito larvae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985;21(1–2):85–90. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Krych VK, Johnson JL, Yousten AA. Deoxyribonucleic-acid homologies among strains of Bacillus sphaericus. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1980;30(2):476–84. doi: 10.1099/00207713-30-2-476. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ge Y, Hu XM, Zheng DS, Wu YM, Yuan ZM. Allelic diversity and population structure of Bacillus sphaericus as revealed by multilocus sequence typing. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77(15):5553–6. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00207-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ahmed I, Yokota A, Yamazoe A, Fujiwara T. Proposal of Lysinibacillus boronitolerans gen. nov sp nov., and transfer of Bacillus fusiformis to Lysinibacillus fusiformis comb. nov and Bacillus sphaericus to Lysinibacillus sphaericus comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2007;57:1117–25. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.63867-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hu X, Fan W, Han B, Liu H, Zheng D, Li Q, et al. Complete genome sequence of the mosquitocidal bacterium Bacillus sphaericus C3-41 and comparison with those of closely related Bacillus species. J Bacteriol. 2008;190(8):2892–902. doi: 10.1128/JB.01652-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jeong H, Jeong DE, Sim YM, Park SH, Choi SK. Genome sequence of Lysinibacillus sphaericus strain KCTC 3346T. Genome Announc. 2013;1(4):e00625–13. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00625-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pena-Montenegro TD, Dussan J. Genome sequence and description of the heavy metal tolerant bacterium Lysinibacillus sphaericus strain OT4b.31. Stand Genomic Sci. 2013;9(1):42–56. doi: 10.4056/sigs.4227894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Agren J, Sundstrom A, Hafstrom T, Segerman B. Gegenees: fragmented alignment of multiple genomes for determining phylogenomic distances and genetic signatures unique for specified target groups. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nakamura LK. Phylogeny of Bacillus sphaericus-like organisms. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2000;50:1715–22. doi: 10.1099/00207713-50-5-1715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tettelin H, Riley D, Cattuto C, Medini D. Comparative genomics: the bacterial pan-genome. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008;11(5):472–7. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2008.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhao Y, Jia X, Yang J, Ling Y, Zhang Z, Yu J, Wu J, Xiao J, et al. PanGP: A tool for quickly analyzing bacterial pan-genome profile. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(9):1297–9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cui YB, Zhou Y, Liu WN, Chen QW, Ma GF, Shi WH, et al. Cloning of the surface layer gene sllB from Bacillus sphaericus ATCC 14577 and its heterologous expression and purification. Int J Mol Med. 2012;29(4):677–82. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Li J, Yang LL, Hu XM, Zheng DS, Yan JP, Yuan ZM. Nanoscale mono- and multi-layer cylinder structures formed by recombinant S-layer proteins of mosquitocidal Bacillus sphaericus C3-41. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;97(16):7275–83. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4664-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hu XM, Li J, Hansen BM, Yuan ZM. Phylogenetic analysis and heterologous expression of surface layer protein SlpC of Bacillus sphaericus C3-41. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008;72(5):1257–63. doi: 10.1271/bbb.70747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zahner V, Priest FG. Distribution of restriction endonucleases among some entomopathogenic strains of Bacillus sphaericus. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1997;24(6):483–7. doi: 10.1046/j.1472-765X.1997.00154.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Xu D, Côté JC. Phylogenetic relationships between Bacillus species and related genera inferred from comparison of 3’ end 16S rDNA and 5’ end 16S-23S ITS nucleotide sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2003;53(3):695–704. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.02346-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Porwal S, Lal S, Cheema S, Kalia VC. Phylogeny in aid of the present and novel microbial lineages: diversity in Bacillus. PLoS One. 2009;4(2):e4438. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fox KA, Ramesh A, Stearns JE, Bourgogne A, Reyes-Jara A, Winkler WC, et al. Multiple posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms partner to control ethanolamine utilization in Enterococcus faecalis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(11):4435–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812194106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nakamura LK. Bacillus pseudomycoides sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1998;48:1031–5. doi: 10.1099/00207713-48-3-1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Abajy MY, Kopec J, Schiwon K, Burzynski M, Doring M, Bohn C, et al. A type IV-secretion-like system is required for conjugative DNA transport of broad-host-range plasmid pIP501 in gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 2007;189(6):2487–96. doi: 10.1128/JB.01491-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lang J, Planamente S, Mondy S, Dessaux Y, Morera S, Faure D. Concerted transfer of the virulence Ti plasmid and companion At plasmid in the Agrobacterium tumefaciens-induced plant tumour. Mol Microbiol. 2013;90(6):1178–89. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hu XM, Van der Auwera G, Timmery S, Zhu L, Mahillon J. Distribution, diversity, and potential mobility of extrachromosomal elements related to the Bacillus anthracis pXO1 and pXO2 virulence plasmids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009;75(10):3016–28. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02709-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Marchler-Bauer A, Lu SN, Anderson JB, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, DeWeese-Scott C, et al. CDD: a conserved domain database for the functional annotation of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:D225–9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zerbino DR, Birney E. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008;18(5):821–9. doi: 10.1101/gr.074492.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schattner P, Brooks AN, Lowe TM. The tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33(Web Server issue):W686–9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rodland EA, Staerfeldt HH, Rognes T, Ussery DW. RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(9):3100–8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chaudhuri RR, Pallen MJ. xBASE, a collection of online databases for bacterial comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:D335–7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chaudhuri RR, Loman NJ, Snyder LAS, Bailey CM, Stekel DJ, Pallen MJ. xBASE2: a comprehensive resource for comparative bacterial genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:D543–6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Huson DH. SplitsTree: analyzing and visualizing evolutionary data. Bioinformatics. 1998;14(1):68–73. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/14.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Delcher AL, Salzberg SL, Phillippy AM. Using MUMmer to identify similar regions in large sequence sets. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2003; Chapter 10:Unit 10. 13. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 37.Kurtz S, Phillippy A, Delcher AL, Smoot M, Shumway M, Antonescu C, Salzberg SL. Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol. 2004;5(2):R12. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-2-r12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Friis C, Wassenaar TM, Javed MA, Snipen L, Lagesen K, Hallin PF, Newell DG, Toszeghy M, Ridley A, Manning G, et al. Genomic characterization of Campylobacter jejuni strain M1. PLoS One. 2010;5(8):e12253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mavromatis K, Ivanova NN, Chen IMA, Szeto E, Markowitz VM, Kyrpides NC. The DOE-JGI standard operating procedure for the annotations of microbial genomes. Stand Genomic Sci. 2009;1(1):63–7. doi: 10.4056/sigs.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Langille MGI, Brinkman FSL. IslandViewer: an integrated interface for computational identification and visualization of genomic islands. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(5):664–5. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Alikhan NF, Petty NK, Ben Zakour NL, Beatson SA. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genomics. 2011;12:402. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Podicheti R, Gollapudi R, Dong Q. WebGBrowse–a web server for GBrowse. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(12):1550–1. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Podicheti R, Dong Q. Using WebGBrowse to visualize genome annotation on GBrowse. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2010;2010(3):pdb prot5392. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot5392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


