Abstract
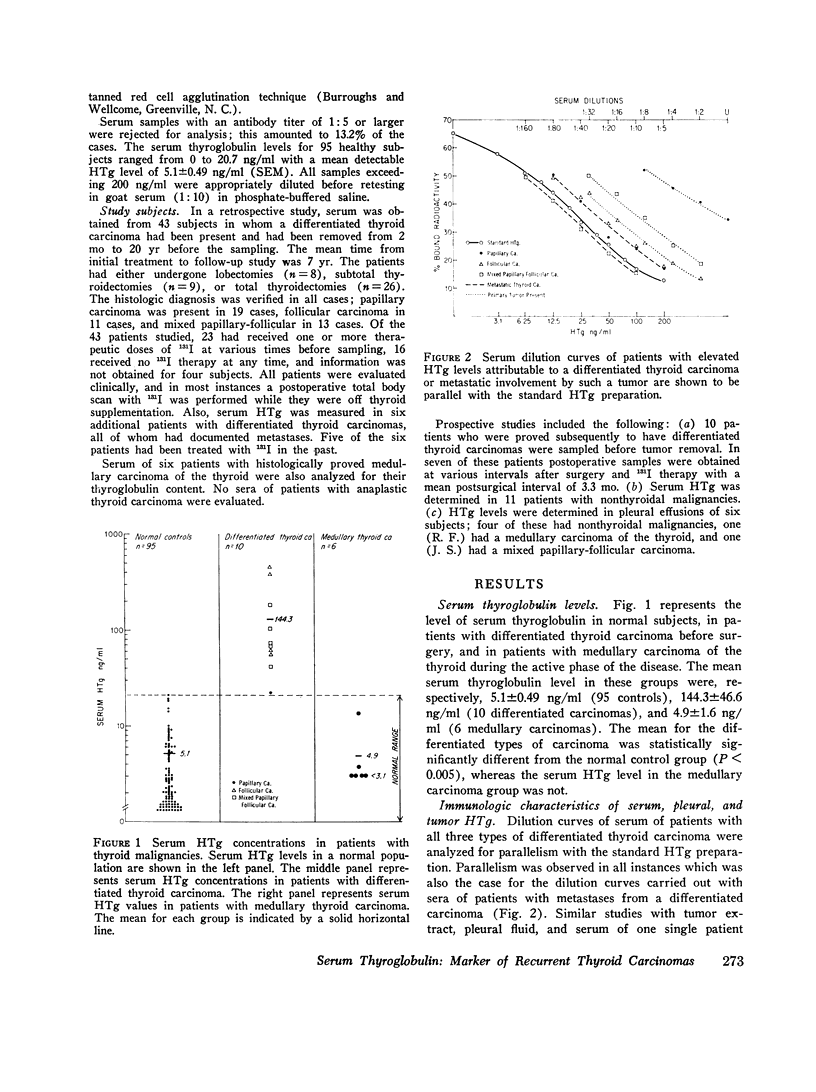
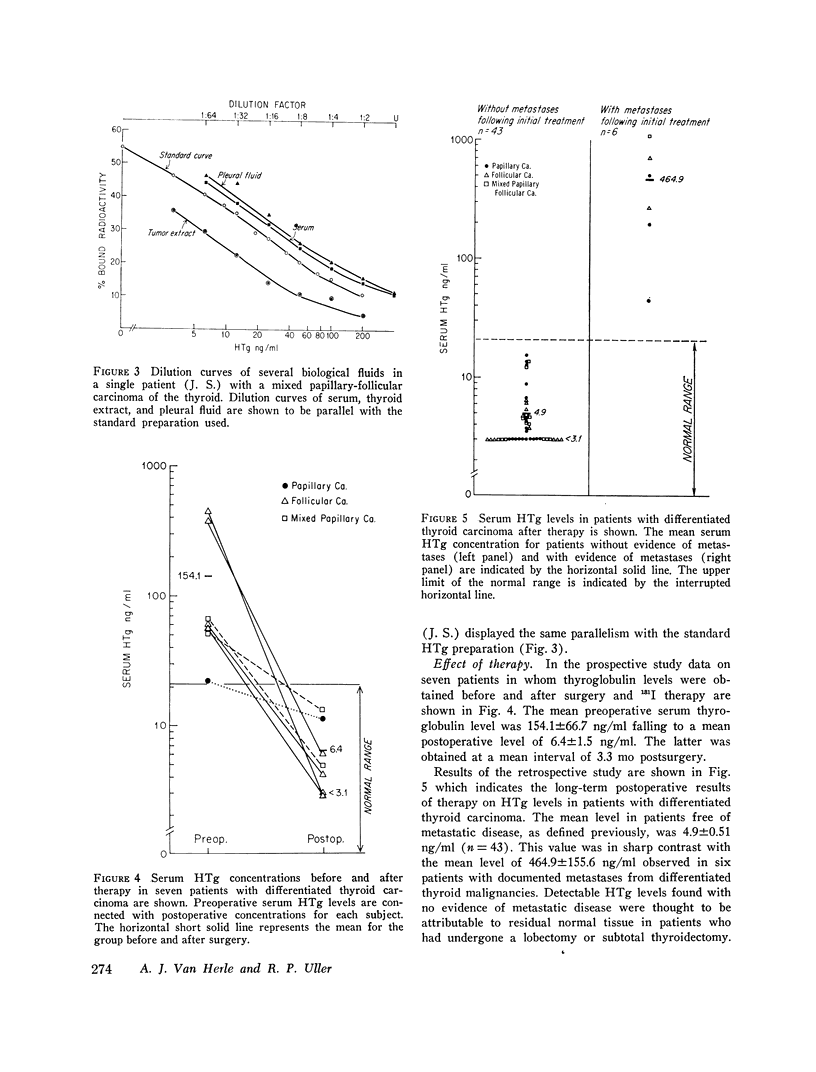
The presence of human thyroglobulin (HTg) in serum of patients was identical by immunological criteria to the serum standard used in the radioimmunoassay. The serum thyroglobulin levels in untreated patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma ranged from 22.0 to 445.0 ng/ml with a mean of 144.3 +/- 46.5 ng/ml (SEM) (n = 10). The mean serum thyroglobulin measured postoperatively in seven of these patients was 6.4 +/- 1.5 ng/ml, not statistacally different from the mean level of 5.1 +/- 0.49 ng/ml (range 0-20.7 ng/ml) observed in 71 out of 95 control subjects with detectable HTg levels. By contrast serum HTg levels were normal or undetectable in subjects with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. HTg levels were within normal limits in sera of patients who had previously undergone successful therapy for a differentiated thyroid carcinoma and in whom no metastases could be documented. The mean level for this group was 4.9 +/- 0.51 ng/ml (n = 43). In contrast, patients with documented metastases had a mean serum thyroglobulin level of 464.9 +/- 155.6 ng/ml (n = 6). The data support the thesis that in differentiated thyroid carcinoma serum thyroglobulin levels are elevated when metastases develop after initial treatment. It is proposed that the measurement of thyroglobulin in the serum represents a simple and valuable adjunct in the posttreatment follow-up of patients with differentiated thyroid cancer.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASSEM E. S. THYROGLOBULIN IN THE SERUM OF PARTURIENT WOMEN AND NEWBORN INFANTS. Lancet. 1964 Jan 18;1(7325):139–141. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92224-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinoer D., Puttemans N., Van Herle A. J., Camus M., Ermans A. M. Sequential study of the impairment of thyroid function in the early stage of subacute thyroiditis. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1974 Sep;77(1):26–34. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0770026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan F. S., Lew W., Okerlund M. D., Lowenstein J. M. Falsely positive bovine TSH radioimmunoassay responses in sera from patients with thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Jun;38(6):1121–1122. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-6-1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan F. S., Lowenstein J. M., West M. N., Okerlund M. D. Immuno-reactive material to bovine TSH in plasma from patients with thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Dec;35(6):795–798. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-6-795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJORT T. Determination of serum-thyroglobulin by a haemagglutination-inhibition test. Lancet. 1961 Jun 10;1(7189):1262–1264. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92767-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWEN C. A., Jr, McCONAHEY W. M., CHILDS D. S., Jr, McKENZIE B. F. Serum "thyroglobulin" in thyroidal carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1960 Feb;20:187–204. doi: 10.1210/jcem-20-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J., RALL J. E., BECKER D. V., RAWSON R. W. The nature of the serum iodine after large doses of I131. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1952 Jul;12(7):856–874. doi: 10.1210/jcem-12-7-856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J. Thyroglobulin in serum after I131 therapy. I. Salting out. J Biol Chem. 1954 May;208(1):377–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roitt I. M., Torrigiani G. Identification and estimation of undegraded thyroglobulin in human serum. Endocrinology. 1967 Sep;81(3):421–429. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-3-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIMAOKA K., SOKAL J. E., PICKREN J. W. Metastatic neoplasms in the thyroid gland. Pathological and clinical findings. Cancer. 1962 May-Jun;15:557–565. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196205/06)15:3<557::aid-cncr2820150315>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrigiani G., Doniach D., Roitt I. M. Serum thyroglobulin levels in healthy subjects and in patients with thyroid disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Mar;29(3):305–314. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-3-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenta L. Radioiodine-labeled proteins in the serum of patients treated with 131I for thyroid disease. Endocrinol Exp. 1971 Jun;5(3):127–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Herle A. J., Uller R. P., Matthews N. I., Brown J. Radioimmunoassay for measurement of thyroglobulin in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1320–1327. doi: 10.1172/JCI107303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



