Abstract
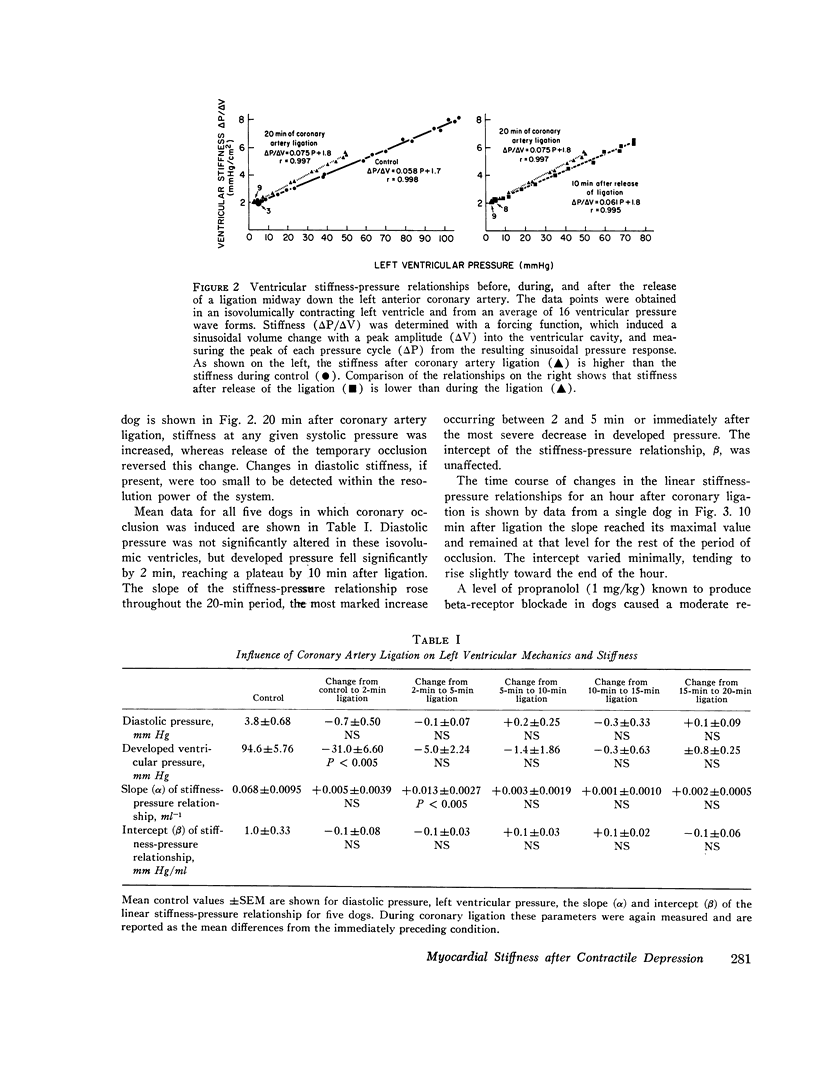
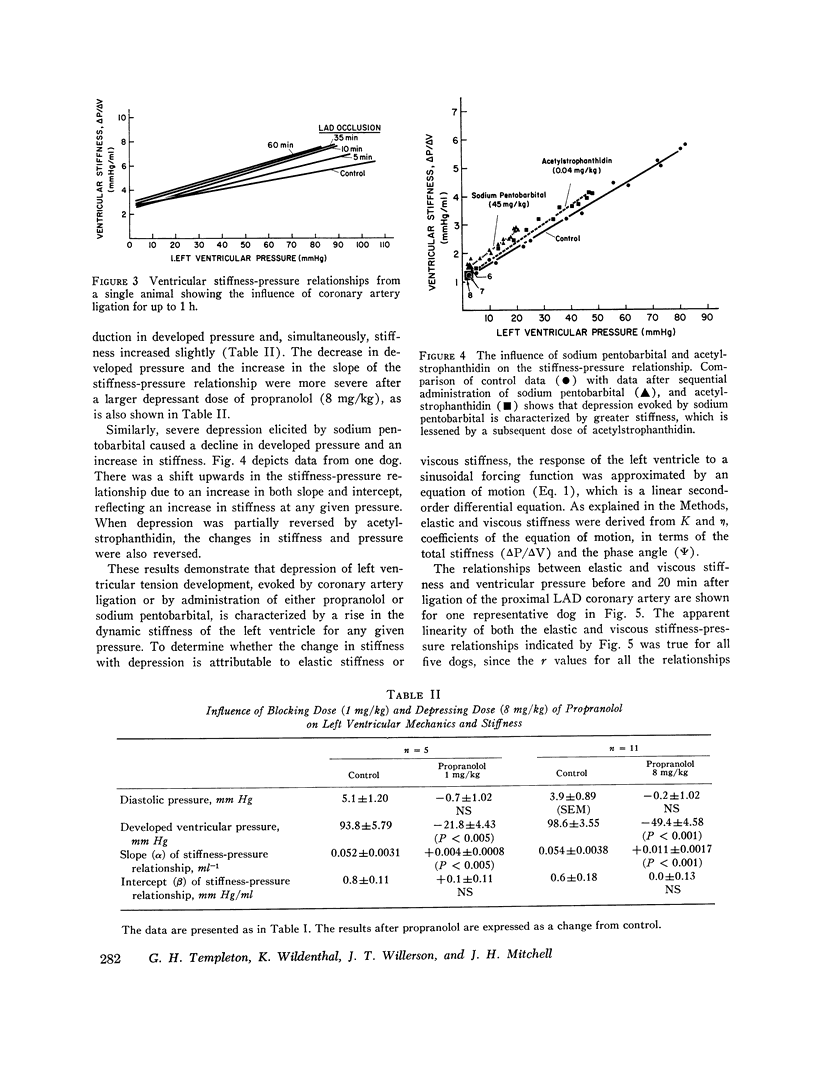
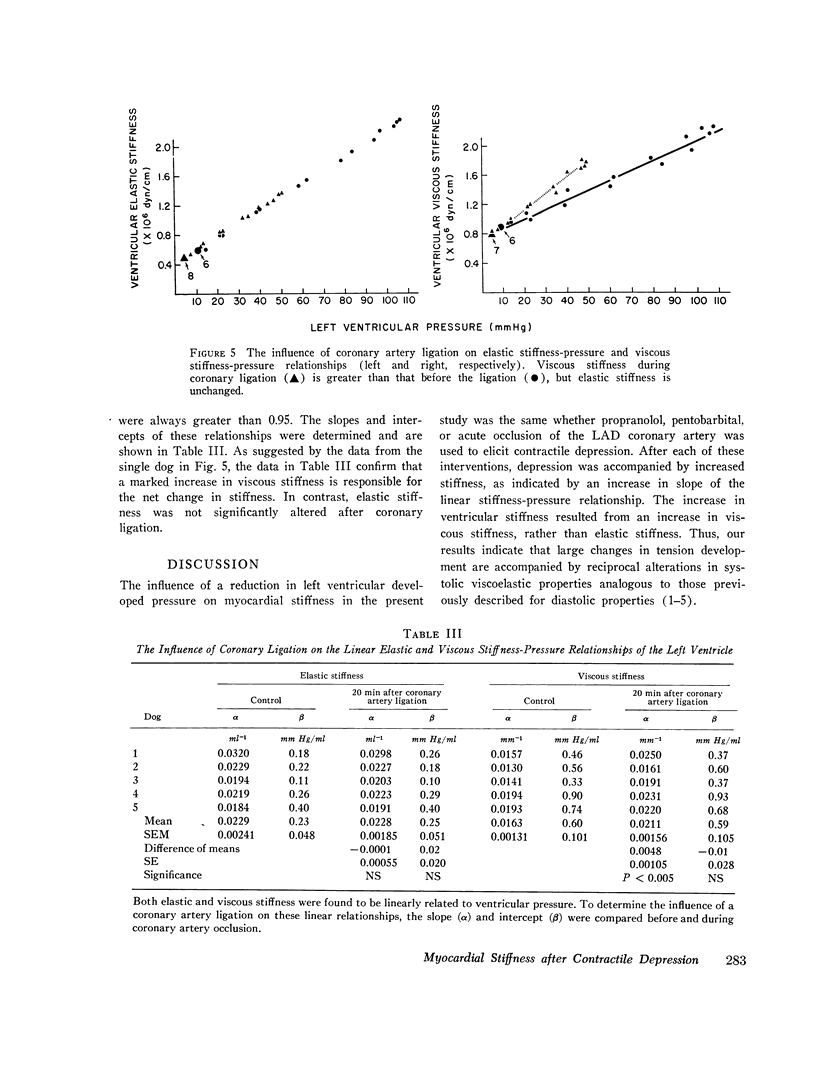
The influence of acute myocardial depression on ventricular stiffness and on its elastic and viscous components was studied in 19 dogs. After the animals were placed on cardiopulmonary bypass, stiffness was measured by sinusoidally injecting volume changes of 0.5 ml (deltaV) at 22 Hz into paced, isovolumically (deltaP) of the sinusoidal pressure response. Stiffness was linearly related to pressure (P) throughout the cardiac cycle, so that deltaP/delta V = alpha P + beta, where alpha and beta are constants. Myocardial depression was induced in one of three different ways: by coronary artery ligation, by administration of propranolol (Inderal), or by administration of pentobarbital. All three interventions caused significant increases in the slope, alpha, of the stiffness-pressure relationship, while the intercept, beta, remained unchanged. Release of the coronary occlusion or administration of acetylstrophantidin partially reversed depression and the change in alpha; Approximation of the mechanical nature of the left ventricle in terms of a linear second-order mechanical system permitted the division of stiffness into its elastic and viscous components. Like total stiffness, both the elastic and the viscous components were linearly related to ventricular pressure. Elastic stiffness was not changed, but the slope of the line relating viscous stiffness to pressure was significantly increased during ischemic depression, indicating that a change in viscosity was primarily responsible for the increase in total ventricular stiffness.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUCHTHAL F., ROSENFALCK P. Dynamic elasticity in the initial phase of an isotonic twitch. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Jul 15;49:198–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauereisen E., Jacob R., Kleinheisterkamp U., Peiper U., Weigand K. H. Enddiastolische Dehnbarkeit des linken Ventrikels in situ bei akuten Anderungen des arteriellen Systemdrucks. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1965 Sep 15;285(4):335–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollery C. T., Paterson J. W., Conolly M. E. Clinical pharmacology of beta-reccer-atefoygolocarahp lnilcc clinical pharmacology of beta-receptor-blocking drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1969 Nov-Dec;10(6):765–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore J. P., Cingolani H. E., Taylor R. R., McDonald R. H., Jr Physical factors and cardiac adaptation. Am J Physiol. 1966 Nov;211(5):1219–1226. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.5.1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. V. The series elastic component of muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1950 Jul 24;137(887):273–280. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1950.0035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEWELL B. R., WILKIE D. R. An analysis of the mechanical components in frog's striated muscle. J Physiol. 1958 Oct 31;143(3):515–540. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach J. K., Wall F. J., Solomon S. Effect of inotropic agents on distensibility of the isolated cat heart. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jan;139(1):310–314. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenblick E. H., Ross J., Jr, Covell J. W., Braunwald E. Alterations in resting length-tension relations of cardiac muscle induced by changes in contractile force. Circ Res. 1966 Nov;19(5):980–988. doi: 10.1161/01.res.19.5.980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton G. H., Ecker R. R., Mitchell J. H. Left ventricular stiffness during diastole and systole: the influence of changes in volume and inotropic state. Cardiovasc Res. 1972 Jan;6(1):95–100. doi: 10.1093/cvr/6.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton G. H., Mitchell J. H., Ecker R. R., Blomqvist G. A method for measurement of dynamic compliance of the left ventricle in dogs. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Nov;29(5):742–745. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.29.5.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton G. H., Mitchell J. H., Wildenthal K. Influence of hyperosmolality on left ventricular stiffness. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jun;222(6):1406–1411. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.6.1406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton G. H., Nardizzi L. R. Elastic and viscous stiffness of the canine left ventricle. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Jan;36(1):123–127. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton G. H., Wildenthal K., Mitchell J. H. Influence of coronary blood flow on left ventricular contractility and stiffness. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1216–1220. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton G. H., Wildenthal K., Willerson J. T., Reardon W. C. Influence of temperature on the mechanical properties of cardiac muscle. Circ Res. 1974 May;34(5):624–634. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.5.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildenthal K., Mullins C. B., Harris M. D., Mitchell J. H. Left ventricular end-diastolic distensibility after norepinephrine and propranolol. Am J Physiol. 1969 Sep;217(3):812–818. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.3.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildenthal K., Skelton C. L., Coleman H. N., 3rd Cardiac muscle mechanics in hyperosmotic solutions. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jul;217(1):302–306. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.1.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



