Abstract
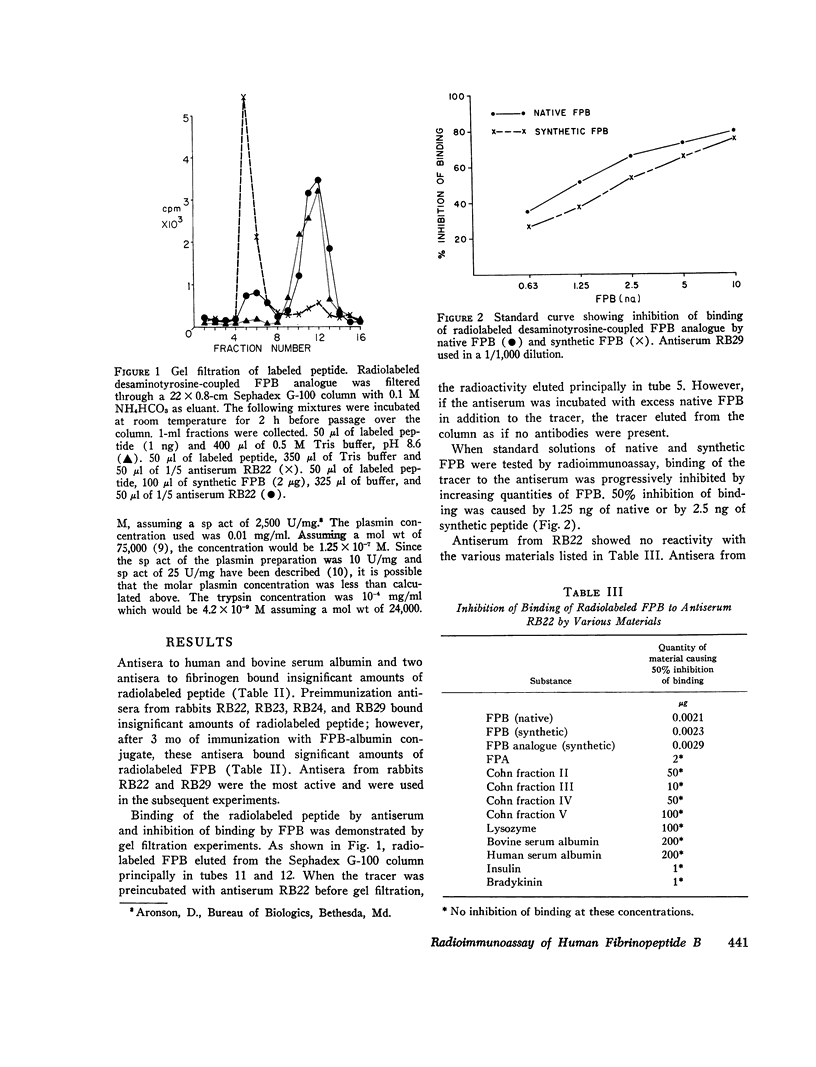
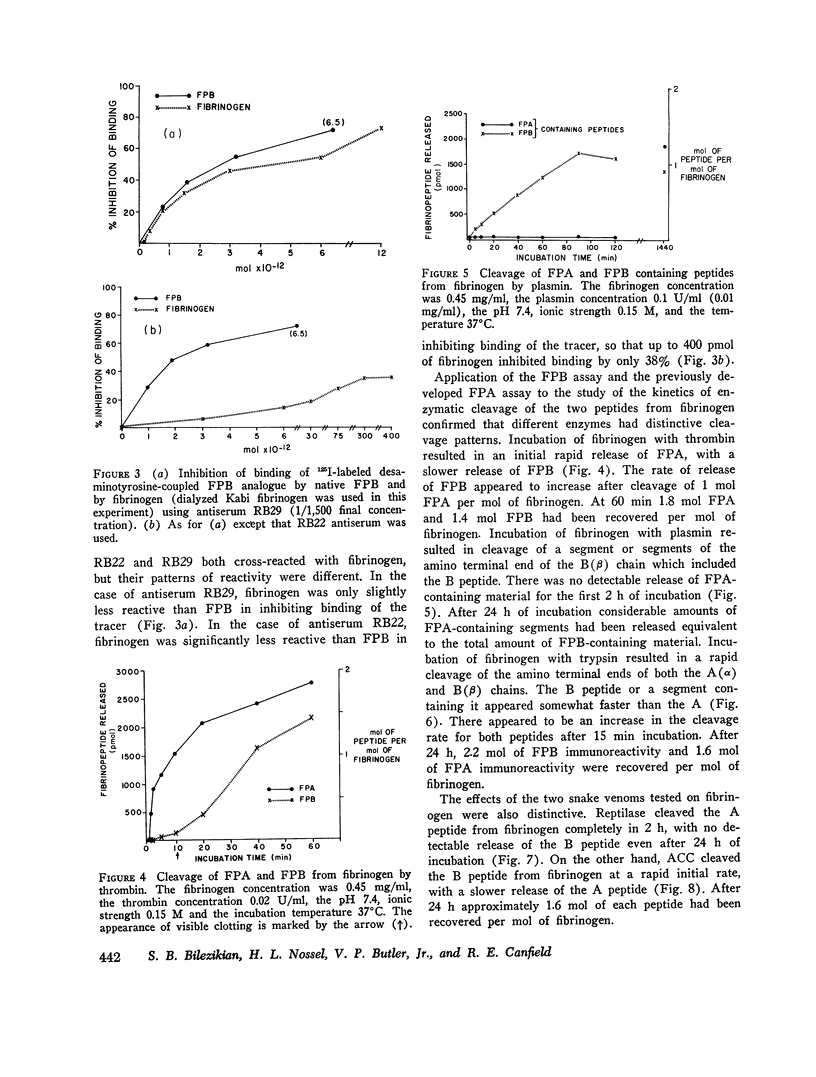
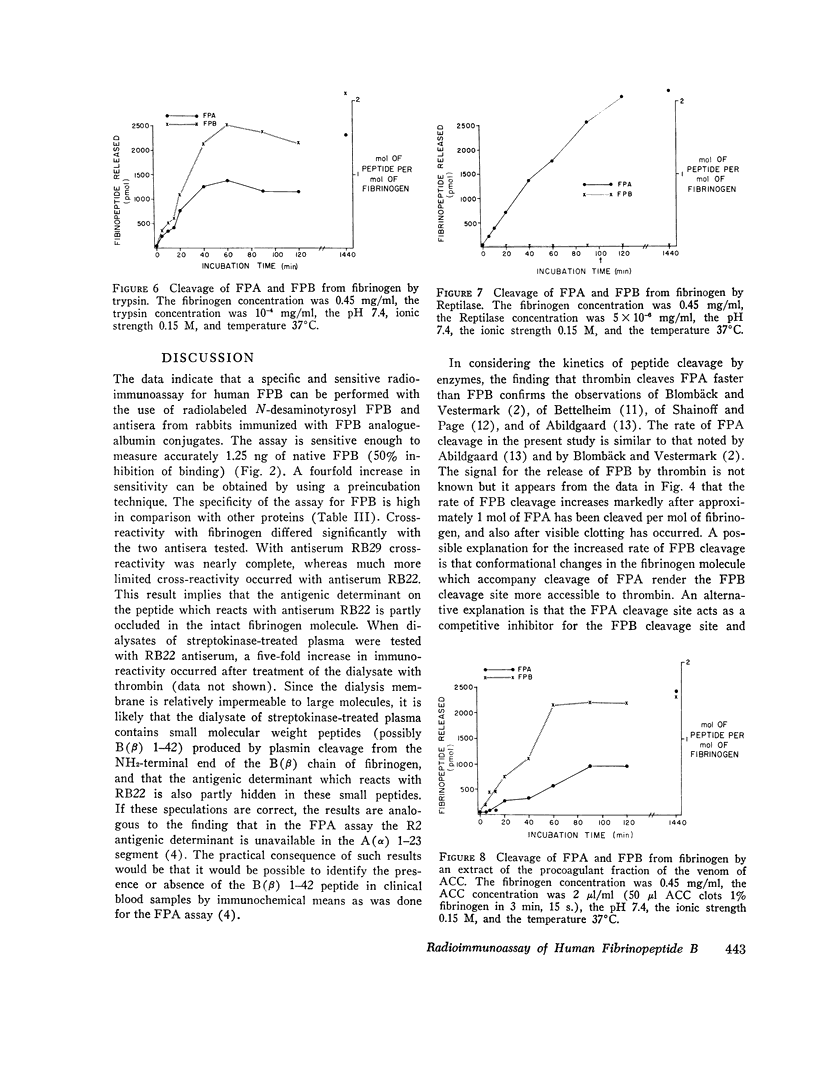
Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin monomer by cleaving fibrinopeptides A and B (FPA and FPB) from the amino terminal ends of the A (alpha) and B (beta) chains. A radioimmunoassay capable of measuring the A peptide in human blood as an index of thrombin action in vivo has been described previously. This paper describes the development of a radioimmunoassay for FPB and the use of both assays in the demonstration of distinctive patterns of cleavage of the amino terminal ends of the A (alha) and B (beta) chains of fibrinogen by various enzymes. Antisera were raised in rabbits to a synthetic analogue of FPB coupled to bovine serum albumin. FPB analogue was couple to desaminotyrosine and radiolabeled with 125I by the chloramine-T technique. The radiolabeled peptide was bound by the antiserum, and binding was inhibited by synthetic or native FPB. Unbound tracer was separated from bound tracer by charcoal adsorption. The senistivity of the assay was such that 50% inhibition of binding of the tracer was caused by 1.25 ng of the native FPB. Fibrinogen was treated with thrombin, plasmin, trypsin, Reptilase, and an extract of the venom from Ancistrodon contortrix contortrix (ACC). After ethanol precipitation and centrifugation, dialysates of enzymatically altered fibrinogen were assayed for FPA and FPB. The action of thrombin on fibrinogen resulted in a rapid release of FPA and a slower release of FPB. Plasmin cleaved a segment(s) of the B (beta) chain which included FPB but cleaved no detectable FPA-containing material for the first 2 h of incubation. In the case of plasmin-treated fibrinogen, the dialysates had been further treated with thrombin before being assayed for FPA and FPB. Trypsin rapidly cleaved both peptides, the B before the A. Reptilase cleaved only FPA in 24 h. ACC cleaved FPB at a rapid rate, with a slowere cleavage of FPA. The distinctive cleavage patterns produced by the serine proteases may be useful in interpreting the levels of FPA and FPB measured in human blood and in studying the generation of FPA and FPB in clinical blood samples.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abildgaard U. N-terminal analysis during coagulation of purified human fibrinogen, fraction I, and plasma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1965;17(6):529–536. doi: 10.1080/00365516509083361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BETTELHEIM F. R. The clotting of fibrinogen. II. Fractionation of peptide material liberated. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Jan;19(1):121–130. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90393-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow G. H., Summaria L., Robbins K. C. Molecular weight studies on human plasminogen and plasmin at the microgram level. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1138–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Blombäck M., Edman P., Hessel B. Human fibrinopeptides. Isolation, characterization and structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 28;115(2):371–396. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzynski A. Z., Marder V. J., Shainoff J. R. Structure of plasmic degradation products of human fibrinogen. Fibrinopeptide and polypeptide chain analysis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2294–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfriend T. L., Ball D. L. Radioimmunoassay of bradykinin: chemical modification to enable use of radioactive iodine. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Mar;73(3):501–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri B., Shainoff J. R. Fate of fibrinopeptides in the reaction between human plasmin and fibrinogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 23;303(1):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90157-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIHALYI E., GODFREY J. E. Digestion of fibrinogen by trypsin. I. Kinetic studies of the reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jan 8;67:73–89. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91798-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER K. D., COPELAND W. H. HUMAN THROMBIN: ISOLATION AND STABILITY. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Aug;26:431–437. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S., Galanakis D. K. The essential covalent structure of human fibrinogen evinced by analysis of derivatives formed during plasmic hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7913–7929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Younger L. R., Wilner G. D., Procupez T., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr Radioimmunoassay of human fibrinopeptide A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2350–2353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Yudelman I., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr, Spanondis K., Wilner G. D., Qureshi G. D. Measurement of fibrinopeptide A in human blood. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):43–53. doi: 10.1172/JCI107749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECHET L., ALEXANDER B. The effect of certain proteolytic enzymes on the thrombin-fibrinogen interaction. Biochemistry. 1962 Sep;1:875–883. doi: 10.1021/bi00911a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallén P. Plasmic degradation of fibrinogen. Scand J Haematol Suppl. 1971;13:3–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1971.tb01979.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



