Abstract
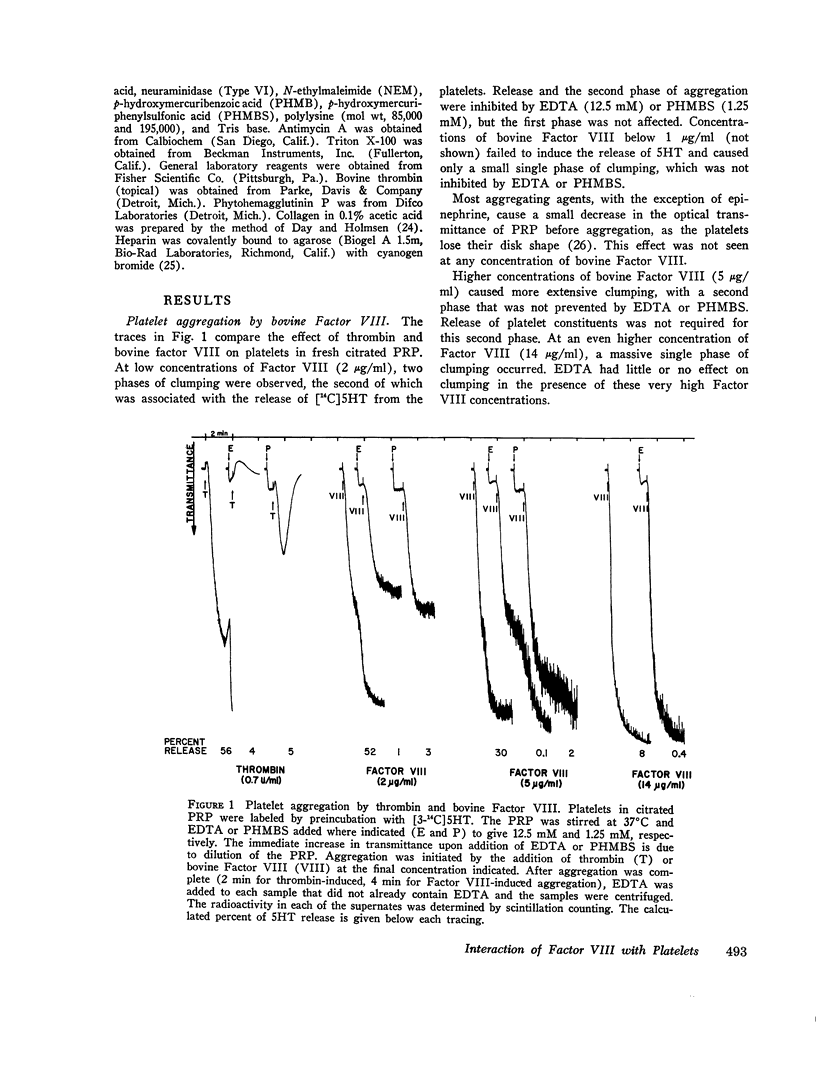
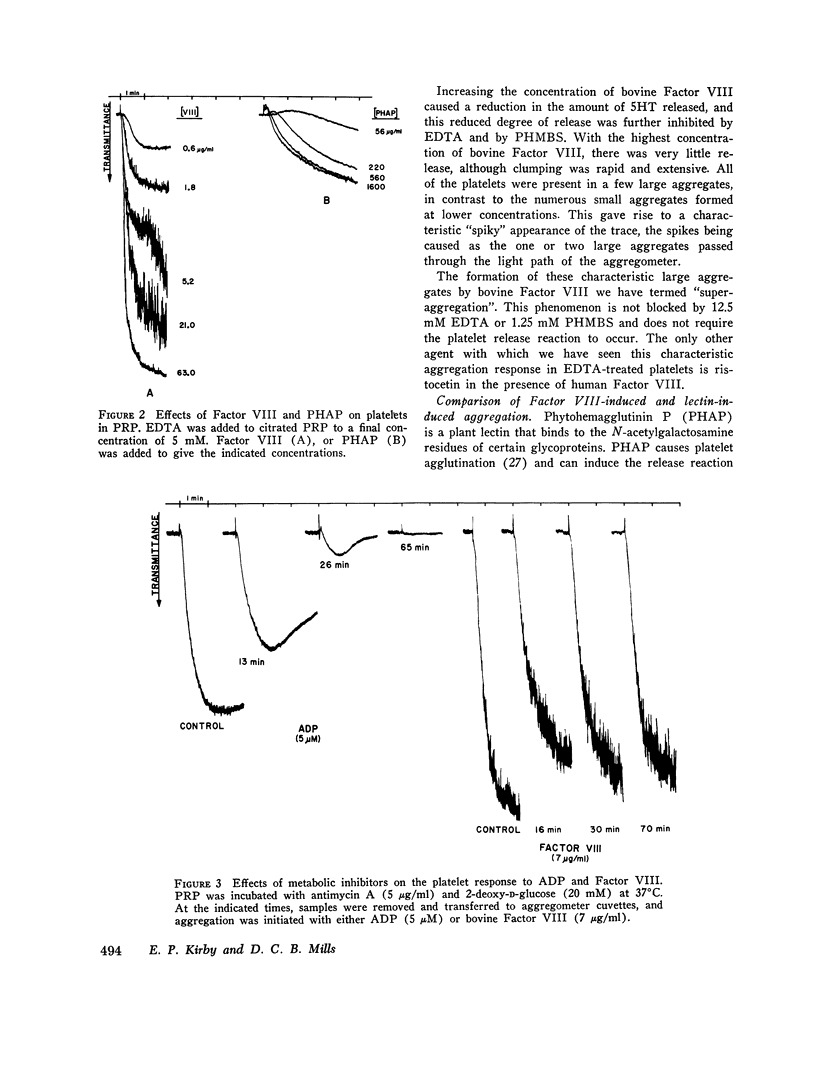
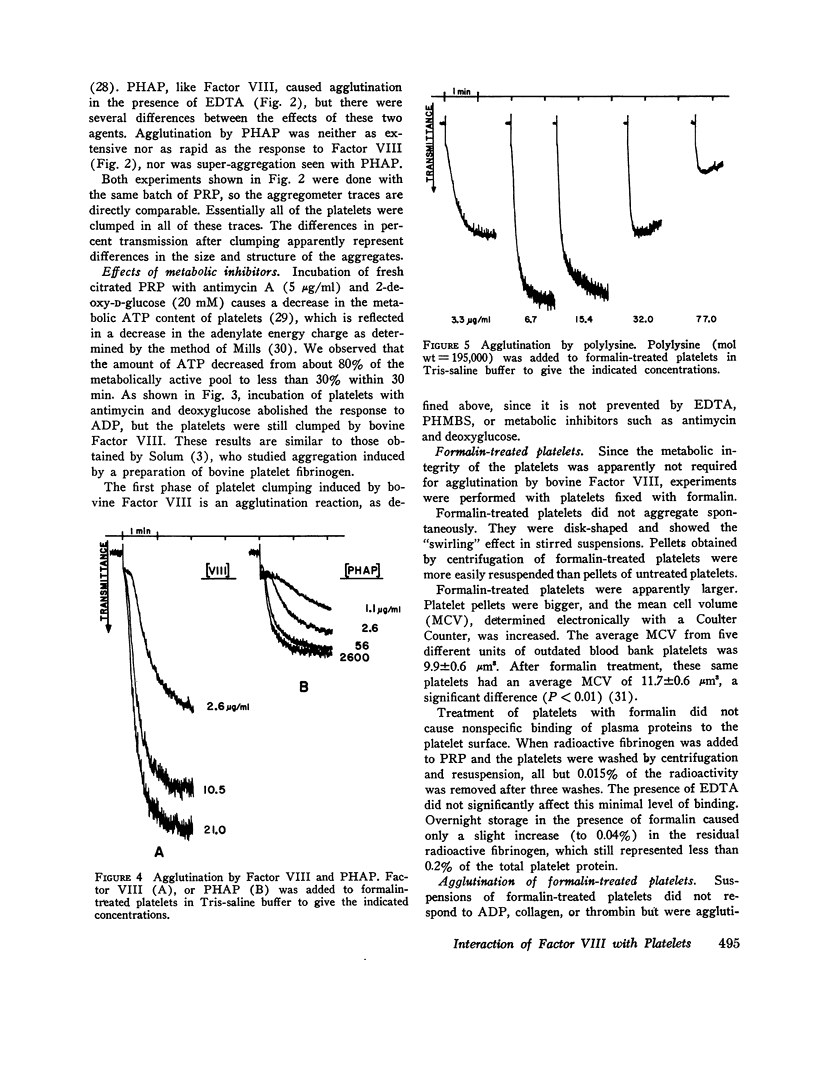
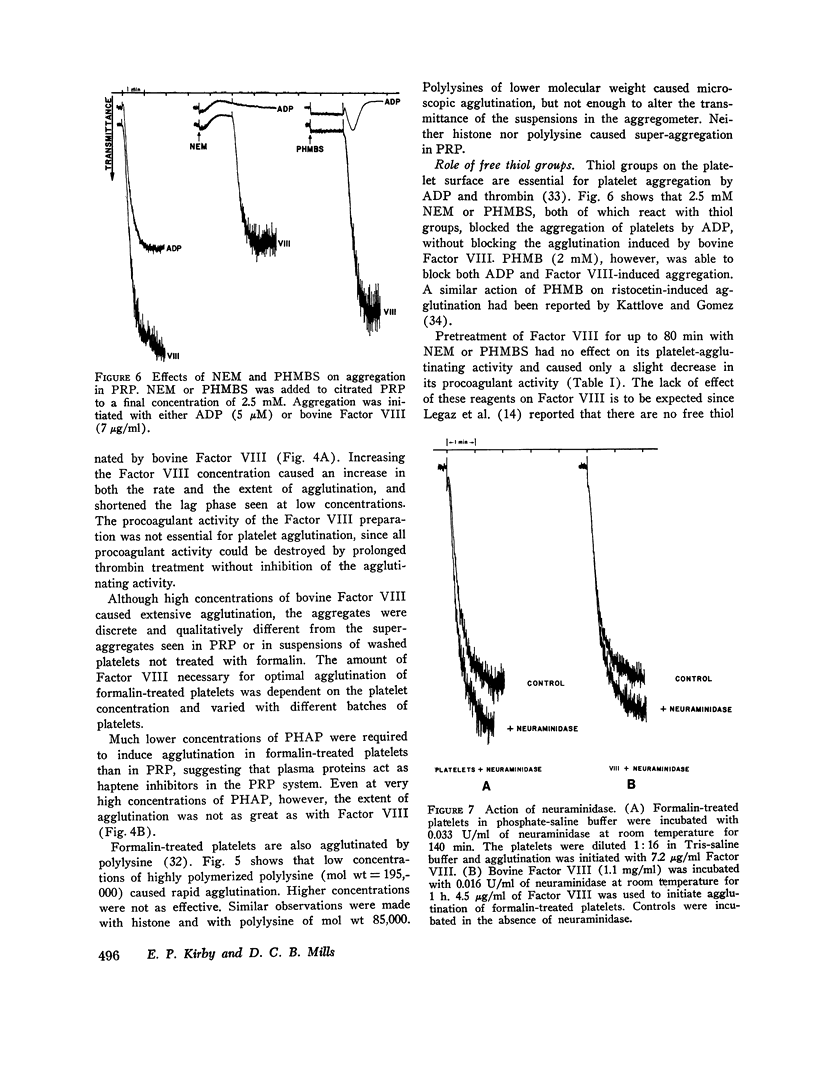
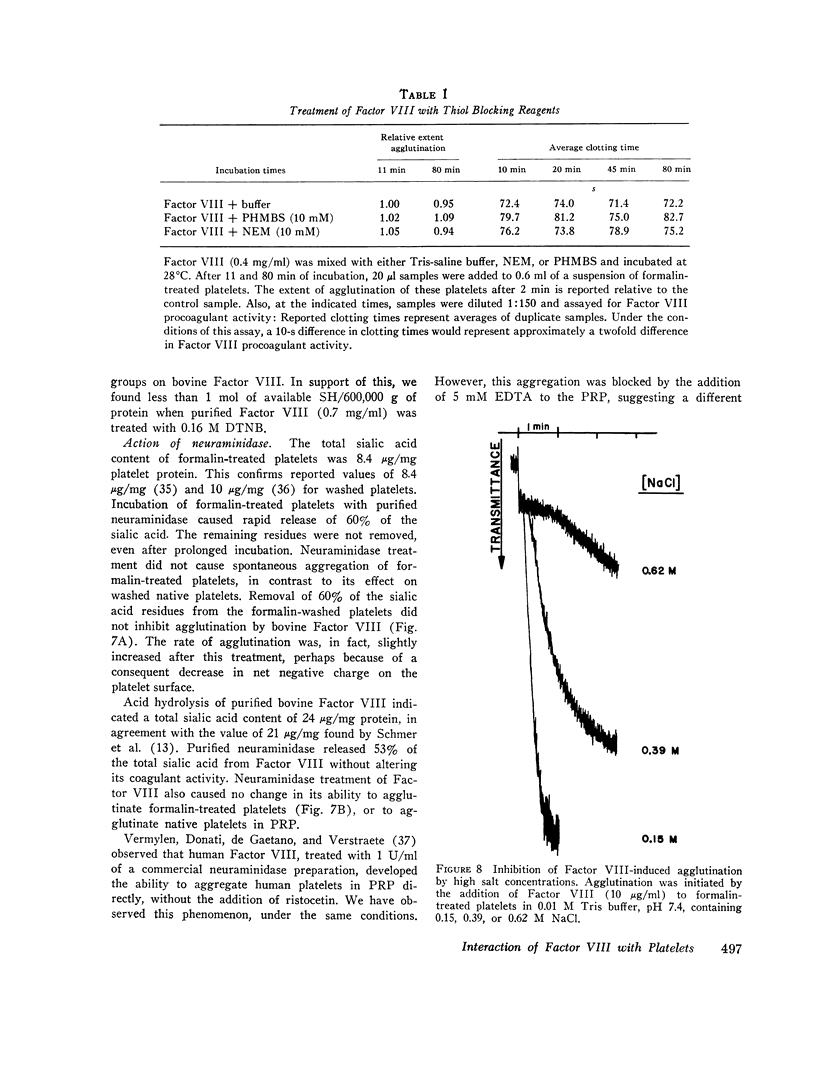
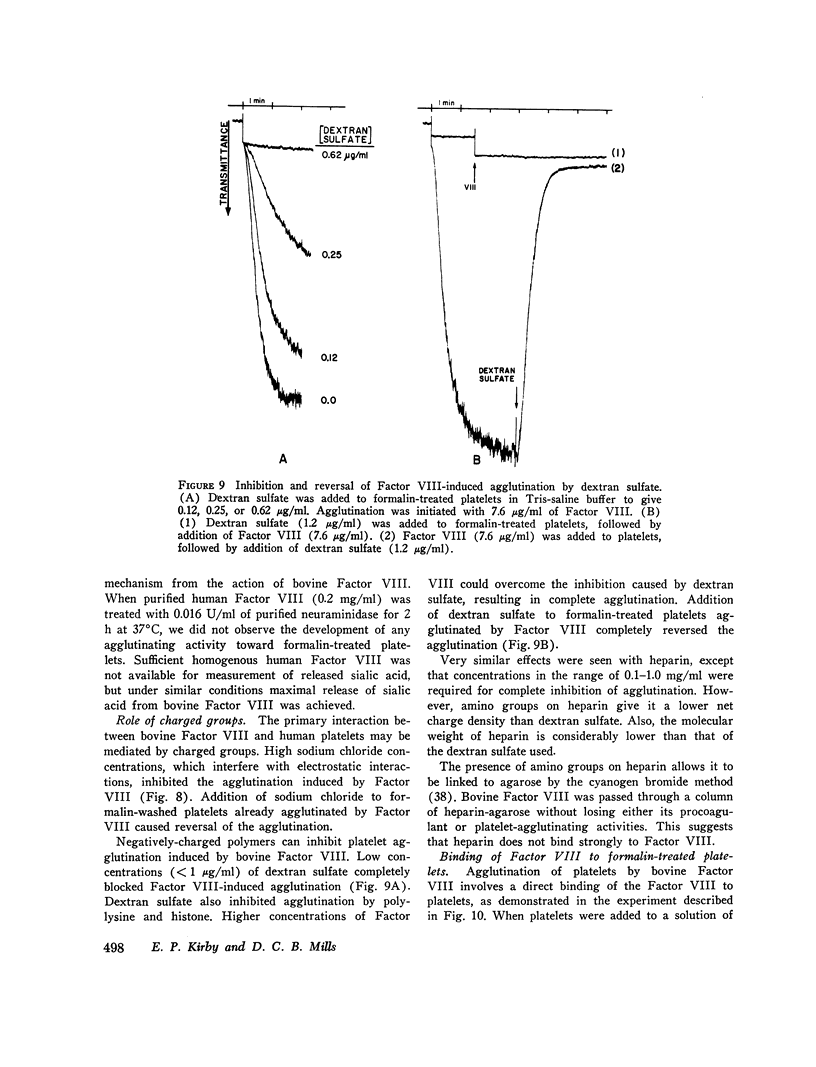
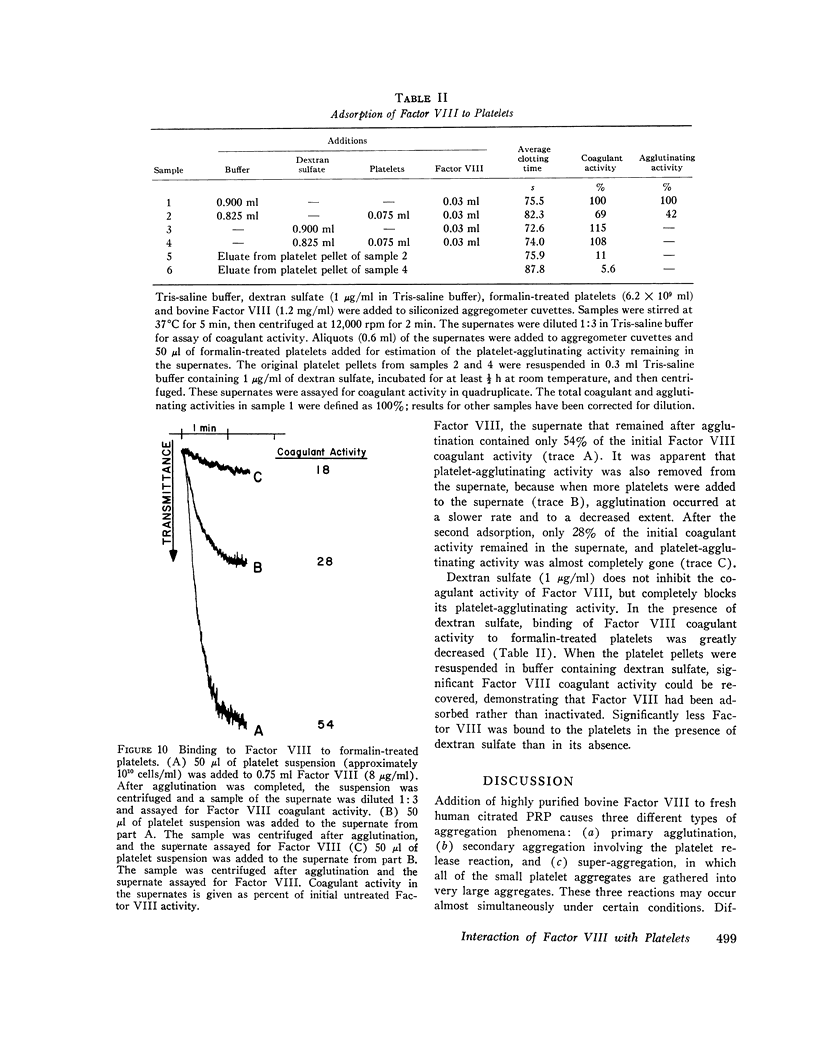
Treatment of human platelets with purified bovine Factor VIII caused three types of aggregation: (a) primary agglutination; (b) secondary aggregation involving the platelet release reaction; and (c) super-aggregation, in which the platelets were gathered into only a few large clumps. Removal of calcium ions or treatment with p-hydroxymercuiriphenyl sulfonate blocked the release reaction, but not primary agglutination or super-aggregation. Platelets treated with formalin were not aggregated by ADP, thrombin, or collagen, but were agglutinated by bovine Factor VIII, although they did not show super-aggregation. For malin-treated platelets were agglutinated by phytohemagglutinin P less extensively and less rapidly than by bovine Factor VIII. Treatment of platelets and Factor VIII with neuraminidase released 60 and 53%, respectively, of the sialic acid residues without affecting the agglutination reaction or the procoagulant activity of the Factor VIII. Agglutination was inhibited by high salt concentrations, dextran sulfate, and heparin. During agglutination, both the procoagulant and platelet-agglutinating activities of Factor VIII became bound to the platelet surface.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austen D. E. Thiol groups in the blood clotting action of factor VIII. Br J Haematol. 1970 Oct;19(4):477–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb06975.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bithell T. C., Parekh S. J., Strong R. R. Platelet-function studies in the Bernard-Soulier syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Oct 27;201:145–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouma B. N., Wiegerinck Y., Sixma J. J., Van Mourik J. A., Mochtar I. A. Immunological characterization of purified anti-haemophilic factor A (factor VIII) which corrects abnormal platelet retention in Von Willebrand's disease. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 29;236(65):104–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio236104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. B. Letter: A note on the molar absorptivity of reduced Ellman's reagent, 3-carboxylato-4-nitrothiophenolate. Anal Biochem. 1973 Nov;56(1):310–311. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day H. J., Holmsen H. Laboratory tests of platelet function. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1972 Jan-Feb;2(1):63–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes C. D., Prentice C. R. Aggregation of human platelets by purified porcine and bovine antihaemophilic factor. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 31;241(109):149–150. doi: 10.1038/newbio241149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry P. W., Alexander B. Specific coagulation factor adsorption to insoluble heparin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 23;50(2):500–509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90868-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs T. R., Cooper H. A., Webster W. P., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Plasma aggregating factor (bovine) for human platelets: a marker for study of antihemophilic and von Willebrand Factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2814–2818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gröttum K. A., Solum N. O. Congenital thrombocytopenia with giant platelets: a defect in the platelet membrane. Br J Haematol. 1969 Mar;16(3):277–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb00402.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton M. W., Regoeczi E. A simple method for the purification of commercial neuraminidase preparations free from proteases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 15;327(1):114–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Setkowsky C. A., Day H. J. Effects of antimycin and 2-deoxyglucose on adenine nucleotides in human platelets. Role of metabolic adenosine triphosphate in primary aggregation, secondary aggregation and shape change of platetets. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;144(2):385–396. doi: 10.1042/bj1440385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. A., Sawers R. J., Firkin B. G. Ristocetin: a means of differentiating von Willebrand's disease into two groups. Blood. 1973 May;41(5):687–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kattlove H. E., Gomez M. H. Studies on the mechanism of ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation. Blood. 1975 Jan;45(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legaz M. E., Schmer G., Counts R. B., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of human Factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3946–3955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Toledano S., Caen J. P., Halmos T., Mester L. Dissociation between human platelet agglomerating activity and factor VIII procoagulant activity of bovine plasma preparations by chemical treatment. I. Effect of neuraminidase. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1973 Nov;21(Suppl):60–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACFARLANE R. G., BIGGS R., BIDWELL E. Bovine antihaemophilic globulin in the treatment of haemophilia. Lancet. 1954 Jun 26;266(6826):1316–1319. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(54)92208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Brodie G. N. The binding of phytohemagglutinins to human platelet plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4253–4257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mester L., Szabados L., Guinebault P. R., Caen J., Levy-Toledano S. Variations de l'acide sialique plaquettaire dans les thrombopathies constitutionnelles et acquises. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1971 Nov 29;273(22):2157–2160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. C. Changes in the adenylate energy charge in human blood platelets induced by adenosine diphosphate. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 13;243(128):220–222. doi: 10.1038/newbio243220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. C., Roberts G. C. Effects of adrenaline on human blood platelets. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):443–453. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. R. Effects of adenosine diphosphate and adrenaline on mean platelet shape. Nature. 1965 Jul 17;207(994):306–307. doi: 10.1038/207306b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCTOR R. R., RAPAPORT S. I. The partial thromboplastin time with kaolin. A simple screening test for first stage plasma clotting factor deficiencies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961 Sep;36:212–219. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/36.3.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Axen R., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1491–1492. doi: 10.1038/2151491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON C. W., Jr, MASON R. G., WAGNER R. H. EFFECT OF SULFHYDRYL INHIBITORS ON PLATELET AGGLUTINABILITY. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Aug-Sep;113:857–861. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scales B. A new scintillator for liquid scintillation counting. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1967 Jan;18(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(67)90165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmer G., Kirby E. P., Teller D. C., Davie E. W. The isolation nd characterization of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2512–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solum N. O. Aggregation of human platelets by bovine platelet fibrinogen. Scand J Haematol. 1968;5(6):474–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1968.tb00868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen D. M., Feagler J. R., Majerus P. W. Induction of the platelet release reaction by phytohemagglutinin. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):211–218. doi: 10.1172/JCI107540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermylen J., Donati M. B., De Gaetano G., Verstraete M. Aggregation of human platelets by bovine or human factor VIII: role of carbohydrate side chains. Nature. 1973 Jul 20;244(5412):167–168. doi: 10.1038/244167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N., Mills D. C., Pareti F. I., Stewart G. J., Macfarlane D. E., Johnson M. M., Egan J. J. Hereditary giant platelet syndrome. Absence of collagen-induced coagulant activity and deficiency of factor-XI binding to platelets. Br J Haematol. 1975 Apr;29(4):639–655. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb02750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Rogers J., Brand H. Defective ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation in von Willebrand's disease and its correction by factor VIII. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2697–2707. doi: 10.1172/JCI107464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Ratnoff O. D., Powell A. E. Immunologic differentiation of classic hemophilia (factor 8 deficiency) and von Willebrand's dissase, with observations on combined deficiencies of antihemophilic factor and proaccelerin (factor V) and on an acquired circulating anticoagulant against antihemophilic factor. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):244–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI106480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



