Abstract
Female exotic dancers are an important, yet understudied group of women who may engage in drug- and sex-related HIV/STI risk behaviors through their work. The study objective was to identify co-occurring indicators of vulnerability (e.g., housing, income, incarceration) associated with HIV/STI risk behavior among female exotic dancers in Baltimore, Maryland. Surveys administered during July 2008–February 2009 captured socio-demographic characteristics, drug use, and sexual practices among dancers (N=101) aged ≥18 years. Multivariate logistic regression was used to assess the relationship between vulnerability and risk behavior. Dancers with a high vulnerability score (i.e., 2 or more indicators) were more likely to report sex exchange (AOR: 10.7, 95% CIs: 2.9, 39.9) and multiple sex partnerships (AOR: 6.4, 95% CIs: 2.3, 18.3), controlling for demographics and drug use, compared to their less vulnerable counterparts. Findings point to primacy of macro-level factors that need to be addressed in HIV/STI prevention efforts targeting this and other high-risk populations.
Keywords: female exotic dancers, sex exchange, illicit drug use, HIV/STIs, vulnerability
Introduction
Worldwide, female sex workers face a disproportionate burden of HIV and other STIs (Baral et al., 2012; Pitpitan et al., 2013). Occupational hazards of sex work are facilitated by unprotected sex with high-risk, concurrent sex partners (Patterson, Semple, & Staines, 2008; Sanders, 2004). In many settings, high-risk sex work is complicated by alcohol and drug use (Pitpitan et al., 2013; Dunkle et al., 2004).
In the U.S. as elsewhere, the nature and location of sex work exists along a continuum. Sex work environments include venue- and street-based, each characterized by varying levels of HIV/STI risk (Baral et al., 2012; Pitpitan et al., 2013). While not inherently defined by sex work, exotic dancing falls within that continuum, with some female exotic dancers (FEDs) exchanging sex for money or drugs within exotic dance clubs (Maticka-Tyndale et al., 1999; Sherman, Lilleston, & Reuben, 2011). Despite these high-risk behaviors, FEDs remain understudied.
Focusing on structural, socioeconomic determinants of HIV/STIs is critical for effective prevention and control of infection among key risk populations (Latkin et al., 2013; Rhodes et al., 2012). For example, HIV/STI risk may be amplified through dancers’ experiences of socioeconomic hardship, e.g., unstable housing, incarceration. While there may be some overlap among previously studied populations, other social and economic stressors experienced by FEDs may differ, given their employment status and associated income (Maticka-Tyndale et al., 1999; Reuben et al., 2011). The impact of these stressors–referred to in this paper as indicators of vulnerability–on exposure to drug- and sex-related harms is not well understood (Maticka-Tyndale et al., 1999; Sherman et al., 2011).
This study characterizes indicators of structural vulnerability associated with HIV/STI risk behavior (drug use, sex exchange, multiple sex partners) and explores the effect of accumulated vulnerability on the likelihood of dancers’ engagement in risk behavior. This timely research has the potential to contribute to innovative multi-level prevention interventions seeking to target populations most-at-risk for HIV/STIs.
Methods
Study population
Data were obtained from a cross-sectional study that examined drug- and sex-related risk behaviors among FEDs, detailed elsewhere (Reuben 2011). Conducted during July 2008–February 2009, surveys captured socio-demographic characteristics, drug use, and sexual practices among FEDs (N=101) working on The Block, a historic red light district in downtown Baltimore. Eligibility criteria were: age (≥18 years), Baltimore City residency, and having danced at an exotic dance club in the past three months. Two trained female study staff recruited and screened participants working in seven of the 20 clubs located on The Block. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Measures
Dependent variables
The main outcomes of interest were recent (past three months) self-report of: drug use (cocaine, crack, or heroin use), exchanging sex for money or drugs (“sex exchange”), and having ≥2 sex partners (“multiple”).
Independent variables
Four indicators of vulnerability were selected based on relevant literature: unstable housing (living in boarding house, streets, or someone else’s apartment in past three months), residential transience (moving ≥2 times in past year), ever in jail, and illegal income sources (Aidala et al., 2005; Bouhnik et al., 2002; German et al., 2007; German & Latkin, 2012; Khan et al., 2009). A cumulative vulnerability score was calculated by summing the number of vulnerability indicators reported per participant (range 0 to 4). Demographic control variables included age, race, and education.
Statistical analysis
We characterized the sample’s demographic characteristics, vulnerability indicators, and HIV/STI risk behaviors. To assess the co-occurrence of multiple vulnerabilities and identify relationships between variables of interest, we ran logistic regression models and estimated bivariate associations between: each possible pair of indicators; each of the three HIV/STI risk behaviors; and each of the vulnerability indicators and risk behaviors.
To visually explore the effect of accumulated vulnerability on HIV/STI risk behavior, we generated histograms displaying the proportion of each reported HIV/STI risk behavior by vulnerability score. For the regression models, vulnerability score was dichotomized into low (0–1 indicator) and high (24 indicators) vulnerability due to small cell sizes. Three unadjusted logistic regression models estimated bivariate associations between vulnerability level and each of the HIV/STI risk behaviors, which informed final multivariate logistic regression models. Potential confounding variables were also included. All statistical analyses were conducted using Stata (Stata Statistical Software: Release 12. College Station, TX: StataCorp LP).
Results
Descriptive statistics are presented in Table 1. More than half of participants were <24 years old, white, high school graduates, and made ≥$2,000 per month. Vulnerability indicators were common among participants: 49% reported unstable housing, 28% were transient, 55% had been in jail, and 30% received illegal income. HIV/STI risk behaviors–drug use (43%), sex exchange (40%), and multiple sex partners (48%)–were also frequent among the study population.
Table 1.
Demographics, structural vulnerability, and HIV/STI risk behaviors among female exotic dancers in Baltimore (n=101)
| Characteristic | n | (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, median (SD), years | 24 | (5.6) |
| Race | ||
| White | 58 | (57.4) |
| Non-white/other | 43 | (42.6) |
| Education | ||
| Less than high school graduate | 44 | (43.6) |
| High school graduate or higher | 57 | (56.4) |
| Monthly income, median (SD) | $2,000 | ($1823.1) |
| Unstable housinga | ||
| Yes | 49 | (48.5) |
| No | 52 | (51.5) |
| Transienceb | ||
| Yes | 28 | (27.7) |
| No | 73 | (72.3) |
| Jail, ever | ||
| Yes | 56 | (55.4) |
| No | 44 | (43.6) |
| Unknown | 1 | (1.0) |
| Illegal incomec | ||
| Yes | 30 | (29.7) |
| No | 71 | (70.3) |
| Drug used | ||
| Yes | 43 | (42.6) |
| No | 58 | (57.4) |
| Sex exchangee | ||
| Yes | 40 | (39.6) |
| No | 56 | (55.5) |
| Unknown | 5 | (4.9) |
| Multiple sex partnersf | ||
| Yes | 48 | (47.5) |
| No | 47 | (46.5) |
| Unknown | 6 | (5.9) |
Notes: Vulnerability variables and behavioral outcomes reported in past 3 months unless otherwise indicated.
Unstable housing: lived in boarding house, streets, or someone else’s apartment.
Transience: moved ≥2 in past year.
Illegal income: answered “yes” to illegal income as ≥1 source of income.
Drug use: cocaine, crack, or heroin.
Sex exchange: exchanged sex for money or drugs.
Multiple sex partners: ≥2 male sex partners.
Table 2 displays the bivariate relationships between vulnerability indicators and HIV/STI risk behaviors. Transience was not associated with unstable housing nor history of jail, but significant associations were identified across all other relationships tested for co-occurrence. All vulnerability indicators were associated with recent drug use and sex exchange; unstable housing and history of jail were associated with multiple sex partnerships.
Table 2.
Bivariate associations among co-occurring indicators of vulnerability and HIV/STI risk behavior (n=101)
| Characteristic | Unstable housinga OR (95% CI) |
Transienceb OR (95% CI) |
Jail, ever OR (95% CI) |
Illegal incomec OR (95% CI) |
Drug used OR (95% CI) |
Sex exchangee OR (95% CI) |
Multiple sex partnersf OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vulnerability | |||||||
| Unstable housinga | -- | 2.0 (0.8, 4.8) | 2.8 (1.2, 6.3) | 2.9 (1.2, 7.1) | 2.8 (1.2, 6.2) | 4.0 (1.7, 9.6) | 4.3 (1.8, 10.2) |
| Transienceb | -- | 2.5 (1.0, 6.4) | 7.1 (2.7, 18.8) | 2.8 (1.1, 6.9) | 3.4 (1.3, 8.6) | 2.0 (0.8, 5.1) | |
| Jail, ever | -- | 3.7 (1.4, 9.7) | 3.1 (1.3, 7.2) | 7.1 (2.7, 18.8) | 4.7 (1.9, 11.3) | ||
| Illegal incomec | -- | 14.7 (4.9, 44.2) | NRg | NRg | |||
| HIV/STI risk behaviors | |||||||
| Drug used | -- | 20.9 (7.3, 59.9) | 8.4 (3.3, 21.7) | ||||
| Sex exchangee | -- | NRg | |||||
| Multiple sex partnersf | -- |
Notes: OR=odds ratio; significant associations in bold font; vulnerability variables and behaviors reported in past 3 months unless otherwise indicated.
Unstable housing: lived in boarding house, streets, or someone else’s apartment.
Transience: moved ≥2 in past year.
Illegal income: answered “yes” to illegal income as ≥1 source of income.
Drug use: cocaine, crack, or heroin.
Sex exchange: exchanged sex for money or drugs (model n=96).
Multiple sex partners: ≥2 male sex partners (model n=95).
Odds ratios not reported. Illegal income highly correlated with sex exchange and having multiple sex partners; sex exchange was highly correlated with having multiple sex partners.
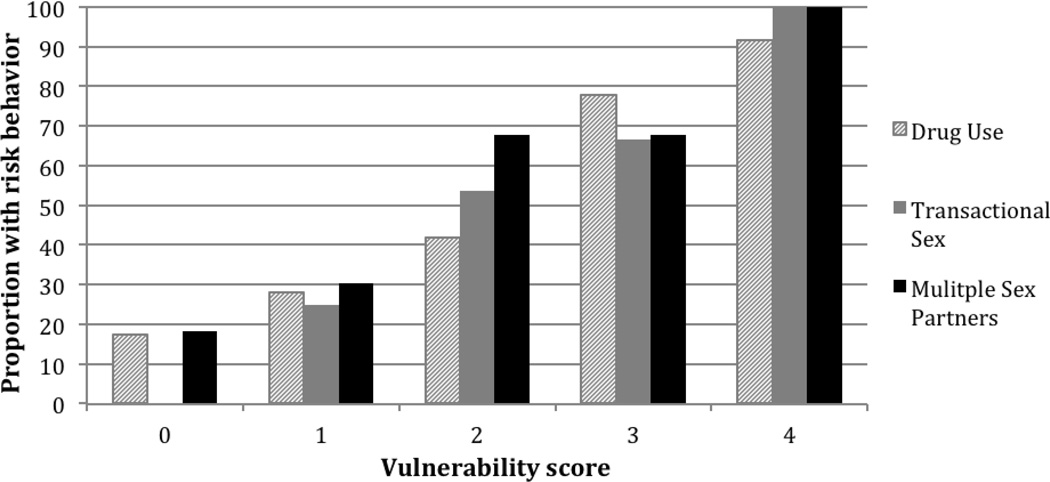
Figure 1 illustrates the effect of multiple vulnerability indicators on the likelihood of engaging in high-risk sexual and drug behaviors. As the vulnerability score increased, the frequency of drug use, sex exchange, and multiple sex partnerships also increased, suggesting a cumulative effect of vulnerability on HIV/STI risk behavior.
Figure 1.
Distribution of reported HIV/STI risk behaviorsa, by vulnerability scoreb
aHIV/STI risk behaviors in past 3 months: drug use (cocaine, crack, or heroin); sex exchange (exchanged sex for money or drugs); multiple sex partnerships (≥2 male sex partners).
bVulnerability score: number of reported indicators of vulnerability (unstable housing, transience, history of jail, illegal income sources).
Table 3 presents the results of unadjusted and adjusted logistic regression models of vulnerability and risk behaviors. In adjusted models, high vulnerability remained significantly associated with both sex exchange and multiple sex partnerships.
Table 3.
Characteristics associated with recent HIV/STI risk behaviors among female exotic dancers in Baltimore
| Drug usea (n=95) | Sex exchangeb (n=96) | Multiple sex partnersc (n=95) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | UOR (95% CI) | AOR (95% CI) | UOR (95% CI) | AOR (95% CI) | UOR (95% CI) | AOR (95% CI) |
| Aged ≥24 years | 3.2 (1.4, 7.2) | 2.2 (0.8, 6.2) | 3.7 (1.6, 8.9) | 3.0 (1.1, 8.6) | 1.7 (0.8, 3.9) | 0.9 (0.3, 2.6) |
| White | 5.4 (2.2, 13.2) | 3.0 (1.0, 9.5) | 3.0 (1.3, 6.9) | 1.2 (0.4, 3.6) | 3.1 (1.3, 7.2) | 1.8 (0.6, 5.7) |
| Less than high school graduation | 2.0 (0.9, 4.5) | 1.1 (0.4, 3.2) | 2.6 (1.1, 6.2) | 2.4 (0.8, 7.3) | 2.3 (1.0, 5.2) | 1.2 (0.4, 3.7) |
| High vulnerabilityd | 5.0 (2.1, 11.9) | 2.3 (0.7, 7.2) | 13.8 (4.8, 39.1) | 10.7 (2.9, 39.9) | 9.5 (3.7, 24.4) | 6.4 (2.3, 18.3) |
| Drug use | -- | -- | 20.9 (7.3, 59.9) | 11.9 (3.5, 41.0) | 8.4 (3.3, 21.7) | 5.4 (1.8, 16.6) |
| Multiple sex partners | 8.4 (3.3, 21.7) | 5.4 (1.7, 16.7) | e | e | -- | -- |
Notes: UOR=unadjusted odds ratio; AOR=adjusted odds ratio; each column represents a single logistic regression model.
Drug use: cocaine, crack, or heroin in past 3 months.
Sex exchange: exchanged sex for money or drugs in past 3 months.
Multiple sex partners: 2 male sex partners in past 3 months.
High vulnerability: 2–4 indicators reported.
Sex exchange was highly correlated with having multiple sex partners and therefore not included as an independent variable in the models.
Discussion
This study is the first to explore the vulnerability profiles of female exotic dancers. We found a dose-response relationship between levels of socioeconomic vulnerability and likelihood of engaging in HIV/STI risk behavior. Specifically, a cluster of vulnerability indicators that included unstable housing, residential transience, history of jail, and illegal income sources were significantly associated with two sexual risk measures. Characterizing the socioeconomic context of such a key population is critical for obtaining a deep understanding of their risk and developing tailored strategies for sustainable HIV/STI prevention interventions.
Although participants reported earning a significant income, they also reported a number of other vulnerabilities (e.g., unstable housing, incarceration), with higher vulnerability associated with drug use and selling sex. Given the sample’s employment status, we explored income source as a potential indicator of vulnerability. As would be expected, illegal income was highly correlated with sex exchange and strongly associated with drug use. Supplementing licit income with illegal sources may be an important proxy for risk among this group of employed women.
HIV/STI risk was also associated with housing type, transience, and history of jail. This finding is consistent with previous research among samples of drug users (Aidala et al., 2005; German et al., 2007) and formerly incarcerated individuals (Inciardi et al., 2007; Khan et al., 2009; Rasch et al., 2013). The dose-response relationship between vulnerability indicators and high-risk behaviors suggests that socioeconomic factors are not only inter-connected, but in combination may amplify HIV/STI risk.
The study is characterized by several limitations. The small sample impacted the precision of the estimates for relationships under study. Sample size precluded us from examining accumulated vulnerability at a more granular level; a dichotomous, rather than continuous, vulnerability score was used in the final multivariate models. Moreover, models were limited to few variables and we were unable to explore the effects of factors such as length and type of exotic dancing employment (part/full-time), relationship status, and having children on the likelihood of engaging in HIV/STI risk behaviors. Sex exchange was highly correlated with having multiple sex partners and excluded from multivariate models. The relationship between transactional sex and other risk behaviors may be important in the presence of other confounding variables, but we were unable to conclude how and to what degree. As the data are self-reported, bias may exist relating to social desirability associated with questions about private or illegal behaviors. The cross-sectional design limited our ability to assess causality. The mechanisms by which selling sex, managing money, and drug use occur could not be teased out with the available data; however, findings suggest that money alone is not protective against HIV/STI vulnerability. Lastly non-random sampling limits generalizability to all exotic dancers.
Despite these limitations, this study is significant given the high levels of HIV/STI risk and the unique constellation of vulnerability indicators that characterize this understudied population. Identifying co-occurring aspects of socioeconomic instability is a critical step in understanding, and ultimately preventing, how and why dancers and other vulnerable populations might turn to drug use and sex exchange. The study findings point to macro-level factors to consider when developing interventions intended to reduce sex- and drug-related risk among FEDs. Policies that promote access to safe and affordable housing may be particularly relevant in this population and could contribute to reducing such risk. Additional research to further understand the synergy between structural vulnerabilities and the forces that drive sex- and drug-risk behavior will help to develop strategies for prevention programs targeting female exotic dancers.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the support of the Baltimore City Health Department, recruitment assistance by Nathan Fields, data collection by Pamela Lilleston and Jacqueline Reuben, and the participation of women who dance on The Block.
Funding
M.L. Reilly was supported for this work by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease [T32 AI050056-12] and the National Institute on Drug Abuse [F31 DA038540].
References
- Aidala A, Cross JE, Stall R, Harre D, Sumartojo E. Housing status and HIV risk behaviors: implications for prevention and policy. AIDS and Behavior. 2005;9(3):251–265. doi: 10.1007/s10461-005-9000-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baral S, Beyrer C, Muessig K, Poteat T, Wirtz AL, Decker MR, Kerrigan D. Burden of HIV among female sex workers in low-income and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2012;12(7):538–549. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70066-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouhnik A, Chesney M, Carrieri P, Gallais H, Moreu J, Moatti J MANIF 2000 Study Group. Nonadherence among HIV-infected injecting drug users: the impact of social instability. Journal of Aquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes. 2002;31:S149–S153. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200212153-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkle KL, Jewkes RK, Brown HC, Gray GE, McIntryre JA, Harlow SD. Transactional sex among women in Soweto, South Africa: prevalence, risk factors and association with HIV infection. Social Science & Medicine. 2004;59(8):1581–1592. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2004.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German D, Davey MA, Latkin CA. Residential transience and HIV risk behaviors among injection drug users. AIDS and Behavior. 2007;11(6 Suppl):21–30. doi: 10.1007/s10461-007-9238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German D, Latkin CA. Social stability and HIV risk behavior: Evaluating the role of accumulated vulnerability. AIDS and Behavior. 2012;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1007/s10461-011-9882-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inciardi JA, Surratt HL, Martin SS, O’Connell DJ, Salandy AD, Beard RA. Developing a multimedia HIV and hepatitis intervention for drug-involved offenders reentering the community. The Prison Journal. 2007;87(1):111–142. [Google Scholar]
- Khan MR, Doherty IA, Schoenbach VJ, Taylor EM, Epperson MW, Adimora AA. Incarceration and high-risk sex partnerships among men in the United States. Journal of Urban Health. 2009;86(4):584–601. doi: 10.1007/s11524-009-9348-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latkin CA, Davey-Rothwell MA, Knowlton AR, Alexander KA, Williams CT, Boodram B. Social network approaches to recruitment, HIV prevention, medical care, and medication adherence. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes. 2013;63:54–58. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3182928e2a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maticka-Tyndale E, Lewis J, Clark JP, Zubick J, Young S. Social and cultural vulnerability to sexually transmitted infection: the work of exotic dancers. Canadian Journal of Public Health. 1999;90(1):19–22. doi: 10.1007/BF03404092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson TL, Semple SJ, Staines H, Lozada R, Orozovich P, Bucardo J, Strathdee SA. Prevalence and correlates of HIV infection among female sex workers in 2 Mexico-US border cities. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2008;197(5):728–732. doi: 10.1086/527379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitpitan EV, Kalichman SC, Eaton LA, Strathdee SA, Patterson TL. HIV/STI risk among venue-based female sex workers across the globe: a look back and the way forward. Current HIV/AIDS Reports. 2013;10(1):65–78. doi: 10.1007/s11904-012-0142-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasch RFR, Davidson D, Seiters J, Macmaster SA, Adams S, Darby K, Cooper RL. Integrated recovery management model for ex-offenders with co-occurring mental health and substance use disorders and high rates of HIV risk behaviors. The Journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care. 2013:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jana.2012.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben J, Serio-Chapman C, Welsh C, Matens R, Sherman SG. Correlates of current transactional sex among a sample of female exotic dancers in Baltimore, MD. Journal of Urban Health. 2011;88(2):342–351. doi: 10.1007/s11524-010-9539-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes T, Wagner K, Strathdee SA, Shannon K, Davidson P, Bourgois P. Structural violence and structural vulnerability within the risk environment: theoretical and methodological perspectives for a social epidemiology of HIV risk among injection drug users and sex workers. In: O'Campo P, Dunn JR, editors. Rethinking social epidemiology: Towards a science of change. 2012. pp. 205–230. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders T. A continuum of risk? The management of health, physical and emotional risks by female sex workers. Sociology of Health and Illness. 2004;26(5):557–574. doi: 10.1111/j.0141-9889.2004.00405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman SG, Lilleston P, Reuben J. More than a dance: the production of sexual health risk in the exotic dance clubs in Baltimore, USA. Social Science & Medicine. 2011;73(3):475–481. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2011.05.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]