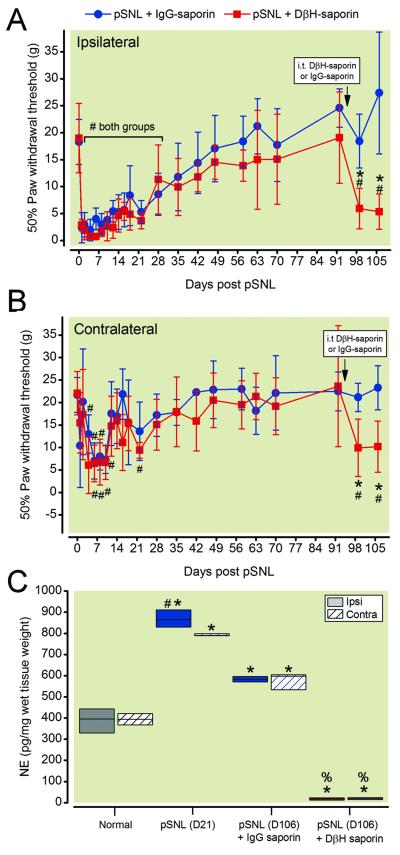
Figure 5.
Spinal norepinephrine tonically inhibits mechanical hypersensitivity after partial spinal nerve ligation (pSNL). Rats received intrathecal treatment with DβH-saporin or IgG-saporin 91 days after pSNL surgery (approximately 7 weeks after mechanical hypersensitivity resolved). Mechanical hypersensitivity was reinstated in the ipsilateral (A) and contralateral (B) paw of DβH-saporin treated rats. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparisons. * p < 0.002 for within timepoint comparison to pSNL + IgG saporin values or # p < 0.003 for within treatment group comparisons to Pre-surgery baseline value. Values represent mean ± SD with n=6 per group. In the same groups of rats, norepinephrine content was significantly reduced in the dorsal spinal cord of DβH-saporin treated pSNL rats compared to IgG saporin treated pSNL rats (C). Norepinephrine content examined in a separate group of normal and pSNL rats showed increased content three weeks postoperatively that persisted through fifteen weeks. Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance on ranks using pairwise multiple comparison procedures (Student –Newman-Keuls method) or Mann Whitney Rank Sum test * p< 0.05 vs. normal. % p < 0.05 vs. pSNL (D106) +IgG-saporin. # p< 0.05 vs. contra within group comparison. Values represent median ± 25th and 75th percentile with n=6 per group. DβH = dopamine β hydroxylase; IgG = immunoglobulin G; contra = contralateral; ipsi = ipsilateral; i.t. = intrathecal; NE = norepinephrine