Abstract
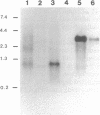
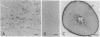
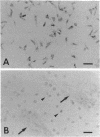
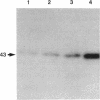
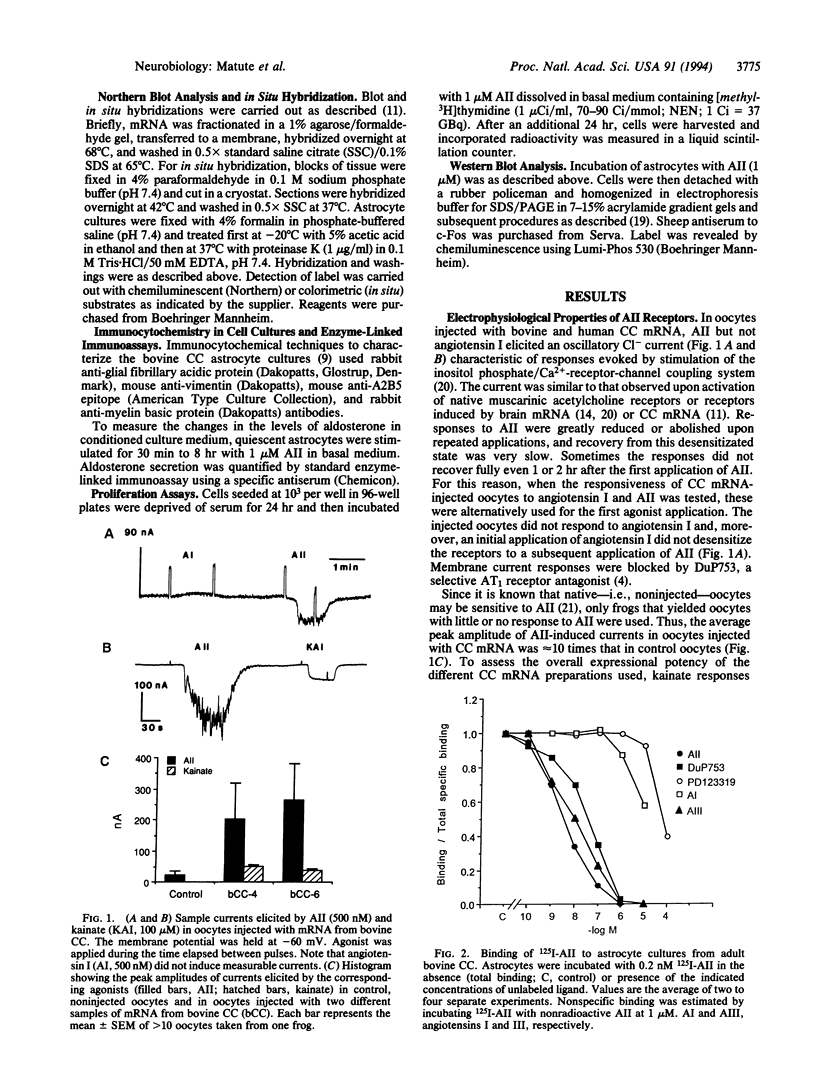
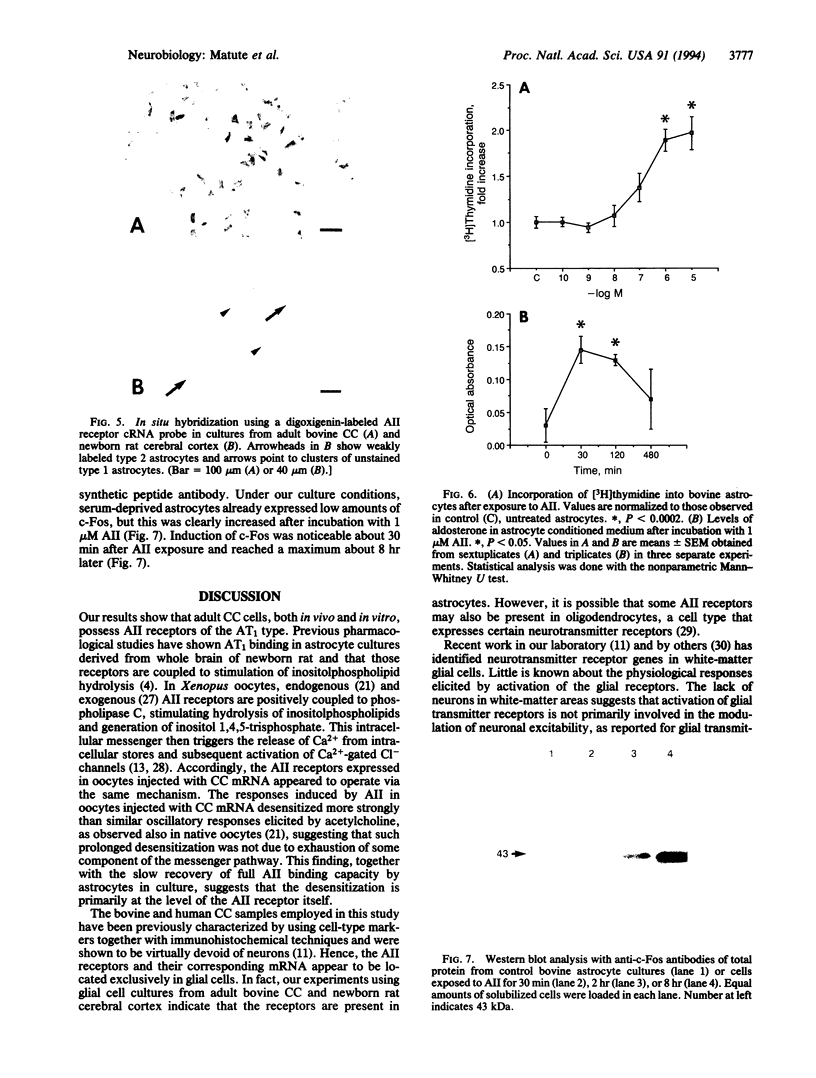
The existence and the properties of angiotensin II receptors in the adult bovine and human corpus callosum (CC) were investigated by using Xenopus oocytes and primary glial cell cultures. In oocytes injected with CC mRNA, angiotensin II elicited oscillatory Cl- currents due to activation of the inositol phosphate/Ca(2+)-receptor-channel coupling system. The receptors expressed in oocytes and in CC cultures were pharmacologically similar to the AT1 receptor type as assayed by binding. Northern blot analysis and in situ hybridization studies in sections from CC and in glial cultures revealed that the receptors were molecularly related to the AT1 receptor and that they were present in astrocytes. In these cells, activation of the receptors with angiotensin II increased de novo DNA synthesis, promoted the release of aldosterone, and induced c-Fos expression. These findings indicate that CC astrocytes possess functional AT1 receptors that participate in various physiological processes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi A., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Acetylcholine analogue stimulates DNA synthesis in brain-derived cells via specific muscarinic receptor subtypes. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):146–150. doi: 10.1038/340146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A., Koroshetz W. J., Chun L. L., Corey D. P. Ion channel expression by white matter glia: the type-1 astrocyte. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):527–544. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90091-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger T., Walz W., Schnitzer J., Kettenmann H. GABA- and glutamate-activated currents in glial cells of the mouse corpus callosum slice. J Neurosci Res. 1992 Jan;31(1):21–27. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490310104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J., Kettenmann H. Patch-clamp study of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor Cl- channels in cultured astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9336–9340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson M. C., Harper C. M., Baukal A. J., Aguilera G., Catt K. J. Physicochemical characterization of photoaffinity-labeled angiotensin II receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Feb;1(2):147–153. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-2-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu A. T., Herblin W. F., McCall D. E., Ardecky R. J., Carini D. J., Duncia J. V., Pease L. J., Wong P. C., Wexler R. R., Johnson A. L. Identification of angiotensin II receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 30;165(1):196–203. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condorelli D. F., Dell'Albani P., Amico C., Kaczmarek L., Nicoletti F., Lukasiuk K., Stella A. M. Induction of primary response genes by excitatory amino acid receptor agonists in primary astroglial cultures. J Neurochem. 1993 Mar;60(3):877–885. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross D., Cifuentes F., Huidobro-Toro J. P., Vío C. P., Inestrosa N. C. Synthesis and expression of functional angiotensin II receptors in Xenopus oocytes injected with rat brain mRNA. Brain Res. 1987 Sep;388(3):268–270. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(87)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluharty S. J., Reagan L. P., White M. M. Endogenous and expressed angiotensin II receptors on Xenopus oocytes. J Neurochem. 1991 Apr;56(4):1307–1311. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb11426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo V., Patrizio M., Levi G. GABA release triggered by the activation of neuron-like non-NMDA receptors in cultured type 2 astrocytes is carrier-mediated. Glia. 1991;4(3):245–255. doi: 10.1002/glia.440040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo V., Suergiu R., Levi G. Kainic acid stimulates GABA release from a subpopulation of cerebellar astrocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Dec 16;132(2-3):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90624-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloor S., Odink K., Guenther J., Nick H., Monard D. A glia-derived neurite promoting factor with protease inhibitory activity belongs to the protease nexins. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):687–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90511-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T. R., Blair L. A., Marshall J., Goedert M., Hanley M. R. The mas oncogene encodes an angiotensin receptor. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):437–440. doi: 10.1038/335437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen A. M., Chiu S. Y. Expression of glutamate receptor genes in white matter: developing and adult rat optic nerve. J Neurosci. 1993 Apr;13(4):1664–1675. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01664.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Miledi R., Stinnakre J. Cholinergic and catecholaminergic receptors in the Xenopus oocyte membrane. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:143–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. L. Synthesis and release of neuroactive substances by glial cells. Glia. 1992;5(2):81–94. doi: 10.1002/glia.440050202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matute C., Arellano R. O., Conde-Guerri B., Miledi R. mRNA coding for neurotransmitter receptors in a human astrocytoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3399–3403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matute C., Miledi R. Neurotransmitter receptors and voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels encoded by mRNA from the adult corpus callosum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3270–3274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matute C., Tigyi G. J., Miledi R. Xenopus oocytes as immunological vectors to produce monoclonal antibodies to rat brain antigens. J Neurosci Res. 1991 May;29(1):77–86. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490290109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy K. D., de Vellis J. Preparation of separate astroglial and oligodendroglial cell cultures from rat cerebral tissue. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):890–902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. A calcium-dependent transient outward current in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jul 22;215(1201):491–497. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I. Chloride current induced by injection of calcium into Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:173–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Woodward R. M. Effects of defolliculation on membrane current responses of Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:601–621. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller T., Möller T., Berger T., Schnitzer J., Kettenmann H. Calcium entry through kainate receptors and resulting potassium-channel blockade in Bergmann glial cells. Science. 1992 Jun 12;256(5063):1563–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.1317969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Murray J. M. Antisense RNA of proto-oncogene c-fos blocks renewed growth of quiescent 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):639–649. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris J. G., Benveniste E. N. Interleukin-6 production by astrocytes: induction by the neurotransmitter norepinephrine. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Jun;45(1-2):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90174-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. A., Jr, Shiverick K. T., Ogilvie S., Buhi W. C., Raizada M. K. Angiotensin II induces secretion of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and a tissue metalloprotease inhibitor-related protein from rat brain astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1928–1932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. I. Functions of angiotensin in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:413–435. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.002213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn S. J., Williams G. H. Regulation of aldosterone secretion. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:409–426. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg K., Ji H., Clark A. J., Shapira H., Catt K. J. Cloning and expression of a novel angiotensin II receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9455–9458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Yamano Y., Bardhan S., Iwai N., Murray J. J., Hasegawa M., Matsuda Y., Inagami T. Cloning and expression of a complementary DNA encoding a bovine adrenal angiotensin II type-1 receptor. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):230–233. doi: 10.1038/351230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Greenberg M. E. The regulation and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90106-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steckelings U. M., Bottari S. P., Unger T. Angiotensin receptor subtypes in the brain. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Sep;13(9):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90110-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumners C., Tang W., Zelezna B., Raizada M. K. Angiotensin II receptor subtypes are coupled with distinct signal-transduction mechanisms in neurons and astrocytes from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7567–7571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usowicz M. M., Gallo V., Cull-Candy S. G. Multiple conductance channels in type-2 cerebellar astrocytes activated by excitatory amino acids. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):380–383. doi: 10.1038/339380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. C., Hart S. D., Zaspel A. M., Chiu A. T., Ardecky R. J., Smith R. D., Timmermans P. B. Functional studies of nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor subtype-specific ligands: DuP 753 (AII-1) and PD123177 (AII-2). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):584–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward R. M., Miledi R. Angiotensin II receptors in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Apr 22;244(1309):11–19. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie D. J., Mathie A., Symonds C. J., Cull-Candy S. G. Activation of glutamate receptors and glutamate uptake in identified macroglial cells in rat cerebellar cultures. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:235–258. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]