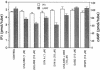
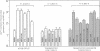Abstract
A full-length cDNA encoding the guinea pig kappa opioid (dynorphin) receptor has been isolated. The deduced protein contains 380 aa and seven hydrophobic alpha-helices characteristic of the G protein-coupled receptors. This receptor is 90% identical to the mouse and rat kappa receptors, with the greatest level of divergence in the N-terminal region. When expressed in COS-7 cells, the receptor displays high affinity and stereospecificity toward dynorphin peptides and other kappa-selective opioid ligands such as U50, 488. It does not bind the mu- and delta-selective opioid ligands. The expressed receptor is functionally coupled to G protein(s) to inhibit adenylyl cyclase and Ca2+ channels. The guinea pig kappa receptor mRNA is expressed in many brain areas, including the cerebellum, a pattern that agrees well with autoradiographic maps of classical guinea pig kappa binding sites. Species differences in the pharmacology and mRNA distribution between the cloned guinea pig and rat kappa receptors may be worthy of further examination.
Full text
PDF

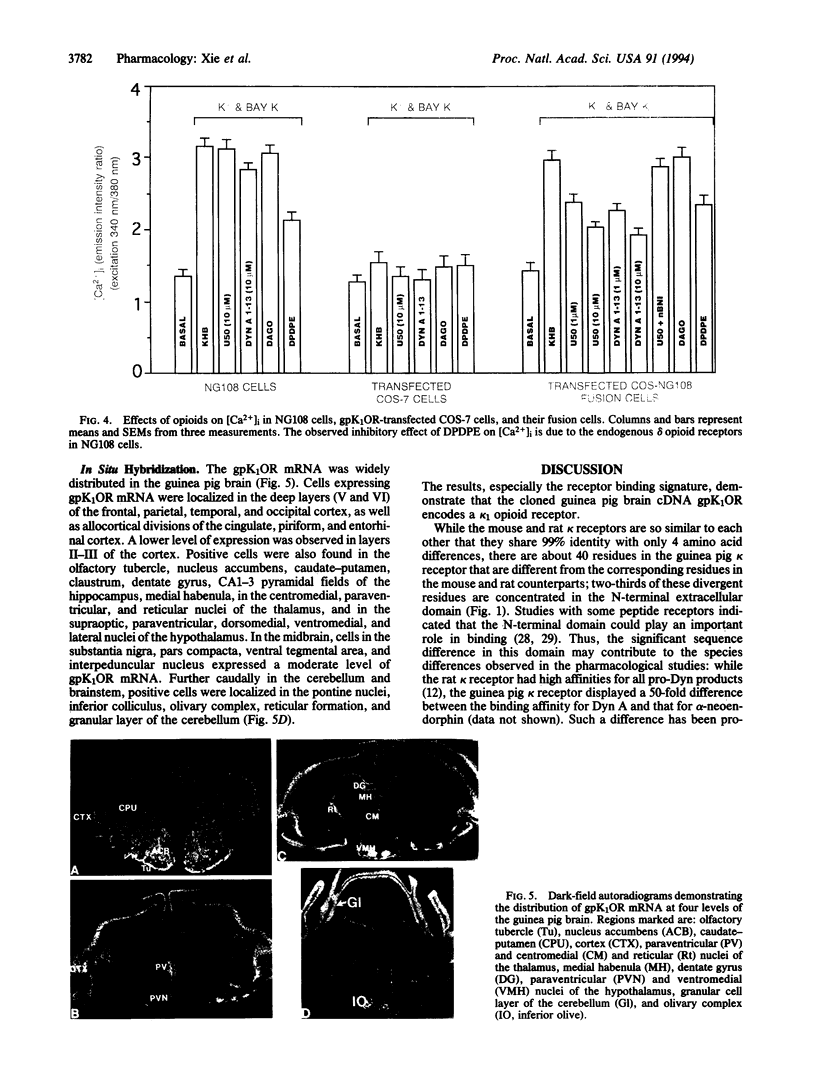

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chavkin C., Goldstein A. Specific receptor for the opioid peptide dynorphin: structure--activity relationships. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6543–6547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., James I. F., Goldstein A. Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the kappa opioid receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 22;215(4531):413–415. doi: 10.1126/science.6120570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Mestek A., Liu J., Hurley J. A., Yu L. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a mu-opioid receptor from rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;44(1):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubini E., North R. A. Mu and kappa opioids inhibit transmitter release by different mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1860–1863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A. L., Kosterlitz H. W., Watt A. J. Mode of action of morphine-like drugs on autonomic neuro-effectors. Nature. 1968 Dec 7;220(5171):1040–1042. doi: 10.1038/2201040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. J., Keith D. E., Jr, Morrison H., Magendzo K., Edwards R. H. Cloning of a delta opioid receptor by functional expression. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1952–1955. doi: 10.1126/science.1335167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda K., Kato S., Mori K., Nishi M., Takeshima H. Primary structures and expression from cDNAs of rat opioid receptor delta- and mu-subtypes. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 2;327(3):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81011-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Naidu A. Multiple opioid receptors: ligand selectivity profiles and binding site signatures. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;36(2):265–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Tachibana S., Lowney L. I., Hunkapiller M., Hood L. Dynorphin-(1-13), an extraordinarily potent opioid peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6666–6670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Snyder S. H. Kappa opiate receptors localized by autoradiography to deep layers of cerebral cortex: relation to sedative effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5703–5707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itzhak Y., Hiller J. M., Simon E. J. Solubilization and characterization of mu, delta, and kappa opioid binding sites from guinea pig brain: physical separation of kappa receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4217–4221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer B. L., Befort K., Gaveriaux-Ruff C., Hirth C. G. The delta-opioid receptor: isolation of a cDNA by expression cloning and pharmacological characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12048–12052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahti R. A., Mickelson M. M., McCall J. M., Von Voigtlander P. F. [3H]U-69593 a highly selective ligand for the opioid kappa receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 26;109(2):281–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law P. Y., Koehler J. E., Loh H. H. Comparison of opiate inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity in neuroblastoma N18tG2 and neuroblastoma x glioma NG108-15 hybrid cell lines. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;21(2):483–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour A., Meador-Woodruff J. H., Zhou Q. Y., Civelli O., Akil H., Watson S. J. A comparison of D1 receptor binding and mRNA in rat brain using receptor autoradiographic and in situ hybridization techniques. Neuroscience. 1991;45(2):359–371. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90233-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Eades C. G., Thompson J. A., Huppler R. E., Gilbert P. E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):517–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng F., Xie G. X., Thompson R. C., Mansour A., Goldstein A., Watson S. J., Akil H. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a rat kappa opioid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):9954–9958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.9954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T., Surprenant A., Christie M. J. Mu and delta receptors belong to a family of receptors that are coupled to potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5487–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman R. B., Bykov V., de Costa B. R., Jacobson A. E., Rice K. C., Brady L. S. Interaction of endogenous opioid peptides and other drugs with four kappa opioid binding sites in guinea pig brain. Peptides. 1990 Mar-Apr;11(2):311–331. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90088-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. E., McCleskey E. W. Inhibition of Ca2+ currents by a mu-opioid in a defined subset of rat sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):867–873. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00867.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Nirenberg M., Klee W. A. Morphine receptors as regulators of adenylate cyclase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Tanaka A., Hara M., Nakanishi S. The primary structure and gene organization of human substance P and neuromedin K receptors. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Mar 15;204(3):1025–1033. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Mansour A., Akil H., Watson S. J. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a rat mu opioid receptor. Neuron. 1993 Nov;11(5):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90120-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Nozaki M., Satoh M. Multiple opioid receptors and GTP-binding proteins. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1991;98(1):157–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonvoigtlander P. F., Lahti R. A., Ludens J. H. U-50,488: a selective and structurally novel non-Mu (kappa) opioid agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werz M. A., Macdonald R. L. Dynorphin and neoendorphin peptides decrease dorsal root ganglion neuron calcium-dependent action potential duration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jul;234(1):49–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollemann M., Benyhe S., Simon J. The kappa-opioid receptor: evidence for the different subtypes. Life Sci. 1993;52(7):599–611. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90451-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie G. X., Miyajima A., Goldstein A. Expression cloning of cDNA encoding a seven-helix receptor from human placenta with affinity for opioid ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4124–4128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Y. B., Wang H., Segaloff D. L. Extracellular domain of lutropin/choriogonadotropin receptor expressed in transfected cells binds choriogonadotropin with high affinity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21411–21414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda K., Raynor K., Kong H., Breder C. D., Takeda J., Reisine T., Bell G. I. Cloning and functional comparison of kappa and delta opioid receptors from mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6736–6740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin R. S., Eghbali M., Olive D., Unterwald E. M., Tempel A. Characterization and visualization of rat and guinea pig brain kappa opioid receptors: evidence for kappa 1 and kappa 2 opioid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]