Abstract
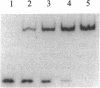
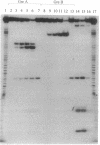
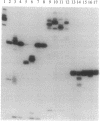
In the absence of DNA, Escherichia coli RNA polymerase (EC 2.7.7.6) can bind RNA to form an equimolar binary complex with the concomitant release of the sigma factor. We show now that E. coli RNA polymerase binds at a region near the 3' terminus of the RNA and that an RNA in such RNA.RNA polymerase complexes undergoes reactions previously thought to be unique to nascent RNA in ternary complexes with DNA. These include GreA/GreB-dependent cleavage of the RNA and elongation by 3'-terminal addition of NMP from NTP. Both of these reactions are inhibited by rifampicin. Hence, by several criteria, the RNA in binary complexes is bound to the polymerase in a manner quite similar to that in ternary complexes. These findings can be explained by a model for the RNA polymerase ternary complex in which the RNA is bound at the 3' terminus through two protein binding sites located up to 10 nt apart. In this model, the stability of RNA binding to the polymerase in the ternary complex is due primarily to its interaction with the protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn B. Y., Gershon P. D., Jones E. V., Moss B. Identification of rpo30, a vaccinia virus RNA polymerase gene with structural similarity to a eucaryotic transcription elongation factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5433–5441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt K. M., Chamberlin M. J. RNA chain elongation by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Factors affecting the stability of elongating ternary complexes. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 5;213(1):79–108. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt K. M., Chamberlin M. J. Transcription termination in Escherichia coli. Measurement of the rate of enzyme release from Rho-independent terminators. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 20;202(2):271–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. L., Koren R., Mildvan A. S. Magnetic resonance studies of the conformation of enzyme-bound adenylyl(3' leads to 5')uridine and adenosine 5'-triphosphate on RNA polymerase from Esherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 26;16(15):3322–3333. doi: 10.1021/bi00634a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borukhov S., Polyakov A., Nikiforov V., Goldfarb A. GreA protein: a transcription elongation factor from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8899–8902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borukhov S., Sagitov V., Goldfarb A. Transcript cleavage factors from E. coli. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremer H., Yegian C., Konrad M. Inactivation of purified Escherichia coli RNA polymerase by transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):94–103. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80265-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Spassky A., Buc H. On the binding of tRNA to Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Interactions between the core enzyme, DNA and tRNA. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;118(3):443–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chafin D. R., Claussen T. J., Price D. H. Identification and purification of a yeast protein that affects elongation by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9256–9262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J., Nierman W. C., Wiggs J., Neff N. A quantitative assay for bacterial RNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10061–10069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M., Kingston R., Gilman M., Wiggs J., deVera A. Isolation of bacterial and bacteriophage RNA polymerases and their use in synthesis of RNA in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:540–568. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX C. F., GUMPORT R. I., WEISS S. B. THE ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID. V. THE INTERACTION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE WITH NUCLEIC ACIDS. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:2101–2109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R., Blumenthal T. Analysis of RNA polymerase by trypsin cleavage. Different structural changes produced by heparin and DNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1702–1704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R., Blumenthal T. Analysis of RNA polymerase by trypsin cleavage. Evidence for a specific association between subunits sigma and beta involved in the closed to open complex transition. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):11056–11062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M. G., Crothers D. M. Kinetics and mechanism in the reaction of gene regulatory proteins with DNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 25;172(3):263–282. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchse, Millette R. L., Zillig W., Walter G. Influence of salts on RNA synthesis by DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Dec;3(2):183–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb19514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamper H. B., Hearst J. E. A topological model for transcription based on unwinding angle analysis of E. coli RNA polymerase binary, initiation and ternary complexes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. C., Yager T. D., von Hippel P. H. Thermodynamic analysis of the transcription cycle in E. coli. Biophys Chem. 1990 Aug 31;37(1-3):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(90)88023-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez N., Wiggs J., Chamberlin M. J. A simple procedure for resolution of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme from core polymerase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Aug;182(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90521-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo H., Price D. H. Mechanism of DmS-II-mediated pause suppression by Drosophila RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18762–18770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Jin D. J., Burgess R. R. Use of Mono Q high-resolution ion-exchange chromatography to obtain highly pure and active Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 28;29(34):7890–7894. doi: 10.1021/bi00486a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagler J., Shuman S. Nascent RNA cleavage by purified ternary complexes of vaccinia RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2166–2173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U. M., McClure W. R. Role of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in initiation. II. Release of sigma from ternary complexes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9564–9570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huaifeng M., Hartmann G. R. RNA polymerase: interaction of RNA and rifampicin with the subassembly alpha 2 beta. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 1;131(1):113–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izban M. G., Luse D. S. SII-facilitated transcript cleavage in RNA polymerase II complexes stalled early after initiation occurs in primarily dinucleotide increments. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12864–12873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izban M. G., Luse D. S. The RNA polymerase II ternary complex cleaves the nascent transcript in a 3'----5' direction in the presence of elongation factor SII. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1342–1356. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izban M. G., Luse D. S. The increment of SII-facilitated transcript cleavage varies dramatically between elongation competent and incompetent RNA polymerase II ternary complexes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12874–12885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Turner D. H., Zuker M. Improved predictions of secondary structures for RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7706–7710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. RNA polymerase marching backward. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):944–945. doi: 10.1126/science.7679800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Nierman W. C., Chamberlin M. J. A direct effect of guanosine tetraphosphate on pausing of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase during RNA chain elongation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2787–2797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S. A., Krakow J. S. Studies on the product binding sites of the Azotobacter vinelandii ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2878–2884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill H. R., Hartmann G. R. Digestion with matrix-bound proteases as a possible probe for the topography of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May;54(1):45–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Wong M. L., Tinker R. L., Geiduschek E. P., Alberts B. M. The DNA replication fork can pass RNA polymerase without displacing the nascent transcript. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):33–39. doi: 10.1038/366033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall T. K., Guo H., Price D. H. Drosophila RNA polymerase II elongation factor DmS-II has homology to mouse S-II and sequence similarity to yeast PPR2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6293–6298. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. On the mechanism of streptolydigin inhibition of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1610–1616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger W., Schickor P., Heumann H. A cinematographic view of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase translocation. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2745–2754. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08416.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D. Elongation factor-dependent transcript shortening by template-engaged RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3795–3800. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Ghanouni P., Li Q. Q., Mote J., Jr The RNA polymerase II elongation complex. Factor-dependent transcription elongation involves nascent RNA cleavage. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15516–15522. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Mote J., Jr Elongation factor SII-dependent transcription by RNA polymerase II through a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1917–1921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R., Bermúdez-Cruz R. M., Chamberlin M. J. Parameters affecting transcription termination by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. I. Analysis of 13 rho-independent terminators. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 5;224(1):31–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90574-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R., Chamberlin M. J. Parameters affecting transcription termination by Escherichia coli RNA. II. Construction and analysis of hybrid terminators. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 5;224(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90575-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz W., Zillig W. Rifampicin inhibition of RNA synthesis by destabilisation of DNA-RNA polymerase-oligonucleotide-complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6889–6906. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddhikol C., Erbstoeszer J. W., Weisblum B. Mode of action of streptolydigin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):151–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.151-155.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spassky A., Busby S. J., Danchin A., Buc H. On the binding of tRNA to Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 15;99(1):187–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. J., Mildvan A. S. Magnetic resonance and kinetic studies of initiator-substrate distances on RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2675–2684. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Studies of the ribonucleic acid polymerase from Escherichia coli. V. Studies of its complexes with polyribonucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):425–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surratt C. K., Milan S. C., Chamberlin M. J. Spontaneous cleavage of RNA in ternary complexes of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and its significance for the mechanism of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):7983–7987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.7983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TISSIERES A., BOURGEOIS S., GROS F. Inhibition of RNA polymerase by RNA. J Mol Biol. 1963 Jul;7:100–103. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usman N., Cedergren R. Exploiting the chemical synthesis of RNA. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Sep;17(9):334–339. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90306-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Hawley D. K. Identification of a 3'-->5' exonuclease activity associated with human RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):843–847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yager T. D., von Hippel P. H. A thermodynamic analysis of RNA transcript elongation and termination in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 29;30(4):1097–1118. doi: 10.1021/bi00218a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Yager T. D. Transcript elongation and termination are competitive kinetic processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2307–2311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]