Abstract
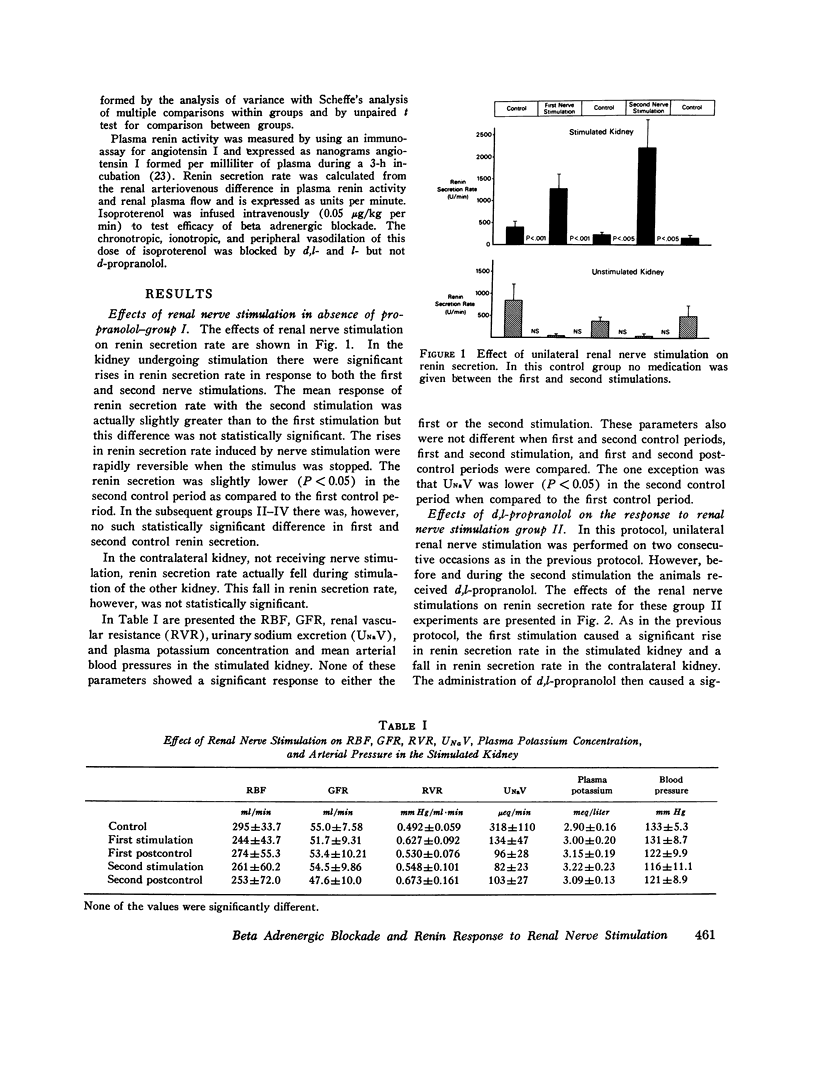
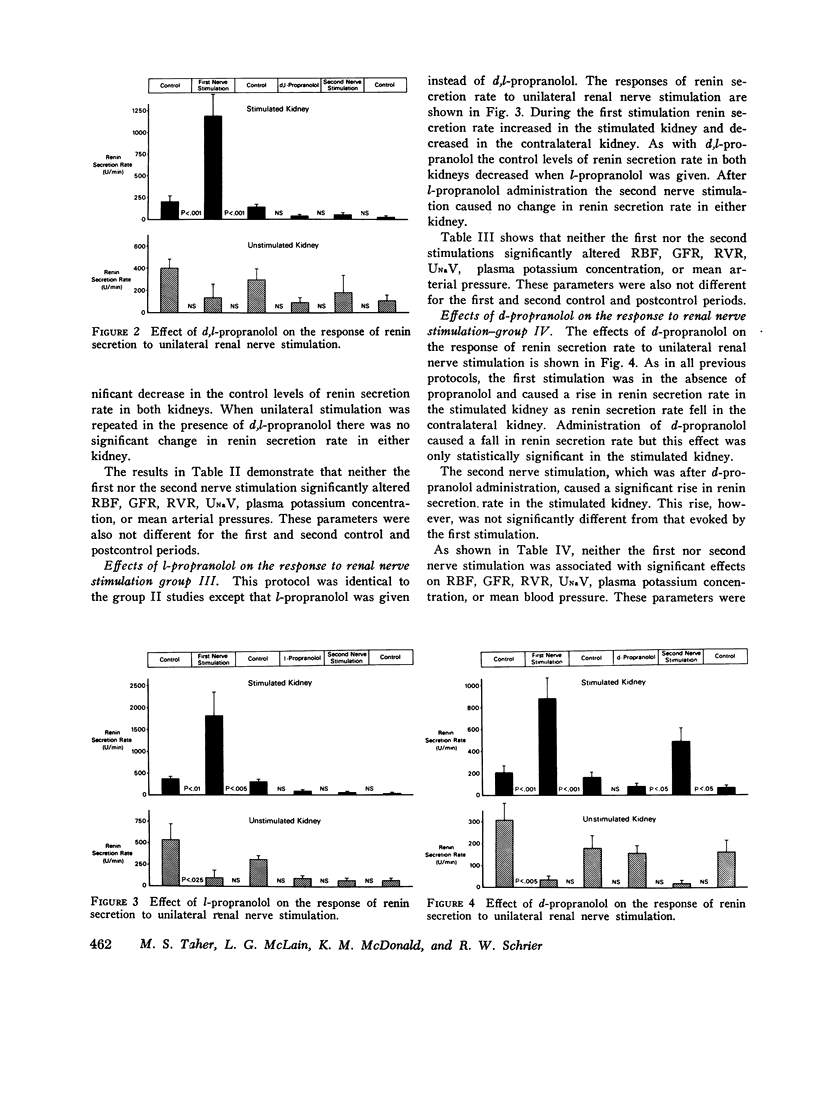
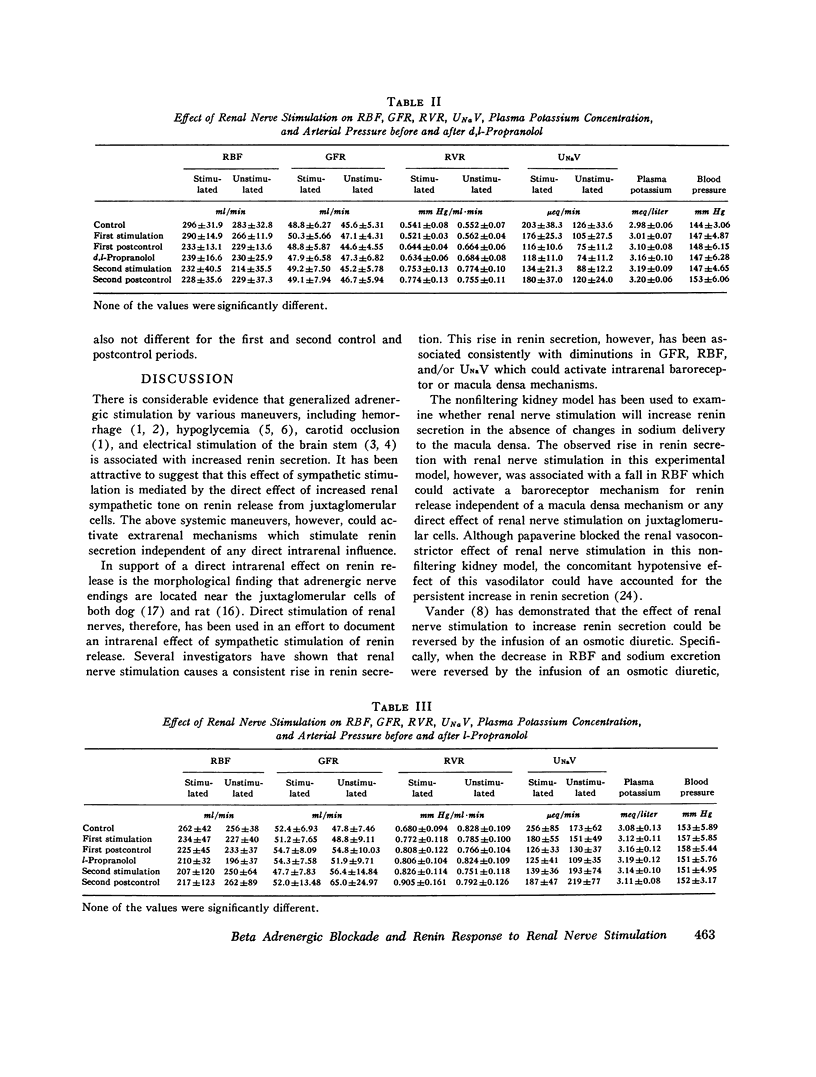
The ability of d,l-propranolol to block renin secretion in response to various extrarenal stimuli, such as hemorrhage and hypoglycemia, has been interpreted to indicate the presence of an intrarenal beta receptor regulating renin release. However, two problems complicate this interpretation: (a) the stimuli have effects outside the kidney, and (b) d,l-propranolol has a local anesthetic, as well as a beta adrenergic blocking, action. In the present study, the effects of a purely intrarenal stimulus, in the form of renal nerve stimulation (RNS), on renin secretion was examined. The effects of d,l-propranolol (anesthetic and beta-blocking activity), l-propranolol (beta-blocking activity only), and d-propranolol (local anesthetic activity only) on the renin response to RNS were examined. In a control group of animals, two sequential RNS increased mean renin secretion from 401 to 1,255 U/min (P less than 0.25) and from 220 to 2,179 U/min (P less than 0.01). In a second group the first RNS increased renin secretion from 201 to 1,181 U/min (P less than 0.01), but after d,l-propranolol was given RNS did not significantly alter renin secretion (33 to 55 U/min). In a third group the initial RNS increased renin secretion from 378 to 1,802 U/min (P less than 0.025), but after l-propranolol was given RNS had no significant effect on renin secretion (84 to 51 U/min). A fourth group of dogs showed a rise in renin secretion from 205 to 880 U/min (P less than 0.001) in response to the first RNS, while the second RNS, given after an infusion of d-propranolol, caused a rise in renin secretion from 80 to 482 (P less than 0.005). The nature of the electrical stimulus was consistent in all groups and caused no detectable changes in renal or systemic hemodynamics or in urinary electrolyte excretion. The results, therefore, indicate that renin secretion can be stimulated through intrarenal beta receptors independent of changes in systemic or renal hemodynamics or in tubular sodium reabsorption. Hence the effect of beta stimulation on renin secretion would appear to result from a direct action on the renin-secreting cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assaykeen T. A., Clayton P. L., Goldfien A., Ganong W. F. The effect of alpha- and beta-adrenergic blocking agents on the renin response to hypoglycemia and epinephrine in dogs. Endocrinology. 1970 Dec;87(6):1318–1322. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-6-1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARAJAS L. THE INNERVATION OF THE JUXTAGLOMERULAR APPARATUS. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE INNERVATION OF THE GLOMERULAR ARTERIOLES. Lab Invest. 1964 Aug;13:916–929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaine E. H., Davis J. O., Witty R. T. Renin release after hemorrhage and after suprarenal aortic constriction in dogs without sodium delivery to the macula densa. Circ Res. 1970 Dec;27(6):1081–1089. doi: 10.1161/01.res.27.6.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunag R. D., Page I. H., McCubbin J. W. Neural stimulation of release of renin. Circ Res. 1966 Oct;19(4):851–858. doi: 10.1161/01.res.19.4.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. H., Johns E. J., Macleod V. H., Singer B. Effect of renal nerve stimulation, renal blood flow and adrenergic blockade on plasma renin activity in the cat. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(1):15–36. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Davis J. O., Witty R. T. Effects of catecholamines and renal nerve stimulation on renin release in the nonfiltering kidney. Circ Res. 1971 Dec;29(6):646–653. doi: 10.1161/01.res.29.6.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Grange R. G., Sloop C. H., Schmid H. E. Selective stimulation of renal nerves in the anesthetized dog. Effect on renin release during controlled changes in renal hemodynamics. Circ Res. 1973 Dec;33(6):704–712. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.6.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeffler J. R., Stockigt J. R., Ganong W. F. Effect of alpha- and beta-adrenergic blocking agents on the increase in renin secretion produced by stimulation of the renal nerves. Neuroendocrinology. 1972;10(3):129–138. doi: 10.1159/000122112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna O. C., Angelakos E. T. Adrenergic innervation of the canine kidney. Circ Res. 1968 Mar;22(3):345–354. doi: 10.1161/01.res.22.3.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley K., Velasco M., Wells J., McNay J. L. Control plasma renin activity and changes in sympathetic tone as determinants of minoxidil-induced increase in plasma renin activity. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):230–235. doi: 10.1172/JCI107926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka K., Assaykeen T. A., Goldfien A., Ganong W. F. Effect of hypoglycemia on plasma renin activity in dogs. Endocrinology. 1970 Dec;87(6):1306–1317. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-6-1306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passo S. S., Assaykeen T. A., Goldfien A., Ganong W. F. Effect of alpha- and beta-adrenergic blocking agents on the increase in renin secretion produced by stimulation of the medulla oblongata in dogs. Neuroendocrinology. 1971;7(2):97–104. doi: 10.1159/000121957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passo S. S., Assaykeen T. A., Otsuka K., Wise B. L., Goldfien A., Ganong W. F. Effect of stimulation of the medulla oblongata on renin secretion in dogs. Neuroendocrinology. 1971;7(1):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000121949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinger W. A., Campbell W. B., Keeton K. Adrenergic component of renin release induced by vasodilating antihypertensive drugs in the rat. Circ Res. 1973 Jul;33(1):82–86. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. A., Schrier R. W., Earley L. E. An effect of extrarenal beta adrenergic stimulation on the release of renin. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1861–1869. doi: 10.1172/JCI106988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D., Stella A., Leonetti G., Bartorelli A., Zanchetti A. Mechanisms of renal release of renin by electrical stimulation of the brainstem in the cat. Circ Res. 1974 Apr;34(4):425–434. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.4.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. W., Earley L. E. Effects of hematocrit on renal hemodynamics and sodium excretion in hydropenic and volume-expanded dogs. J Clin Invest. 1970 Sep;49(9):1656–1667. doi: 10.1172/JCI106383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockigt J. R., Collins R. D., Biglieri E. G. Determination of plasma renin concentration by angiotensin I immunoassay. Diagnotic import of precise measurement of subnormal renin in hyperaldosteronism. Circ Res. 1971 May;28(5 Suppl):175–191. doi: 10.1161/01.res.28.5.ii-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Yasuda H., Takabatake Y., Iizuka M., Iizuka T. Increased renin release evoked by mesencephalic stimulation in the dog. Jpn Heart J. 1967 Sep;8(5):498–506. doi: 10.1536/ihj.8.498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Yasuda H., Takabatake Y., Iizuka M., Iizuka T. Observations on the mechanism of renin release by catecholamines. Circ Res. 1970 Oct;27(Suppl):195+–195+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Effect of catecholamines and the renal nerves on renin secretion in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1965 Sep;209(3):659–662. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.3.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandongen R., Peart W. S., Boyd G. W. Andrenergic stimulation of renin secretion in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Circ Res. 1973 Feb;32(2):290–296. doi: 10.1161/01.res.32.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M. A., Stokes G. S., Gain J. M. Comparison of the effects on renin release of beta adrenergic antagonists with differing properties. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1413–1419. doi: 10.1172/JCI107888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wågermark J., Ungerstedt U., Ljungqvist A. Sympathetic innervation of the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney. Circ Res. 1968 Feb;22(2):149–153. doi: 10.1161/01.res.22.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



