Abstract
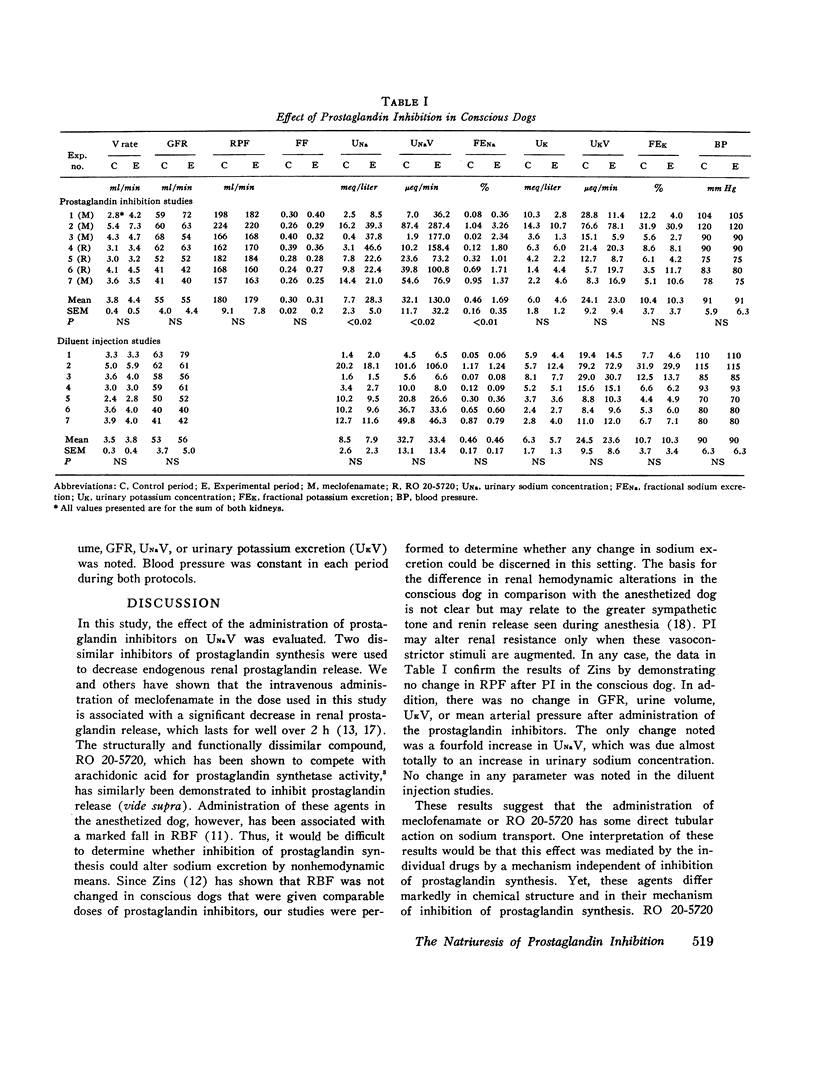
Studies were performed to determine the effect of decreased endogenous release of renal prostaglandins on urinary sodium excretion. Two structurally dissimilar inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis were employed, and studies were performed in conscious dogs allowed to recover from prior surgical instrumentation. Either meclofenamate (2 mg/kg) or the competitive prostaglandin inhibitor RO 20-5720 (1 mg/kg) was given to seven unanesthetized dogs undergoing a water diuresis. The administration of either prostaglandin inhibitor did not alter glomerular filtration rate, renal plasma flow, urinary volume, or potassium excretion. Sodium excretion, however, increased from 32 to 130 mueq/min (P less than 0.02). Essentially, the entire increase in sodium excretion was due to an increase in urinary sodium concentration from 7.7 to 28.3 meq/liter (P less than 0.02). On a different day, the same animals were studied before and after administration of the diluent of the prostaglandin inhibitor. No change was noted in sodium excretion or any other parameter. Thus, these findings suggest that prostaglandin inhibition in the conscious dog is associated with a natriuresis without a change in urinary volume or potassium excretion during water diuresis. This may indicate that the natruiresis was due to diminished sodium reabsorption beyond the distal tubule.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arruda J. A., Boonjarern S., Westenfelder C., Kurtzman N. A. Measurement of renal blood flow with radioactive microspheres. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 May;146(1):263–264. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. W., Baehler R. W., Sharma H., O'Dorisio T., Osgood R. W., Stein J. H., Ferris T. F. Studies of the mechanism of oliguria in a model of unilateral acute renal failure. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1546–1558. doi: 10.1172/JCI107705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowshaw K. Prostaglandin biosynthesis from endogenous precursors in rabbit kidney. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):240–242. doi: 10.1038/newbio231240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowshaw K. The incorporation of (1-14C) arachidonic acid into the lipids of rabbit renal slices and conversion to prostaglandins E2 and F2 . Prostaglandins. 1973 May;3(5):607–620. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(73)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels E. G., Hinman J. W., Leach B. E., Muirhead E. E. Identification of prostaglandin E2 as the principal vasodepressor lipid of rabbit renal medulla. Nature. 1967 Sep 16;215(5107):1298–1299. doi: 10.1038/2151298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earley L. E., Friedler R. M. The effects of combined renal vasodilatation and pressor agents on renal hemodynamics and the tubular reabsorption of sodium. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):542–551. doi: 10.1172/JCI105368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUHR J., KACZMARCZYK J., KRUTTGEN C. D. Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr. 1955 Aug 1;33(29-30):729–730. doi: 10.1007/BF01473295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins: their disappearance from and release into the circulation. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):868–873. doi: 10.1038/216868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Drugs which inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Mar;26(1):33–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschenbaum M. A., White N., Stein J. H., Ferris T. F. Redistribution of renal cortical blood flow during inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1974 Oct;227(4):801–805. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.4.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. B. Hypertension, natriuresis and the renomedullary prostaglandins: an overview. Prostaglandins. 1973 May;3(5):551–579. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(73)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson L. C., Sharp G. W. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on sodium transport and osmotic water flow in the toad bladder. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):1046–1052. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonigro A. J., Itskovitz H. D., Crowshaw K., McGiff J. C. Dependency of renal blood flow on prostaglandin synthesis in the dog. Circ Res. 1973 Jun;32(6):712–717. doi: 10.1161/01.res.32.6.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Itskovitz H. D. Prostaglandins and the kidney. Circ Res. 1973 Nov;33(5):479–488. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.5.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Terragno N. A., Strand J. C., Lee J. B., Lonigro A. J., Ng K. K. Selective passage of prostaglandins across the lung. Nature. 1969 Aug 16;223(5207):742–745. doi: 10.1038/223742b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinger W. A., Marchelle M., Augusto L. Renin suppression by DOC and NaCl in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1071–1074. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splawinski J. A., Nies A. S., Sweetman B., Oates J. A. The effects of arachidonic acid, prostaglandin E2 and prostaglandin F2alpha on the longitudinal stomach strip of the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Dec;187(3):501–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. H., Ferris T. F., Huprich J. E., Smith T. C., Osgood R. W. Effect of renal vasodilatation on the distribution of cortical blood flow in the kidney of the dog. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1429–1438. doi: 10.1172/JCI106626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum J., Splawinski J. A., Oates J. A., Nies A. S. Enhanced renal prostaglandin production in the dog. I. Effects on renal function. Circ Res. 1975 Jan;36(1):197–203. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Direct effects of prostaglandin on renal function and renin release in anesthetized dog. Am J Physiol. 1968 Feb;214(2):218–221. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venuto R. C., O'Dorisio T., Ferris T. F., Stein J. H. Prostaglandins and renal function. II. The effect of prostaglandin inhibition on autoregulation of blood flow in the intact kidney of the dog. Prostaglandins. 1975 May;9(5):817–828. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(75)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zins G. R. Renal prostaglandins. Am J Med. 1975 Jan;58(1):14–24. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90528-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



