Abstract
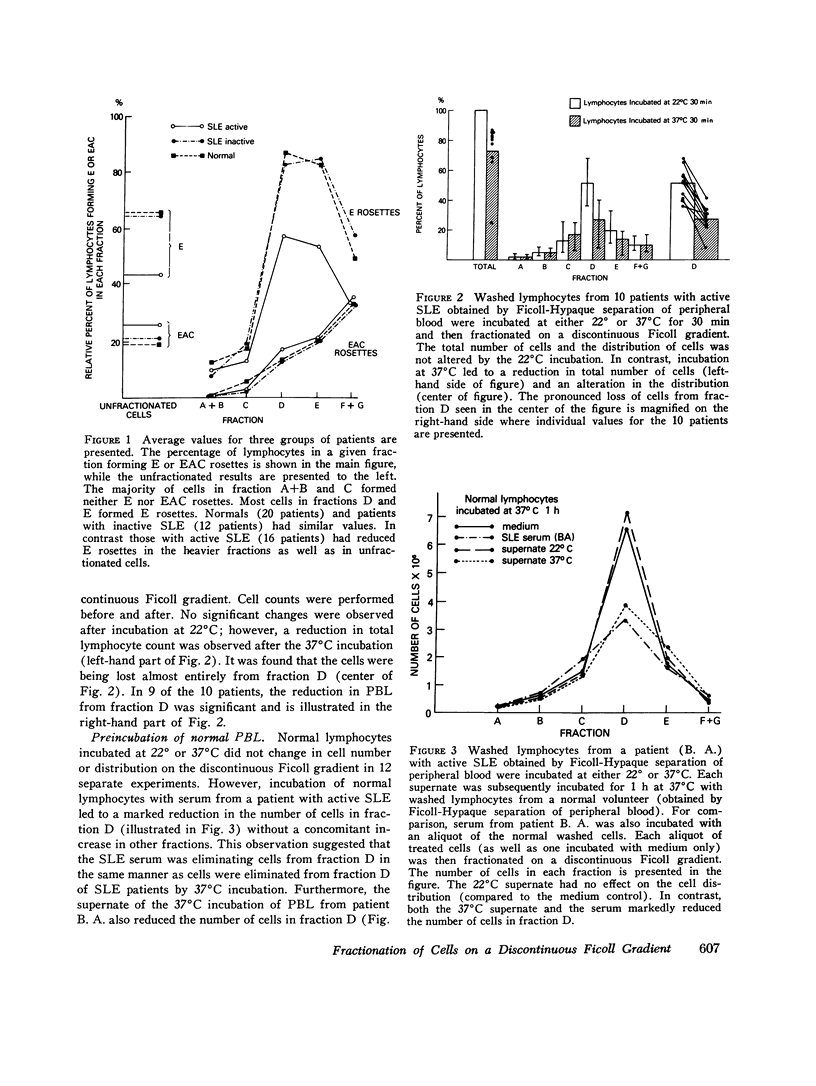
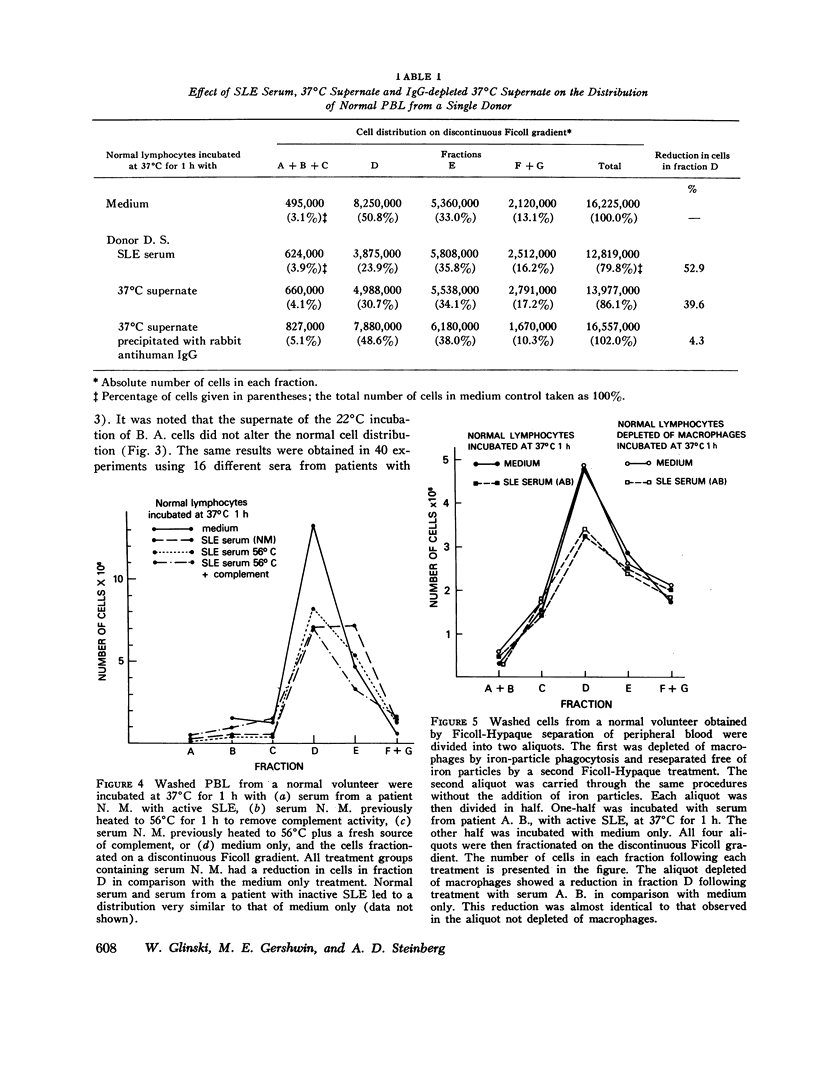
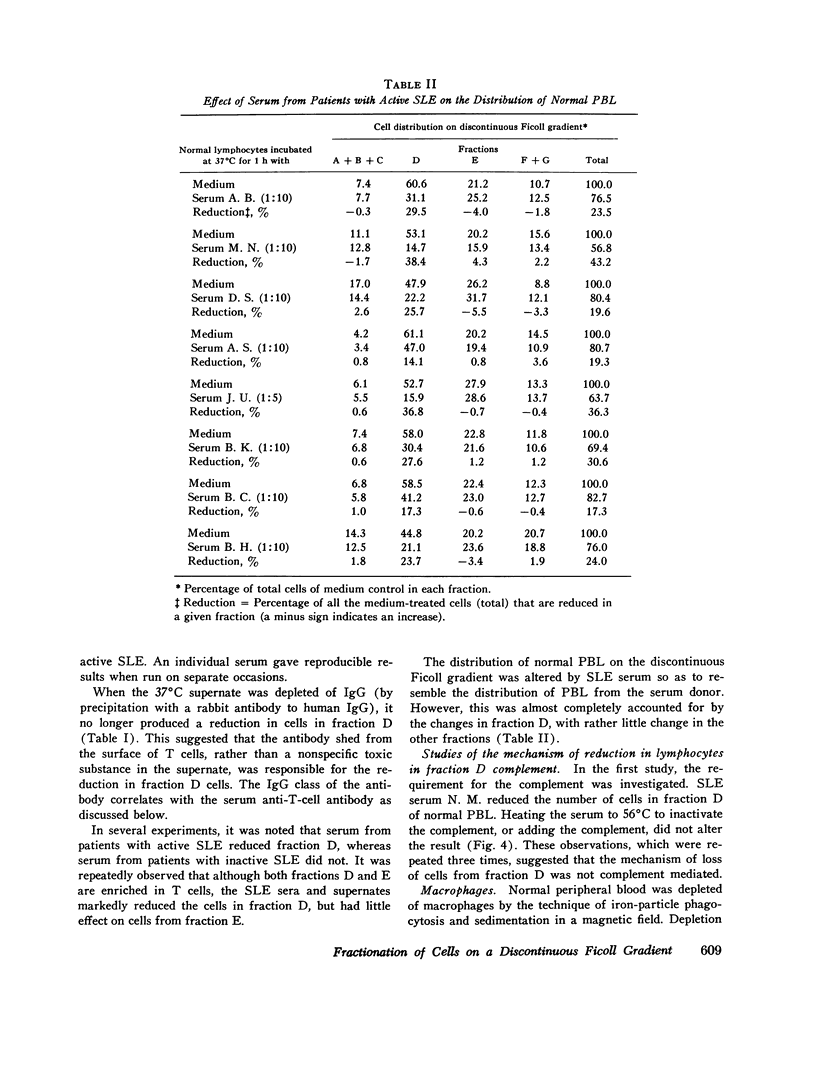
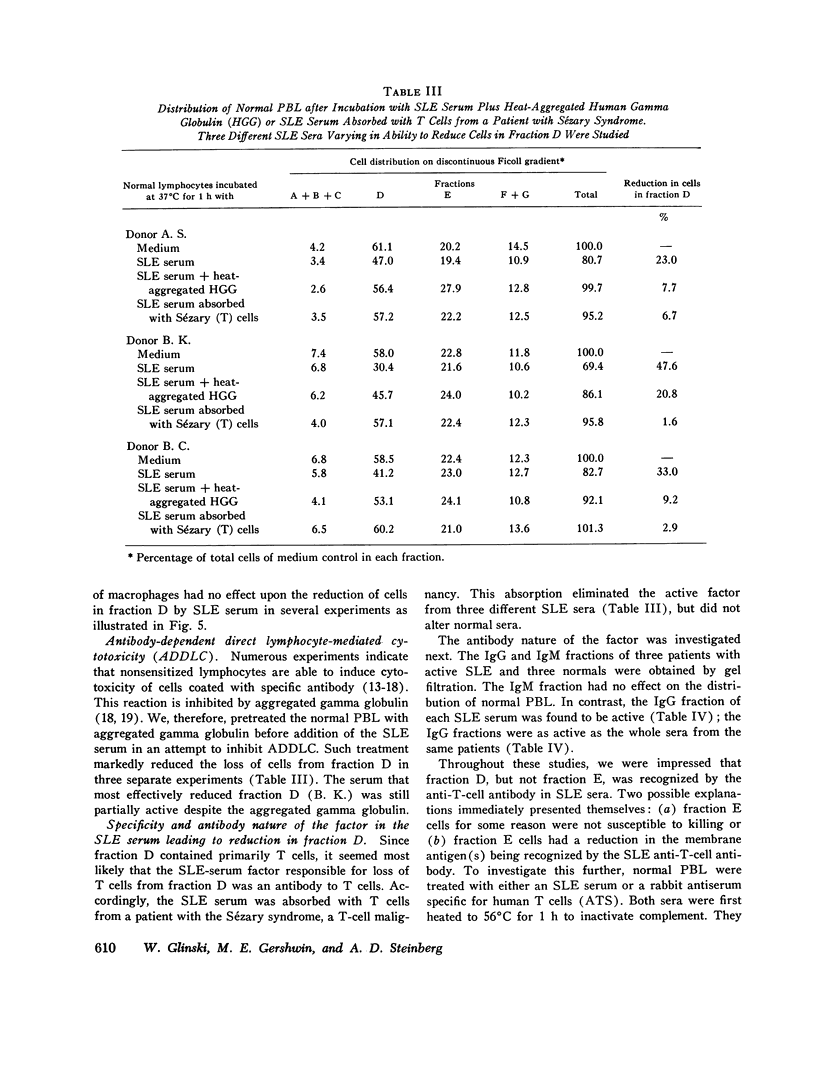
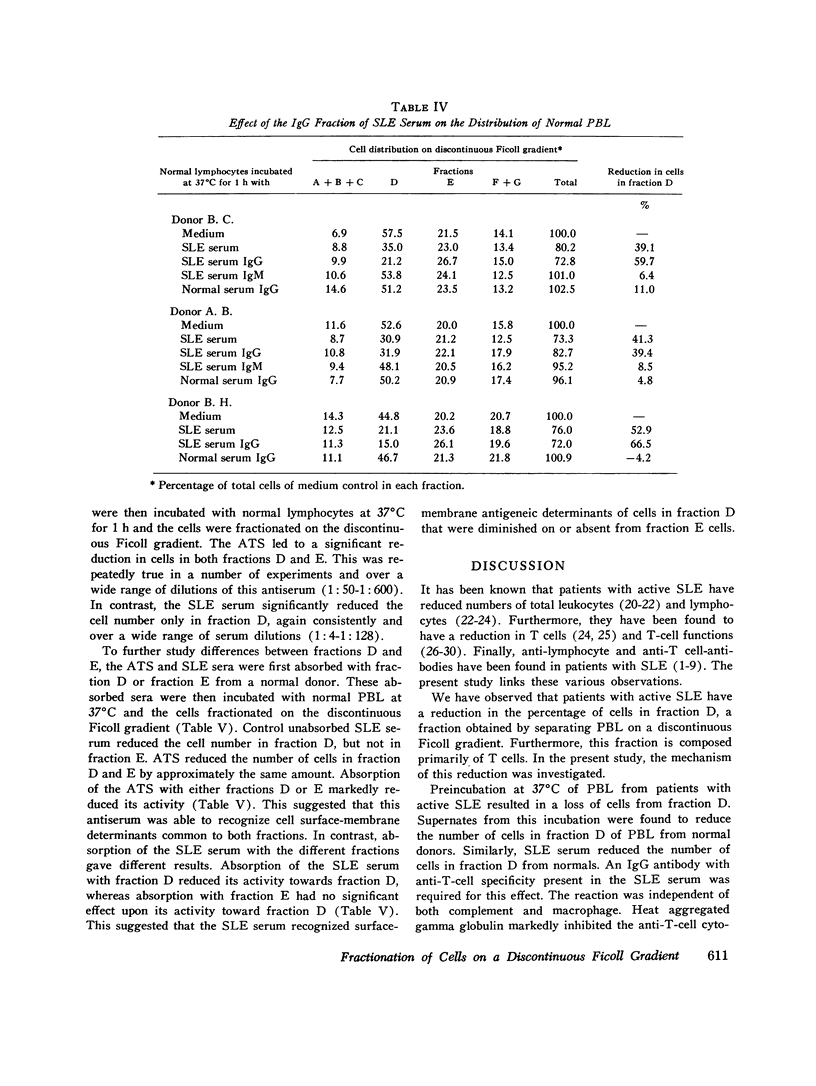
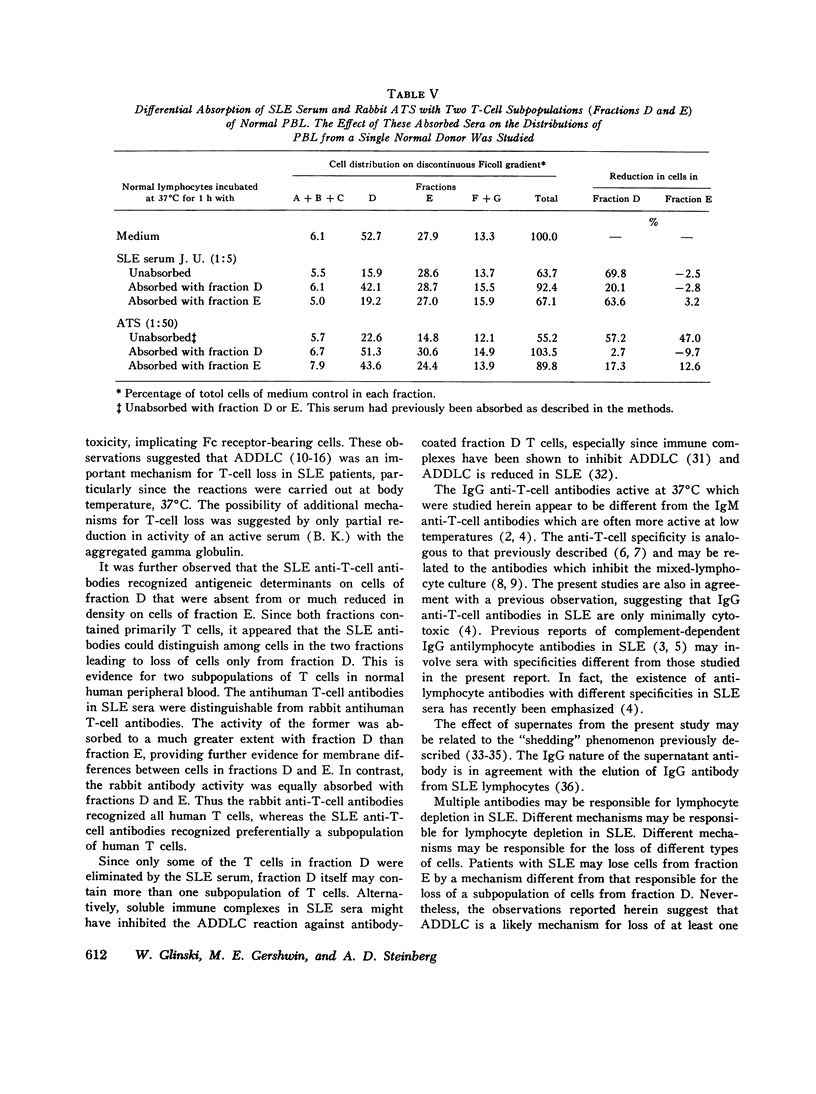
Patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) had a decrease in a subpopulation of cells (fraction D) when peripheral blood lymphocytes were separated on a discontinuous Ficoll gradient. Preincubation of SLE cells at 37 degrees C for 30 min led to a marked decrease in this fraction, composed primarily of thymus-derived (T) cells. Supernates of such preincubations were found to cause a reduction in fraction D cells from normal humans. The active factor in the supernate was found to be an IgG antibody. Similarly, serum from patients with active SLE produced a reduction in fraction D cells from normal donors. This activity was also found in the IgG fraction, and could be absorbed with a pure T-cell population. Depletion of macrophages and complement did not reduce the SLE anti-T-cell antibody-mediated loss of cells from fraction D; however, heat-aggregated human gamma globulin led to impairment of the reaction. These findings suggest that antibody-dependent direct lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity may play a role in T-cell lymphopenia of SLE. It was further noted that the SLE anti-T-cell antibodies, in contrast to rabbit antihuman thymocyte serum, recognized fraction D cells but not fraction E cells from normals. Since both fractions are largely T cells, it appeared that the SLE serum was directed against cell-membrane antigenic determinants present on fraction D T cells, which were absent or reduced in quantity on fraction E T cells. Thus, evidence was presented indicating the presence of at least two subpopulations of cells in man. This was supported by differential absorption of the anti-T-cell sera with fractions D and E.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach M. K., Brashler J. R. Isolation of subpopulations of lymphocytic cells by the use of isotonically balanced solutions of Ficoll. I. Development of methods and demonstration of the existence of a large but finite number of subpopulations. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Aug;61(2):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90462-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold D. R., Kysela S., Steinberg A. D. Decline in suppressor T cell function with age in female NZB mice. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):9–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauphinee M. J., Talal N. Reversible restoration by thymosin of antigen-induced depression of spleen DNA synthesis in NZB mice. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1713–1716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbarre F., Pompidou A., Kahan A., Brouilhet H., Le Gô A., Amor B. Etude des lymphocytes du sang au cours de la maladie lupique. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1971 Apr;19(7):379–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber N. L., Hardin J. A., Chused T. M., Steinberg A. D. Loss with age in NZB-W mice of thymic suppressor cells in the graft-vs-host reaction. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1618–1625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershwin M. E., Steinberg A. D. Suppression of autoimmune hemolytic anemia in New Zealand (NZB) mice by syngeneic young thymocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 May;4(1):38–45. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY A. M., SHULMAN L. E., TUMULTY P. A., CONLEY C. L., SCHOENRICH E. H. Systemic lupus erythematosus: review of the literature and clinical analysis of 138 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 1954 Dec;33(4):291–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Bagby K. K., Osterland C. K. Abnormalities of delayed hypersensitivity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1973 Jul;55(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg T. Inhibition of cytotoxicity of nonimmune human lymphocytes for sensitized chicken erythrocytes by aggregated human IgG. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(1):117–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A. Impaired delayed hypersensitivity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jul-Aug;15(4):353–359. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lies R. B., Messner R. P., Williams R. C., Jr Relative T-cell specificity of lymphocytotoxins from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 May-Jun;16(3):369–375. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAEL S. R., VURAL I. L., BASSEN F. A., SCHAEFER L. The hematologic aspects of disseminated (systemic) lupus erythematosus. Blood. 1951 Nov;6(11):1059–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C. Competition for receptors for immunoglobulin on cytotoxic lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Feb;10(2):275–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malavé I., Layrisse Z., Layrisse M. Dose-dependent hyporreactivity to phytohemagglutinin in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Immunol. 1975 Feb;15(2):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Kennedy M. S., Jelinek J. G. Antilymphocyte antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Effect on lymphocyte surface characteristics. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 May-Jun;18(3):201–206. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Lindström F. D., Williams R. C., Jr Peripheral blood lymphocyte cell surface markers during the course of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3046–3056. doi: 10.1172/JCI107503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. K., Rossen R. D., Sharp J. T., Lidsky M. D., Butler W. T. Lymphocyte cytotoxic antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nature. 1970 Mar 28;225(5239):1255–1256. doi: 10.1038/2251255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi B. S., Orlina A. R., Pesce A. J., Mendoza N., Masaitis L., Pollak V. E. Lymphocytotoxic antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jun;17(2):237–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Holm G. Cytotoxic effects of lymphoid cells in vitro. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:117–193. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60479-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Franklin E. C. Depression of cellular-mediated immunity in systemic lupus erythematosus. relation to disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 May-Jun;18(3):207–217. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg M. A., Cathcart E. S. B cell and T cell lymphopenia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Immunol. 1974 May;12(2):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J., Chin W., Friou G. J., Cooper S. M., Harding B., Hill R. L., Quismorio F. P. Reduced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 May;20(2):187–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scornik J. C., Cosenza H., Lee W., Köhler H., Rowley D. A. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. I. Differentiation from antibody-independent cytotoxicity by "normal" IgG. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1510–1518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Mellors R. C. Natural thymocytotoxic autoantibody and reactive antigen in New Zealand black and other mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1412–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P., Ziff M. Antibodies against cell membrane constituents in systemic lupus erythematosus and related diseases. I. Cytotoxic effect of serum from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) for allogeneic and for autologous lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Apr;8(4):543–550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P., Ziff M. Lymphocyte and platelet autoantibodies in S.L.E. Lancet. 1971 Jun 12;1(7711):1239–1240. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91751-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D. Pathogenesis of autoimmunity in New Zealand mice. V. Loss of thymic suppressor function. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jan-Feb;17(1):11–14. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suciu-Foca N., Buda J. A., Thiem T., Reemtsma K. Impaired responsiveness of lymphocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):295–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Steinberg A. D. The pathogenesis of autoimmunity in New Zealand black mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1974;64(0):79–103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65848-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. B. Antibodies specific for human T lymphocytes in cold agglutinin and lymphocytotoxic sera. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Dec;3(12):824–828. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Boxel J. A., Stobo J. D., Paul W. E., Green I. Antibody-dependent lymphoid cell-mediated cytotoxicity: no requirement for thymus-derived lymphocytes. Science. 1972 Jan 14;175(4018):194–196. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4018.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernet P., Kunkel H. G. Antibodies to a specific surface antigen of T cells in human sera inhibiting mixed leukocyte culture reactions. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):1021–1026. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr, Lies R. B., Messner R. P. Inhibition of mixed leukocyte culture responses by serum and gamma-globulin fractions from certain patients with connective tissue disorders. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Sep-Oct;16(5):597–605. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Winfield J. B., Siegal F., Wernet P., Bentwich Z., Kunkel H. G. Analyses of lymphocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Occurrence of interfering cold-reactive antilymphocyte antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1082–1092. doi: 10.1172/JCI107852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisloff F., Froland S. S. Antibody-dependent lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity in man: no requirement for lymphocytes with membrane-bound immunoglobulin. Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(2):151–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D. T., Peter B. J., Paulus H. E., Machleder H. I. Lymphocyte populations: separation by discontinuous density gradient centrifugation. J Immunol. 1973 Jun;110(6):1615–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



