Abstract
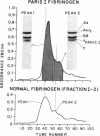
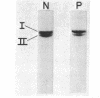
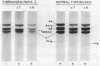
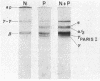
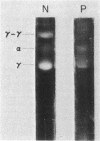
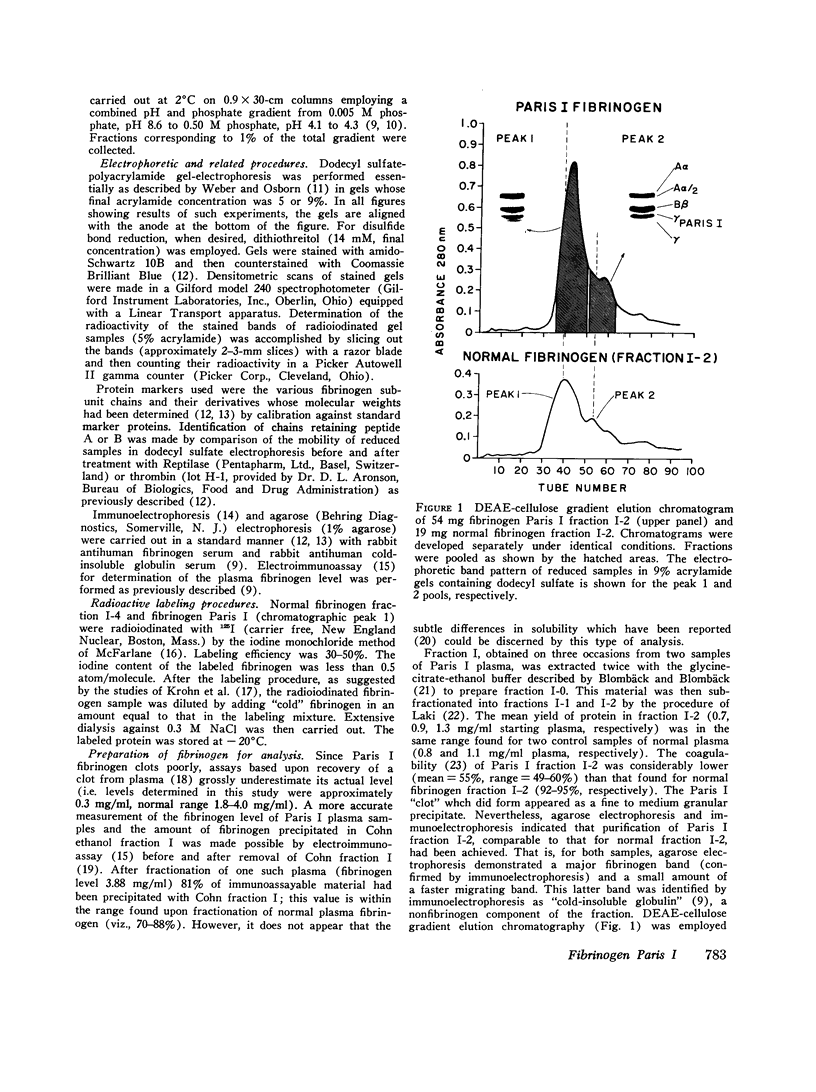
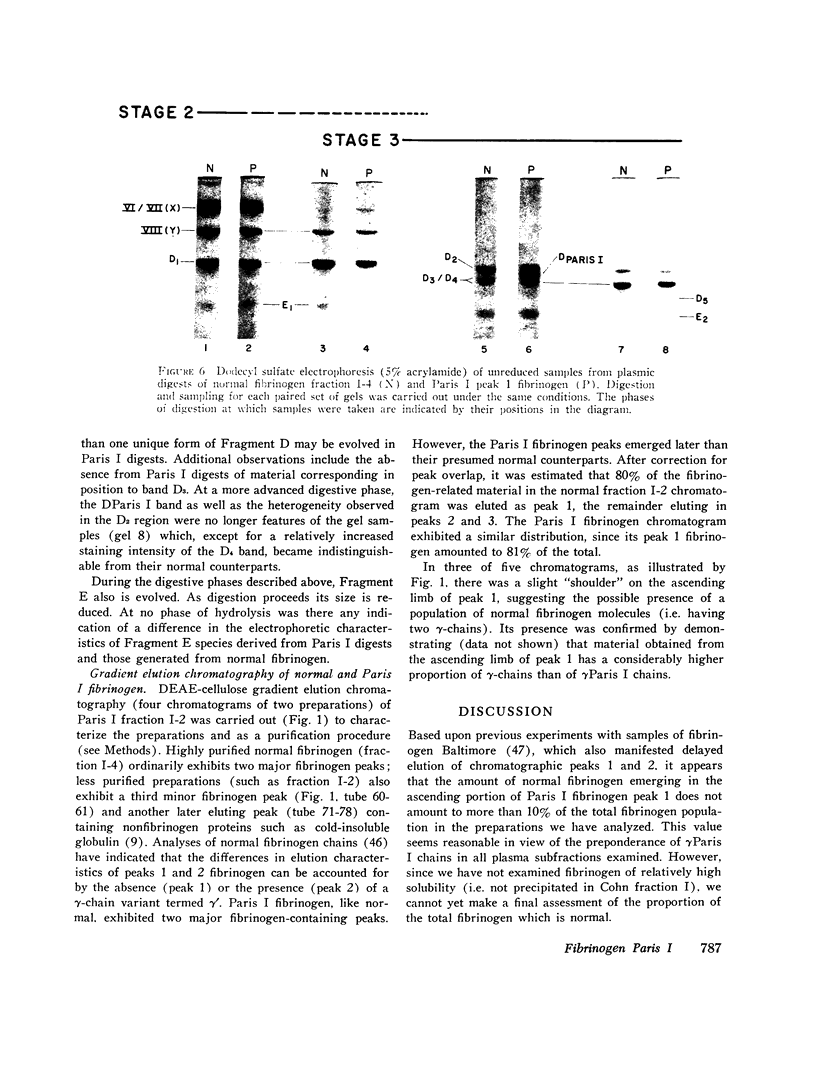
The structural properties of an inherited fibrinogen abnormality designated fibrinogen Paris I were investigated. Dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis of unreduced samples revealed no discernible differences in molecular weight from normal; this implied that in fibrinogen Paris I, the normal fibrinogen architecture of six covalently linked chains per molecule is preserved. Examination of dithiothreitol reduced samples before and after treatment with Reptilase or thrombin revealed that the Aalpha- and Bbeta-chains could release the A and B peptides, respectively. A mutant chain (mol wt 52,500, termed gammaParis I) which replaces a large proportion of gamma-chains (mol wt 49,400) was shown, like normal gamma-chains, to lack thrombin- and Reptilase-sensitive sites. The gamma-chains and alpha-chains of Paris I fibrin underwent Factor XIIIa-catalyzed cross-linking slowly; this behavior was not attributable to an intrinsic abnormality of these chains themselves but rather to the inhibitory effect of the mutant gammaParis I chains on this process. Results of DEAE-cellulose gradient elution chromatography of Paris I fibrinogen preparations revealed the presence of small amounts of normal fibrinogen molecules and also indicated that the gammaParis I chains possessed structural overlap with gamma-chains. Unlike gamma-chains however, the gammaParis I chains did not incorporate dansylcadaverine in the prescence of Factor XIIIa, nor, as previously reported, did they undergo cross-linking. The observations indicate that the amine acceptor site found in the COOH-terminal region of the gamma-chain is either not present on the gammaParis I chain or is unavailable for cross-linking. Further support for localization of the abnormality in the COOH-terminal region of the molecule was obtained from the observation that during plasmic hydrolysis of Paris I fibrinogen, at least one unique form of core Fragment D (DParis I) was evolved, whereas Fragment E did not differ from normal.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blomback B., Blomback M. Molecular defects and variants of fibrinogen. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1970 Sep-Oct;10(5):671–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzynski A. Z., Marder V. J., Ménaché D., Guillin M. C. Defect in the gamma polypeptide chain of a congenital abnormal fibrinogen (Paris I). Nature. 1974 Nov 1;252(5478):66–68. doi: 10.1038/252066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzynski A. Z., Marder V. J., Shainoff J. R. Structure of plasmic degradation products of human fibrinogen. Fibrinopeptide and polypeptide chain analysis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2294–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Doolittle R. F. - cross-linking sites in human and bovine fibrin. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4487–4491. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Doolittle R. F. Identification of the polypeptide chains involved in the cross-linking of fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):420–427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. I., Folk J. E. Kinetic studies with transglutaminases. The human blood enzymes (activated coagulation factor 13 and the guinea pig hair follicle enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2798–2807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Contopolou-Griva I., Caroutsos K., Poungouras P., Tsevrenis H. Haemoglobin Icaria, a new chain-termination mutant with causes alpha thalassaemia. Nature. 1974 Sep 20;251(5472):245–247. doi: 10.1038/251245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Milner P. F. Haemoglobin Constant Spring--a chain termination mutant? Nature. 1971 Dec 10;234(5328):337–340. doi: 10.1038/234337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlayson J. S., Mosesson M. W., Bronzert T. J., Pisano J. J. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. II. Cross-linking capacity of high solubility catabolic intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5220–5222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatz G., Kinderlerer J. L., Kilmartin J. V., Lehmann H. Haemoglobin Tak: a variant with additional residues at the end of the beta-chains. Lancet. 1971 Apr 10;1(7702):732–733. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91994-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Beck E. A. Plasmic degradation of human fibrinogen. I. Structural characterization of degradation products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 18;263(3):631–644. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause W. H., Heene D. L., Lasch H. G. Congenital dysfibrinogenemia (fibrinogen Giessen). Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1973 Jun 28;29(3):547–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohn K., Sherman L., Welch M. Studies of radioiodinated fibrinogen. I. Physicochemical properties of the ICl, chloramine-T, and electrolytic reaction products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 28;285(2):404–413. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90327-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKI K. The polymerization of proteins; the action of thrombin on fibrinogen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Jul;32(2):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEWY A. G., DUNATHAN K., KRIEL R., WOLFINGER H. L., Jr Fibrinase. I. Purification of substrate and enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1961 Oct;236:2625–2633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Chenoweth D., Gray A. Titration of the acceptor cross-linking sites in fibrin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:155–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Budzyński A. Z., James H. L. High molecular weight derivatives of human fibrinogen produced by plasmin. 3. Their NH2-terminal amino acids and comparison with the "NH2-terminal disulfide knot". J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 10;247(15):4775–4781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Shulman N. R., Carroll W. R. High molecular weight derivatives of human fibrinogen produced by plasmin. I. Physicochemical and immunological characterization. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2111–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matacić S., Loewy A. G. The identification of isopeptide crosslinks in insoluble fibrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Feb 26;30(4):356–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90750-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh R. P., McDonagh J., Blombäck M., Blombäck B. Crosslinking of human fibrin: Evidence for intermolecular crosslinking involving alpha-chains. FEBS Lett. 1971 Apr 12;14(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane A. S. IN VIVO BEHAVIOR OF I-FIBRINOGEN. J Clin Invest. 1963 Mar;42(3):346–361. doi: 10.1172/JCI104721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee P. A., Mattock P., Hill R. L. Subunit structure of human fibrinogen, soluble fibrin, and cross-linked insoluble fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):738–744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. A. A molecular model for the proteolysis of human fibrinogen by plasmin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 18;263(3):619–630. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D., Karpatkin S. The initial macromolecular derivatives of human fibrinogen produced by plasmin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 22;271(1):163–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Alkjaersig N., Sweet B., Sherry S. Human fibrinogen of relatively high solubility. Comparative biophysical, biochemical, and biological studies with fibrinogen of lower solubility. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3279–3287. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Beck E. A. Chromatographic, ultracentrifugal, and related studies of fibrinogen "Baltimore". J Clin Invest. 1969 Sep;48(9):1656–1662. doi: 10.1172/JCI106130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S., Galanakis D. K. The essential covalent structure of human fibrinogen evinced by analysis of derivatives formed during plasmic hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7913–7929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S., Umfleet R. A., Galanakis D. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. I. Structural and related studies of plasma fibrinogens which are high solubility catabolic intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5210–5219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S., Umfleet R. A. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. 3. Identification of chain variants. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5223–5227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Galanakis D. K., Finlayson J. S. Comparison of human plasma fibrinogen subfractions and early plasmic fibrinogen derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4656–4664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Sherry S. The preparation and properties of human fibrinogen of relatively high solubility. Biochemistry. 1966 Sep;5(9):2829–2835. doi: 10.1021/bi00873a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Umfleet R. A. The cold-insoluble globulin of human plasma. I. Purification, primary characterization, and relationship to fibrinogen and other cold-insoluble fraction components. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5728–5736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUSSENZWEIG V., SELIGMANN M., PELMONT J., GRABAR P. [The products of degradation of human fibrinogen by plasmin. I. Separation and physicochemical properties]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1961 Mar;100:377–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Finlayson J. S., Peyton M. P. [Cross-link in fibrin polymerized by factor 13: epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine]. Science. 1968 May 24;160(3830):892–893. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3830.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzo S. V., Schwartz M. L., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. The effect of plasmin on the subunit structure of human fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):636–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., MENZIE C. A new method for the determination of fibrinogen in small samples of plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Feb;37(2):316–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SGOURIS J. T., INMAN J. K., McCALL K. B., HYNDMAN L. A., ANDERSON H. D. The preparation of human fibrinolysin (plasmin). Vox Sang. 1960 Jul;5:357–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1960.tb03750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi T., Iwanaga S. Polypeptide chain involved in the cross-linking of stabilized bovine fibrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 6;38(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]