Abstract
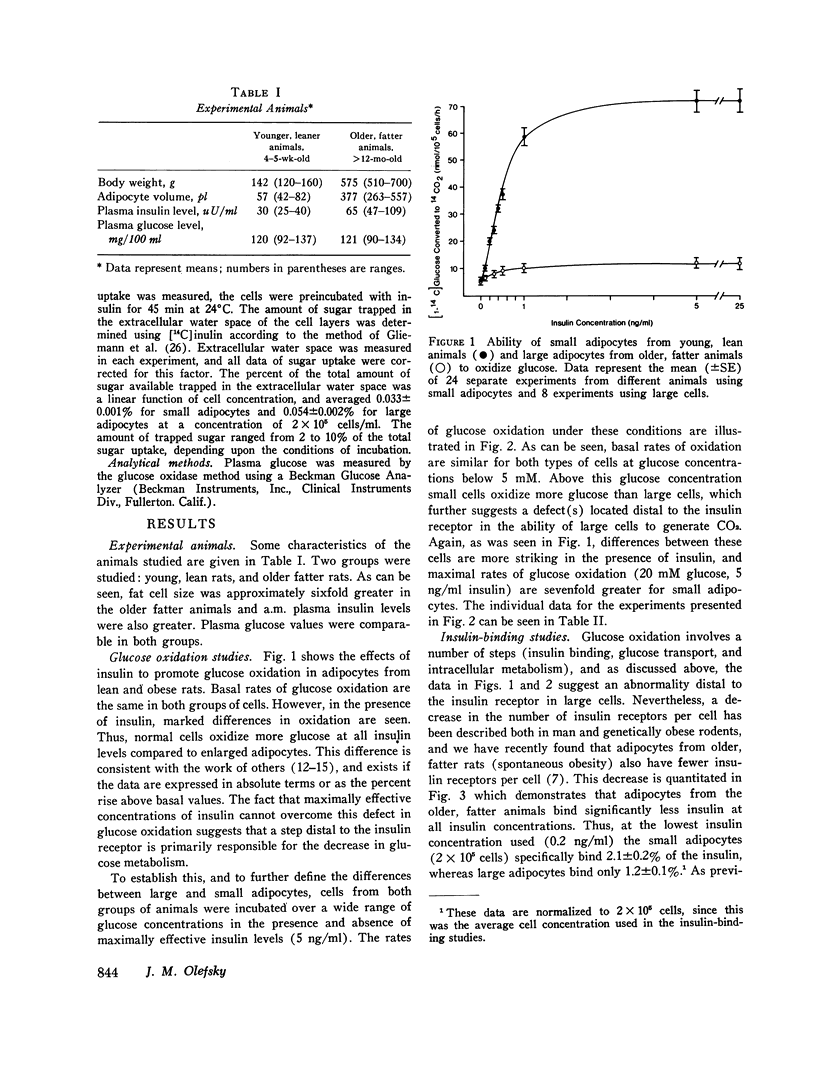
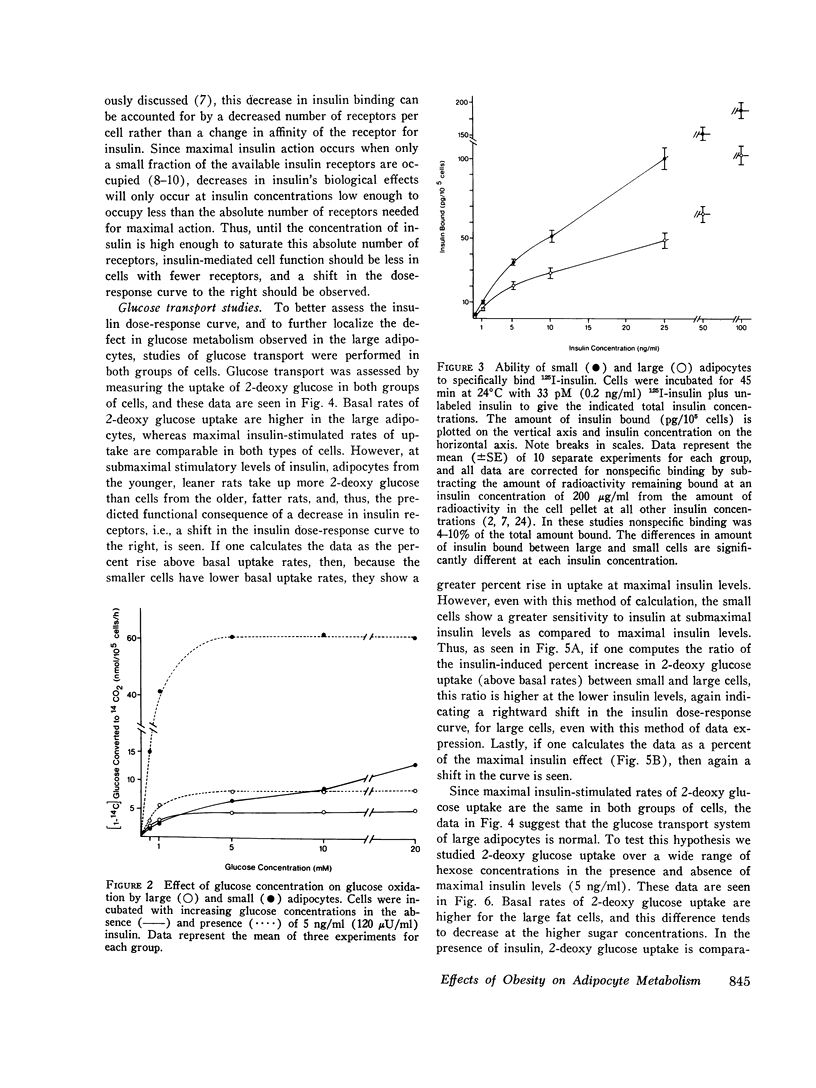
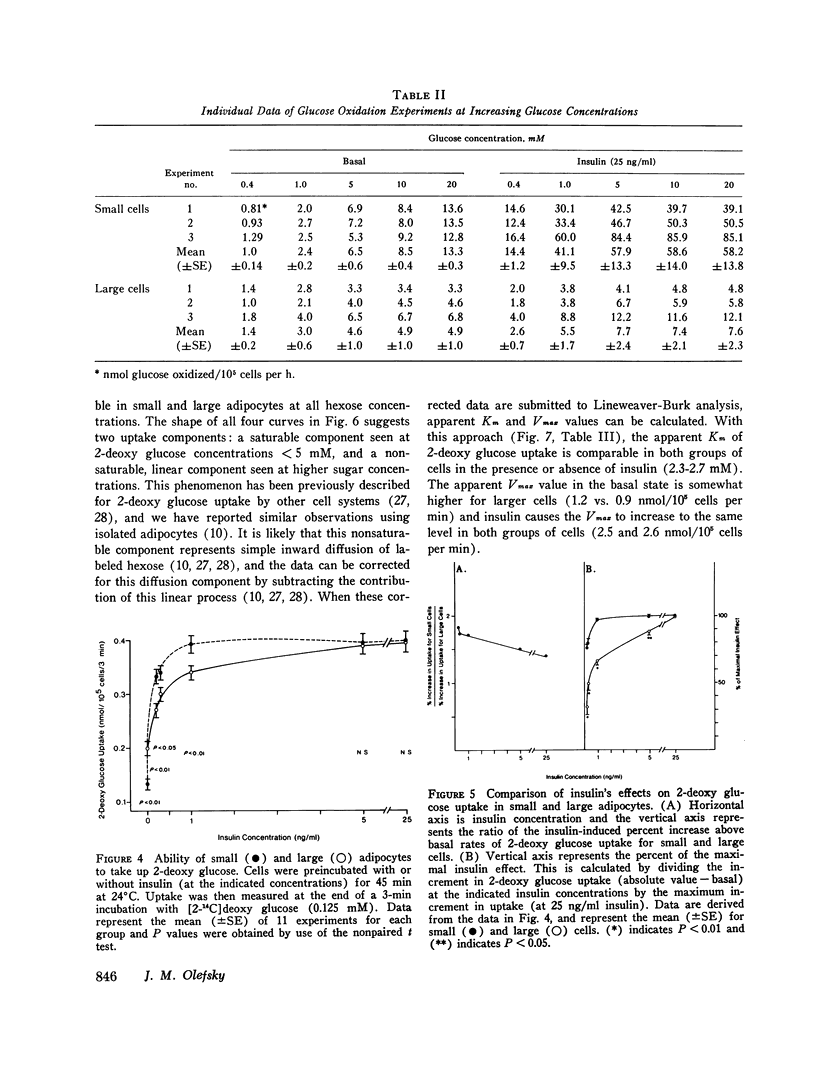
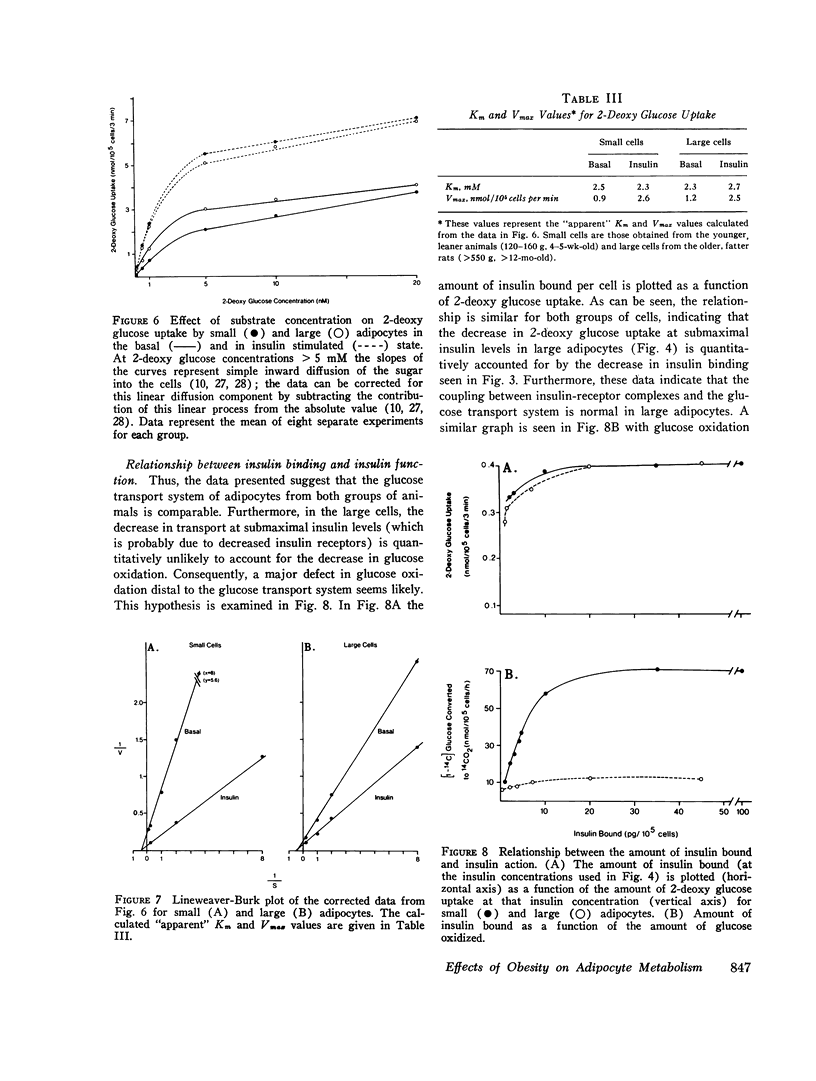
We have studied insulin, binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation, using large adipocytes isolated from older, fatter rats (greater than 12-mo-old, greater than 550 g), and smaller cells obtained from younger, leaner animals (4-5-wk-old, 120-160 g). At media glucose levels less than 5 mM, basal (absence of insulin) rates of glucose oxidation are comparable in both groups of cells. However, in the presence of insulin, the increase in glucose oxidation is much greater in the smaller cells. Maximally effective insulin levels could not overcome the defect in glucose oxidation by larger cells, and thus, even though studies of insulin binding demonstrated a 30-40% decrease in insulin receptors on the larger cells, it is probable that the defect in glucose oxidation is distal to the insulin receptor. Glucose transport was assessed by direct measurement of 2-deoxy glucose uptake. Basal levels of uptake were greater for the larger cells, whereas at maximally effective insulin concentrations, rates of 2-deoxy glucose uptake were the same for both groups of cells. Thus, in the presence of maximally effective levels of insulin, the apparent Km (2.3-2.7 mM) and Vmax values (2.6 and 2.7 nmol/10(5) cells per min) of 2-deoxy glucose uptake were comparable, indicating that the glucose transport system of the larger cells was intact. However, at submaximal levels of insulin, small adipocytes took up more 2-deoxy glucose than larger cells. These findings represent a rightward shift in the insulin dose-response curve in the cells from the older, fatter animals, and this is the predicted functional sequelae of the observed decrease in insulin receptors. Finally, when the amount of insulin bound was plotted as a function of 2-deoxy glucose uptake, no difference was seen between both groups of cells. This indicates that coupling between insulin receptor complexes and the glucose transport system is intact in large adipocytes, and is further evidence that a defect(s) in intracellular glucose metabolism is responsible for the decrease in glucose oxidation of adipocytes from older, fatter rats. In conclusion: (a) insulin-mediated glucose oxidation is markedly decreased in large adipocytes from older, fatter rats, and since this decrease cannot be corrected by maximally effective insulin levels, the defect is probably distal to the insulin receptor; (b) the glucose transport system is basically normal in large adipocytes; (c) insulin binding to receptors is decreased in large cells and the functional sequelae of this decrease in insulin binding i.e., a rightward shift in the insulin dose-response curve for 2-deoxy glucose uptake, was observed, and (d) since the decreased rates of insulin-mediated glucose oxidation can not be attributed to changes in insulin receptors or to changes in glucose transport, an intracellular defect in glucose metabolism is suggested.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer J. A., Gorden P., Gavin J. R., 3rd, Lesniak M. A., Roth J. Insulin receptors in human circulating lymphocytes: application to the study of insulin resistance in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Apr;36(4):627–633. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-4-627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer J. A., Gorden P., Roth J. Defect in insulin binding to receptors in obese man. Amelioration with calorie restriction. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):166–174. doi: 10.1172/JCI107907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. S., Kipnis D. M. Regulation of rat hexokinase isoenzymes. I. Assay and effect of age, fasting and refeeding. Diabetes. 1973 Dec;22(12):913–922. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.12.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo M., Mendlinger S., Fertig J. W. A simple method to determine fat cell size and number in four mammalian species. Am J Physiol. 1971 Sep;221(3):850–858. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.3.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo M., Mendlinger S. Glucose metabolism and responsiveness to bovine insulin by adipose tissue from three mammalian species. Diabetes. 1972 Dec;21(12):1151–1161. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.12.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo M., Rudman D. Variations in glucose metabolism and sensitivity to insulin of the rat's adipose tissue, in relation to age and body weight. Endocrinology. 1968 Jun;82(6):1133–1141. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-6-1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Laudat M. H., Laudat P., Rosselin G., Kahn C. R., Gorden P., Roth J. Impairment of insulin binding to the fat cell plasma membrane in the obese hyperglycemic mouse. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Monoiodoinsulin: demonstration of its biological activity and binding to fat cells and liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Gliemann J. Binding and degradation of 125I-labelled insulin by isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 17;320(1):16–32. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Gorden P., Roth J., Archer J. A., Buell D. N. Characteristics of the human lymphocyte insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2202–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J. Insulin-like activity of dilute human serum assayed by an isolated adipose cell method. Diabetes. 1965 Oct;14(10):643–649. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.10.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Osterlind K., Vinten J., Gammeltoft S. A procedure for measurement of distribution spaces in isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 24;286(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J., Gallian E. Methods for the determination of adipose cell size in man and animals. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jan;9(1):110–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin-receptor interaction in the obese-hyperglycemic mouse. A model of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kletzien R. F., Perdue J. F. Sugar transport in chick embryo fibroblasts. I. A functional change in the plasma membrane associated with the rate of cell growth. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3366–3374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Barham F. W. The relationship between the insulin-binding capacity of fat cells and the cellular response to insulin. Studies with intact and trypsin-treated fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6210–6216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston J. N., Lockwood D. H. Direct measurements of sugar uptake in small and large adipocytes from young and adult rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 11;61(3):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Effect of dexamethasone on insulin binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation of isolated rat adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1499–1508. doi: 10.1172/JCI108231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Jen P., Reaven G. M., Alto P. Insulin binding to isolated human adipocytes. Diabetes. 1974 Jul;23(7):565–571. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.7.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Johnson J., Liu F., Jen P., Reaven G. M. The effects of acute and chronic dexamethasone administration on insulin binding to isolated rat hepatocytes and adipocytes. Metabolism. 1975 Apr;24(4):517–527. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Effects of age and obesity on insulin binding to isolated adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1975 Jun;96(6):1486–1498. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-6-1486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J., Reaven G. M. The human lymphocyte: a model for the study of insulin-receptor interaction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Apr;38(4):554–560. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-4-554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ D., ZIERLER K. L. Forearm metabolism in obesity and its response to intra-arterial insulin. Characterization of insulin resistance and evidence for adaptive hyperinsulinism. J Clin Invest. 1962 Dec;41:2173–2181. doi: 10.1172/JCI104676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner E. D., Plagemann P. G., Bernlohr R. W. Permeation of glucose by simple and facilitated diffusion by Novikoff rat hepatoma cells in suspension culture and its relationship to glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5765–5776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salans L. B., Dougherty J. W. The effect of insulin upon glucose metabolism by adipose cells of different size. Influence of cell lipid and protein content, age, and nutritional state. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1399–1410. doi: 10.1172/JCI106623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll A. H., Goldfine I. D., Roth J., Kahn C. R. Thymic lymphocytes in obese (ob-ob) mice. A mirror of the insulin receptor defect in liver and fat. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4127–4131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WICK A. N., DRURY D. R., NAKADA H. I., WOLFE J. B. Localization of the primary metabolic block produced by 2-deoxyglucose. J Biol Chem. 1957 Feb;224(2):963–969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M. J. Hexose transport in normal and in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):2978–2983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



