Abstract
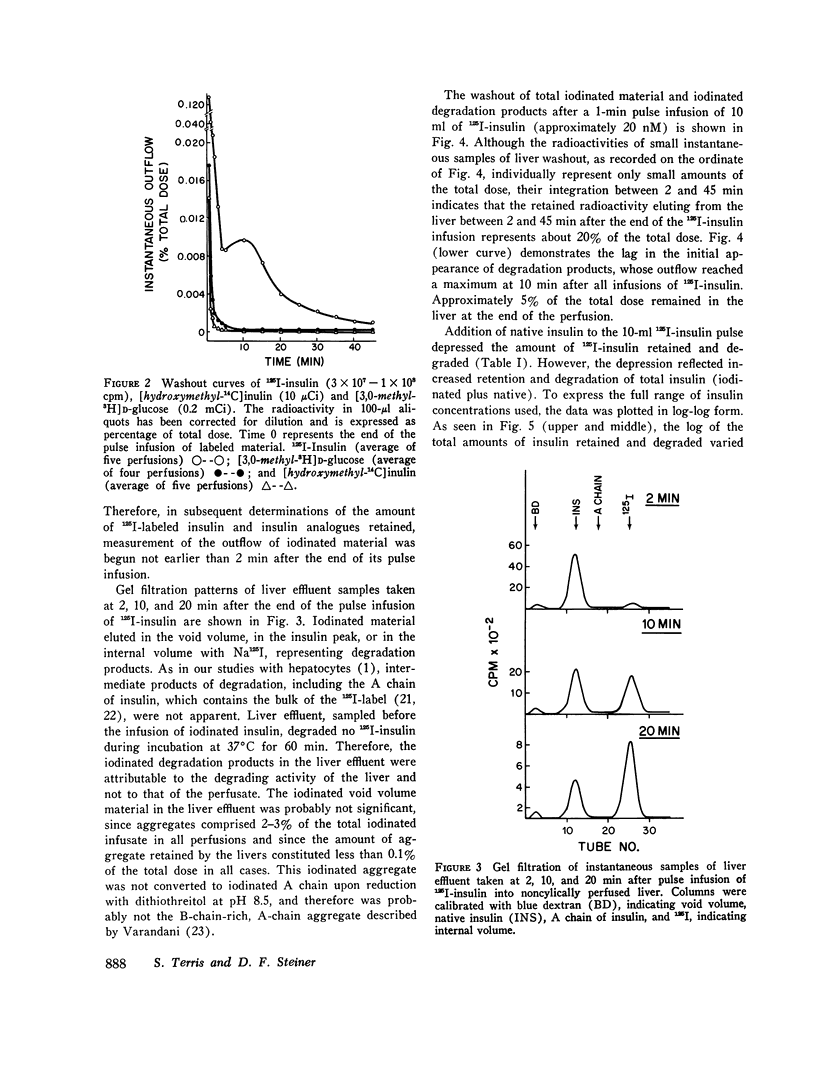
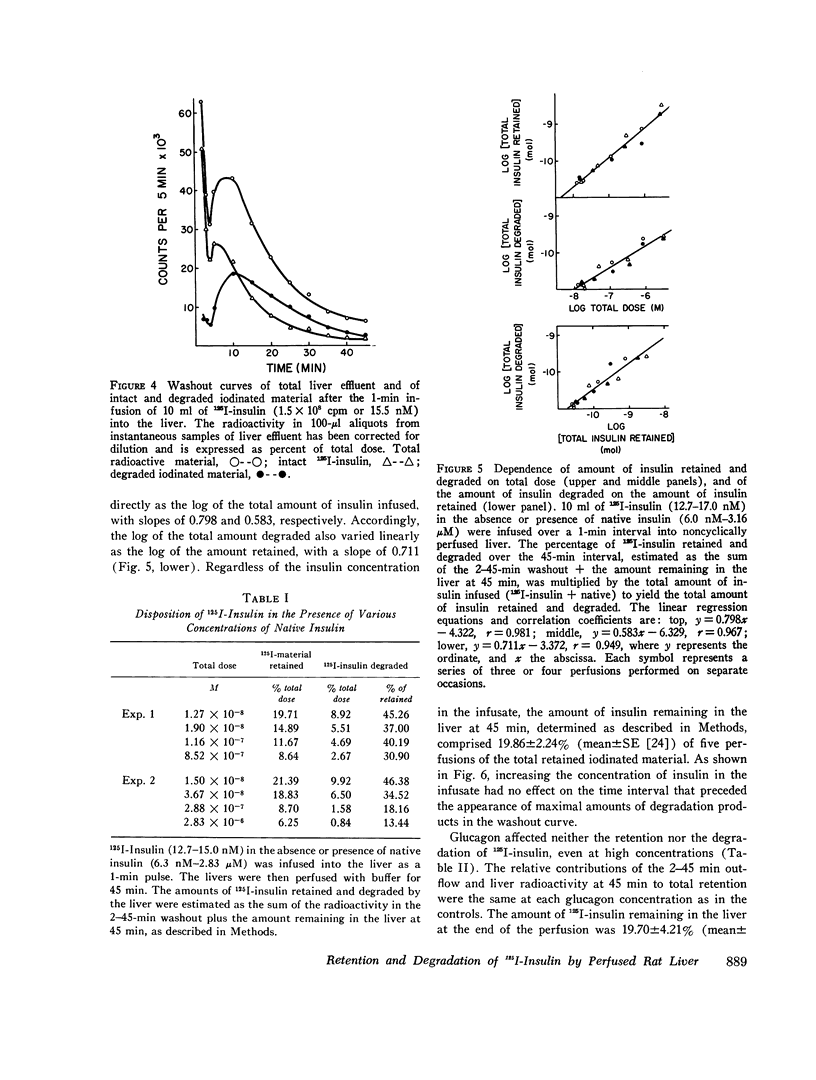
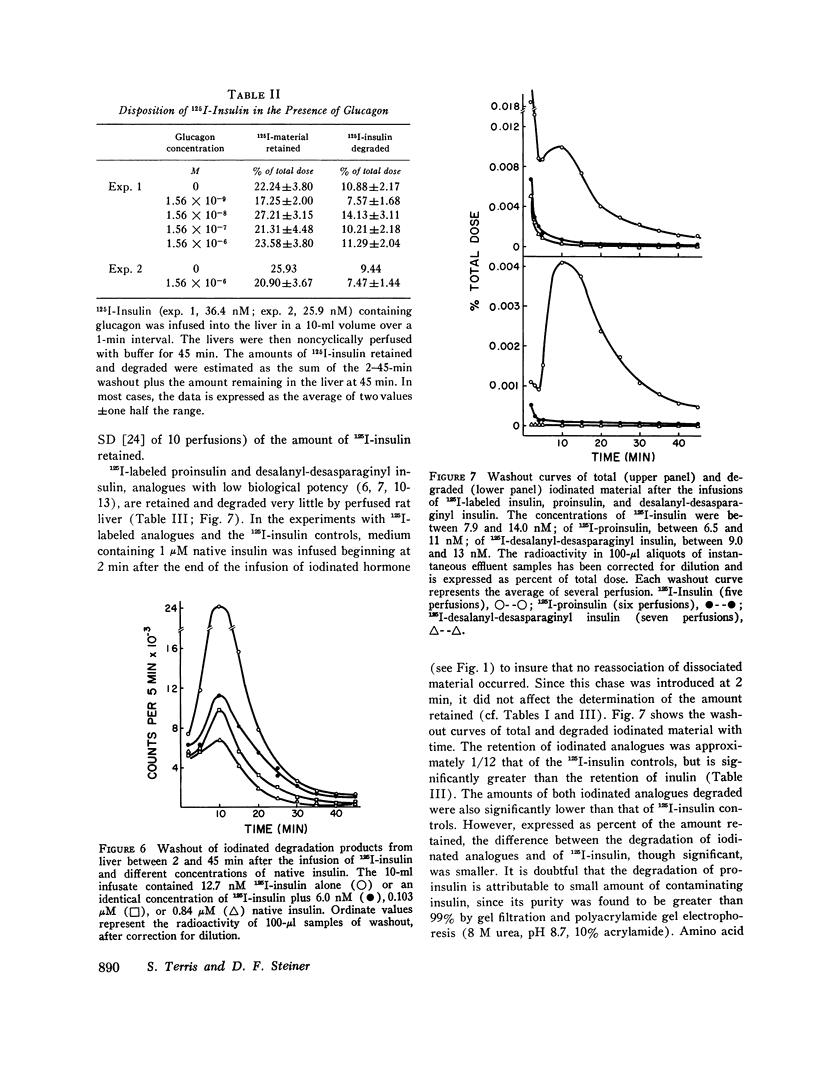
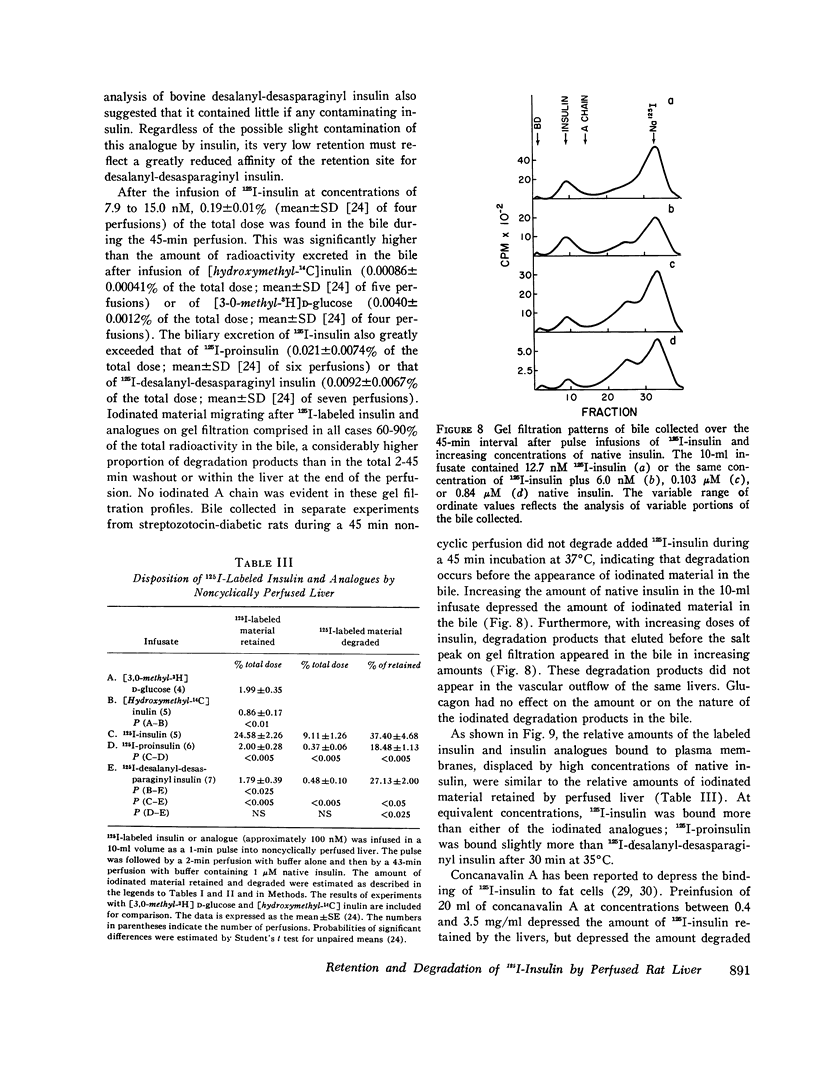
The retention of degradation of insulin by isolated perfused liver have been examined. Noncyclically perfused livers from streptozotocin-diabetic rats retained 25% and degraded 10% of 125I-insulin administered as a 1-min pulse. On gel filtration (Sephadex G50F), the degradation products released into the vascular effluent eluted in the salt peak. During the 45-min interval after the end of the 125I-insulin infusion, 0.19% of the total dose was excreted in the bile. 60-90% of this material consisted of iodinated, low-molecular-weight degradation products. Inclusion of native insulin with the 125I-insulin in the pulse depressed both the retention and degradation of iodinated material; however, this reflected increased retention and degradation of the total insulin dose (125I-insulin plus native hormone). The log of the total amounts of insulin retained and degraded were linearly related to the log of the total amount of insulin infused at concentrations between 12.7 nM and 2.84 muM. Increasing the amount of native insulin in the infused pulse also depressed the total amount of iodinated material found in the bile and led to the appearance in the bile of intermediate-sized degradation products that did not simultaneously appear in the vascular effluent. Addition of high concentrations of glucagon to the infused 125I-insulin had no effect on the retention or degradation of the labeled hormone, or on the apparent size and amount of iodinated degradation products found in the vascular effluent or in the bile. Preinfusion of concanavalin A inhibited both 125I-insulin retention and degradation. A greater depression by concanavalin A of degradation than binding was also observed with isolated hepatocytes. In contrast to 125I-insulin, the retention and degradation of two iodinated insulin analogues of relative low biological potency, proinsulin and desalanyl-desasparaginyl insulin, were small. The amount of radioactivity appearing in the bile after infusion of these analogues was almost negligible. However, degradation products of these analogues that appeared in the bile and in the vascular effluent was qualitatively similar to those found after the infusion of 125I-insulin. Our findings suggest that the rapid initial uptake of 125I-insulin after its infusion into noncyclically perfused liver, as well as its subsequent degradation, behaves in a qualitatively similar fashion to the binding of 125I-insulin and its degradation by isolated rat hepatocytes. This uptake and the subsequent phase of degradation may be attributable to binding of insulin at specific recognition sites, preliminary to its transfer to a degradative site(s) presumed to be located inside the cell.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUERGI H., SCHWARZ K., KOPETZ K., FROESCH E. R. FATE OF RAT INSULIN IN RAT-LIVER PERFUSION STUDIED BY ADIPOSE-TISSUE ASSAY. Lancet. 1963 Aug 17;2(7303):314–316. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92987-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin R. D. Effect of concanavalin A on phagocytosis. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 12;235(54):44–45. doi: 10.1038/newbio235044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyns A. R., Pearce N., Mahler R. F. Insulin in bile. The effect of monosaccharides and hypoglycaemic agents. Diabetologia. 1969 Oct;5(5):304–308. doi: 10.1007/BF00452903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brush J. S. Purification and characterization of a protease with specificity for insulin from rat muscle. Diabetes. 1971 Mar;20(3):140–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan K. D., Solomon S. S., Vance J. E., Porter H. P., Williams R. H. Glucagon clearance by the isolated perfused rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jun;128(2):620–623. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler M. L., Varandani P. T. Insulin degradation. II. The widespread distribution of glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase in the tissues of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 24;286(1):136–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey J. W., De Duve C. Digestive activity of lysosomes. I. The digestion of proteins by extracts of rat liver lysosomes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3255–3263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crofford O. B., Rogers N. L., Russell W. G. The effect of insulin on fat cells. An insulin degrading system extracted from plasma membranes of insulin responsive cells. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):403–413. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Desbuquois B., Krug F. Insulin-receptor interactions in liver cell membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90604-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin--receptor interactions in adipose tissue cells: direct measurement and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1264–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of concanavalin A and wheat germ agglutinin with the insulin receptor of fat cells and liver. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3528–3534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Tell G. P. Insulin-like activity of concanavalin A and wheat germ agglutinin--direct interactions with insulin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):485–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C., Heinemann M. A., Kitabchi A. E. Purification of insulin-specific protease by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3698–3702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Yahara I., Wang J. L. Receptor mobility and receptor-cytoplasmic interactions in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1442–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenreich B. A., Cohn Z. A. Fate of hemoglobin pincytosed by macrophages in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jul;38(1):244–248. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenreich B. A., Cohn Z. A. The uptake and digestion of iodinated human serum albumin by macrophages in vitro. J Exp Med. 1967 Nov 1;126(5):941–958. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.5.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin receptors in the liver: specific binding of ( 125 I)insulin to the plasma membrane and its relation to insulin bioactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Monoiodoinsulin: demonstration of its biological activity and binding to fat cells and liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P. The interactions of proinsulin with insulin receptors on the plasma membrane of the liver. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1020–1031. doi: 10.1172/JCI107845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Gliemann J. Binding and degradation of 125I-labelled insulin by isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 17;320(1):16–32. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Gorden P., Roth J., Archer J. A., Buell D. N. Characteristics of the human lymphocyte insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2202–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Jen P., Freychet P. Insulin receptors in human circulating cells and fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):747–751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Sorensen H. H. Assay of insulin-like activity by the isolated fat cell method. IV. The biological activity of proinsulin. Diabetologia. 1970 Oct;6(5):499–504. doi: 10.1007/BF01211891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Gardner J. D., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin action in isolated rat thymocytes. I. Binding of 125 I-insulin and stimulation of -aminoisobutyric acid transport. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6919–6926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway C. V., Stark R. D. Hepatic vascular bed. Physiol Rev. 1971 Jan;51(1):23–65. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House P. D.R. Kinetics of 125I-insulin binding to rat liver plasma membranes. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 1;16(4):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80385-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo J. L., Bartlett J. W., Roncone A., Izzo M. J., Bale W. F. Physiological processes and dynamics in the disposition of small and large doses of biologically active and inactive 131-I-insulins in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2343–2355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo J. L., Roncone A., Izzo M. J., Foley R., Bartlett J. W. Degradation of 131 I-insulins by rat liver. Studies in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1219–1226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Quantitative aspects of the insulin-receptor interaction in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2249–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzen H. M., Tietze F. Studies on the specificity and mechanism of action of hepatic glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3561–3570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabchi A. E., Stentz F. B. Degradation of insulin and proinsulin by various organ homogenates of rat. Diabetes. 1972 Nov;21(11):1091–1101. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.11.1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P., Lenoir P. Degradation of insulin by isolated rat liver cells. Diabetes. 1975 Jun;24(6):566–573. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.6.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIRSKY I. A., PERISUTTI G., DIXON F. J. The destruction of I131-labeled insulin by rat liver extracts. J Biol Chem. 1955 May;214(1):397–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTIMORE G. E., TIETZE F. Studies on the mechanism of capture and degradation of insulin-1131 by the cyclically perfused rat liver. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:329–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarroll A. M., Buchanan K. D. Insulin clearance by the isolated perfused livers of insulin deficient rats. Diabetologia. 1973 Dec;9(6):457–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00461688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondon C. E., Olefsky J. M., Dolkas C. B., Reaven G. M. Removal of insulin by perfused rat liver: effect of concentration. Metabolism. 1975 Feb;24(2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C. R., Wiesman H. J. Liver insulinase activity in insulin deficient rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Mar;127(3):763–765. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimore G. E., Neely A. N., Cox J. R., Guinivan R. A. Proteolysis in homogenates of perfused rat liver: responses to insulin, glucagon and amino acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 5;54(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90892-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely A. N., Mortimore G. E. Localization of products of endogenous proteolysis in lysosomes of perfused rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 24;59(2):680–687. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Isolation of an organ specific protein antigen from cell-surface membrane of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 9;154(3):540–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J., Johnson J., Liu F., Edwards P., Baur S. Comparison of 125-I-insulin binding and degradation to isolated rat hepatocytes and liver membranes. Diabetes. 1975 Sep;24(9):801–810. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.9.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. H., Pottenger L. A., Mako M., Getz G. S., Steiner D. F. The metabolism of proinsulin and insulin by the liver. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):912–921. doi: 10.1172/JCI106886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudman D., Garcia L. A., Del Rio A. Effects on mammalian adipose tissue of fragments of bovine insulin and of certain synthetic peptides. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1875–1881. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLOBIN L. I., CARPENTER F. H. Action of carboxypeptidase- A on bovine insulin: preparation of desalanine-desasparagine-insulin. Biochemistry. 1963 Jan-Feb;2:16–22. doi: 10.1021/bi00901a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of rat liver cells. 3. Enzymatic requirements for tissue dispersion. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Dec;82(2):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90357-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J., Freychet P., Rosselin G. Chicken insulin: radioimmunological characterization and enhanced activity in rat fat cells and liver plasma membranes. Endocrinology. 1974 Nov;95(5):1439–1449. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-5-1439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon S. S., Fenster L. F., Ensinck J. W., Williams R. H. Clearance studies of insulin and nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) in the rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):166–169. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Hallund O., Rubenstein A., Cho S., Bayliss C. Isolation and properties of proinsulin, intermediate forms, and other minor components from crystalline bovine insulin. Diabetes. 1968 Dec;17(12):725–736. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.12.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll R. W., Touber J. L., Menahan L. A., Williams R. H. Clearance of porcine insulin, proinsulin, and connecting peptide by the isolated rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Mar;133(3):894–896. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMIZAWA H. H. Properties of glutathione insulin transhydrogenase from beef liver. J Biol Chem. 1962 Nov;237:3393–3396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Binding and degradation of 125I-insulin by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8389–8398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T. Insulin degradation. VI. Feedback control by insulin of liver glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase in rat. Diabetes. 1974 Feb;23(2):117–125. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T. Insulin degradation. X. Identification of insulin degrading activity of rat liver plasma membrane as glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T. Mode of action of glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Studies on the precipitate produced by its action on insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 12;118(1):198–201. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T., Shroyer L. A., Nafz M. A. Sequential degradation of insulin by rat liver homogenates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1681–1684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahara I., Edelman G. M. Restriction of the mobility of lymphocyte immunoglobulin receptors by concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):608–612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. S., Kitbachi A. E. Biological activity of proinsulin and related polypeptides in the fat tissue. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3753–3761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meyts P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, Gavin J. R., 3rd, Lesniak M. A. Insulin interactions with its receptors: experimental evidence for negative cooperativity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 1;55(1):154–161. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



