Abstract
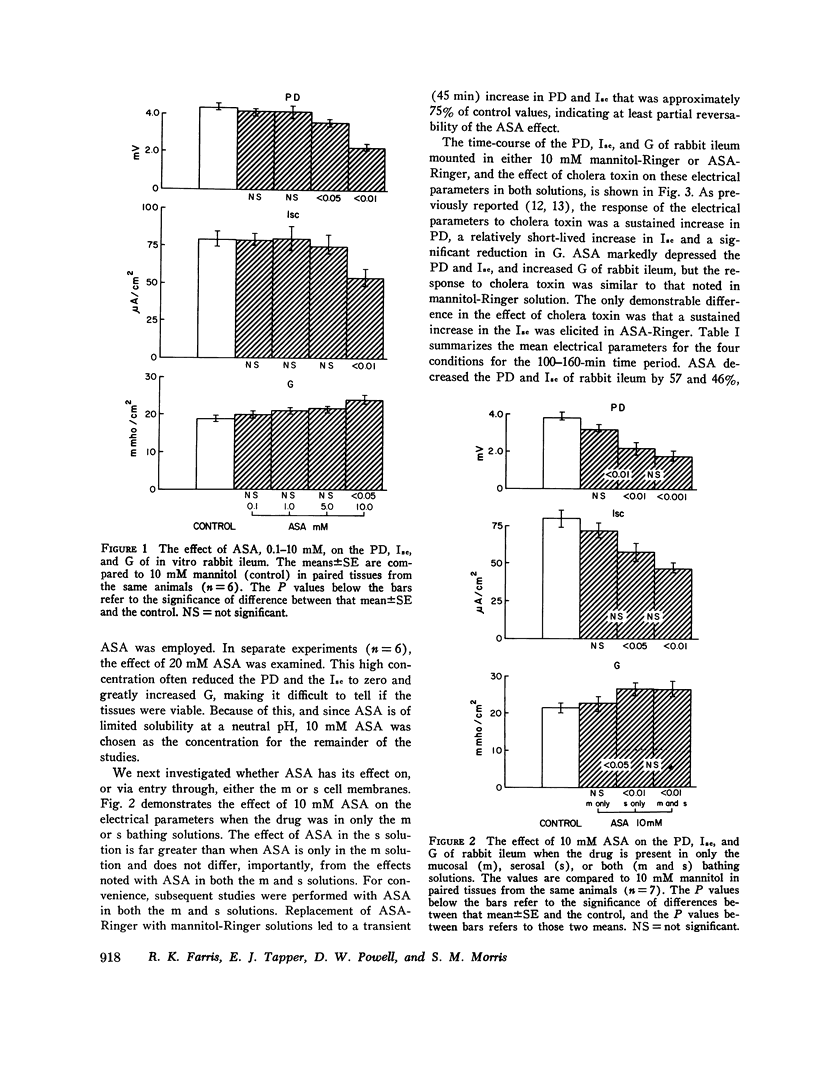
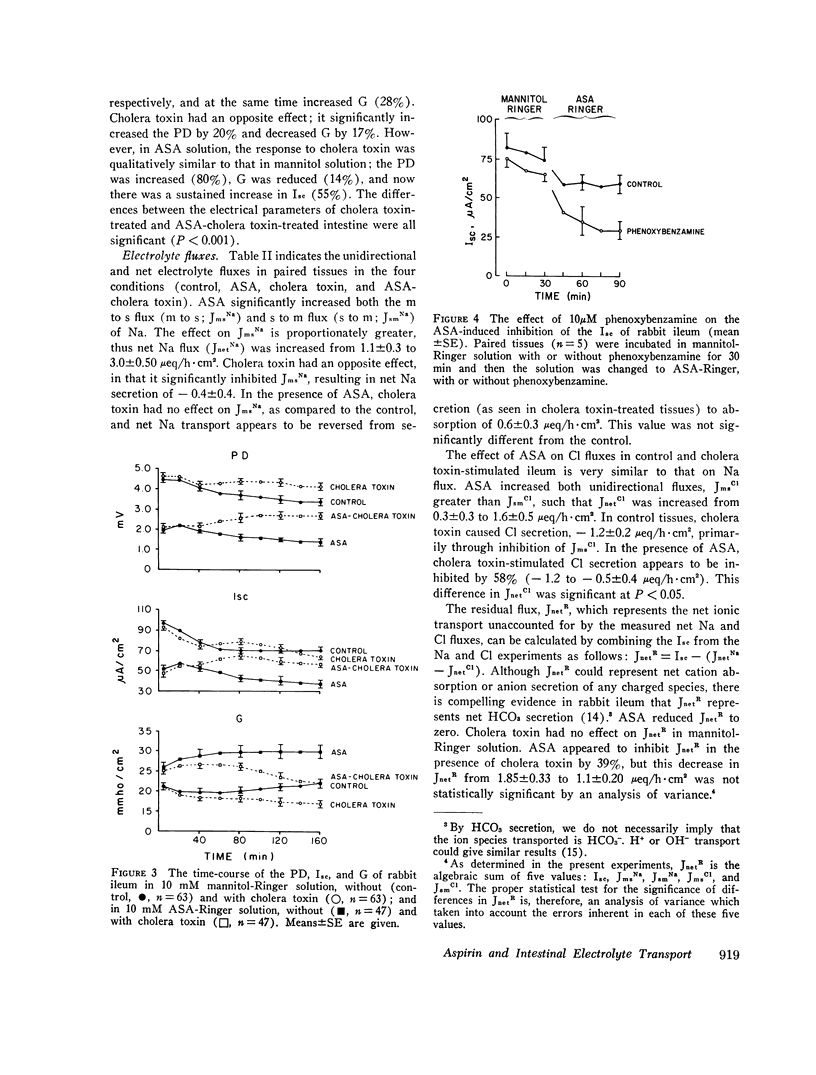
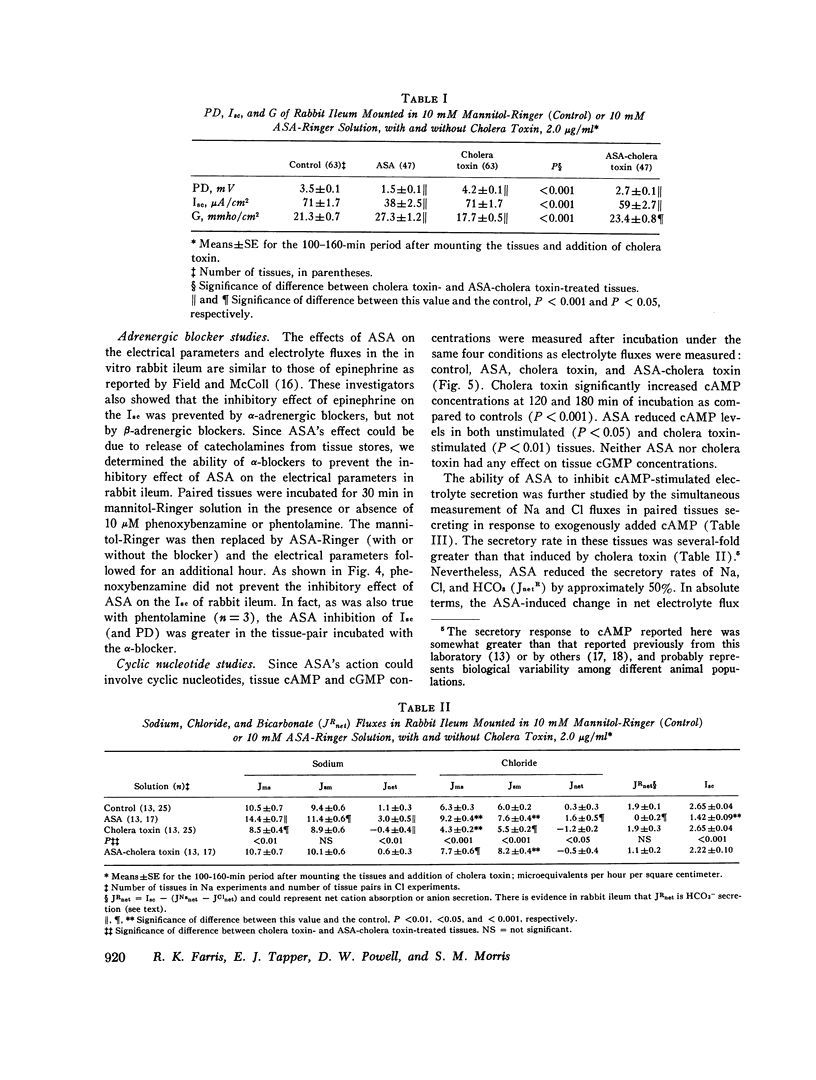
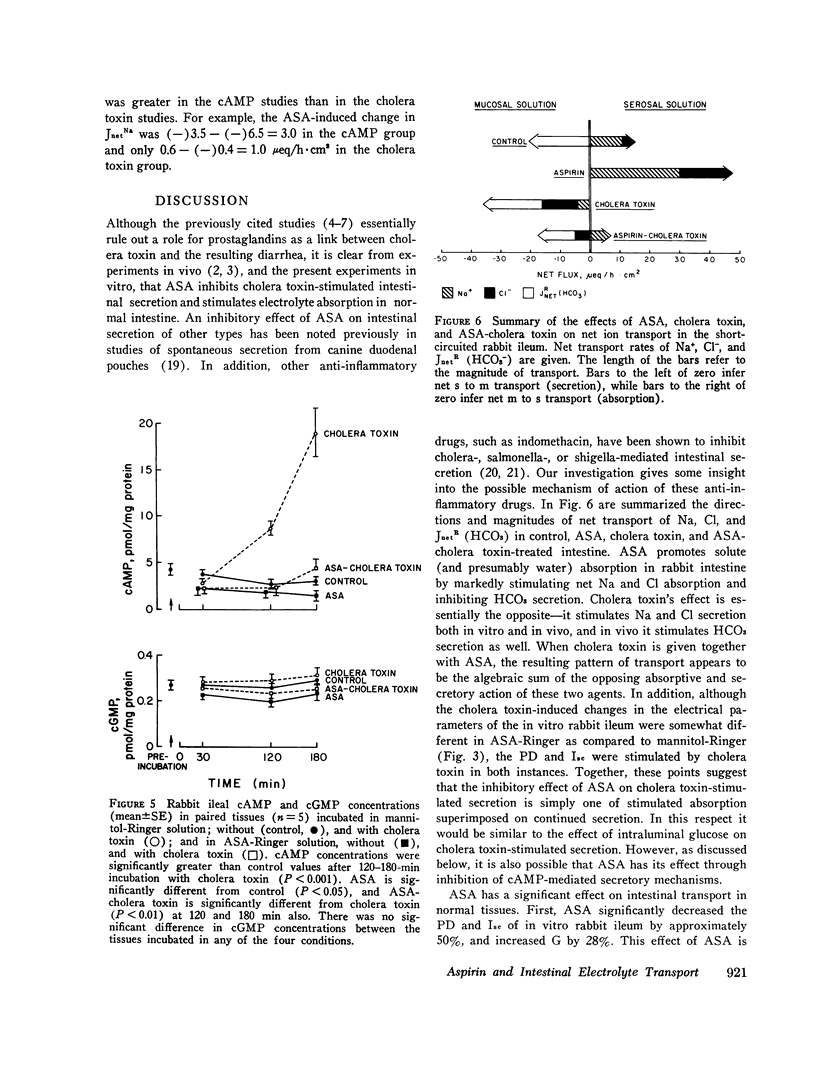
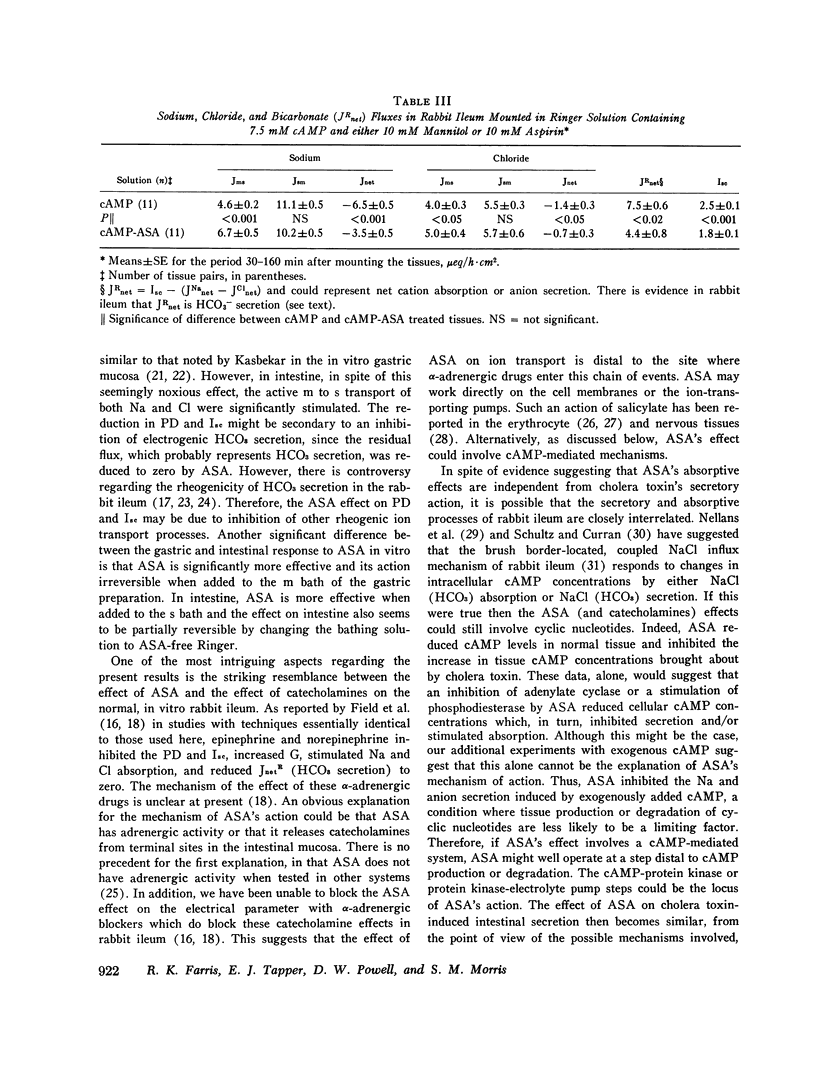
The effect of aspirin on normal and cholera toxin-stimulated electrolyte transport has been investigated in vitro, because this drug appears to inhibit cholera toxin-induced intestinal secretion in in vivo animal models. In the Ussing chamber, 10 mM aspirin decreased the control rabbit ileal potential difference and short-circuit current by 50% and increased conductance by 28%. Bidirectional electrolyte flux determinations showed that aspirin significantly increased both Na and Cl absorption and reduced flux (which probably represents HCO3 secretion) to zero. This effect of aspirin appears to be identical to that reported to others with catecholamines as determined with similar techniques. However, alpha-adrenergic blockers did not prevent the electrical effects of aspirin, suggesting that aspirin does not have its effect through release of tissue stores of catecholamines. In the presence of aspirin, cholera toxin increased the potential difference and short-circuit current, and decreased the conductance of rabbit ileum in a fashion qualitatively similar to control tissues. However, aspirin reversed cholera toxin-stimulated Na transport from secretion to absorption, inhibited cholera toxin, induced Cl secretion by 58% and partially, but not significantly, inhibited HCO3 secretion. Thus, the inhibitory effect of aspirin on cholera toxin-induced electrolyte secretion appears to be due to aspirin-stimulated Na and Cl absorption. Although aspirin reduced tissue cyclic AMP concentrations in normal and cholera toxin-stimulated ileum, it also inhibited the electrolyte secretion induced by exogenous cyclic AMP. Thus, if aspirin's stimulatory effect on sodium and anion absorption in normal tissue and its inhibitory effect on cholera toxin-stimulated sodium and anion secretion involves a cyclic AMP-mediated system, the effect must be a step distal to cyclic AMP production or degradation. The exact mechanism of aspirin's effect on normal and cholera toxin-induced electrolyte transport, and its possible usefulness in the treatment of cholera diarrhea, remains to be determined.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett A. Cholera and prostaglandins. Nature. 1971 Jun 25;231(5304):536–536. doi: 10.1038/231536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Cholera enterotoxin: failure of anti-inflammatory agents to prevent cyclic AMP accumulation. Nature. 1973 Feb 9;241(5389):399–399. doi: 10.1038/241399a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O. A pharmacological analysis of aspirin. Adv Pharmacol Chemother. 1969;7:333–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz J., Field M. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. IV. Bicarbonate secretion. Am J Physiol. 1973 Oct;225(4):858–861. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.4.858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinnendahl V., Peters H. D., Schönhöfer P. S. Effects of sodium salicylate and acetylsalicylic acid on cyclic 3',5'-AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Sep 15;22(18):2223–2228. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., McColl I. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. I. Na and Cl fluxes and short-circuit current. Am J Physiol. 1971 May;220(5):1388–1396. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.5.1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. II. Effects of cyclic 3', 5'-AMP. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):992–997. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., McColl I. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. 3. Effects of catecholamines. Am J Physiol. 1973 Oct;225(4):852–857. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.4.852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Sheerin H. E., Henderson A., Smith P. L. Catecholamine effects on cyclic AMP levels and ion secretion in rabbit ileal mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jul;229(1):86–92. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finck A. D., Katz R. L. Prevention of cholera-induced intestinal secretion in the cat by aspirin. Nature. 1972 Aug 4;238(5362):273–274. doi: 10.1038/238273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gots R. E., Formal S. B., Giannella R. A. Indomethacin inhibition of Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella flexneri, and cholera-mediated rabbit ileal secretion. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):280–284. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel K. A. The mechanism of bicarbonate secretion in rabbit ileum exposed to choleragen. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):964–970. doi: 10.1172/JCI107662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby H. I., Marshall C. H. Antagonism of cholera enterotoxin by anti-inflammatory agents in the rat. Nature. 1972 Jan 21;235(5334):163–165. doi: 10.1038/235163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasbekar D. K. Effects of salicylate and related compounds on gastric HCl secretion. Am J Physiol. 1973 Sep;225(3):521–527. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Gershon E., Henderson A. Effects of prostaglandins and cholera enterotoxin on intestinal mucosal cyclic AMP accumulation. Evidence against an essential role for prostaglandins in the action of toxin. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):941–949. doi: 10.1172/JCI107635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan H., Barker J. L. Membrane permeability: cation selectivity reversibly altered by salicylate. Science. 1972 Oct 6;178(4056):63–64. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4056.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellans H. N., Frizzell R. A., Schultz S. G. Brush-border processes and transepithelial Na and Cl transport by rabbit ileum. Am J Physiol. 1974 May;226(5):1131–1141. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.5.1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellans H. N., Frizzell R. A., Schultz S. G. Coupled sodium-chloride influx across the brush border of rabbit ileum. Am J Physiol. 1973 Aug;225(2):467–475. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.2.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W., Binder H. J., Curran P. F. Active electrolyte secretion stimulated by choleragen in rabbit ileum in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1973 Oct;225(4):781–787. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.4.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W., Binder H. J., Curran P. F. Electrolyte secretion by the guinea pig ileum in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1972 Sep;223(3):531–537. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.3.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W., Farris R. K., Carbonetto S. T. Theophylline, cyclic AMP, choleragen, and electrolyte transport by rabbit ileum. Am J Physiol. 1974 Dec;227(6):1428–1435. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.6.1428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W. Intestinal conductance and permselectivity changes with theophylline and choleragen. Am J Physiol. 1974 Dec;227(6):1436–1443. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.6.1436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell T. R., Jones R. S., Postlethwait R. W. The effect of aspirin on duodenal secretion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Mar;145(3):967–969. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-37934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönhöfer P. S., Sohn J., Peters H. D., Dinnendahl V. Effects of sodium salicylate and acetylsalicylic acid on the lipolytic system of fat cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Mar 1;22(5):629–637. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Pagliara A. S., Chase L. R., Kipnis D. M. Radioimmunoassay for cyclic nucleotides. II. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in mammalian tissues and body fluids. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1114–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone D. B., Brown J. D., Steele A. A. Effect of sodium salicylate on induced lipolysis in isolated fat cells of the rat. Metabolism. 1969 Jul;18(7):620–624. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieth J. O. Effect of some monovalent anions on chloride and sulphate permeability of human red cells. J Physiol. 1970 May;207(3):581–609. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieth J. O. Paradoxical temperature dependence of sodium and potassium fluxes in human red cells. J Physiol. 1970 May;207(3):563–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



