Abstract
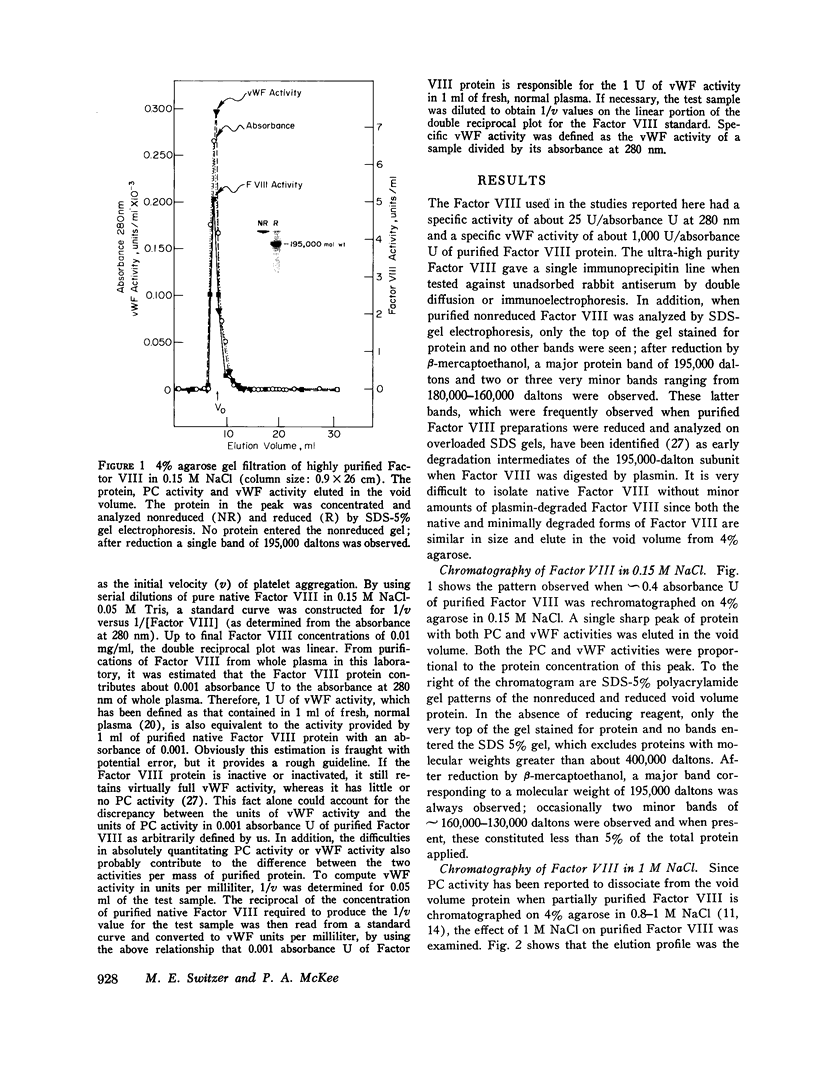
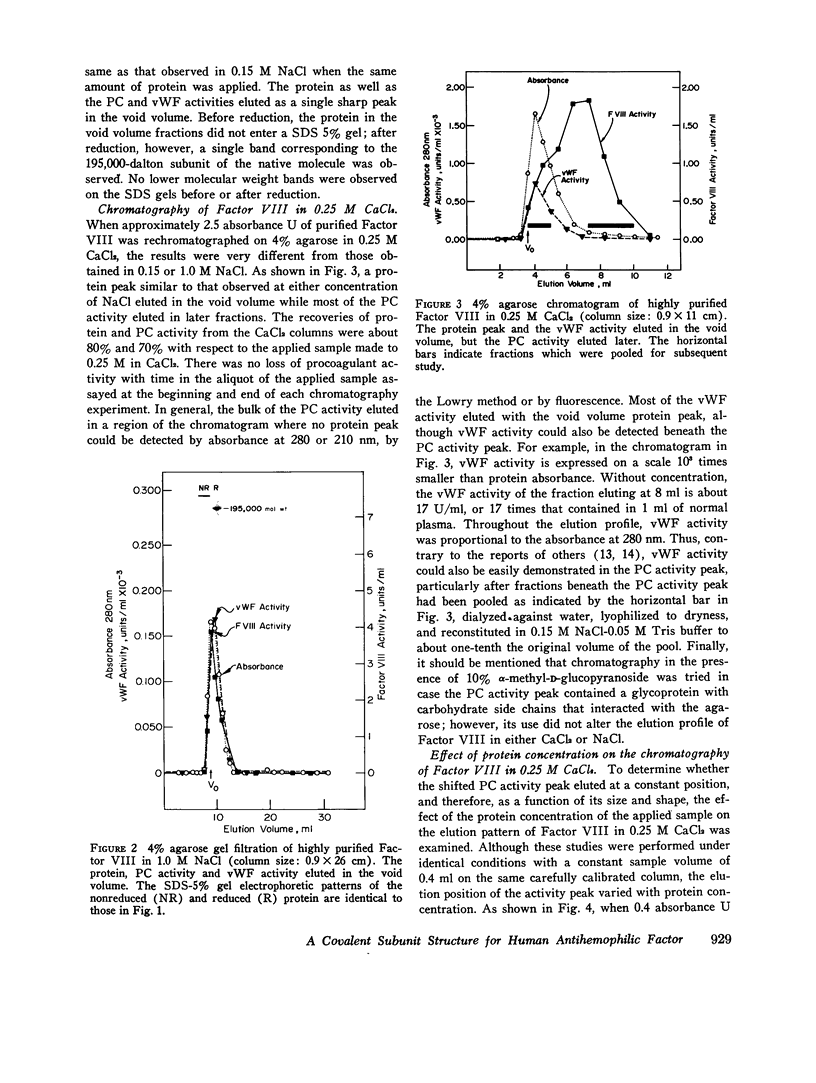
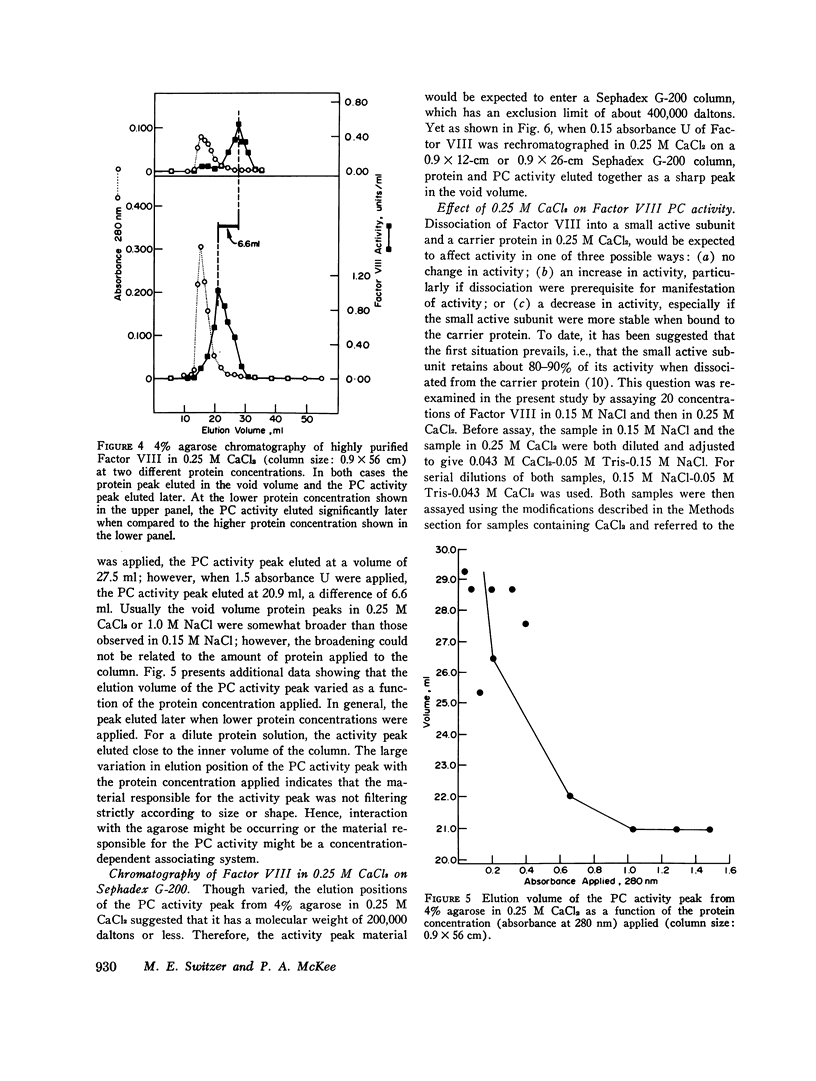
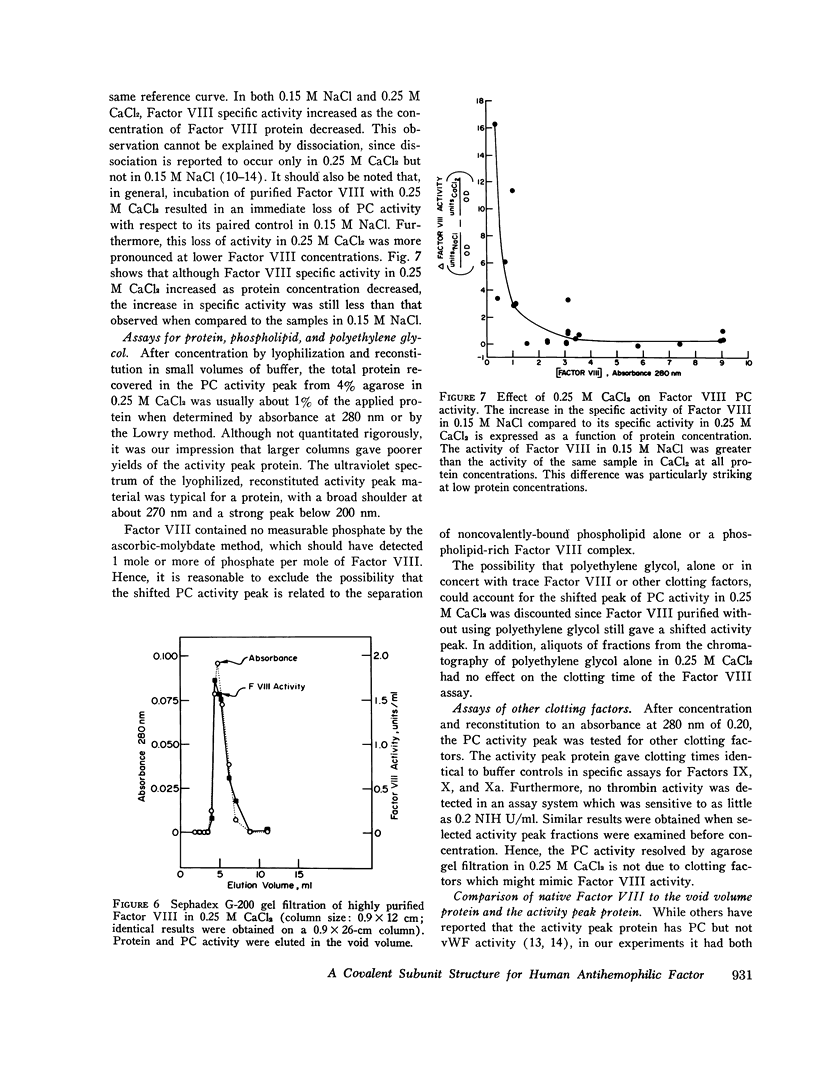
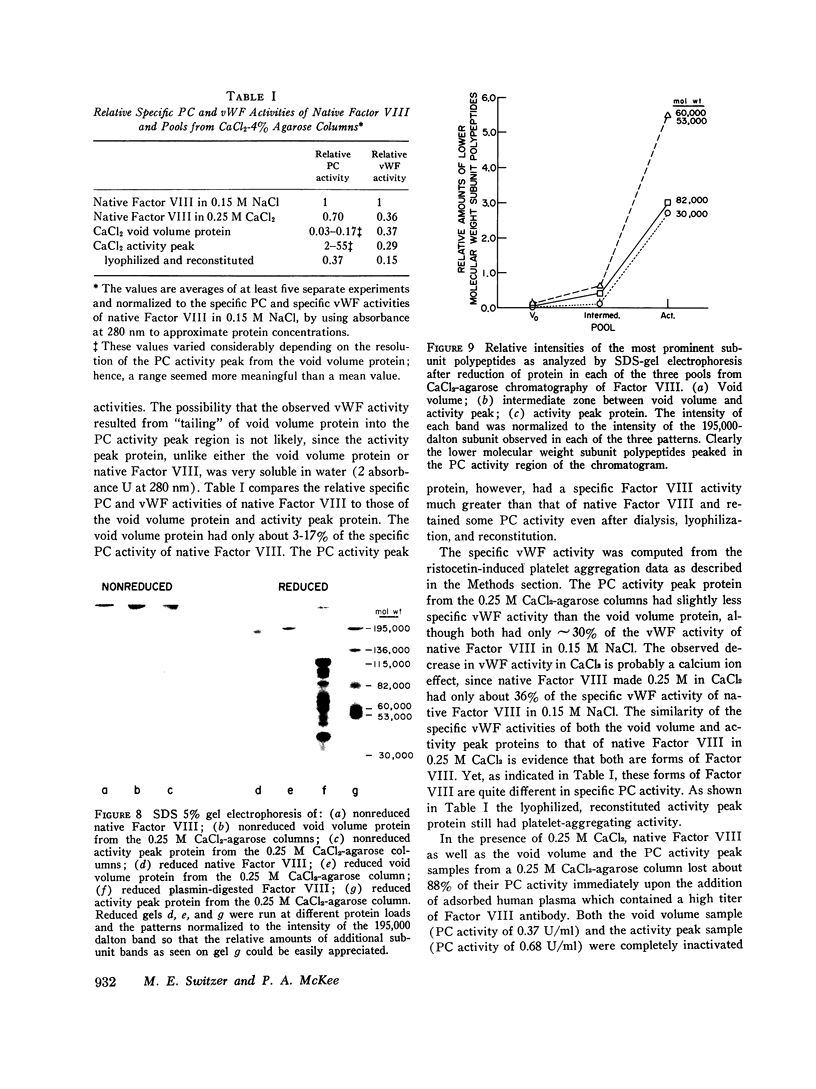
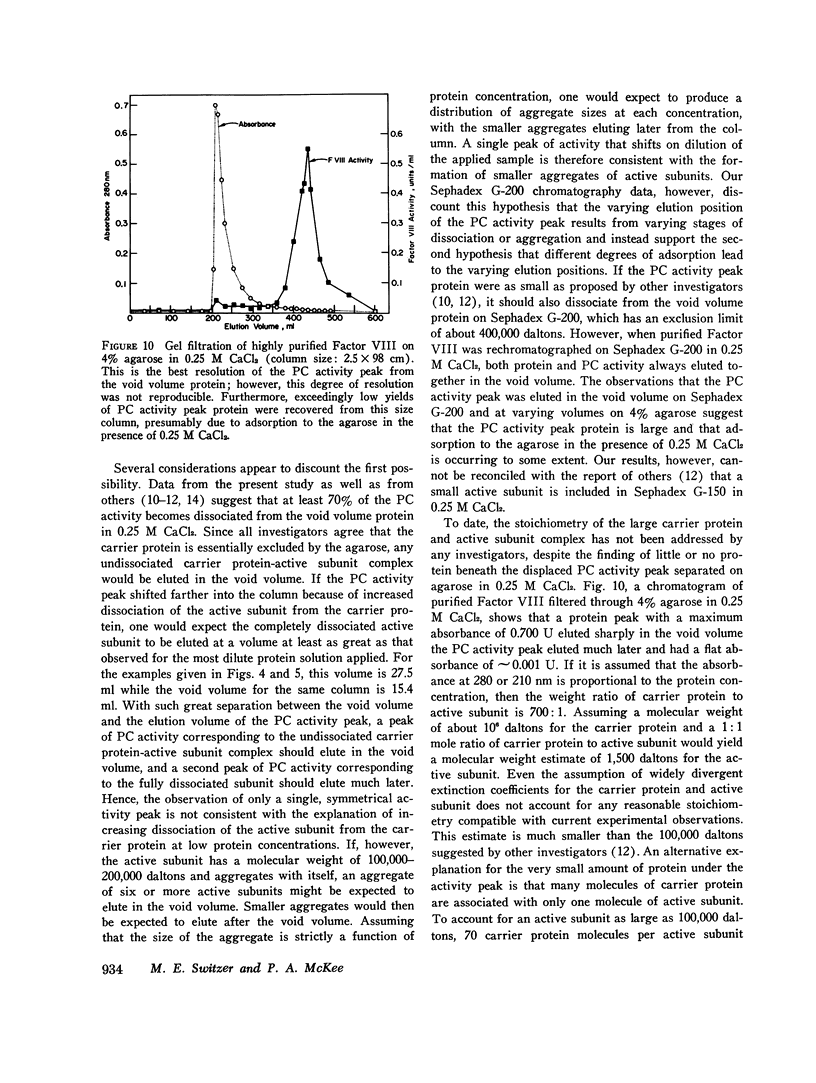
When purified antihemophilic factor (Factor VIII) was rechromatographed on 4% agarose in 0.15 M NaCl or 1.0 M NaCl, a single protein peak, containing both procoagulant activity and von Willebrand factor activity, as defined by ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation, was eluted in the void volume. Purified Factor VIII immediately lost about 30% of its procoagulant activity when dissolved in 0.25 M CaCl2, and when rechromatographed on 4% agarose in 0.25 M CaCl2, the protein peak and von Willebrand factor activity remained coincident in the void volume; however, most of the remaining procoagulant activity was eluted after the void volume. The elution position of Factor VIII procoagulant activity from 4% agarose in 0.25 M CaCl2, and hence its apparent molecular weight, varied with the protein concentration applied to the column; at low protein concentrations it was eluted close to the inner volume. Yet on Sephadex G-200 in 0.25 M CaCl2, the protein and procoagulant activity were eluted together in the void volume. These observations suggested that the Factor VIII procoagulant activity was not eluting according to size or shape, but was adsorbing to some extent to the agarose. Isolated activity peak material from the 0.25 M CaCl2 columns contained protein and had a typical ultraviolet spectrum. Even at high concentrations, the protein contained no thrombin, Factors IX, X, or Xa activity, or detectable phospholipid. In addition to Factor VIII procoagulant activity, which could be inactivated by a human antibody to Factor VIII, the activity peak protein also contained von Willebrand factor activity. Like native Factor VIII and the void volume protein, the activity peak contained protein that did not enter a sodium dodecyl sulfate 5% polyacrylamide gel in the absence of reducing reagent. After reduction of disulfide bonds, several subunits ranging from 195,000 to 30,000 daltons were observed. These results indicate that the protein in the shifted Factor VIII procoagulant activity peak is large and that its anomalous elution pattern from 4% agarose in 0.25 M CaCl2 results from interaction with the agarose. The Factor VIII-like properties of the activity peak protein and its electrophoretic pattern on sodium dodecyl sulfate gels suggest that it is a species of Factor VIII modified by proteolytic cleavage. These results allow an interpretation that is different from the recently proposed "carrier protein-small active subunit" hypotheses for the structure-function relationships of the Factor VIII molecule.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett B., Forman W. B., Ratnoff O. D. Studies on the nature of antihemophilic factor (factor VIII). Further evidence relating the AHF-like antigens in normal and hemophilic plasmas. J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2191–2197. doi: 10.1172/JCI107404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouma B. N., Wiegerinck Y., Sixma J. J., Van Mourik J. A., Mochtar I. A. Immunological characterization of purified anti-haemophilic factor A (factor VIII) which corrects abnormal platelet retention in Von Willebrand's disease. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 29;236(65):104–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio236104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. A., Griggs T. R., Wagner R. H. Factor VIII recombination after dissociation by CaCl12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2326–2329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. A., Wagner R. H. The defect in hemophilic and von Willebrand's disease plasmas studied by a recombination technique. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1093–1099. doi: 10.1172/JCI107853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs T. R., Cooper H. A., Webster W. P., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Plasma aggregating factor (bovine) for human platelets: a marker for study of antihemophilic and von Willebrand Factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2814–2818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershgold E. J., Davison A. M., Janszen M. E. Isolation and some chemical properties of human factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Feb;77(2):185–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass L., Ratnoff O. D., Leon M. A. Studies on the purification of antihemophilic factor (factor 8. I. Precipitation of antihemophilic factor by concanavalin A. J Clin Invest. 1969 Feb;48(2):351–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI105991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legaz M. E., Schmer G., Counts R. B., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of human Factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3946–3955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi S. L., Shulman N. R., Gralnick H. R. Studies on the purification and characterization of human factor 8. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2151–2161. doi: 10.1172/JCI107022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee P. A., Andersen J. C., Switzer M. E. Molecular structural studies of human factor VIII. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jan 20;240:8–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb53319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D., Jenkins C. S., Dreyfus M., Larrieu M. J. Letter: Experimental model for von Willebrand's disease. Nature. 1973 Jun 1;243(5405):293–294. doi: 10.1038/243293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J., Johnson A. J., Karpatkin M. H., Puszkin S. Methods for the production of clinically effective intermediate- and high-purity factor-VIII concentrates. Br J Haematol. 1971 Jul;21(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb03413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Wagner R. H. Antihemophilic factor: separation of an active fragment following dissociation by salts or detergents. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Jul 31;27(3):502–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Kass L., Lang P. D. Studies on the purification of antihemophilic factor (factor VIII). II. Separation of partially purified antihemophilic factor by gel filtration of plasma. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):957–962. doi: 10.1172/JCI106055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick M. E., Hoyer L. W. Activation of low molecular weight fragment of antihaemophilic factor (factor VIII) by thrombin. Nature. 1974 Nov 29;252(5482):404–405. doi: 10.1038/252404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick M. E., Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). V. Immunologic properties of AHF subunits produced by salt dissociation. Blood. 1973 Nov;42(5):737–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarji K. E., Stratton R. D., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Nature of von Willebrand factor: a new assay and a specific inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2937–2941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro G. A., Andersen J. C., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. The subunit structure of normal and hemophilic factor VIII. J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2198–2210. doi: 10.1172/JCI107405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther P. J., Steinman H. M., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. Activation of human plasminogen by urokinase. Partial characterization of a pre-activation peptide. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1173–1181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Hoyer I. W. Von Willebrand factor: dissociation from antihemophilic factor procoagulant activity. Science. 1973 Dec 14;182(4117):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4117.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Hoyer L. W., Rickles F. R., Varma A., Rogers J. Quantitative assay of a plasma factor deficient in von Willebrand's disease that is necessary for platelet aggregation. Relationship to factor VIII procoagulant activity and antigen content. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2708–2716. doi: 10.1172/JCI107465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Phillips L. L., Rosner W. Separation of sub-units of antihemophilic factor (AHF) by agarose gel chromatography. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Apr 30;27(2):212–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Rogers J., Brand H. Defective ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation in von Willebrand's disease and its correction by factor VIII. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2697–2707. doi: 10.1172/JCI107464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]