Abstract
Obese-hyperglycemic (ob/ob) mice have the interesting feature of being hyperinsulinemic, thus having some characteristics in common with human maturity-onset diabetics. As the cause of hyperinsulinemia in these mice is not established, and as the liver is known to play a role in determining the amount of hormone that reaches the periphery, it was hypothesized that an anomaly in the hepatic handling of insulin might prevail in obese-hyperglycemic mice. Immunoreactive insulin was therefore measured in the perfusate before and after a single passage through perfused livers of lean and ob/ob mice, permitting. It was found that the removal of insulin by livers of lean mice increased with increasing concentrations of the hormone in the portal vein. The removal process had a limited capacity, however, and as a consequence the percentage of hormone removed by the liver actually decreased when portal insulin concentrations increased. Insulin removal by livers of ob/ob mice had qualitatively the same characteristics but was considerably less efficient than in normal livers. Due to this, more insulin was found in the perfusate leaving the liver of ob/9b mice than in that of controls, at any insulin concentration tested. These observations suggest that in obese-hyperglycemic mice more of the hormone may reach the periphery and thus contribute to hyperinsulinemia. The present study further suggests that the anomaly of insulin removal observed in perfused livers of ob/ob mice might be secondary to hyperinsulinemia, since it was partly corrected upon artificially decreasing the circulating levels of insulin (e.g. via a fast, anti-insulin serum, or streptozotocin treatment) before perfusion. The characteristics of hepatic insulin removal reported in this study, as well as the differences observed between livers of lean and ob/ob mice, may reflect changes in membrane insulin receptors and/or in processes responsible for the degradation of the horomone.
Full text
PDF

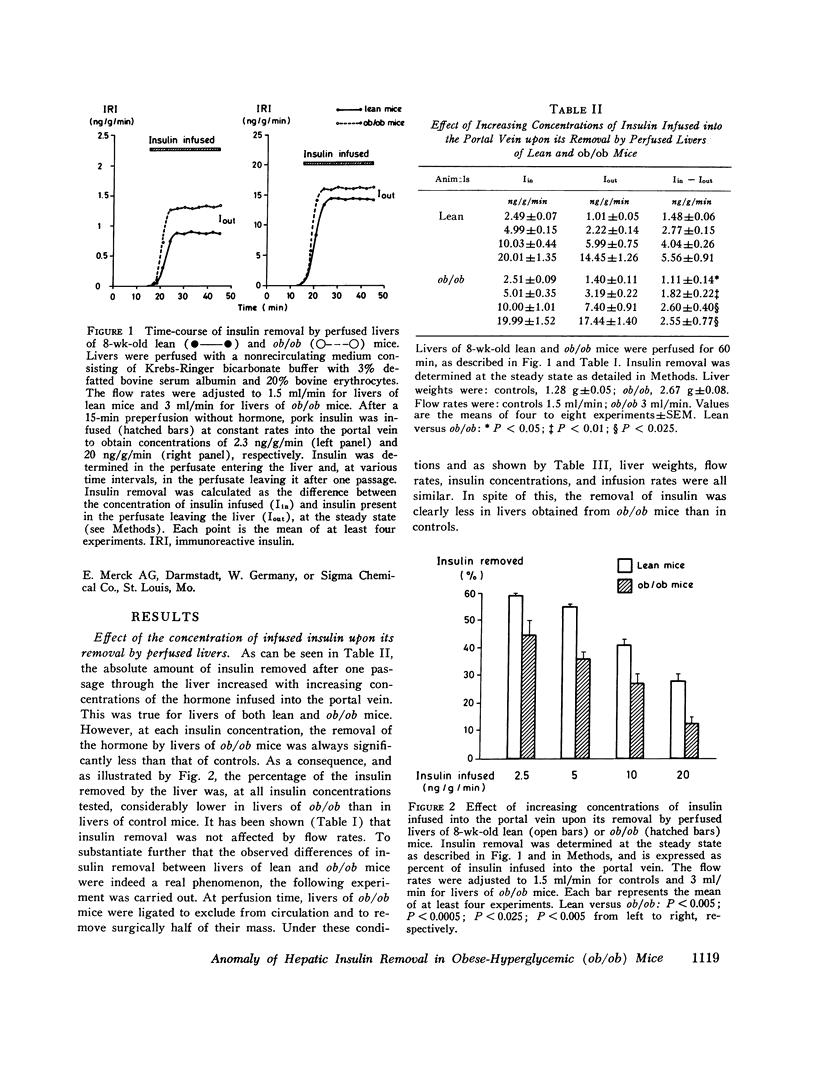
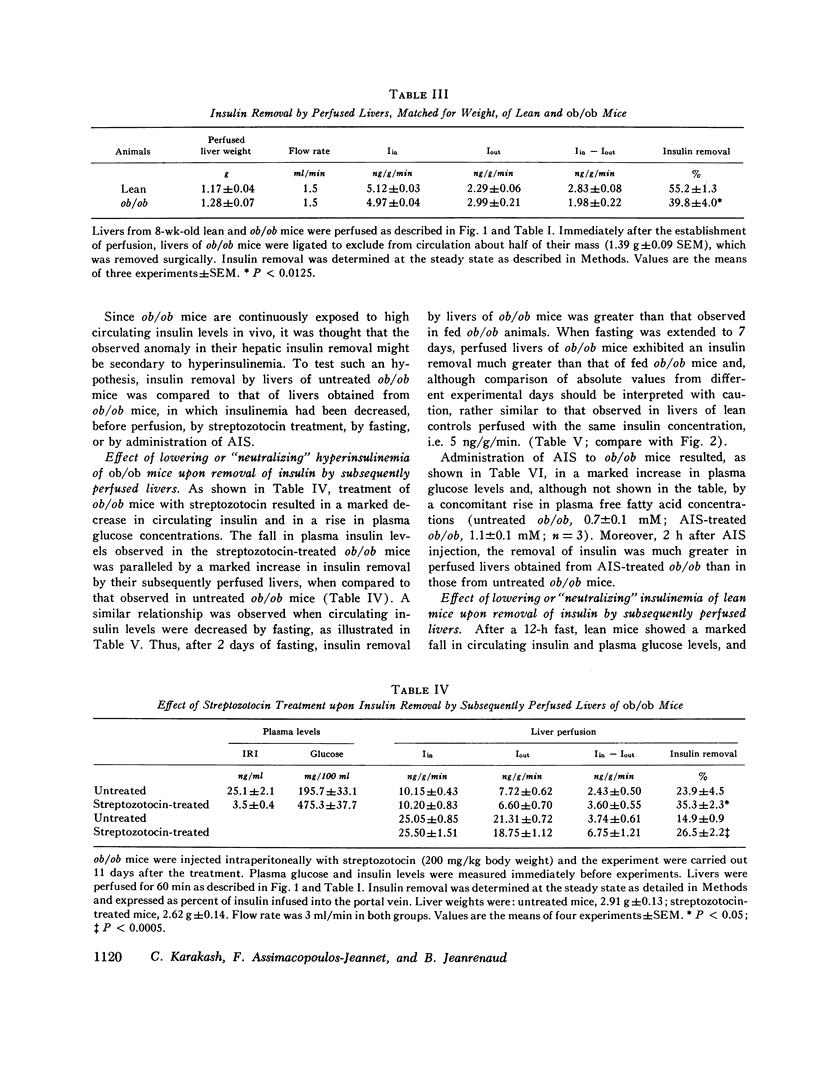
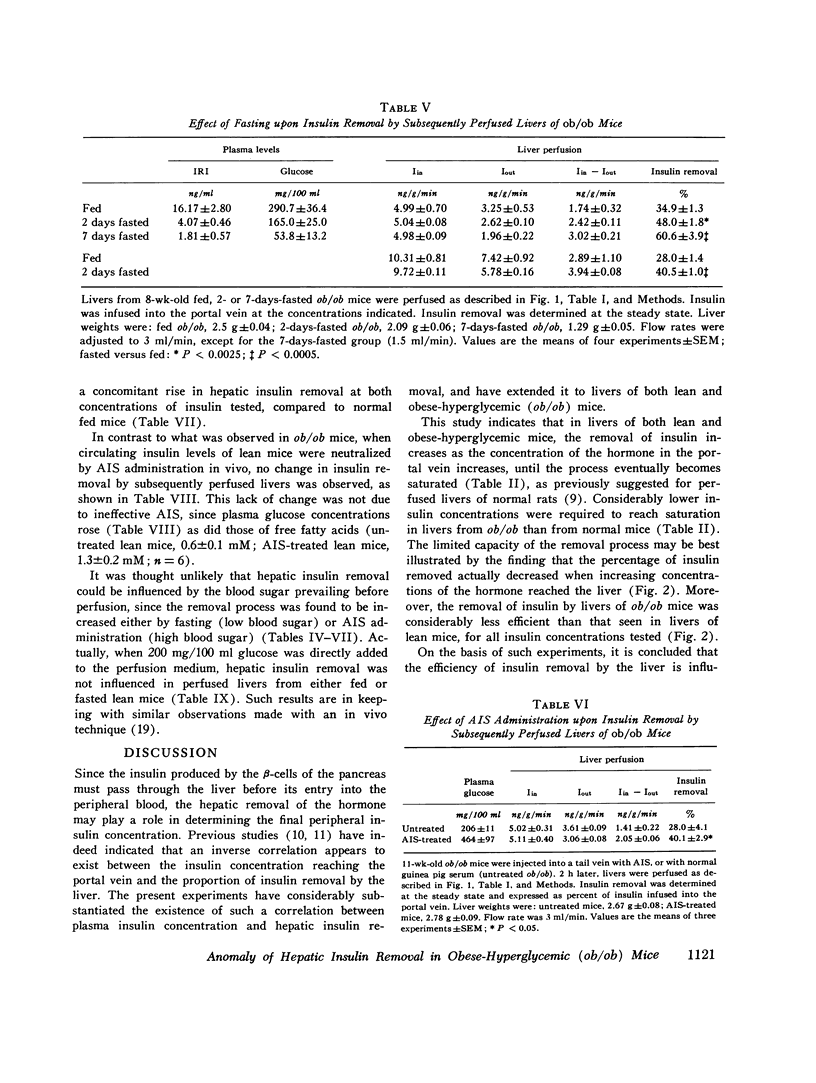
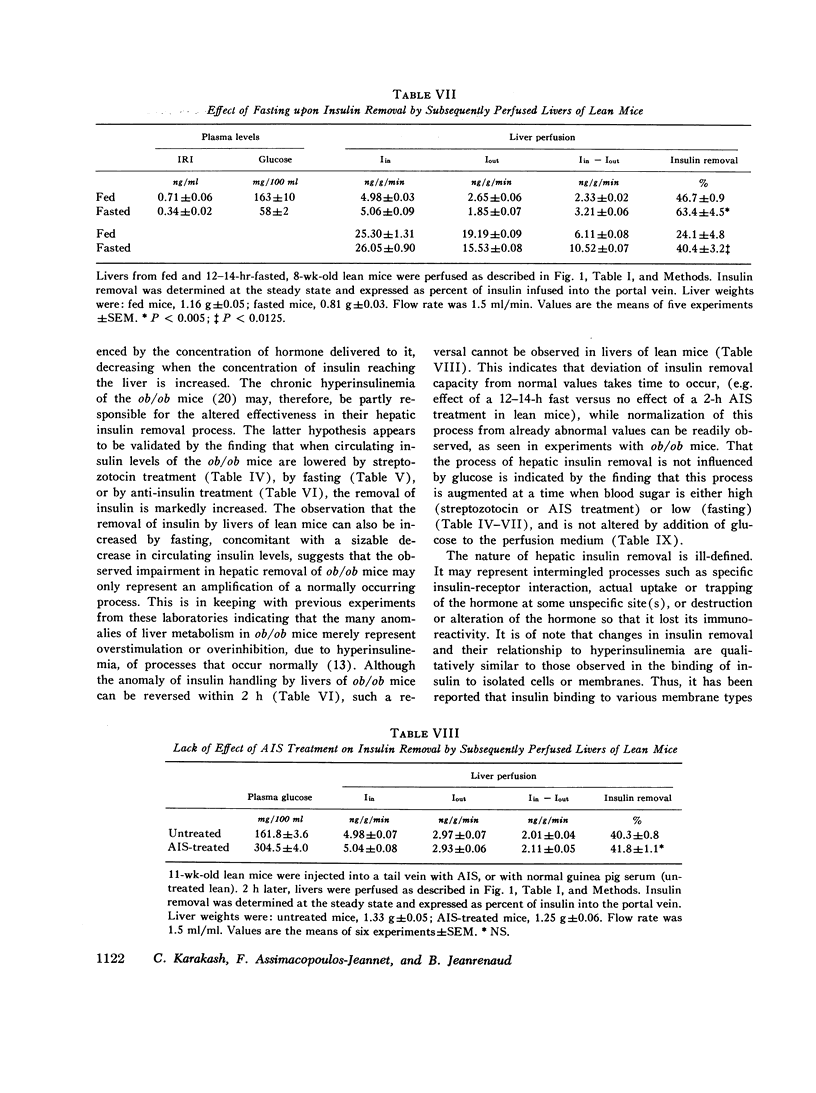


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F., Singh A., Le Marchand Y., Loten E. G., Jeanrenaud B. Abnormalities in lipogenesis and triglyceride secretion by perfused livers of obese-hyperglycaemic (ob-ob) mice: relationship with hyperinsulinaemia. Diabetologia. 1974 Apr;10(2):155–162. doi: 10.1007/BF01219673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Laudat M. H., Laudat P., Rosselin G., Kahn C. R., Gorden P., Roth J. Impairment of insulin binding to the fat cell plasma membrane in the obese hyperglycemic mouse. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P. Recent studies on insulin-receptor interactions. Isr J Med Sci. 1975 Jul;11(7):679–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoff S. N., Weich N. L., Antoniades H. N. Production of nonimmunoassayable insulin-like material by perfused rat liver. Diabetes. 1970 May;19(5):296–301. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.5.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaden M., Harding P., Field J. B. Effect of intraduodenal glucose administration on hepatic extraction of insulin in the anesthetized dog. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):2016–2028. doi: 10.1172/JCI107386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Gorden P., Freychet P., Roth J. Insulin receptor defect in insulin resistance: studies in the obese-hyperglycimic mouse. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90354-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin-receptor interaction in the obese-hyperglycemic mouse. A model of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loten E. G., Rabinovitch A., Jeanrenaud B. In vivo studies on lipogenesis in obese hyperglycaemic (ob-ob) mice: possible role of hyperinsulinaemia. Diabetologia. 1974 Feb;10(1):45–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00421413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTIMORE G. E., TIETZE F. Studies on the mechanism of capture and degradation of insulin-1131 by the cyclically perfused rat liver. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:329–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarroll A. M., Buchanan K. D. Insulin clearance by the isolated perfused livers of insulin deficient rats. Diabetologia. 1973 Dec;9(6):457–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00461688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondon C. E., Olefsky J. M., Dolkas C. B., Reaven G. M. Removal of insulin by perfused rat liver: effect of concentration. Metabolism. 1975 Feb;24(2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Batchelder T., Colome S., Reaven G. M. Effect of intravenous glucose infusion on plasma insulin removal rate. Metabolism. 1974 Jun;23(6):543–548. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soli A. H., Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin receptor deficiency in genetic and acquired obesity. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):769–780. doi: 10.1172/JCI108155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon S. S., Fenster L. F., Ensinck J. W., Williams R. H. Clearance studies of insulin and nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) in the rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):166–169. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffacher W., Orci L., Cameron D. P., Burr I. M., Renold A. E. Spontaneous hyperglycemia and-or obesity in laboratory rodents: an example of the possible usefulness of animal disease models with both genetic and environmental components. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1971;27:41–95. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571127-2.50026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll R. W., Touber J. L., Menahan L. A., Williams R. H. Clearance of porcine insulin, proinsulin, and connecting peptide by the isolated rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Mar;133(3):894–896. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell W. R., Sussman K. E. Plasma insulin after diversion of portal and pancreatic venous blood to vena cava. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Apr;22(4):808–812. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.4.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westman S. Development of the obese-hyperglycaemic syndrome in mice. Diabetologia. 1968 Jun;4(3):141–149. doi: 10.1007/BF01219435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



