Abstract
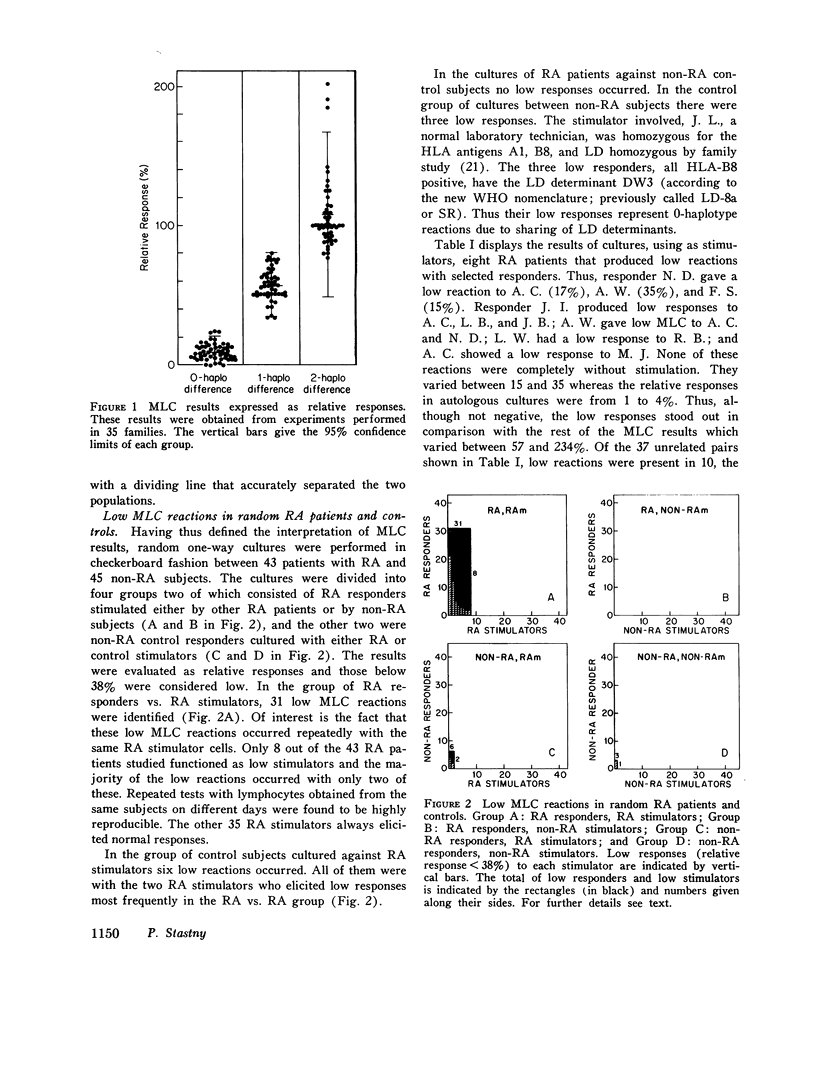
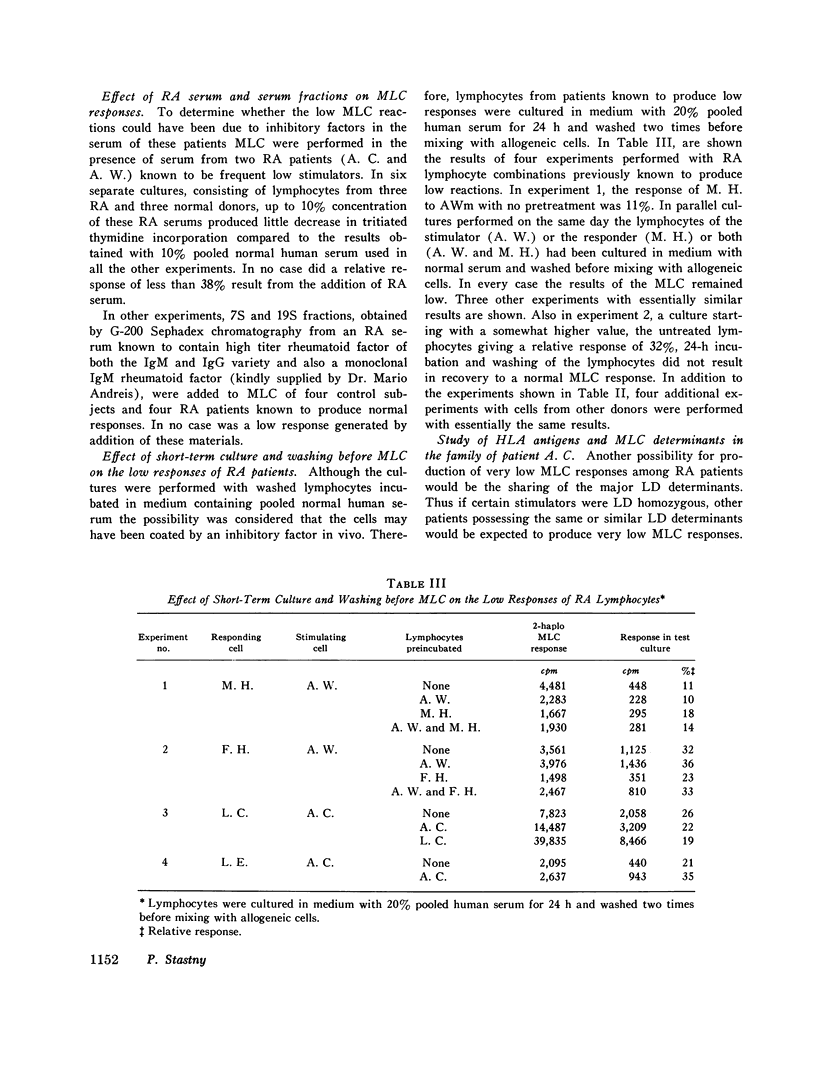
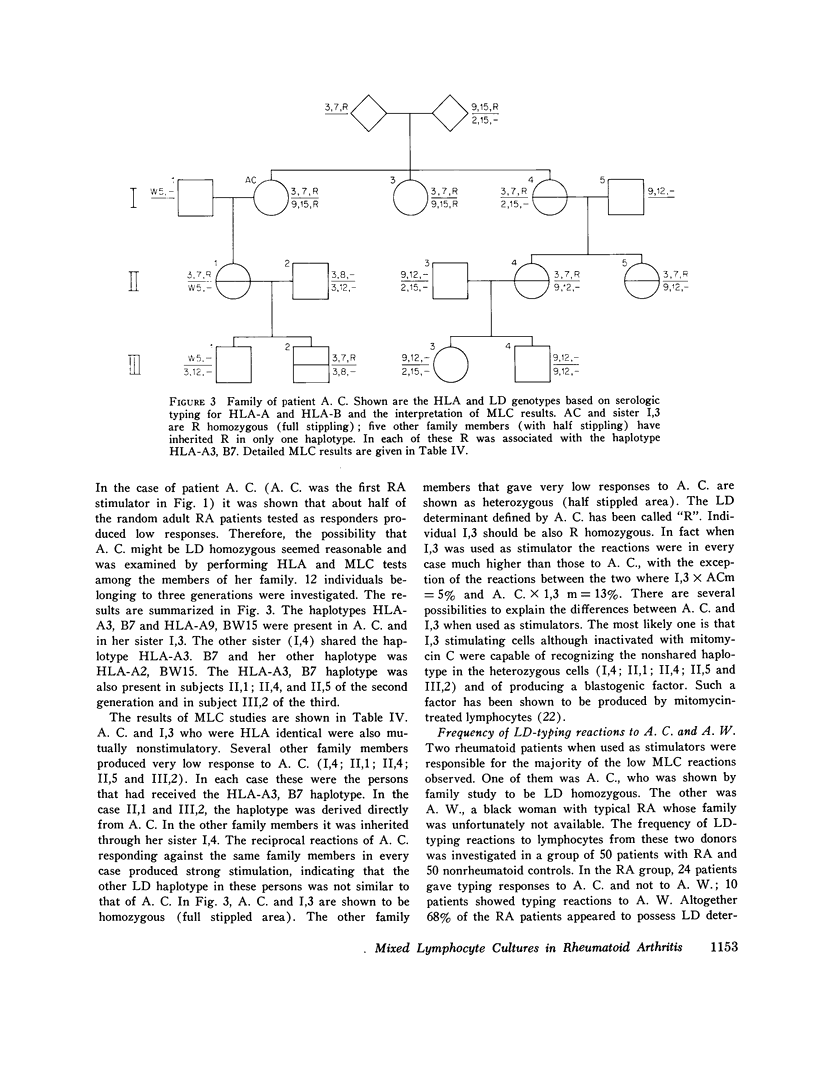
Random one-way microtiter mixed lymphocyte cultures between 43 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and 45 controls consisting of 26 normal subjects and 19 miscellaneous non-RA patients were performed and results were evaluated as relative responses. Low responses (consisting of relative response less than 38%) were found in 31 out of 43 RA patients in cultures against eight of the RA stimulators. The remaining 35 RA stimulators tested yielded only normal mixed lymphocyte culture reactions. The same RA patients used as responders never produced low responses when stimulated by non-RA lymphocytes. But six of the control subjects gave low responses to two RA stimulators. The low responses did not appear to correlate with intake of aspirin, prednisolone, or gold salts, nor could they be reproduced by addition of RA serum of 7S or 19S fractions thereof containing either polyclonal or monoclonal rheumatoid factors. Short-term culture and washing before mixing with the allogeneic cells did not change the low responses suggesting that in vivo bound autoantibodies against lymphocyte receptors were not involved. Study of the inheritance of HLA and mixed lymphocyte culture determinants in the family of patient A. C. who most frequently elicited low responses indicated she was homozygous for a lymphocyte-defined determinant which has been called R. The low responses to A. C. could be interpreted as typing responses based on sharing of the same or of a similar lymphocyte-defined determinant. This gene appears to be increased in patients with RA with respect to non-RA controls and may reflect an association of genes within the HLA chromosomal region leading to predisposition for the development of RA.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astorga G. P., Williams R. C., Jr Altered reactivity in mixed lymphocyte culture of lymphocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1969 Dec;12(6):547–554. doi: 10.1002/art.1780120602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrams J., Kuwert E., Liedtke U. HL-A antigens and multiple sclerosis. Tissue Antigens. 1972;2(5):405–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1972.tb00060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner A. I., Scheinberg M. A., Cathcart E. S. Surface characteristics of synovial fluid and peripheral blood lymphocytes in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Jul-Aug;18(4):297–303. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crout J. E., Hepburn B., Ritts R. E., Jr Suppression of lymphocyte transformation after aspirin ingestion. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jan 30;292(5):221–223. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197501302920501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont B., Good R. A., Hansen G. S., Jersild C., Nielsen L. S., Park B. H., Svejgaard A., Thomsen M., Yunis E. J. Two separate genes controlling stimulation in mixed lymphocyte reaction in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):52–56. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont B., Jersild C., Hansen G. S., Nielsen L. S., Thomsen M., Svejgaard A. Typing for MLC determinants by means of LD-homozygous and LD-heterozygous test cells. Transplant Proc. 1973 Dec;5(4):1543–1549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eijsvoogel V. P., de Groot-Kooy L., Huismans L., van Rood J. J., van Leeuwen A., DuToit E. D. Mixed lymphocyte culture and HL-A. Transplant Proc. 1972 Jun;4(2):199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froland S. S., Natvig J. B., Husby G. Immunological characterization of lymphocytes in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(1):67–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu S. M., Stern R., Kunkel H. G., Dupont B., Hansen J. A., Day N. K., Good R. A., Jersild C., Fotino M. Mixed lymphocyte culture determinants and C2 deficiency: LD-7a associated with C2 deficiency in four families. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):495–506. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M. Effect of steroids on lysosomes. Transplant Proc. 1975 Mar;7(1):21–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzman R. J., Bach M. L., Bach F. H., Thurman G. B., Sell K. W. Precipitation of radioactively labeled samples: a semi-automatic multiple-sample processor. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jun;4(2):182–186. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedberg H., Källén B., Löw B., Nilsson O. Impaired mixed leucocyte reaction in some different diseases, notably multiple sclerosis and various arthritides. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Aug;9(2):201–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg H., Rankin B., Thorsby E. Production of blastogenic factor by mitomycin-treated cells in mixed lymphocyte cultures. Transplantation. 1974 Mar;17(3):323–325. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197403000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jersild C., Fog T., Hansen G. S., Thomsen M., Svejgaard A., Dupont B. Histocompatibility determinants in multiple sclerosis, with special reference to clinical course. Lancet. 1973 Dec 1;2(7840):1221–1225. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90970-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jersild C., Svejgaard A., Fog T. HL-A antigens and multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 1972 Jun 3;1(7762):1240–1241. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90962-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen F., Lamm L. U., Kissmeyer-Nielsen F. Mixed lymphocyte cultures with inbred individuals: an approach to MLC typing. Tissue Antigens. 1973;3(4):323–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1973.tb01010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Benacerraf B. The function and interrelationships of T-cell receptors, Ir genes and other histocompatibility gene products. Transplant Rev. 1975;22:175–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb01559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lies R. B., Messner R. P., Troup G. M. Histocompatibility antigens and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Sep-Oct;15(5):524–529. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O., Benacerraf B. Genetic control of specific immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:31–74. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. K., Mickey M. R., Singal D. P., Terasaki P. I. Serotyping for homotransplantation. 18. Refinement of microdroplet lymphocyte cytotoxicity test. Transplantation. 1968 Nov;6(8):913–927. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196811000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito S., Namerow N., Mickey M. R., Terasaki P. I. Multiple sclerosis: association with HL-A3. Tissue Antigens. 1972;2(1):1–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1972.tb00111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien W. M. The genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Dec;2(Suppl):785–802. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opelz G., Terasaki P. I., Hirata A. A. Suppression of lymphocyte transformation by aspirin. Lancet. 1973 Sep 1;2(7827):478–480. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlosstein L., Terasaki P. I., Bluestone R., Pearson C. M. High association of an HL-A antigen, W27, with ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 5;288(14):704–706. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304052881403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seignalet J., Clot J., Sany J., Serre H. HL-A antigens in rheumatoid arthritis. Vox Sang. 1972;23(5):468–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1972.tb03839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. D., Sachs C., Ziff M. In vitro synthesis of immunoglobulin by rheumatoid synovial membrane. J Clin Invest. 1968 Mar;47(3):624–632. doi: 10.1172/JCI105758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P., Rosenthal M., Andreis M., Ziff M. Lymphokines in the rheumatoid joint. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 May-Jun;18(3):237–243. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P. Tissue typing antisera from immunization by pregnancy. Tissue Antigens. 1972;2(2):123–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1972.tb00126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Winfield J. B., Siegal F., Wernet P., Bentwich Z., Kunkel H. G. Analyses of lymphocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Occurrence of interfering cold-reactive antilymphocyte antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1082–1092. doi: 10.1172/JCI107852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis E. J., Plate J. M., Ward F. E., Seigler H. F., Amos D. B. Anomalous MLR responsiveness among siblings. Transplant Proc. 1971 Mar;3(1):118–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff M. Relation of cellular infiltration of rheumatoid synovial membrane to its immune response. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 May-Jun;17(3):313–319. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Tweel J. G., van Oud Alblas A. B., Keuning J. J., Goulmy E., Termijtelen A., Bach M. L., van Rood J. J. Typing for MLC (LD). I. Lymphocytes from cousin-marriage offspring as typing cells. Transplant Proc. 1973 Dec;5(4):1535–1538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




