Abstract
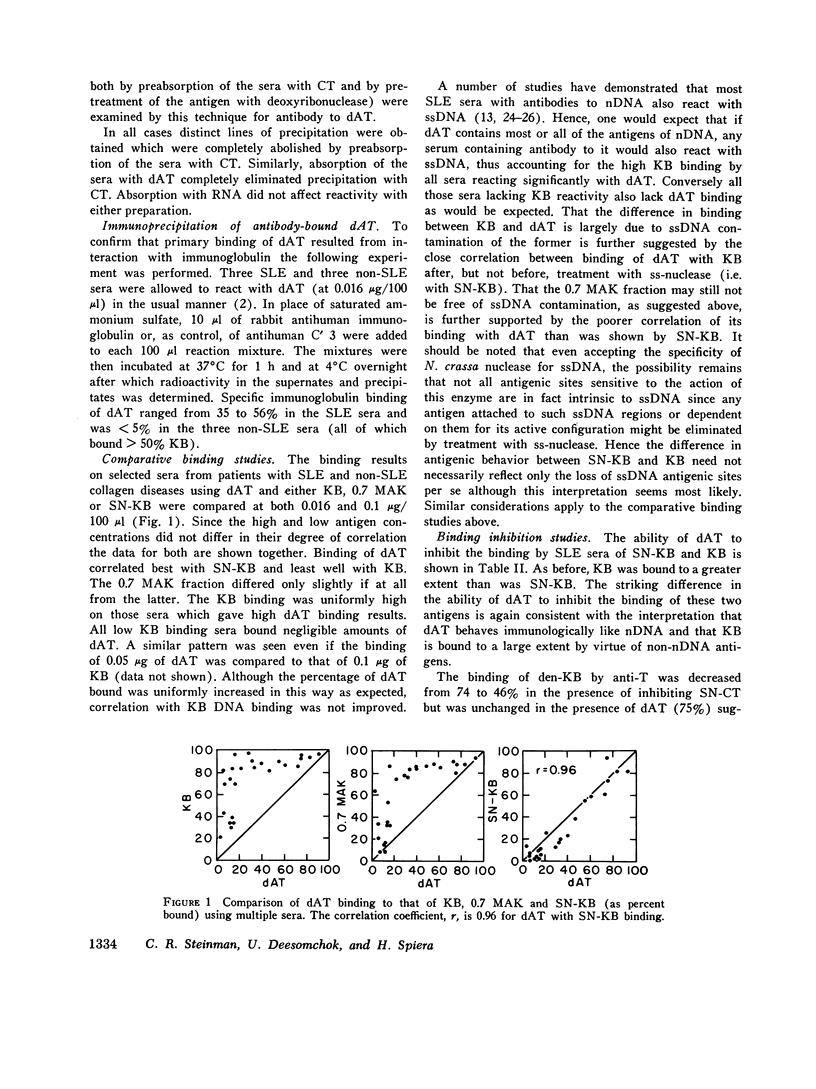
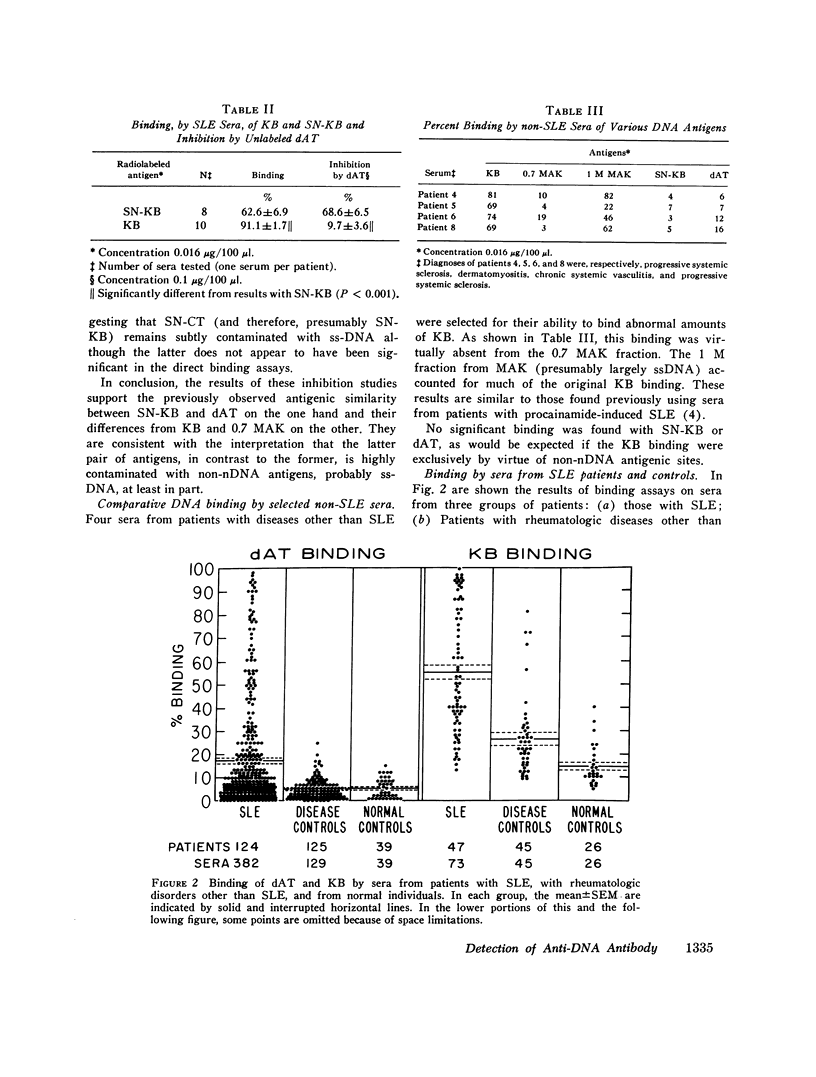
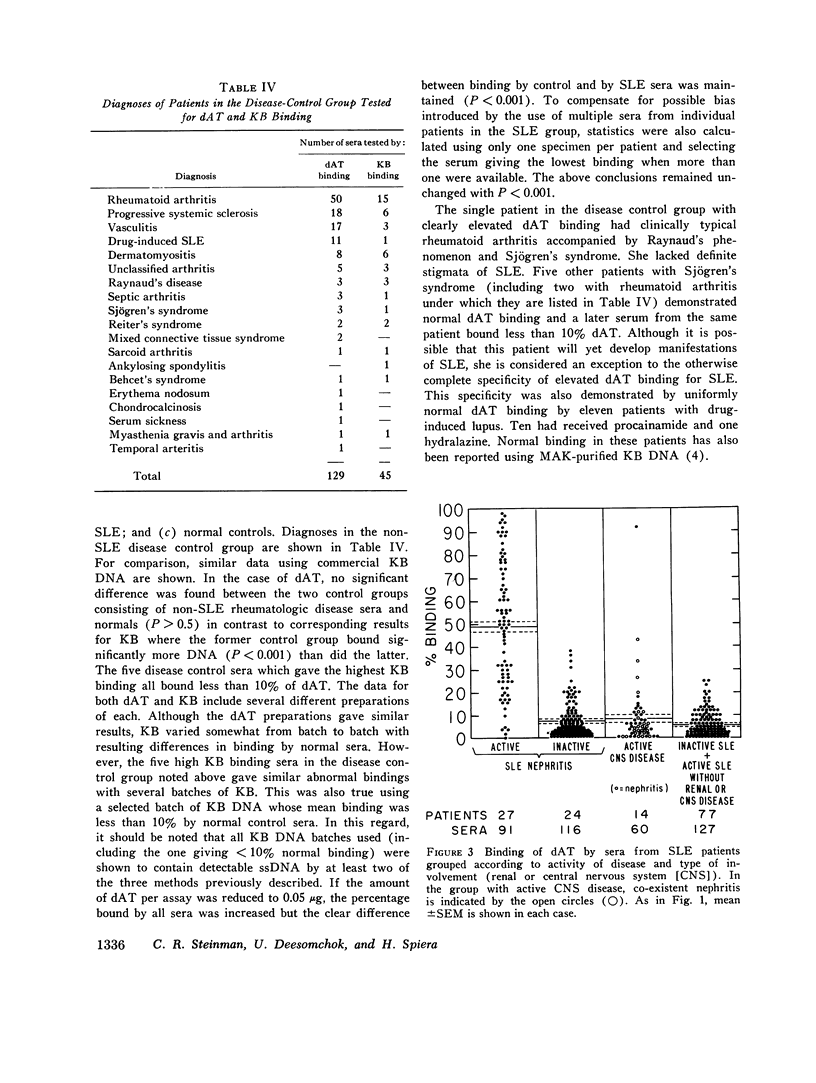
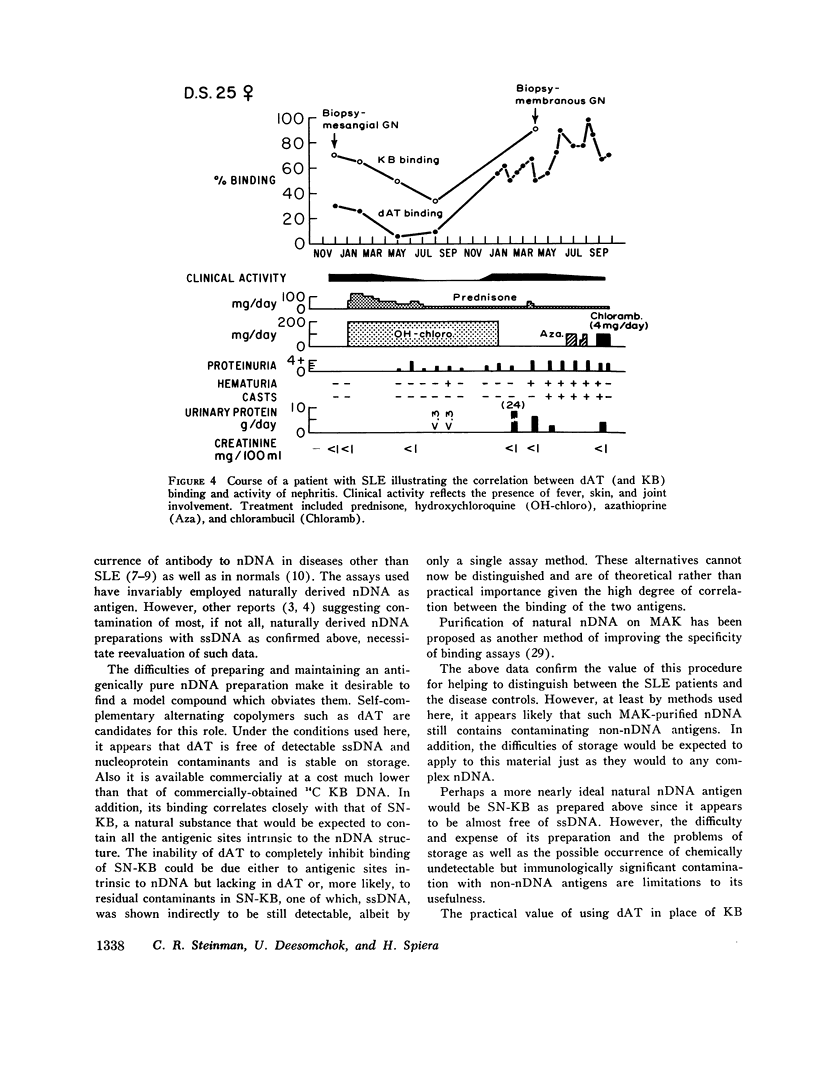
Virtually all preparations of DNA used to detect antibody to native DNA (nDNA) by binding assays have been found to be subtly contaminated by single stranded DNA. Because recent DNA binding data have directly challenged the unique role previously attributed to these antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), resolution of the consequent ambiguity is of theoretical and practical importance. It is proposed that a synthetic nDNA molecule (dAT) might circumvent this difficulty by being antigenically equivalent to nDNA while, on theoretical grounds, lacking significant contamination with single stranded DNA or other cellular antigens. These expectations were generally confirmed by biochemical and immunological analyses. In clinical studies, sera from 124 pateints with SLE and from controls were examined for their ability to bind dAT. In contrast to results with KB binding, patients with non-SLE rheumatologic disorders were indistinguishable from normals by dAT binding. dAT binding was elevated in 85% of sera from SLE patients with clinically-judged active nephritis but in only 9% of those with inactive renal disease. Active non-renal disease, including cerebritis, was not associated with increased dAT binding. Individual non-lupus sera which bound increased amounts of KB DNA, failed to bind dAT. It is suggested that such binding resulted from contaminating non-nDNA antigens. When elevated, dAT binding, like KB binding, varied with disease activity and might thus be useful as a parameter thereof. In several patients elevated dAT binding led to the finding, on biopsy, of clinically silent, active, diffuse proliferative nephritis. It is concluded that use of synthetic nDNA antigens such as dAT may offer theoretical and practical advantages over naturally-derived preparations in detecting anti-nDNA, both clinically and for investigational purposes. Also, caution is urged in interpreting DNA binding data derived from incompletely characterized systems, particularly with regard to the occurrence of anti-nDNA antibodies in serum.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arana R., Seligmann M. Antibodies to native and denatured deoxyribonucleic acid in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1867–1882. doi: 10.1172/JCI105677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hukins D. W., Smith P. J., Watts L. Structural details of double-helix observed for DNAs containing alternating purine and pyrimidine sequences. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90499-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm S. P., Hoch S. O., Hoch J. A. DNA-binding proteins in human serum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Mar 3;63(1):24–31. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. A., Hughes G. R., Noel G. L., Christian C. L. Character of anti-DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Apr;8(4):551–561. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. L., Jr, Davis J. S., 4th Detection of circulating DNA by counterimmunoelectrophoresis (CIE). Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Jan-Feb;16(1):52–58. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. V., Tan M., Easterbrook M. Serum antibody to double-stranded RNA and DNA in patients with idiopathic and secondary uveitis. N Engl J Med. 1971 Dec 30;285(27):1502–1506. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197112302852703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIDUSCHEK E. P. On the factors controlling the reversibility of DNA denaturation. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:467–487. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grishman E., Porush J. G., Lee S. L., Churg J. Renal biopsies in lupus nephritis. Correlation of electron microscopic findings with clinical course. Nephron. 1973;10(1):25–36. doi: 10.1159/000180175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERSHEY A. D., GOLDBERG E., BURGI E., INGRAHAM L. Local denaturation of DNA by shearing forces and by heat. J Mol Biol. 1963 Mar;6:230–243. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Sharp G. C., Irvin W. S., Kantor O. S., Gardner C. A., Bagby M. K., Perry H. M., Jr, Osterland C. K. Immune responses to hydralazine and nuclear antigens in hydralazine-induced lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Mar;76(3):365–374. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-3-365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbacher P., LeRoy E. C. Serum DNA binding activity in healthy subjects and in rheumatic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jan-Feb;17(1):63–71. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes G. R., Cohen S. A., Christian C. L. Anti-DNA activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. A diagnostic and therapeutic guide. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 May;30(3):259–264. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Carr R., Agnello V., Thoburn R., Kunkel H. G. Antibodies to polynucleotides in human sera: antigenic specificity and relation to disease. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):294–312. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubinski H., Javid M. Proteins from human cerebrospinal fluid: binding with nucleic acids. Science. 1973 Oct 19;182(4109):296–297. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4109.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINN S., LEHMAN I. R. AN ENDONUCLEASE FROM NEUROSPORA CRASSA SPECIFIC FOR POLYNUCLEOTIDES LACKING AN ORDERED STRUCTURE. I. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE ENZYME. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1287–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Schur P. H., Rose J. A., Decker J. L., Talal N. Measurement of serum DNA-binding activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 25;281(13):701–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909252811304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyeritz R. E., Schlegel R. A., Thomas C. A., Jr Hydrodynamic shear breakage of DNA may produce single-chained terminals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 31;272(4):504–509. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90505-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochmis P. G., Palefsky H., Becker M., Roth H., Zvaifler N. J. Native DNA binding in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Jul;33(4):357–360. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.4.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizès G. A nuclease from Neurospora crassa specific for d(A-T) rich regions in double stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Mar;1(3):443–453. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHACHMAN H. K., ADLER J., RADDING C. M., LEHMAN I. R., KORNBERG A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. VII. Synthesis of a polymer of deoxyadenylate and deoxythymidylate. J Biol Chem. 1960 Nov;235:3242–3249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samaha R. J., Irvin W. S. Deoxyribonucleic acid strandedness. Partial characterization of the antigenic regions binding antibodies in lupus erythematosus serum. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):446–457. doi: 10.1172/JCI108111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Natali P. G. Comparative study of antibodies to native and denatured DNA. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):902–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Schur P. H., Carr R. I., Kunkel H. G. Deoxybonucleic acid (DNA) and antibodies to DNA in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1732–1740. doi: 10.1172/JCI105479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoburn R., Hurvitz A. I., Kunkel H. G. A DNA-binding protein in the serum of certain mammalian species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3327–3330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utiyama H., Doty P. Kinetic studies of denaturation and reaction with formaldehyde on polydeoxyribonucleotides. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 30;10(7):1254–1264. doi: 10.1021/bi00783a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VONHIPPEL P. H., FELSENFELD G. MICROCOCCAL NUCLEASE AS A PROBE OF DNA CONFORMATION. Biochemistry. 1964 Jan;3:27–39. doi: 10.1021/bi00889a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold R. T., Young F. E., Tan E. M., Farr R. S. Deoxyribonucleic acid antibody: a method to detect its primary interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid. Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):806–807. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



