Abstract
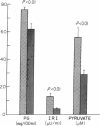
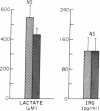
Arterial blood concentrations of insulin, glucagon, and various substrates were determined in six anephric subjects in the postabsorptive state and immediately after hemodialysis. Plasma glucose and serum insulin concentrations were normal, and declined during dialysis. Plasma glucagon was elevated and remained unchanged. There was moderate hypertriglyceridemia before dialysis, but this decreased significantly after administration of heparin just before the start of dialysis, and at the end of dialysis was lowered further into the normal range. Comparison of postabsorptive whole blood concentrations of amino acids with those in normal, healthy adults revealed striking differences. Glutamine, proline, citrulline, glycine and both 1- and 3-methyl-histidines were increased, while serine, glutamate, tyrosine, lysine, and branched-chain amino acids were decreased. The glycine/serine ratio was elevated to 300% and tyrosine/phenylalanine ratio was lowered to 60% of normal. To investigate the potential role of blood cells in amino acid transport, the distribution of individual amino acids in plasma and blood cell compartments was studied. Despite a markedly diminished blood cell mass (mean hematocrit, 20.6 +/- 1.4%), there was no significant decrease in the fraction of most amino acids present in the cell compartment, and this was explained by increases of several amino acids in cellular water. None were decreased. Furthermore, during dialysis, whole blood and plasma amino acids declined by approximately 30% and 40%, respectively, whereas no significant change was observed in the cell compartment. Alanine was the only amino acid whose concentration declined in the cells as well as in plasma. The results indicate (a) significant alterations in the concentrations of hormones and substrates in patients on chronic, intermittent hemodialysis; (b) removal of amino acids during hemodialysis, predominantly from the plasma compartment, with no significant change in cell content; and (c) a redistribution of amino acids in plasma and blood cell compartments with increased gradients of most of the amino acids per unit cell water, by mechanism(s) as yet undetermined.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addae S. K., Lotspeich W. D. Glutamine balance in metabolic acidosis as studied with the artificial kidney. Am J Physiol. 1968 Aug;215(2):278–281. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.2.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki T. T., Brennan M. F., Müller W. A., Cahill G. F., Jr Amino acid levels across normal forearm muscle: whole blood vs. plasma. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1974;12:157–165. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(74)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki T. T., Muller W. A., Brennan M. F., Cahill G. F., Jr Blood cell and plasma amino acid levels across forearm muscle during a protein meal. Diabetes. 1973 Oct;22(10):768–775. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.10.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviram A., Peters J. H., Gulyassy P. F. Dialysance of amino acids and related substances. Nephron. 1971;8(5):440–454. doi: 10.1159/000179948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade J. D., Porte D., Jr, Bierman E. L. Hypertriglyceridemia. A metabolic consequence of chronic renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jul 25;279(4):181–185. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196807252790403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilbrey G. L., Faloona G. R., White M. G., Knochel J. P. Hyperglucagonemia of renal failure. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):841–847. doi: 10.1172/JCI107624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Aoki T. T. Renal gluconeogenesis and amino-acid metabolism in man. Med Clin North Am. 1975 May;59(3):751–761. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condon J. R., Asatoor A. M. Amino acid metabolism in uraemic patients. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 May;32(3):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90433-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramp D. G., Moorhead J. F., Wills M. R. Disorders of blood-lipids in renal disease. Lancet. 1975 Mar 22;1(7908):672–673. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91770-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Andres R., Edgar P., Walker W. G. Carbohydrate metabolism in uremia: a review. Medicine (Baltimore) 1973 Sep;52(5):469–481. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197309000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwyn D. H., Launder W. J., Parikh H. C., Wise E. M., Jr Roles of plasma and erythrocytes in interorgan transport of amino acids in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1972 May;222(5):1333–1342. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.5.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P. The glucose-alanine cycle. Metabolism. 1973 Feb;22(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J., Räf L. Evidence of inter-organ amino-acid transport by blood cells in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1775–1779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber A. J., Bier D. M., Cryer P. E., Pagliara A. S. Hypoglycemia in compensated chronic renal insufficiency. Substrate limitation of gluconeogenesis. Diabetes. 1974 Dec;23(12):982–986. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.12.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginn H. E., Frost A., Lacy W. W. Nitrogen balance in hemodialysis patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 1968 May;21(5):385–393. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/21.5.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyassy P. F., Aviram A., Peters J. H. Evaluation of amino acid and protein requirements in chronic uremia. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Nov;126(5):855–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyassy P. F., Peters J. H., Lin S. C., Ryan P. M. Hemodialysis and plasma amino acid composition in chronic renal failure. Am J Clin Nutr. 1968 Jun;21(6):565–573. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/21.6.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman R. A., Shalhoub R. J., Wade A. D., O'Connell J. M., Recant L. Hypertriglyceridemia in chronic nonnephrotic renal failure. Am J Clin Nutr. 1973 Feb;26(2):165–172. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/26.2.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held E., Winkelmann W., Finke K., von Dehn H., Seyffart G., Gurland H. J. Plasma-aminosäuren bei chronischer Niereninsuffizienz. Klin Wochenschr. 1974 Oct 15;52(20):948–978. doi: 10.1007/BF01468657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopple J. D., Swendseid M. E., Shinaberger J. H., Umezawa C. Y. The free and bound amino acids removed by hemodialysis. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1973;19:309–313. doi: 10.1097/00002480-197301900-00052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letteri J. M., Scipione R. A. Phenylalanine metabolism in chronic renal failure. Nephron. 1974;13(5):365–371. doi: 10.1159/000180412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marliss E. B., Aoki T. T., Unger R. H., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Glucagon levels and metabolic effects in fasting man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2256–2270. doi: 10.1172/JCI106445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGale E. H., Pickford J. C., Aber G. M. Quantitative changes in plasma amino acids in patients with renal disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 May;38(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMenamy R. H., Lund C. C., Neville G. J., Wallach D. F. STUDIES OF UNBOUND AMINO ACID DISTRIBUTIONS IN PLASMA, ERYTHROCYTES, LEUKOCYTES AND URINE OF NORMAL HUMAN SUBJECTS. J Clin Invest. 1960 Nov;39(11):1675–1687. doi: 10.1172/JCI104191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikhail M. M., Waslien C. I., Gabr M. K., Mansour M. M. In vitro uptake of labeled amino acids by red blood cells of children with protein-calorie malnutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1975 Mar;28(3):233–237. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/28.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murase T., Cattran D. C., Rubenstein B., Steiner G. Inhibition of lipoprotein lipase by uremic plasma, a possible cause of hypertriglyceridemia. Metabolism. 1975 Nov;24(11):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWEN E. E., ROBINSON R. R. Amino acid extraction and ammonia metabolism by the human kidney during the prolonged administration of ammonium chloride. J Clin Invest. 1963 Feb;42:263–276. doi: 10.1172/JCI104713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padilla H., Sanchez A., Powell R. N., Umezawa C., Swendseid M. E., Prado P. M., Sigala R. Plasma amino acids in children from Guadalajara with kwashiorkor. Am J Clin Nutr. 1971 Mar;24(3):353–357. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/24.3.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. H., Gulyassy P. F., Lin S. C., Ryan P. M., Berridge B. J., Jr, Chao W. R., Cummings J. G. Amino acid patterns in uremia: comparative effects of hemodialysis and transplantation. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1968;14:405–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts R. F., Damian A. C., MacLeod M. B. Synthesis of serine by rat kidney in vivo and in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1970 Sep;219(3):584–589. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.3.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubini M. E., Gordon S. Individual plasma-free amino acids in uremics: effects of hemodialysis. Nephron. 1968;5(5):339–351. doi: 10.1159/000179644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B. Muscle amino acid metabolism and gluconeogenesis. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:245–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.001333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. R., Pozefsky T., Chhetri M. K. Nitrogen and amino acid metabolism in adults with protein-calorie malnutrition. Metabolism. 1974 Jul;23(7):603–618. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(74)80020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeldner J. S., Slone D. Critical variables in the radioimmunoassay of serum insulin using the double antibody technic. Diabetes. 1965 Dec;14(12):771–779. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.12.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourian A., Goddard J., Puck T. T. Phenylalanine hydroxylase activity in mammalian cells. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Apr;73(2):159–170. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040730210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Aguilar-Parada E., Müller W. A., Eisentraut A. M. Studies of pancreatic alpha cell function in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):837–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI106297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir G. C., Turner R. C., Martin D. B. Glucagon radioimmunoassay using antiserum 30K: interference by plasma. Horm Metab Res. 1973 Jul;5(4):241–244. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. D., Lowy C., Fraser T. R., Spitz I. M., Rubenstein A. H., Bersohn I. Serum-growth hormone and glucose intolerance in renal failure. Lancet. 1968 Oct 12;2(7572):798–801. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92456-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]