Abstract
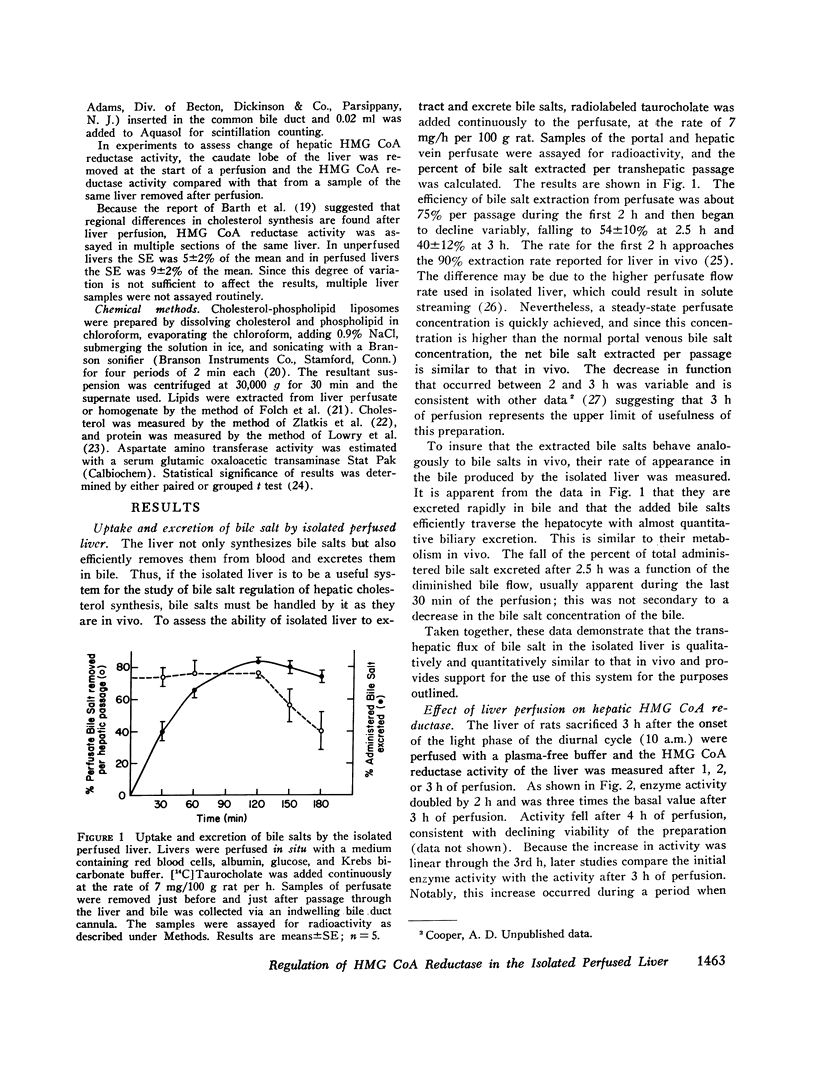
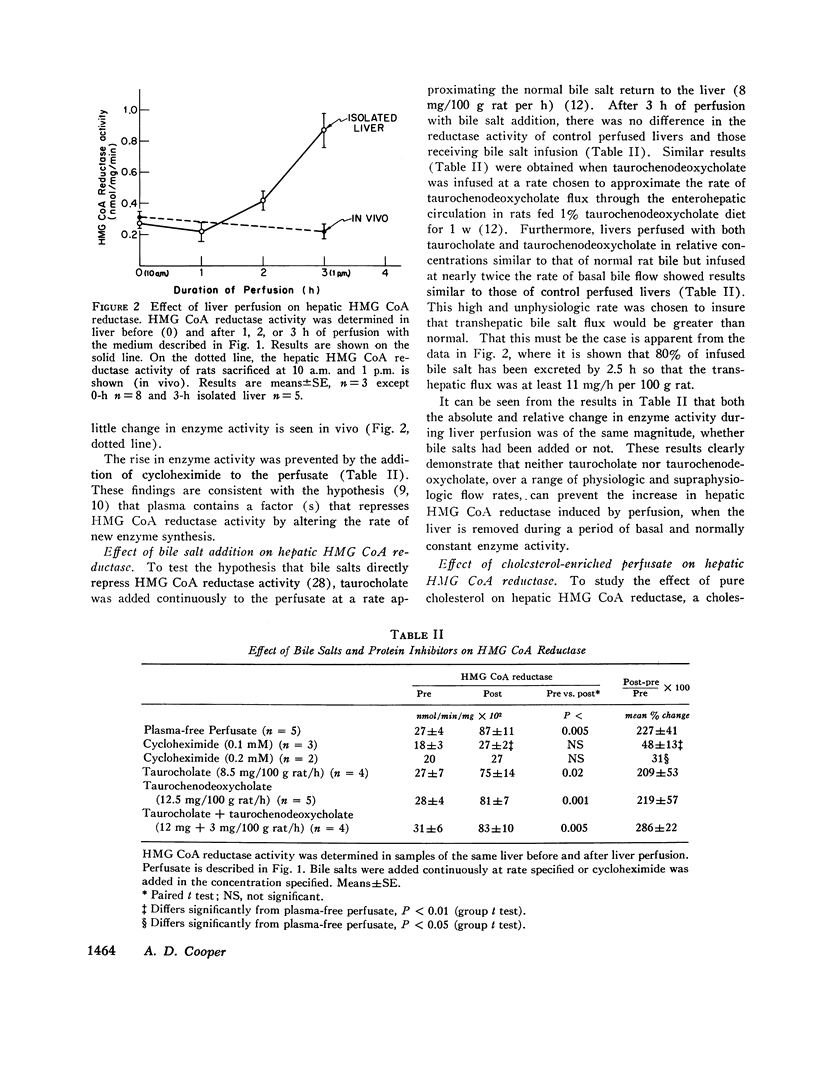
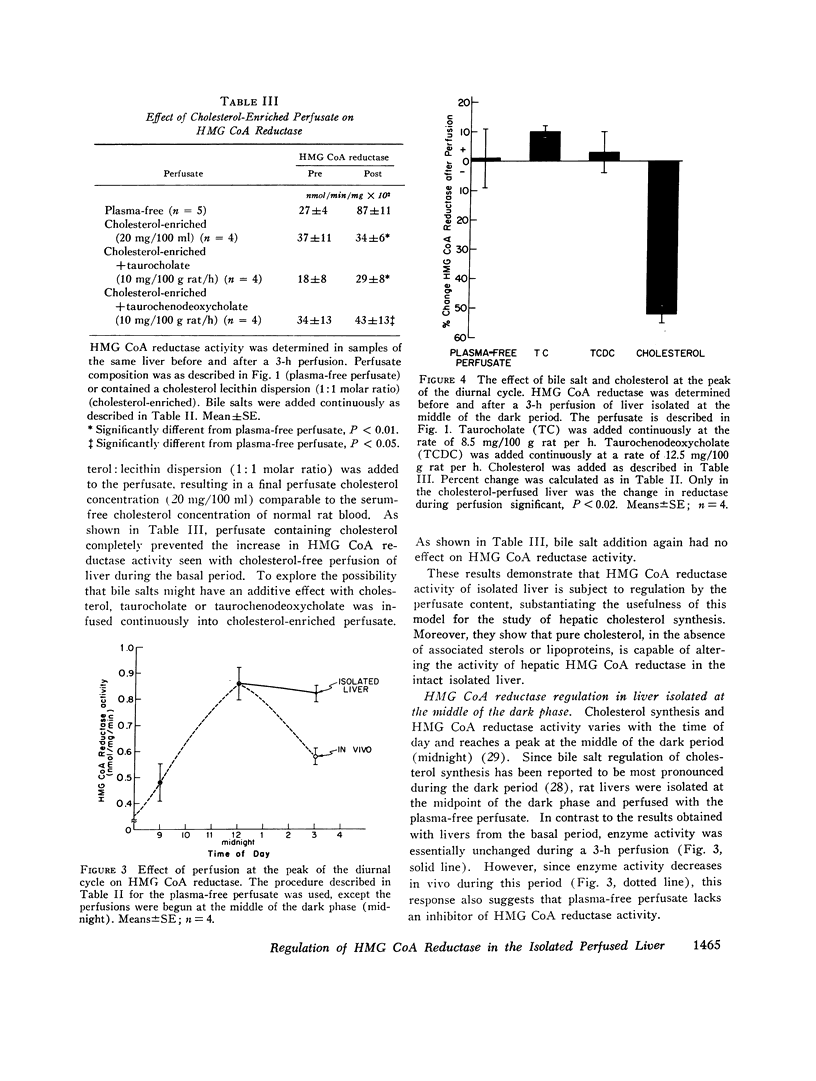
The effect of perfusion of an isolated rat liver on hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase was studied. In liver removed during the basal period of the diurnal cycle of enzyme activity, a 227 +/- 41% increase in enzyme activity occurred after 3 h of a plasma-free perfusion. This could be prevented by the addition of cycloheximide or pure cholesterol (dispersed with lecithin) to the perfusate. In contrast, the continuous addition of taurocholate or taurochenodeoxycholate, alone or in combination, at a variety of rates did not prevent the increase in enzyme activity. The added bile salts were efficiently extracted from the perfusate and excreted in the bile. The addition of these bile salts to a cholesterol-enriched perfusate did not alter the effect obtained with cholesterol alone. If the perfusate contained whole serum, the increase induced by perfusion in the basal period was smaller (88 +/- 27%) than with plasma-free perfusate. Again, the major bile salts of the rat failed to prevent the increase in enzyme activity induced by liver perfusion. If livers were removed and perfused at the height of the diurnal cycle of enzyme activity, the enzyme activity remained high (2 +/- 10% increase) rather than decreasing, as occurs in vivo. If cholesterol was added to these perfusions, a 52 +/- 4% decrease was induced. Bile salt addition induced no decrease. From the results it is concluded that the major bile salts are not direct regulators of hepatic cholesterol synthesis, but pure cholesterol, in the absence of bile salt or lipoprotein, is able to initiate the mechanism that represses hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEHER W. T., BAKER G. D. Effect of dietary bile acids on in vivo cholesterol metabolism in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Aug-Sep;98(4):892–894. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEHER W. T., BAKER G. D., PENNEY D. G. A comparative study of the effects of bile acids and cholesterol on cholesterol metabolism in the mouse, rat, hamster and guinea pig. J Nutr. 1963 Apr;79:523–530. doi: 10.1093/jn/79.4.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGSTROM S., DANIELSSON H. On the regulation of bile acid formation in the rat liver. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Jul 17;43(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back P., Hamprecht B., Lynen F. Regulation of cholesterol biosynthesis in rat liver: diurnal changes of activity and influence of bile acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Aug;133(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90482-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth C., Liersch M., Hackenschmidt J., Ullmann H., Decker K. Cholesterol biosynthesis in the isolated perfused rat liver. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Jul;353(7):1085–1093. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.2.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortz W. M. On the control of cholesterol synthesis. Metabolism. 1973 Dec;22(12):1507–1524. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Dana S. E., Goldstein J. L. Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity in cultured human fibroblasts. Comparison of cells from a normal subject and from a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):789–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow J. C., Higgins M. J., Rudney H. The inhibitory effect of ATP on HMGCoA reductase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 21;63(4):1077–1084. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90679-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D., Ockner R. K. Studies of hepatic cholesterol synthesis in experimental acute biliary obstruction. Gastroenterology. 1974 Apr;66(4):586–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Arner E. C., Wiley J. S., Shattil S. J. Modification of red cell membrane structure by cholesterol-rich lipid dispersions. A model for the primary spur cell defect. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):115–126. doi: 10.1172/JCI107901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Brown M. S. Effect of alterations of the specific activity of the intracellular acetyl CoA pool on apparent rates of hepatic cholesterogenesis. J Lipid Res. 1974 Sep;15(5):508–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., McGarry J. D. Limitations of acetate as a substrate for measuring cholesterol synthesis in liver. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):52–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A. Effect of plasma lipoproteins and lecithin-cholesterol dispersions on the activity of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase of isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 21;409(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A., Gould R. G. Turnover rate of hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase as determined by use of cycloheximide. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1520–1524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. The perfused rat liver. Methods Enzymol. 1975;39:25–36. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)39006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORESKY C. A. INITIAL DISTRIBUTION AND RATE OF UPTAKE OF SULFOBROMOPHTHALEIN IN THE LIVER. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jul;207:13–26. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo-Torres H. E., Miller O. N., Hamilton J. G. A comparison of the effects of bile salts on the absorption of cholesterol from the intestine of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 29;176(3):605–615. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90227-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb S., Pitot H. C. Improved assay of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. J Lipid Res. 1971 Jul;12(4):512–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. G., Kojola V. B., Swyryd E. A. Effects of hypophysectomy, adrenalectomy, cholesterol feeding, and puromycin on the radiation-induced increase in hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis in rats. Radiat Res. 1970 Jan;41(1):57–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Berry M. N., Williams M. C., Severinghaus E. M. A simple and inexpensive membrane "lung" for small organ perfusion. J Lipid Res. 1974 Mar;15(2):182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamprecht B., Roscher R., Waltinger G., Nüssler C. Influence of bile acids on the activity of rat liver 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. 2. Effect of cholic acid in lymph fistula rats. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jan 1;18(1):15–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harry D. S., Dini M., McIntyre N. Effect of cholesterol feeding and biliary obstruction on hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 19;296(1):209–220. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M., Kawachi T., Rudney H. The mechanism of the diurnal variation of hepatic HMG-CoA reductase activity in the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 1;45(1):138–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M., Rudney H. Regulation of rat liver beta-hydroxy-beta-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase activity by cholesterol. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):60–61. doi: 10.1038/newbio246060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandutsch A. A., Chen H. W. Inhibition of sterol synthesis in cultured mouse cells by 7alpha-hydroxycholesterol, 7beta-hydroxycholesterol, and 7-ketocholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 25;248(24):8408–8417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandutsch A. A., Chen H. W. Inhibition of sterol synthesis in cultured mouse cells by cholesterol derivatives oxygenated in the side chain. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6057–6061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsten E. S., Watson J. A. Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in hepatoma tissue culture cells by serum lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6104–6109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liersch M. E., Barth C. A., Hackenschmidt H. J., Ullmann H. L., Decker K. F. Influence of bile salts on cholesterol synthesis in the isolated perfused rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 15;32(2):365–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C. The demonstration and solubilization of beta-hydroxy-beta-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase from rat liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):984–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTIMORE G. E. Effect of insulin on potassium transfer in isolated rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jun;200:1315–1319. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.6.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara D. J., Rodwell V. W. Regulation of hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. In vitro inhibition by a protein present in bile. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):378–385. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nervi F. O., Weis H. J., Dietschy J. M. The kinetic characteristics of inhibition of hepatic cholesterogenesis by lipoproteins of intestinal origin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4145–4151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Máille E. R., Richards T. G., Short A. H. The influence of conjugation of cholic acid on its uptake and secretion: hepatic extraction of taurocholate and cholate in the dog. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(2):337–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope J. L. Crystallization of sodium taurocholate. J Lipid Res. 1967 Mar;8(2):146–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarfordt S. H., Goodman D. S. Metabolism of doubly-labeled chylomicron cholesteryl esters in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1967 May;8(3):264–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raicht R. F., Cohen B. I., Mosbach E. H. Effects of sodium taurochenodeoxycholate and sodium taurocholate on cholesterol absorption in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1974 Dec;67(6):1155–1161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G. Formation of cholesteryl ester-rich particulate lipid during metabolism of chylomicrons. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):465–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI106255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Hauser S., Lapar V., Mosbach E. H. Regulatory effects of sterols and bile acids on hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase and cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1973 Sep;14(5):573–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siperstein M. D., Fagan V. M. Feedback control of mevalonate synthesis by dietary cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):602–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis H. J., Dietschy J. M. Failure of bile acids to control hepatic cholesterogenesis: evidence for endogenous cholesterol feedback. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2398–2408. doi: 10.1172/JCI106206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler H. O., King K. K. Biliary excretion of lecithin and cholesterol in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1337–1350. doi: 10.1172/JCI106930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. D. The role of bile acids in the overall regulation of steroid metabolism. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Oct;130(4):493–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Spaeth A. E. Perfusion in situ with tritium oxide to measure hepatic lipogenesis and lipid secretion. Normal and orotic acid-fed rats. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jun 25;241(12):2891–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZLATKIS A., ZAK B., BOYLE A. J. A new method for the direct determination of serum cholesterol. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Mar;41(3):486–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



