Abstract
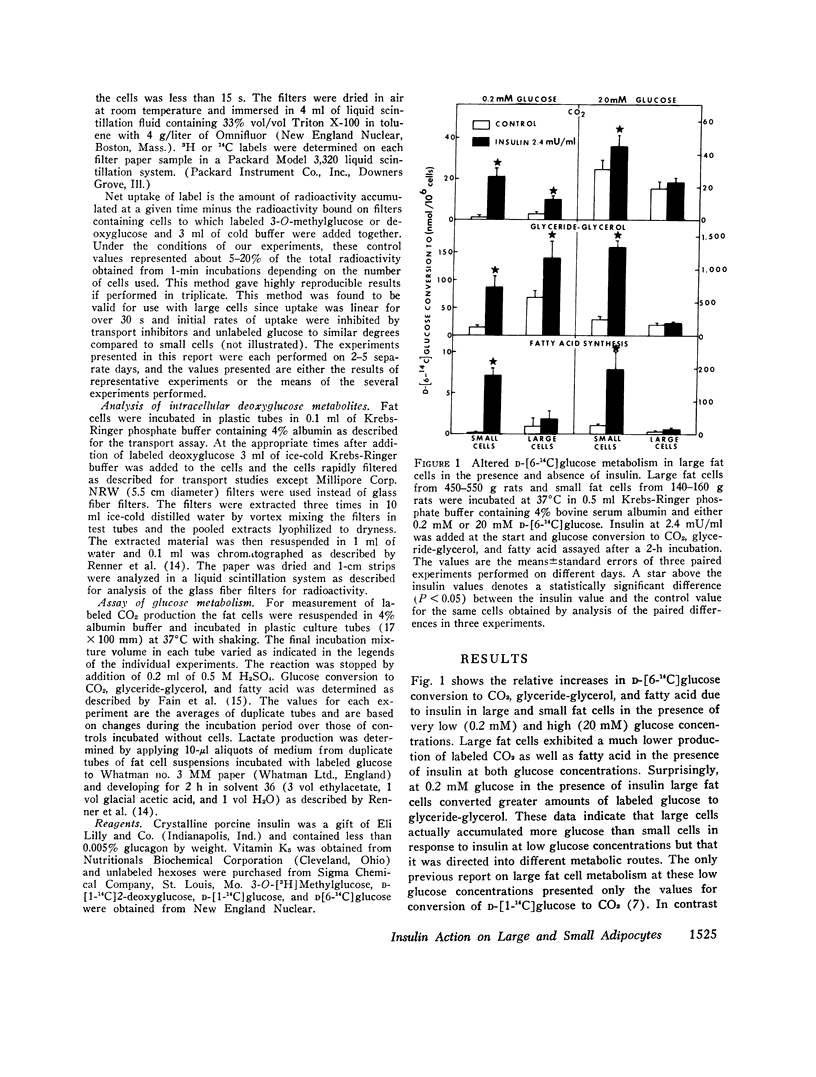
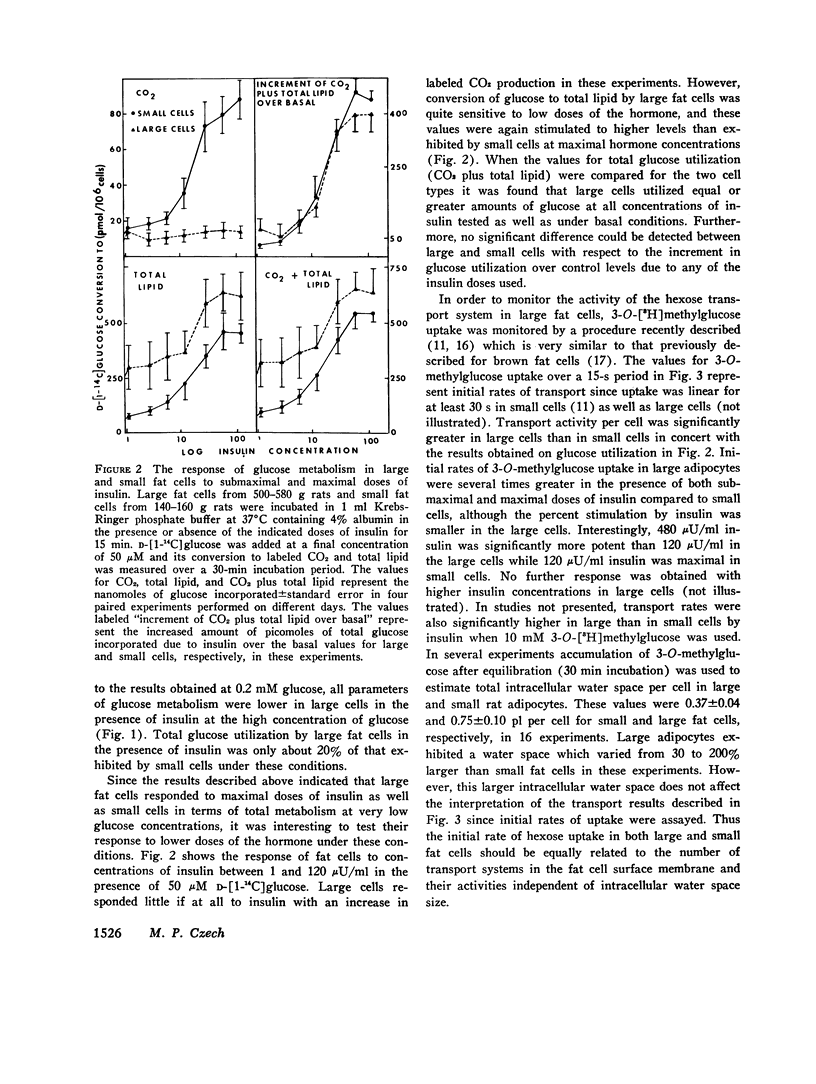
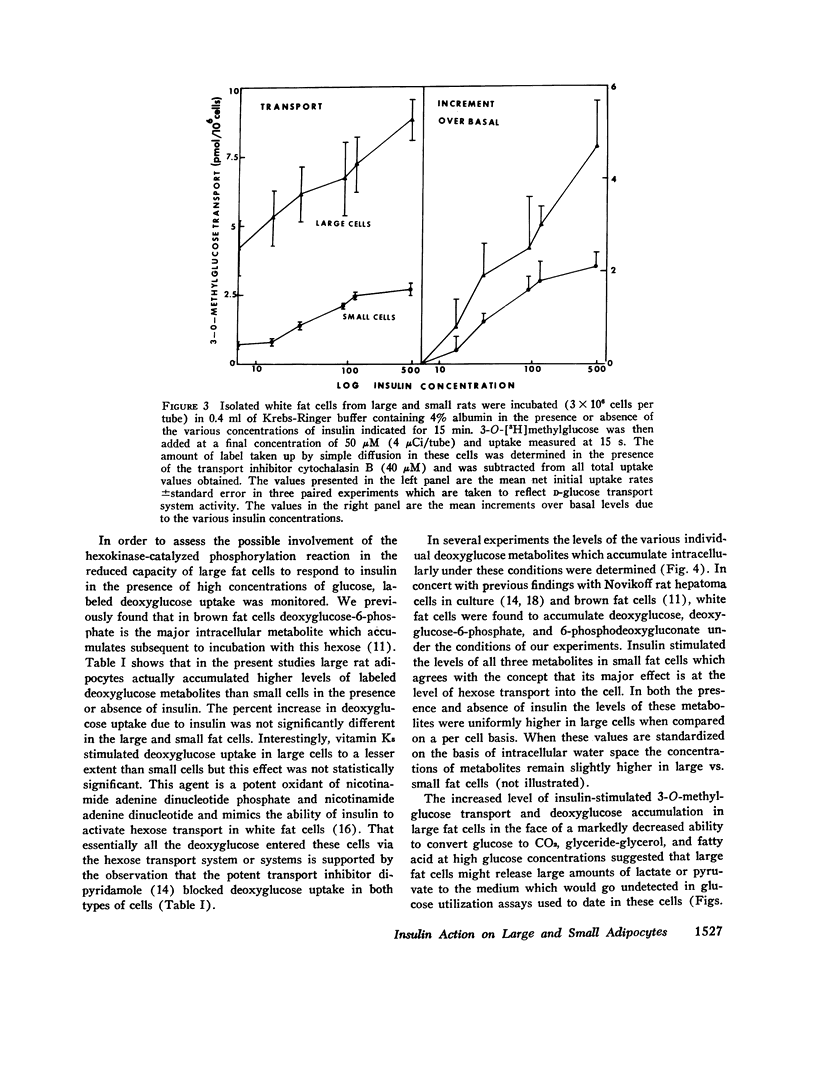
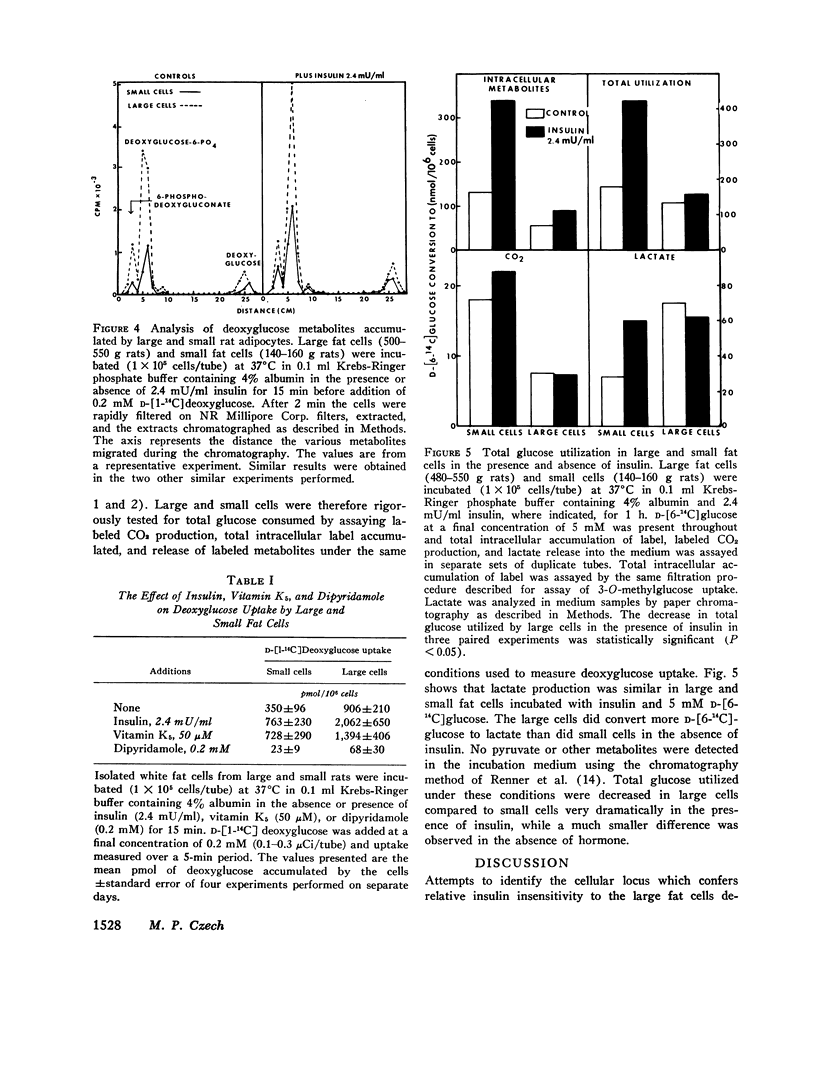
The marked stimulatory effect of insulin on the conversion of 20 mM D-[6-14C]glucose to CO2, glyceride-glycerol, and fatty acid observed in small rat adipocytes was greatly diminished in large cells from older rats. Similarly, total glucose utilization as estimated by summing the total metabolites accumulated intracellularly plus the release of labeled CO2 and lactate was substantially lower in large cells in the presence of insulin and 5 mM labeled glucose. However, under conditions of 0.2 mM medium glucose where transport of the hexose into adipocytes is relatively more rate-limiting for subsequent metabolism, large cells actually utilized slightly greater total amounts of glucose than small cells in the presence of insulin. Increments of total glucose utilization due to both submaximal and maximal doses of insulin were similar in large and small cells incubated with a low glucose concentration. Under these conditions, conversion of labeled glucose to CO2 and fatty acid in response to insulin was somewhat diminished in large cells, while conversion to glyceride-glycerol was enhanced. The activity of the D-glucose transport system in large and small cells was estimated by monitoring initial rates and small cells was estimated by monitoring initial rates of 3-O-[3H]methylglucose uptake by a rapid filtration method. Transport system activity on a per cell basis was actually severalfold higher in large adipocytes in the basal state as well as in the presence of submaximal and maximal concentrations of insulin compared to small cells. However, the percent stimulation by insulin was less in the large cells. Uptake of 2-deoxyglucose under basal conditions and in response to insulin was also higher in large cells compared to small cells. Analysis of the accumulated label in extracts from fat cells incubated with D-[14C]deoxyglucose revealed the presence of free deoxyglucose, deoxyglucose-6-phosphate, and 6-phosphodeoxygluconate. The levels of these metabolites were significantly higher in large cells compared to small cells indicating hexokinase activity appears not to account for the defective glucose utilization in large cells at high glucose concentrations. It is concluded that (a) possible defects in insulin receptor components, the D-glucose transport system, and the coupling mechanism which links these entities do not significantly contribute to the apparent insulin-insensitivity of large fat cells and (b) the principal cellular defect which confers this blunted insulin response to large rat adipocytes involves one or more intracellular enzymes involved in glucose metabolism.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amatruda J. M., Livingston J. N., Lockwood D. H. Insulin receptor: role in the resistance of human obesity to insulin. Science. 1975 Apr 18;188(4185):264–266. doi: 10.1126/science.164059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer J. A., Gorden P., Roth J. Defect in insulin binding to receptors in obese man. Amelioration with calorie restriction. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):166–174. doi: 10.1172/JCI107907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. S., Kipnis D. M. Regulation of rat hexokinase isoenzymes. I. Assay and effect of age, fasting and refeeding. Diabetes. 1973 Dec;22(12):913–922. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.12.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A. Effect of diet and triiodothyronine on the activity of sn-glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and on the metabolism of glucose and pyruvate by adipose tissue of obese patients. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1413–1422. doi: 10.1172/JCI106107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L., Hummel K. P. Studies with the mutation, diabetes, in the mouse. Diabetologia. 1967 Apr;3(2):238–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01222201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Differential effects of sulfhydryl reagents on activation and deactivation of the fat cell hexose transport system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):1164–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Lawrence J. C., Jr, Lynn W. S. Hexose transport in isolated brown fat cells. A model system for investigating insulin action on membrane transport. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5421–5427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo M., Rudman D. Variations in glucose metabolism and sensitivity to insulin of the rat's adipose tissue, in relation to age and body weight. Endocrinology. 1968 Jun;82(6):1133–1141. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-6-1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGirolamo M., Howe M. D., Esposito J., Thurman L., Owens J. L. Metabolic patterns and insulin responsiveness of enlarging fat cells. J Lipid Res. 1974 Jul;15(4):332–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Reed N., Saperstein R. The isolation and metabolism of brown fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1887–1894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Laudat M. H., Laudat P., Rosselin G., Kahn C. R., Gorden P., Roth J. Impairment of insulin binding to the fat cell plasma membrane in the obese hyperglycemic mouse. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J. Insulin-like activity of dilute human serum assayed by an isolated adipose cell method. Diabetes. 1965 Oct;14(10):643–649. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.10.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldrick R. B., McLoughlin G. M. Lipolysis and lipogenesis from glucose in human fat cells of different sizes. Effects of insulin, epinephrine, and theophylline. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1213–1223. doi: 10.1172/JCI106335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman A. D., Cohen A. I., Richane C. J., Hsu T. Lipolytic response and adenyl cyclase activity of rat adipocytes as related to cell size. J Lipid Res. 1971 Jul;12(4):498–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J., Han P. W. Cellularity of rat adipose tissue: effects of growth, starvation, and obesity. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsson B., Smith U. Effect of cell size on lipolysis and antilipolytic action of insulin in human fat cells. J Lipid Res. 1972 Sep;13(5):651–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Gorden P., Freychet P., Roth J. Insulin receptor defect in insulin resistance: studies in the obese-hyperglycimic mouse. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90354-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin-receptor interaction in the obese-hyperglycemic mouse. A model of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEONARDS J. R., LANDAU B. R. METABOLISM OF FRUCTOSE BY ADIPOSE TISSUE, AND THE EFFECT OF INSULIN. Endocrinology. 1964 Jan;74:142–144. doi: 10.1210/endo-74-1-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston J. N., Cuatrecasa P., Lockwood D. H. Insulin insensitivity of large fat cells. Science. 1972 Aug 18;177(4049):626–628. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4049.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston J. N., Lockwood D. H. Direct measurements of sugar uptake in small and large adipocytes from young and adult rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 11;61(3):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER J., RUSSELL R. E., BATES M. W., DICKIE M. M. Metabolic, nutritional and endocrine studies of the hereditary obesity-diabetes syndrome of mice and mechanism of its development. Metabolism. 1953 Jan;2(1):9–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Effects of age and obesity on insulin binding to isolated adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1975 Jun;96(6):1486–1498. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-6-1486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Deoxyglucose transport of uninfected, murine sarcoma virus-transformed, and murine leukemia virus-infected mouse cells. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Dec;82(3):421–433. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040820312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ D., ZIERLER K. L. Forearm metabolism in obesity and its response to intra-arterial insulin. Characterization of insulin resistance and evidence for adaptive hyperinsulinism. J Clin Invest. 1962 Dec;41:2173–2181. doi: 10.1172/JCI104676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner E. D., Plagemann P. G., Bernlohr R. W. Permeation of glucose by simple and facilitated diffusion by Novikoff rat hepatoma cells in suspension culture and its relationship to glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5765–5776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salans L. B., Dougherty J. W. The effect of insulin upon glucose metabolism by adipose cells of different size. Influence of cell lipid and protein content, age, and nutritional state. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1399–1410. doi: 10.1172/JCI106623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith U., Kral J., Björntorp P. Influence of dietary fat and carbohydrate on the metabolism of adipocytes of different size in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 25;337(2):278–285. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll A. H., Goldfine I. D., Roth J., Kahn C. R. Thymic lymphocytes in obese (ob-ob) mice. A mirror of the insulin receptor defect in liver and fat. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4127–4131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann Bennett G., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor of fat cells in insulin-resistant metabolic states. Science. 1972 May 19;176(4036):805–806. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4036.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



