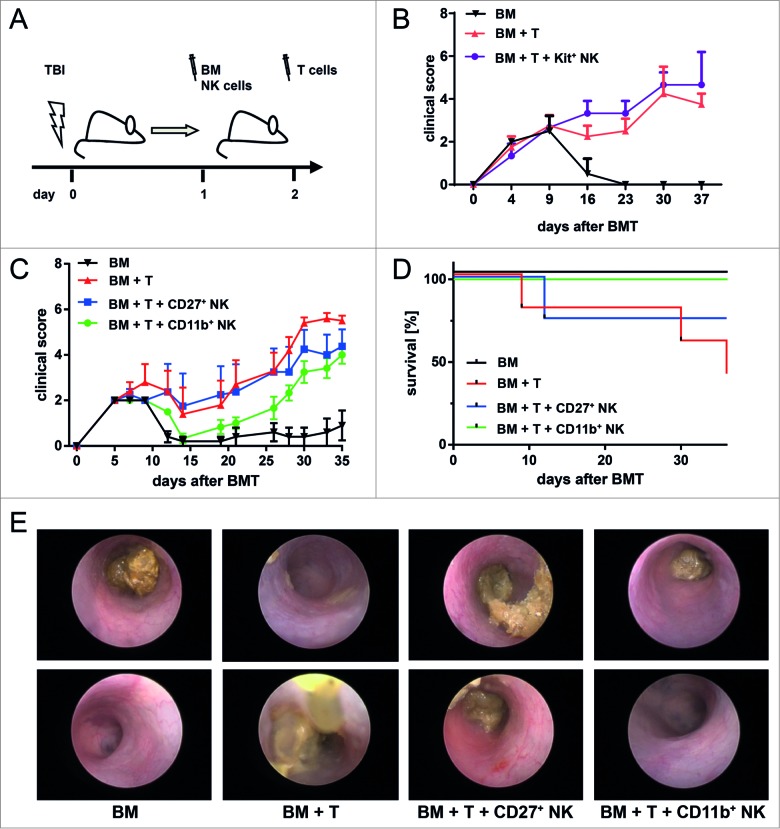
Figure 1.
CD11b+ NK cells as main effectors reducing GVHD symptoms. (A) Murine allogeneic BMT model. One day after lethal total body irradiation (TBI), Balb/c mice were co-transplanted with 5×106 freshly isolated T-cell depleted bone marrow (BM) cells plus 1×106 MoFlo-sorted NK subsets from C57Bl/6 donors. Two days after TBI, 7×105 T cells from C57Bl/6 origin were injected i.v. to induce acute graft-versus host disease (GVHD). The control bone marrow transplant (BMT) group did not receive any additional T cells. (B) Course of GVHD score is depicted that has been assessed by clinical monitoring every 2-3 days following transfer of BM (black, n = 4) with additional transfer of allogeneic T cells to induce GVHD (red, n = 4) plus IL-18-induced Kit+CD27+CD11b− natural killer (NK) cells (Kit+, violet curve, n = 4). (C) Course of GVHD-score comparing a BMT control group (BM, black, n = 6) with mice developing GVHD induced by allogeneic T cells (BM+T, red, n = 5) and mice that additionally received either Kit−CD27+CD11b− (CD27+, blue, n = 4) or Kit−CD27−CD11b+ NK cells (CD11b+, green curve, n = 5). All NK cell subsets were expanded by 1,500 U/mL IL-2 for 5 days as described in Methods. (D) Survival of the same cohorts as described above. In the above panels, (B-D) one representative experiment out of 3 is depicted showing, the mean (4-6 mice/group) ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by Student's t-test; p<0.05 CD11b+NK with GVHD group at day 28; ns for all other groups. (E) Colonoscopy on day 14 of mice from the BMT control, GVHD group, and mice that additionally received IL-2 expanded CD27+ or CD11b+ NK cell subsets. Two representative photographs are shown for each group with n = 2-5 mice/group.