Abstract
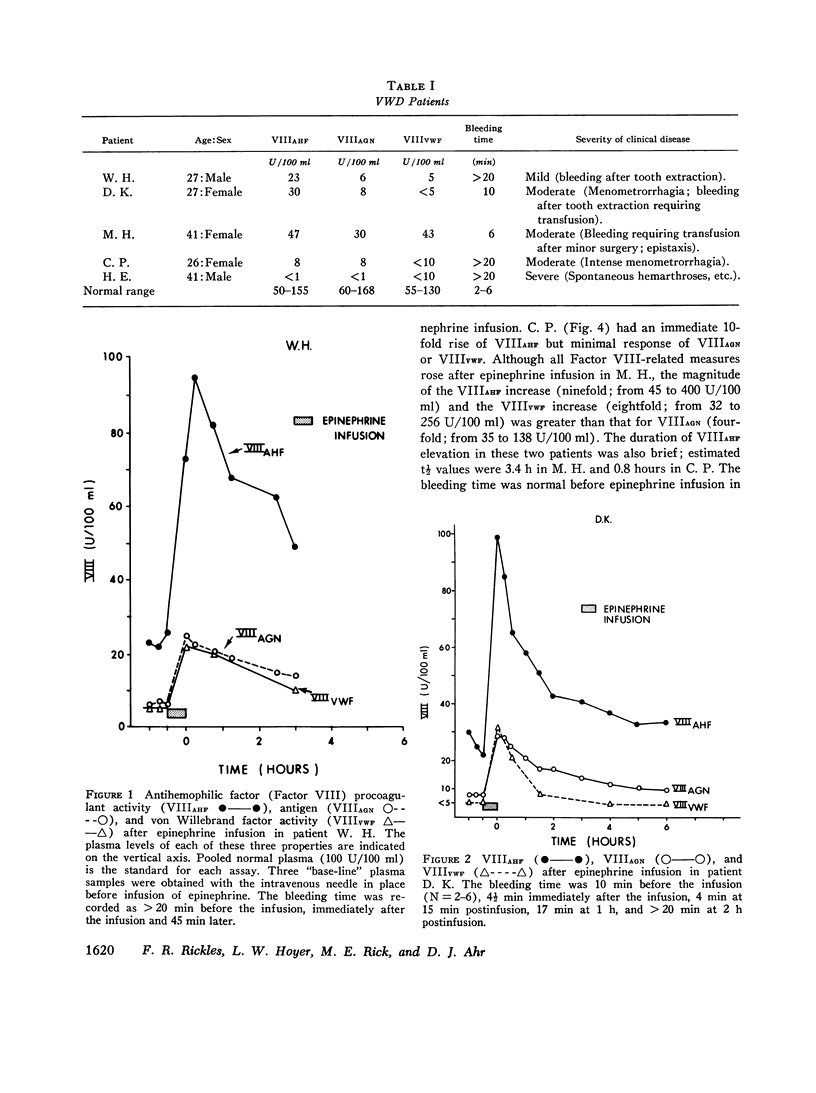
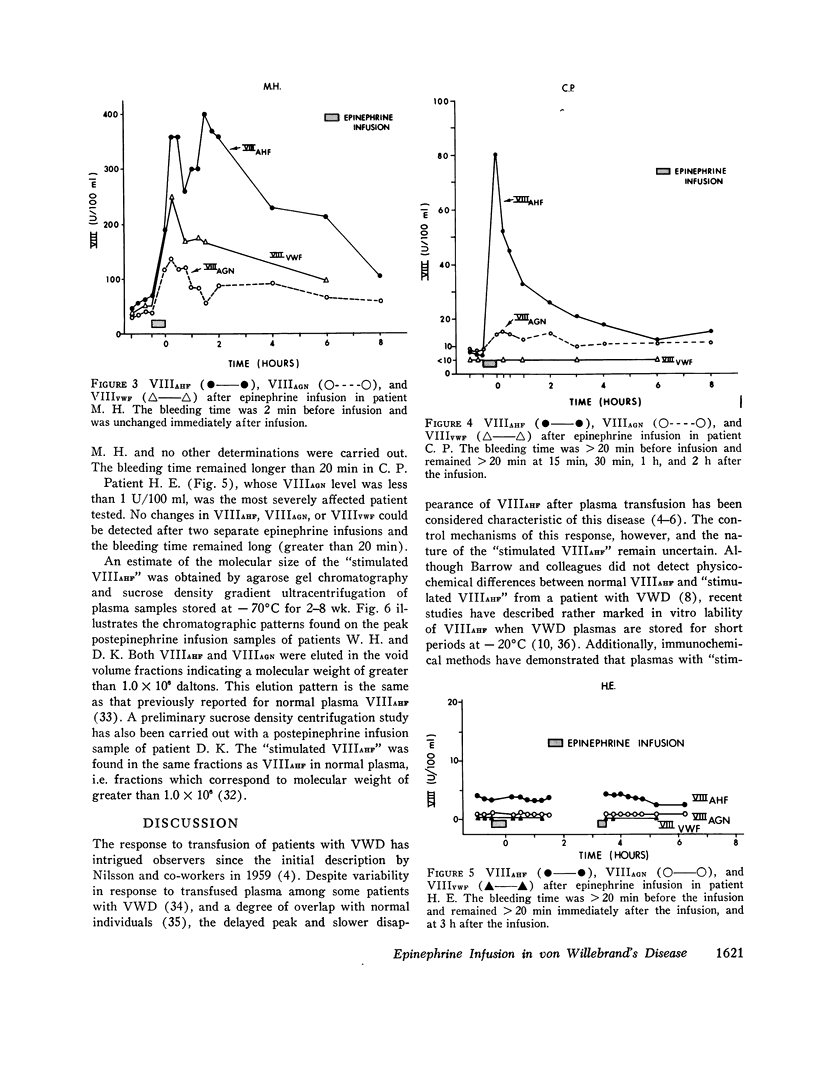
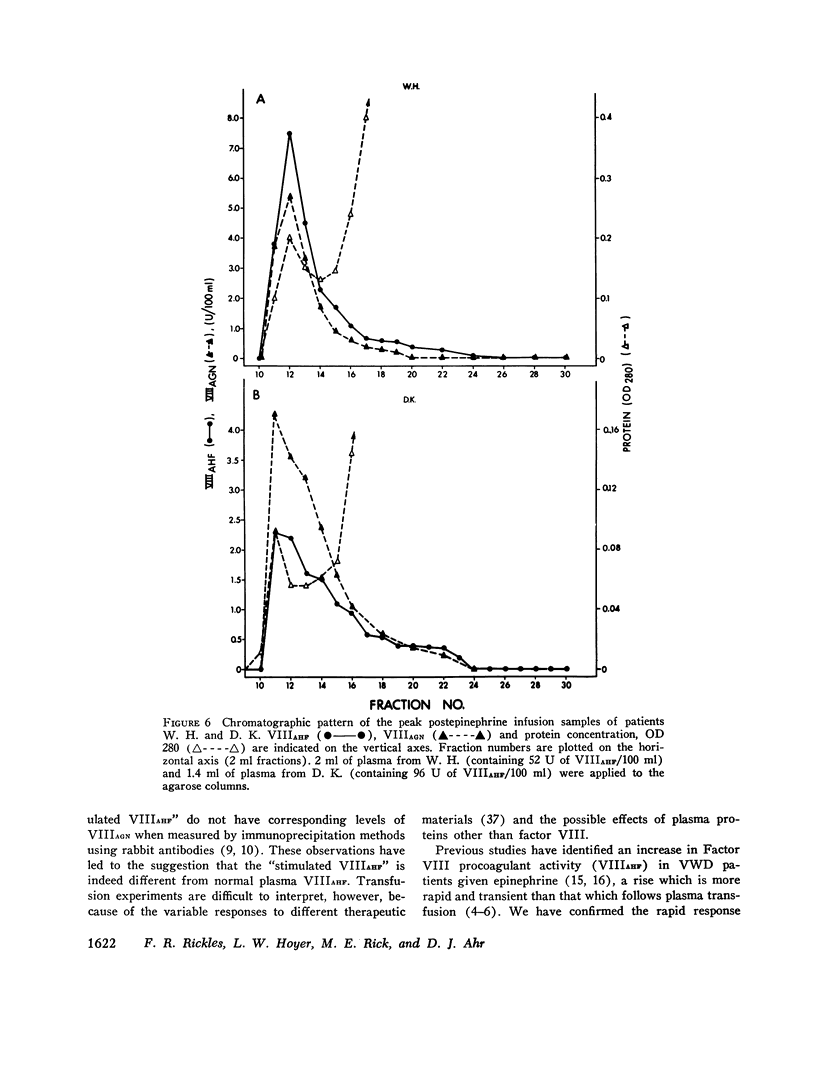
Epinephrine infusion causes variable increases in the components of the Factor VIII (antihemophilic factor) complex in patients with von Willebrand's disease. The increase in antihemophilic factor procoagulant activity was greater than that of Factor VIII-related antigen and von Willebrand factor activity in two patients with von Willebrand's disease. Similar increases in the three individual factors were demonstrated in two other patients. A 4-10-fold increase in Factor VIII-related properties was identified in each of these individuals after infusion. One patient has been studied with very severe von Willebrand's disease; none of the Factor VIII-related properties increased despite two infusions of epinephrine. Bleeding times were normalized or remained normal in the two patients whose von Willebrand factor activity was greater than 25 U/100 ml. It remained prolonged in those three patients whose von Willebrand factor activity levels remained below that concentration. The increase in procoagulant activity was transient in all patients and t 1/2 values were estimated to be between 0.8 and 3.4 h.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARROW E. M., ROBERTS H. R., PONS K., GRAHAM J. B. STUDIES OF THE ANTIHEMOPHILIC FACTOR (AHF, FACTOR VIII) PRODUCED IN VON WILLEBRAND'S DISEASE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Mar;115:760–763. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIGGS R., MATTHEWS J. M. The treatment of haemorrhage in von Willebrand's disease and the blood level of factor VIII (AHG). Br J Haematol. 1963 Apr;9:203–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1963.tb05458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECKENRIDGE R. T., RATNOFF C. D. Studies on the nature of the circulating anticoagulant directed against antihemophilic factor: with notes on an assay for anthemophilic factor. Blood. 1962 Aug;20:137–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett B., Ratnoff O. D. Changes in antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor 8) procoagulant activity and AHF-like antigen in normal pregnancy, and following exercise and pneumoencephalography. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Aug;80(2):256–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett B., Ratnoff O. D., Levin J. Immunologic studies in von Willebrand's disease. Evidence that the antihemophilic factor (AHF) produced after transfusions lacks an antigen associated with normal AHF and the inactive material produced by patients with classic hemophilia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2597–2601. doi: 10.1172/JCI107077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom A. L., Giddings J. C., Wilks C. J. Factor 8 on the vascular intima: possible importance in haemostasis and thrombosis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 14;241(111):217–219. doi: 10.1038/newbio241217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORNU P., LARRIEU M. J., CAEN J., BERNARD J. Transfusion studies in von Willebrand's disease: effect on bleeding time and factor VIII. Br J Haematol. 1963 Apr;9:189–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1963.tb05457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. A., Reisner F. F., Hall M., Wagner R. H. Effects of thrombin treatment of preparations of factor VIII and the Ca2+-dissociated small active fragment. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):751–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI108146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denson K. W. The detection of factor-VIII-like antigen in haemophilic carriers and in patients with raised levels of biologically active factor VIII. Br J Haematol. 1973 Apr;24(4):451–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGEBERG O. CHANGES IN THE ACTIVITY OF ANTIHEMOPHILIC A FACTOR (F. VIII) AND IN THE BLEEDING TIME ASSOCIATED WITH MUSCULAR EXERCISE AND ADRENALIN INFUSION. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1963;15:539–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. J., Ratnoff O. D. Elevated antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII) procoagulant activity and AHF-like antigen in alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Feb;83(2):189–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Mannucci P. M., Turesson I., Ruggeri Z. M., Nilsson I. M. Factor VIII antigen in the vessel walls in von Willebrand's disease and haemophilia A. Scand J Haematol. 1974;13(1):33–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1974.tb00232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Nilsson I. M. AHF related protein in clinical praxis. Scand J Haematol. 1974;12(3):221–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1974.tb00202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., De los Santos R. P., Hoyer J. R. Antihemophilic factor antigen. Localization in endothelial cells by immunofluorescent microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2737–2744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). IV. Radioimmunoassay of AHF antigen. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Dec;80(6):822–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGRAM G. I. Increase in antihaemophilic globulin activity following infusion of adrenaline. J Physiol. 1961 Apr;156:217–224. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of von Willebrand factor by cultured human endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1906–1909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libre E. P., Cowan D. H., Watkins S. P., Jr, Shulman N. R. Relationships between spleen, platelets and factor 8 levels. Blood. 1968 Mar;31(3):358–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Aberg M., Nilsson I. M., Robertson B. Mechanism of plasminogen activator and factor VIII increase after vasoactive drugs. Br J Haematol. 1975 May;30(1):81–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D., Larrieu M. J., Maroteaux P., Caen J. P. Biological findings in Von Willebrand's pedigrees: implications for inheritance. J Clin Pathol. 1967 Mar;20(2):190–194. doi: 10.1136/jcp.20.2.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielke C. H., Jr, Kaneshiro M. M., Maher I. A., Weiner J. M., Rapaport S. I. The standardized normal Ivy bleeding time and its prolongation by aspirin. Blood. 1969 Aug;34(2):204–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muntz R. H., Ekert H., Helliger H. Properties of post-infusion factor VIII in von Willebrand's disease. Thromb Res. 1974 Aug;5(2):111–123. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON I. M., BLOMBACK M., BLOMBACK B. v. Willebrand's disease in Sweden; its pathogenesis and treatment. Acta Med Scand. 1959 Jun 30;164:263–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozge-Anwar A. H., Connell G. E., Mustard J. F. The activation of factor 8 by thrombin. Blood. 1965 Oct;26(4):500–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCTOR R. R., RAPAPORT S. I. The partial thromboplastin time with kaolin. A simple screening test for first stage plasma clotting factor deficiencies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961 Sep;36:212–219. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/36.3.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins H. A. Correction of the hemostatic defects in Von Willebrand's disease. Blood. 1967 Sep;30(3):375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPAPORT S. I., SCHIFFMAN S., PATCH M. J., AMES S. B. The importance of activation of antihemophilic globulin and proaccelerin by traces of thrombin in the generation of intrinsic prothrombinase activity. Blood. 1963 Feb;21:221–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Bennett B. Clues to the pathogenesis of bleeding in von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1973 Nov 29;289(22):1182–1183. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197311292892209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Kass L., Lang P. D. Studies on the purification of antihemophilic factor (factor VIII). II. Separation of partially purified antihemophilic factor by gel filtration of plasma. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):957–962. doi: 10.1172/JCI106055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Saito H. Letter: Bleeding in von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 9;290(19):1089–1089. doi: 10.1056/nejm197405092901921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick M. E., Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). V. Immunologic properties of AHF subunits produced by salt dissociation. Blood. 1973 Nov;42(5):737–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles F. R., Hardin J. A., Pitlick F. A., Hoyer L. W., Conrad M. E. Tissue factor activity in lymphocyte cultures from normal individuals and patients with hemophilia A. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1427–1434. doi: 10.1172/JCI107316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza C. R., Eipe J. Exercise, factor VIII and the spleen. Br J Haematol. 1971 Jun;20(6):629–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb00801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Pareti F. I., Bintadish P., Mannucci P. M. Letter: Clotting factors in von Willebrand's disease. Lancet. 1974 Jul 13;2(7872):105–106. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91668-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALZMAN E. W. MEASUREMENT OF PLATELET ADHESIVENESS. A SIMPLE IN VITRO TECHNIQUE DEMONSTRATING AN ABNORMALITY IN VON WILLEBRAND'S DISEASE. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Nov;62:724–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The physiologic basis for therapy of classic hemophilia (factor 8 deficiency) and related disorders. Combined clinical staff conference at the National Institutes of Health. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Oct;67(4):856–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Hoyer I. W. Von Willebrand factor: dissociation from antihemophilic factor procoagulant activity. Science. 1973 Dec 14;182(4117):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4117.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Hoyer L. W., Rickles F. R., Varma A., Rogers J. Quantitative assay of a plasma factor deficient in von Willebrand's disease that is necessary for platelet aggregation. Relationship to factor VIII procoagulant activity and antigen content. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2708–2716. doi: 10.1172/JCI107465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Kochwa S. Molecular forms of antihaemophilic globulin in plasma, cryoprecipitate and after thrombin activation. Br J Haematol. 1970 Jan;18(1):89–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J. Letter: Relation of the von Willebrand factor to the bleeding time. N Engl J Med. 1974 Aug 22;291(8):420–420. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197408222910817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


