Abstract
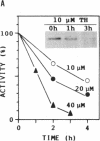
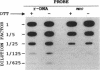
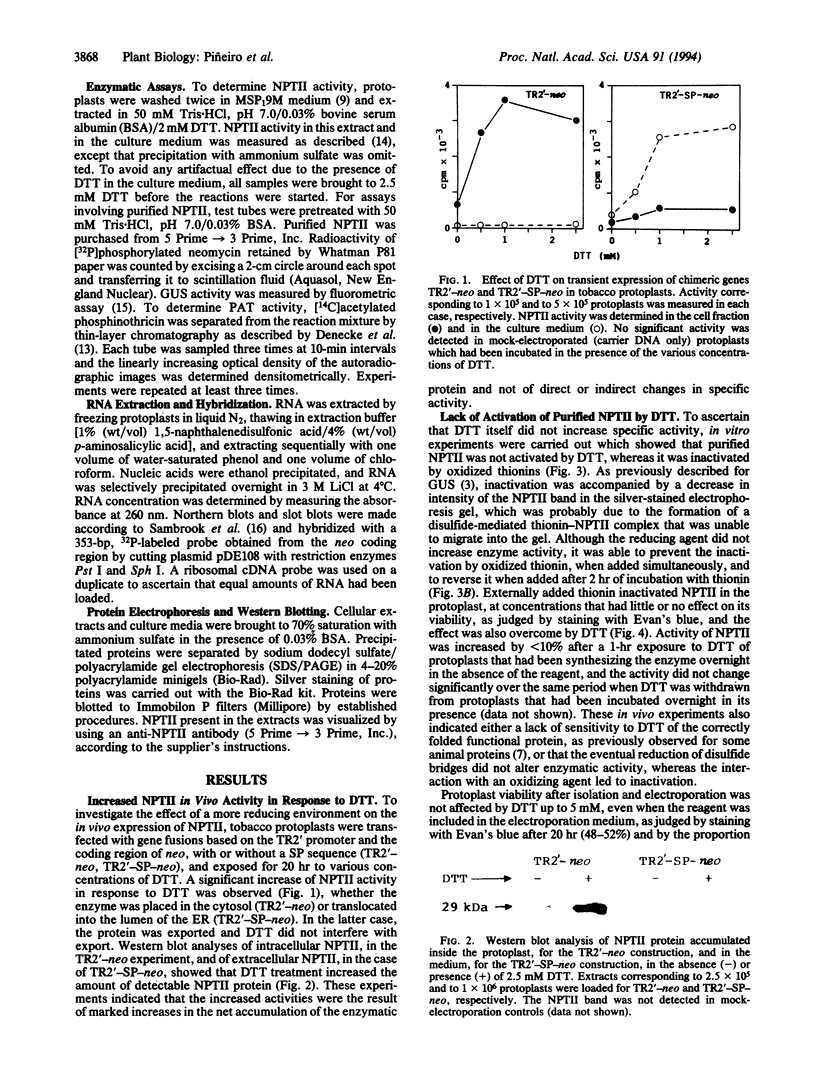
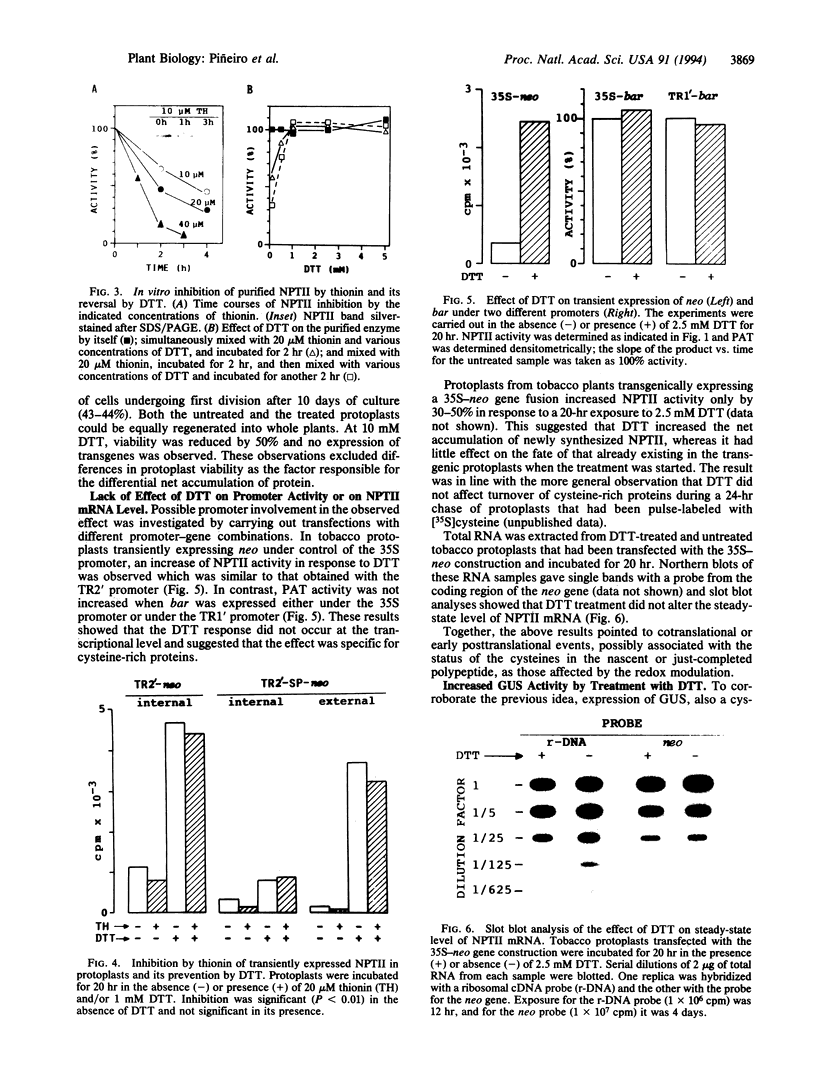
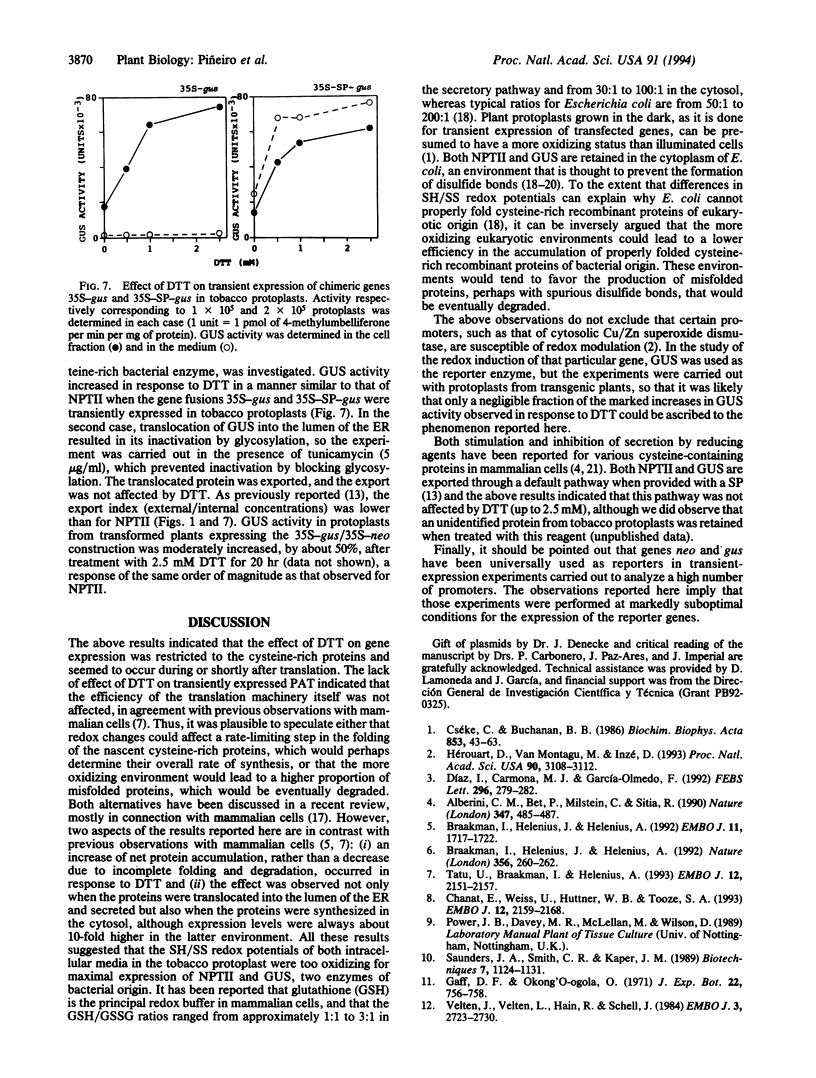
Activity of neomycin phosphotransferase II (NPTII; gene, neo; five cysteines) in tobacco protoplasts transfected with fusions of the octopine TR2' or cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter and the neo gene, with or without a signal peptide, increased up to 8-fold in response to externally added dithiothreitol at concentrations that did not affect protoplast viability (up to 2.5 mM). Activity of phosphinothricin acetyltransferase (PAT; gene, bar; one cysteine) expressed under control of the TR1' or 35S promoter was not similarly affected, thus excluding a redox modulation of transcription as the mechanism of NPTII activation by dithiothreitol. Western-blot analyses showed an increase in the amount of protein in response to dithiothreitol, whereas neither the steady-state level of NPTII mRNA nor the specific activity of the purified enzyme was affected. The same type of modulation was observed for transiently expressed beta-glucuronidase (nine cysteines) produced from a fusion with the 35S promoter, with or without a signal peptide. Limitation of cotranslational and/or early posttranslational steps by excessively oxidizing sulfhydryl/disulfide redox potentials is postulated to explain the low net accumulation of cysteine-rich proteins of bacterial origin (i.e., NPTII and beta-glucuronidase) when expressed in plant protoplasts, and the marked increase in such proteins in response to externally added dithiothreitol.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberini C. M., Bet P., Milstein C., Sitia R. Secretion of immunoglobulin M assembly intermediates in the presence of reducing agents. Nature. 1990 Oct 4;347(6292):485–487. doi: 10.1038/347485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braakman I., Helenius J., Helenius A. Manipulating disulfide bond formation and protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1717–1722. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05223.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braakman I., Helenius J., Helenius A. Role of ATP and disulphide bonds during protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):260–262. doi: 10.1038/356260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanat E., Weiss U., Huttner W. B., Tooze S. A. Reduction of the disulfide bond of chromogranin B (secretogranin I) in the trans-Golgi network causes its missorting to the constitutive secretory pathways. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2159–2168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05864.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denecke J., Botterman J., Deblaere R. Protein secretion in plant cells can occur via a default pathway. Plant Cell. 1990 Jan;2(1):51–59. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman A. I., Beckwith J. Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase fails to acquire disulfide bonds when retained in the cytoplasm. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7719–7722. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7719-7722.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz I., Carmona M. J., García-Olmedo F. Effects of thionins on beta-glucuronidase in vitro and in plant protoplasts. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jan 27;296(3):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80304-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtley S. M., Helenius A. Protein oligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hérouart D., Van Montagu M., Inzé D. Redox-activated expression of the cytosolic copper/zinc superoxide dismutase gene in Nicotiana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):3108–3112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.3108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke R. Protein folding: local structures, domains, subunits, and assemblies. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3147–3161. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollitt S., Zalkin H. Role of primary structure and disulfide bond formation in beta-lactamase secretion. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.27-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. A., Smith C. R., Kaper J. M. Effects of electroporation pulse wave on the incorporation of viral RNA into tobacco protoplasts. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1124–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatu U., Braakman I., Helenius A. Membrane glycoprotein folding, oligomerization and intracellular transport: effects of dithiothreitol in living cells. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2151–2157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05863.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velten J., Velten L., Hain R., Schell J. Isolation of a dual plant promoter fragment from the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2723–2730. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02202.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]