Abstract
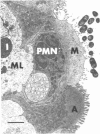
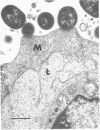
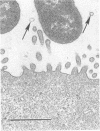
The RDEC-1 strain Escherichia coli is an enteroadherent bacterium that produces diarrhea in the rabbit. A histopathologically similar disease has been described in humans. The RDEC-1 bacterium adheres to the epithelium of lymphoid follicles in rabbit ileal Peyer's patches by 4 h postinoculation, 3-4 d before its adherence to absorptive epithelium. The purpose of this study was to determine whether the RDEC-1 bacterium adheres to a specific cell type in the lymphoid follicle epithelium. RDEC-1 bacteria were given in a dose of 2 X 10(6) by the orogastric route to postweanling rabbits. The distal ileal Peyer's patch, taken from 5 control rabbits and 43 rabbits at intervals in the first 24 h postinoculation, was examined by routine and high-voltage electron microscopy. The RDEC-1 bacterium adhered specifically to M (membranous) rather than absorptive epithelial cells of the lymphoid follicle epithelium. Further understanding of how the bacterium attaches to M cells, which transport antigens to intraepithelial lymphocytes, could be useful in designing vaccines to protect mucosal surfaces.
Full text
PDF


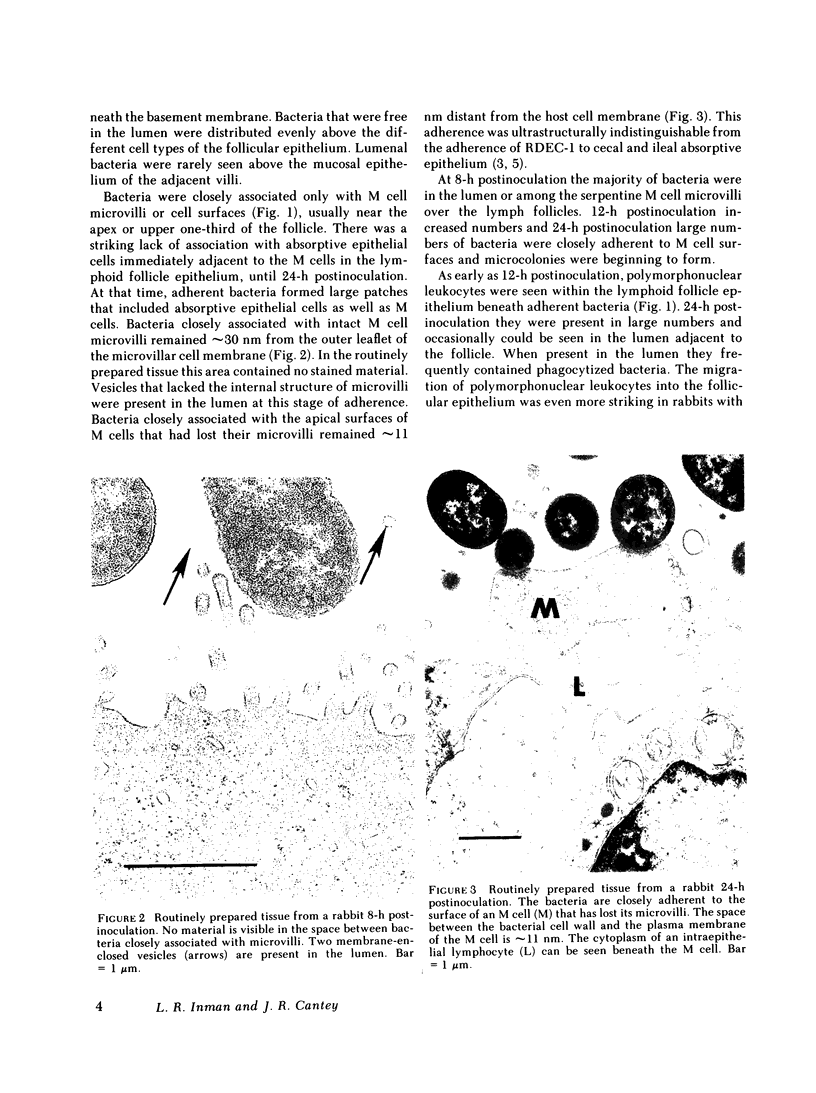

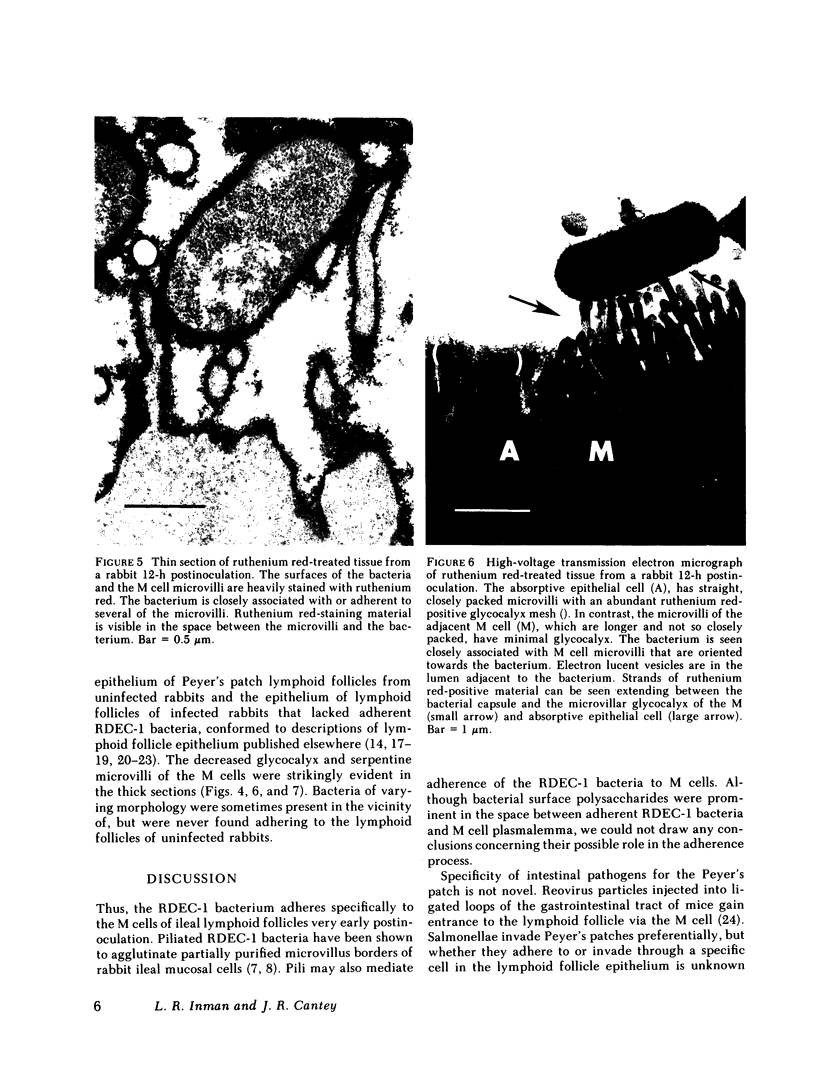


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer M. E., Thurow H. Polysaccharide capsule of Escherichia coli: microscope study of its size, structure, and sites of synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):911–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.911-936.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla D. K., Owen R. L. Cell renewal and migration in lymphoid follicles of Peyer's patches and cecum--an autoradiographic study in mice. Gastroenterology. 1982 Feb;82(2):232–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Blake R. K. Diarrhea due to Escherichia coli in the rabbit: a novel mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):454–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Hosterman D. S. Characterization of colonization of the rabbit gastrointestinal tract by Escherichia coli RDEC-1. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1099–1103. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1099-1103.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Inman L. R. Diarrhea due to Escherichia coli strain RDEC-1 in the rabbit: the peyer's patch as the initial site of attachment and colonization. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):440–446. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Lushbaugh W. B., Inman L. R. Attachment of bacteria to intestinal epithelial cells in diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli strain RDEC-1 in the rabbit: stages and role of capsule. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):219–230. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Collins F. M. The route of enteric infection in normal mice. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1189–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney C. P., Boedeker E. C., Formal S. B. Quantitation of the adherence of an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to isolated rabbit intestinal brush borders. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):736–743. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.736-743.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney C. P., Schad P. A., Formal S. B., Boedeker E. C. Species specificity of in vitro Escherichia coli adherence to host intestinal cell membranes and its correlation with in vivo colonization and infectivity. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1019–1027. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1019-1027.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen C. R., Christie D. L. Chronic diarrhea in infants caused by adherent enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Pediatr. 1982 Mar;100(3):358–361. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80429-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., McCormick J. N., Goodman J. R., Yoffey J. M., Fudenberg H. H. Peyer's patches: morphologic studies. Cell Immunol. 1970 Nov;1(5):500–520. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann A. W., Schmidt G., Rowley D. Intestinal colonization and virulence of Salmonella in mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):763–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.763-770.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey C. D., Lushbaugh W. B., Condon C. W., Pittman J. C., Pittman F. E. Light and electron microscopic studies of antibiotic associated colitis in the hamster. Gut. 1979 Jan;20(1):6–15. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. II. Fine structural localization in animal tissues. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):369–415. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hanley P. D., Cantey J. R. Surface structures of Escherichia coli that produce diarrhea by a variety of enteropathic mechanisms. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):874–878. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.874-878.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L., Allen C. L., Stevens D. P. Phagocytosis of Giardia muris by macrophages in Peyer's patch epithelium in mice. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):591–601. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.591-601.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L., Jones A. L. Epithelial cell specialization within human Peyer's patches: an ultrastructural study of intestinal lymphoid follicles. Gastroenterology. 1974 Feb;66(2):189–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L. Sequential uptake of horseradish peroxidase by lymphoid follicle epithelium of Peyer's patches in the normal unobstructed mouse intestine: an ultrastructural study. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):440–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. D. Small intestinal mucosa in childhood in health and disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1981;70:65–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman F. E., Pittman J. C., Humphrey C. D. Colitis following oral lincomycin therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Aug;134(2):368–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. W., Peacock M. A. "M" cell distribution in follicle-associated epithelium of mouse Peyer's patch. Am J Anat. 1980 Oct;159(2):167–175. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001590205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Inman L. R., O'Hanley P. D., Cantey J. R., Lushbaugh W. B. Scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of Escherichia coli O15 (RDEC-1) enteric infection in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):686–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.686-694.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulshen M. H., Rollo J. L. Pathogenesis of escherichia coli gastroenteritis in man--another mechanism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):99–101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J. L., Rubin D. H., Finberg R., Kauffman R. S., Sharpe A. H., Trier J. S., Fields B. N. Intestinal M cells: a pathway for entry of reovirus into the host. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):471–472. doi: 10.1126/science.6259737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]