Abstract
Shigella is the leading cause for dysentery worldwide. Together with several virulence factors employed for invasion, the presence and length of the O antigen (OAg) of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) plays a key role in pathogenesis. S. flexneri 2a has a bimodal OAg chain length distribution regulated in a growth-dependent manner, whereas S. sonnei LPS comprises a monomodal OAg. Here we reveal that S. sonnei, but not S. flexneri 2a, possesses a high molecular weight, immunogenic group 4 capsule, characterized by structural similarity to LPS OAg. We found that a galU mutant of S. sonnei, that is unable to produce a complete LPS with OAg attached, can still assemble OAg material on the cell surface, but a galU mutant of S. flexneri 2a cannot. High molecular weight material not linked to the LPS was purified from S. sonnei and confirmed by NMR to contain the specific sugars of the S. sonnei OAg. Deletion of genes homologous to the group 4 capsule synthesis cluster, previously described in Escherichia coli, abolished the generation of the high molecular weight OAg material. This OAg capsule strongly affects the virulence of S. sonnei. Uncapsulated knockout bacteria were highly invasive in vitro and strongly inflammatory in the rabbit intestine. But, the lack of capsule reduced the ability of S. sonnei to resist complement-mediated killing and to spread from the gut to peripheral organs. In contrast, overexpression of the capsule decreased invasiveness in vitro and inflammation in vivo compared to the wild type. In conclusion, the data indicate that in S. sonnei expression of the capsule modulates bacterial pathogenesis resulting in balanced capabilities to invade and persist in the host environment.
Author Summary
Shigellosis is a major global health concern. Recently, a shift in the dominance of types of Shigella that cause disease has been observed with S. sonnei increasing in prevalence under improved socio-economic conditions leading to a replacement of S. flexneri. Most of the knowledge of Shigella disease mechanisms has been obtained from studies of S. flexneri. We found that S. sonnei possesses a high molecular weight sugar capsule that is absent in S. flexneri 2a. Removal of the capsule made S. sonnei bacteria highly invasive in vitro and strongly inflammatory in vivo, but in contrast, there was reduced spreading of these mutant bacteria from the gut to peripheral organs in rabbits and higher sensitivity to complement-mediated lysis. Thus, the capsule plays a role in both, invasion and protection of the bacteria against the innate immune defense of the host during the infection. These findings indicate that the capsule is an important virulence factor for S. sonnei. Based on the substantial changes in pathogenesis observed upon removal and overexpression of the capsule, we hypothesize that its level of expression may be under significant evolutionary pressure.
Introduction
Shigellosis, or bacillary dysentery, is an acute human inflammatory disease of the large intestine, characterized by watery diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain, and bloody and mucus stools, caused by Gram-negative Shigella enterobacteria [1]. This disease is a major global health concern, responsible for more than 7 million Disability-Adjusted Life Years and 100,000 deaths per year [2], predominantly affecting children under 5 years of age from developing countries [3]. Deaths caused by shigellosis have been linked to intestinal but also systemic complications, including pneumonia, hypoglycemia, and hemolytic-uremic syndrome [4]. Shigella bacteremia is generally rare in adults and in individuals with no underlying condition but has been described in young children with frequencies up to 7% of cases [5,6], with malnutrition being an important risk factor, or in immunocompromised individuals [7] and has been associated with high mortality rates [5,6,7,8].
Fifty Shigella serotypes belonging to the four serogroups of the genus (S. dysenteriae, S. flexneri, S. boydii, S. sonnei) are distinguished based on the structure of the O antigen (OAg) polysaccharide of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [9]. Among them, S. flexneri and S. sonnei are endemic and have been linked to most infections [10]. For both species, similar mortality rates [11] and frequencies of bacteremia per number of cases [5] have been reported. While S. flexneri is the most common cause of shigellosis, S. sonnei is replacing S. flexneri in locations where socio-economic conditions are improving and thus has become an important pathogen in developing countries [12,13]. In addition, S. sonnei bacteremia is likely to be underestimated as it is usually detected within the first 24 h of onset of disease when patients do not always seek medical attention [8].
S. sonnei comprises a single clonal group, characterized by low genetic variability and antigenic homogeneity [14,15]. All S. sonnei isolates have Phase I O somatic antigen, the immunodominant and protective antigen [16]. Phase I polysaccharide has an OAg repeating unit of two uncommon sugars not present in other Shigella serogroups, 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-L-altruronic acid (L-AltNAcA) and 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-L-fucose (FucNAc4N) [17]. For Shigella and genetically related E. coli species, LPS OAg biosynthesis is a Wzx/Wzy-dependent process, encoded by genes for synthesis of sugars of the repeating unit (called wbg cluster in S. sonnei [18] and rfb cluster in S. flexneri [19]), and for OAg unit transport (wzx) and polymerization (wzy) on the independently synthesized LPS core-lipid A moieties [9]. Unlike in other Shigella, the S. sonnei wbg OAg synthesis cluster is not located on the chromosome but on the S. sonnei large virulence plasmid (pSS) [20]. To invade and colonize the intestinal epithelium and to survive the strong inflammatory host response, Shigella requires expression of protein factors encoded by the virulence plasmid, such as the Type III Secretion System (T3SS) and its secreted effectors [1]. The LPS is also a key virulence determinant [21]. S. flexneri (2a and 5a) has LPS OAg with a bimodal chain length distribution which is regulated in a growth-dependent manner [22] and is important for bacterial mobility and serum resistance [23]. Moreover, phage-encoded glucosylation of the OAg is essential for optimized LPS and T3SS functions in S. flexneri 5a M90T [24]. Less is known about S. sonnei LPS: Phase I bacteria possess a single modal OAg with a predominant chain length of 20–25 units [18]. Expression of Phase I polysaccharide and virulence are strongly interconnected and loss of the pSS virulence plasmid in vitro results in the S. sonnei Phase II cell type, lacking both the OAg and the virulent phenotype [25,26].
Besides the OAg side chain of LPS, Gram-negative exopolysaccharides generally include other structures, e.g. capsules. These enhance the bacterial survival in the environment and their fitness within hosts, by avoiding elimination by innate immune killing [27]. E. coli capsules have historically been classified into four groups based on genetic and biochemical criteria [28]. Group 4 capsules (G4C) are comprised of a high molecular weight surface polysaccharide and are also known as ‘O antigen capsules’ due to their structural similarity to the OAg side chain of the LPS [28]. In a more recent classification distinguishing two major groups based on the primary mechanisms of biosynthesis, i.e. the ABC transporter-dependent and the Wzy-dependent capsular polysaccharides [29], group 4 capsules, together with group 1 capsules, belong to the Wzy-dependent group. OAg capsules have been found in intestinal pathogenic E. coli, such as enteropathogenic (EPEC) [30] and enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) [31], as well as in Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis [32], and have been shown to confer enhanced colonization [31] and environmental persistence [32]. G4C share the Wzy-dependent synthesis cluster for OAg units with the LPS, but require an additional g4c operon for secretion and assembly of the OAg polysaccharide from the periplasm into the capsular structure [28]. All seven genes of the E. coli g4c transcriptional unit (ymcDCBA, yccZ, etp, etk) were required for capsule production in EPEC serotype O127 [30]. Despite Shigella being classified as uncapsulated bacteria, genes homologous to the E. coli g4c operon are present in different strains [30], but expression of G4C as component of Shigella exopolysaccharide and its potential contribution to pathogenicity have not been described.
In this study, we show that S. sonnei, but not S. flexneri 2a, possesses a g4c operon-dependent OAg capsule. Deletion of the capsule in S. sonnei results in substantially increased invasiveness of HeLa cells in vitro and triggers increased inflammation in the intestine but decreases resistance to complement-mediated killing and spreading ability in the rabbit model. Thus, the S. sonnei G4C is an important factor in the regulation of pathogenesis and persistence.
Results
S. sonnei ΔgalU lacking LPS-linked O antigen still has O antigen on the surface that is immunogenic and antigenic
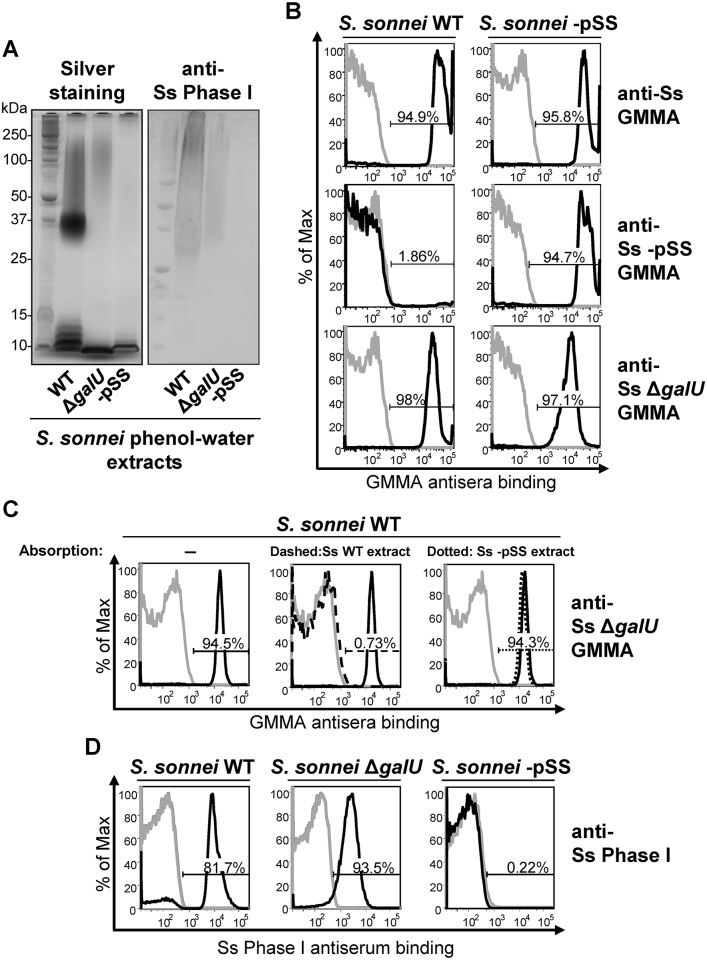
By SDS-PAGE (Fig. 1A), the phenol-water extract of S. sonnei WT had a typical LPS ladder with a predominant chain length of 20 to 25 OAg repeating units [18] and additional lower mobility material above the position of 25 units. S. sonnei strain lacking the pSS OAg-encoding virulence plasmid (S. sonnei -pSS) had only the low molecular weight band corresponding to the LPS core-lipid A moieties. S. sonnei ΔgalU is a deep rough LPS mutant with a defect in the pathway that transfers the OAg onto the LPS core region [21]. Its extract had slowly migrating material in addition to the low molecular weight band of the LPS inner core-lipid A molecules, but no LPS ladder. A Western blot probed with a monovalent anti-S. sonnei Phase I typing serum displayed a band with similar low mobility in phenol-water extracts of S. sonnei WT and S. sonnei ΔgalU but not in S. sonnei -pSS extract (Fig. 1A). To immunize mice, we generated outer membrane particles, called Generalized Modules for Membrane Antigens (GMMA), from S. sonnei WT, S. sonnei ΔgalU and S. sonnei-pSS strains genetically modified to induce high level shedding of these particles (hyperblebbing) by deletion of the tolR gene [33]. GMMA are highly immunogenic and present surface antigens in their natural context. By flow cytometry (Fig. 1B), sera raised against S. sonnei GMMA with unmodified LPS reacted with S. sonnei WT and S. sonnei -pSS bacteria. Sera raised against S. sonnei -pSS GMMA reacted with S. sonnei -pSS but not with S. sonnei WT, indicating that the OAg on the target S. sonnei WT bacteria shields the surface antigens from the antibodies raised against OAg-negative GMMA. Sera raised against S. sonnei ΔgalU GMMA reacted like sera raised against S. sonnei GMMA with unmodified LPS, staining S. sonnei WT and S. sonnei -pSS bacteria, suggesting that they had anti-OAg activity despite lacking LPS-linked OAg. This immunoreactivity was not an artifact of GMMA immunization, as sera raised against whole formalin-fixed S. sonnei WT, S. sonnei with a knockout of the wbg OAg biosynthesis cluster in the pSS virulence plasmid (S. sonnei ΔOAg), and S. sonnei ΔgalU bacteria gave similar results (S1 Fig). Unlike S. sonnei ΔgalU, sera raised against whole inactivated S. flexneri 2a ΔgalU did not react with its homologous S. flexneri 2a WT strain, indicating the lack of OAg-specific immunogenicity in this background (S1 Fig).
Fig 1. S. sonnei ΔgalU LPS mutant possesses immunogenic and antigenic Phase I material on the surface.
(A) Silver staining and immunoblot analysis of phenol-water extracts from S. sonnei WT, S. sonnei ΔgalU and S. sonnei -pSS bacteria. Samples were run on 12% Bis-Tris SDS-PAGE, blotted, and membranes were incubated with S. sonnei Phase I monovalent antiserum (anti-Ss Phase I) at a dilution of 1:1000. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of surface staining of live S. sonnei WT and S. sonnei -pSS. Bacteria were stained with sera raised against GMMA from hyperblebbing S. sonnei with WT LPS (anti-Ss GMMA), S. sonnei -pSS with rough LPS (anti-Ss -pSS GMMA), or S. sonnei ΔgalU with deep rough LPS (anti-Ss ΔgalU GMMA). Gray profiles: staining with preimmune sera; black profiles: staining with GMMA antisera (1:1000). Representative results of three experiments are shown. (C) Competitive surface staining of S. sonnei WT live bacteria with sera raised against GMMA from hyperblebbing S. sonnei ΔgalU strain (anti-Ss ΔgalU GMMA). Gray profiles: staining with preimmune sera; black solid profiles: staining with anti-Ss ΔgalU GMMA; black dashed profile: staining with anti-Ss ΔgalU GMMA absorbed with S. sonnei WT (Ss WT) phenol-water extract; black dotted profile: staining with anti-Ss ΔgalU GMMA absorbed with S. sonnei -pSS (Ss -pSS) phenol-water extract. Sera dilution was 1:10000. (D) Surface staining of formalin-fixed S. sonnei WT, S. sonnei ΔgalU and S. sonnei -pSS with S. sonnei Phase I monovalent antiserum (anti-Ss Phase I). Gray profiles: staining with S. flexneri type II monovalent antiserum; black profiles: staining with anti-Ss Phase I. Sera dilution was 1:5000.
We performed a competitive staining experiment (Fig. 1C) to test if OAg-specific antibodies in S. sonnei ΔgalU GMMA antisera were responsible for the binding to S. sonnei WT. Pre-absorption of anti-S. sonnei ΔgalU GMMA sera with phenol-water extract from S. sonnei WT but not from S. sonnei -pSS bacteria abolished reactivity (Fig. 1C). In addition, flow cytometry of formalin-fixed S. sonnei WT, ΔgalU and -pSS bacteria stained with the S. sonnei Phase I typing antiserum gave strong signals with the WT and the ΔgalU strains, while no binding was revealed on the control S. sonnei -pSS strain (Fig. 1D). These results confirm that S. sonnei ΔgalU expresses an OAg material on the surface. However, the ΔgalU OAg may be loosely attached to the outer membrane since the anti-Phase I surface staining of live S. sonnei ΔgalU target bacteria was variable and much less pronounced (S1 Table).
S. sonnei g4c operon encodes the high molecular weight O antigen capsule
Genomic analysis showed a gene cluster in S. sonnei 53G and 046 with ≥ 99% identity to the E. coli g4c operon in the coding regions and the same genetic orientation (ymcDCBA, yccZ, etp, etk) (S2 Fig). Homologous genes are also present in S. flexneri 2a 2457T and 301 genomes, but a deletion of 14 bases (TGTCGCTTACTCGC) in the etk locus (position 135 to 148) causes a frame-shift mutation and thus inactivation of the operon (S2 Fig).
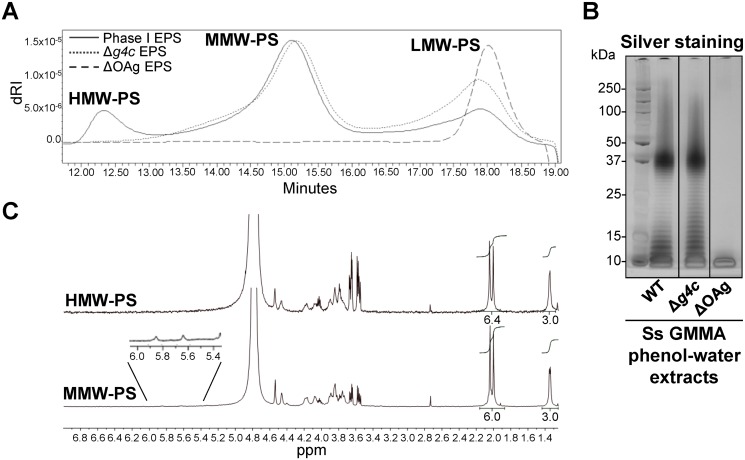
A S. sonnei g4c mutant strain (S. sonnei Δg4c) was generated to assess the functionality of the cluster. Furthermore, we inserted a selectable marker into the OAg-encoding pSS (replacement of virG by a resistance gene) to avoid loss of the plasmid during in vitro culture, and thereby obtained S. sonnei strains with stable OAg expression. These modifications were also introduced into hyperblebbing strains with the aim to use GMMA as source of exopolysaccharides for biochemical analyses. GMMA mainly contain outer membrane components and have negligible amounts of nucleic acids and cytoplasmic impurities [33]. We found acid-cleaved phenol-water exopolysaccharide extracts from GMMA to be suitable for polysaccharide analysis without need for further purification. Exopolysaccharide molecular weight distribution was examined by HPLC-SEC (Fig. 2A). The Phase I exopolysaccharide (Fig. 2A, solid line) from S. sonnei with unmodified LPS possessed a trimodal distribution of low, medium and high molecular weight (LMW, MMW, HMW, respectively) polysaccharides. A single LMW polysaccharide population was obtained from S. sonnei ΔOAg exopolysaccharide (Fig. 2A, dashed line). Exopolysaccharide from S. sonnei Δg4c had similar MMW and LMW populations as the S. sonnei Phase I exopolysaccharide, but no HMW polysaccharide (Fig. 2A, dotted line). Silver stained SDS-PAGE of the corresponding phenol-water GMMA extracts (Fig. 2B) correlated with the HPLC-SEC analysis but did not differentiate between the patterns from S. sonnei with trimodal WT exopolysaccharide and from S. sonnei Δg4c deficient for the HMW polysaccharide. In S. sonnei ΔgalU exopolysaccharide, only the HMW polysaccharide and a very LMW polysaccharide were present (S3 Fig). The Phase I exopolysaccharide was fractionated by HPLC-SEC and eluted fractions were analyzed by 1H-NMR (Fig. 2C). Spectra of the HMW and the MMW polysaccharides had peaks from the FucNAc4N and the L-AltNAcA residues of the S. sonnei OAg [34]. Integration of these signals confirmed the 1:1 ratio between FucNAc4N and L-AltNAcA expected for the S. sonnei OAg units. Anomeric signals of terminal and internal α-galactose residues from the outer core of S. sonnei LPS (5.82 ppm and 5.62 ppm, respectively) [34] were detected in the MMW polysaccharide. From the ratio between signals of the N-acetyl groups of the OAg residues (2.00–2.04 ppm) and signals of the outer core α-galactose residues (5.82 and 5.62 ppm), we calculated that the MMW polysaccharide has about 23–30 OAg units, in line with the SDS gels and literature values for the main LPS population [18]. The size of the HMW polysaccharide was estimated by HPLC-SEC in comparison with a dextran standard curve at 206–269 OAg units. To assess the presence of LPS core in the different polysaccharide populations, we analyzed the content of core residue 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO) after acid hydrolysis at the reducing end [35]. KDO was detected in the LMW and MMW polysaccharide, but not in the capsular HMW polysaccharide (S4 Fig). Thus, the g4c operon is functional in S. sonnei and encodes for the formation of an LPS-unlinked high molecular weight OAg polysaccharide, i.e. a group 4 capsule.
Fig 2. S. sonnei g4c cluster encodes for a high molecular weight O antigen polysaccharide.
(A) HPLC-SEC (dRI) analysis showing molecular weight distribution (high, medium, and low molecular weight polysaccharides, respectively HMW, MMW, LMW-PS) of acid-cleaved exopolysaccharide (EPS) purified from GMMA of hyperblebbing S. sonnei (Phase I EPS, solid line), S. sonnei Δg4c (Δg4c EPS, dotted line) and S. sonnei ΔOAg (ΔOAg EPS, dashed line). Polysaccharide samples were run on TosoHaas TSK gel G3000 PWXL-CP column (distribution coefficients (Kd): KdHMW-PS = 0.09, KdMMW-PS = 0.31). Apparent average molecular weight of HMW-PS (197.49 kDa) and of MMW-PS (22.04 kDa) was estimated by running Phase I EPS with a dextran standard curve. (B) 12% Bis-Tris SDS-PAGE and silver staining of S. sonnei (Ss) phenol-water extracts from GMMA of hyperblebbing S. sonnei (WT EPS), S. sonnei Δg4c (EPS lacking HMW-PS), and S. sonnei ΔOAg (only LMW-PS). (C) 1H-NMR spectra of S. sonnei Phase I EPS populations. Integral of the signals at 2.00 and 2.04 ppm belonging to the N-acetyl groups of the FucNAc4N and the L-AltNAcA OAg residues and of the signal at 1.34–1.36 ppm of the FucNAc4N methyl group are reported. Region of anomeric signals of terminal and internal α-galactose residues from LPS outer core in MMW-PS (5.82 ppm and 5.62 ppm, respectively) is shown enlarged.
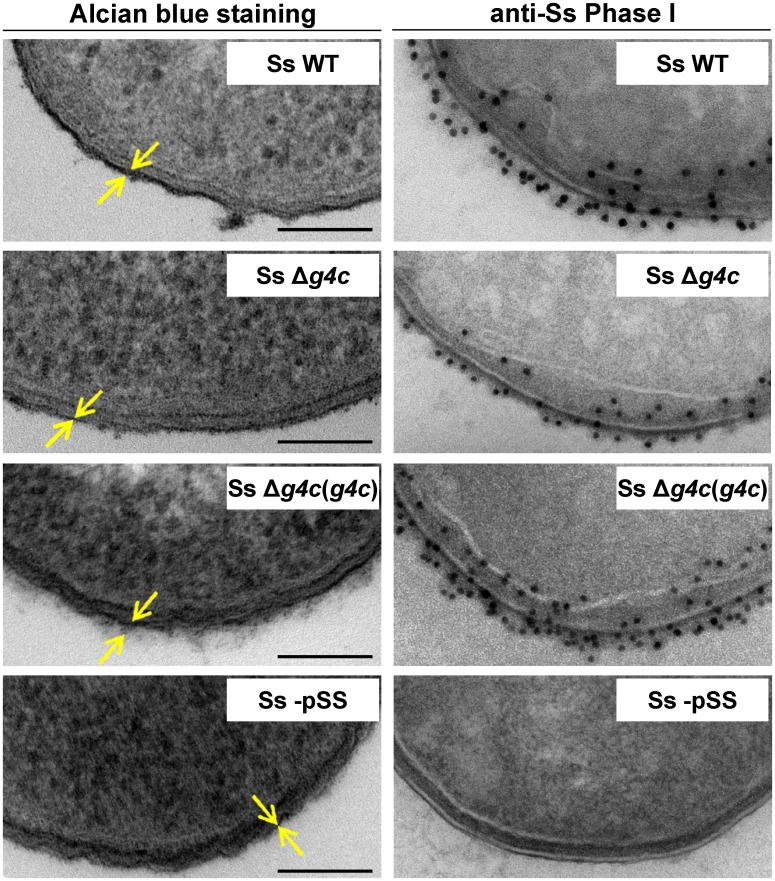
Transmission electron microscopy of alcian blue stained S. sonnei WT displayed a dark layer of electron-dense material corresponding to the exopolysaccharides (Fig. 3). Immunogold staining using anti-Phase I serum localized the Phase I antigens on the external surface of the outer membrane, protruding about 10–20 nm, and within the periplasmic space. In the absence of the G4C, S. sonnei Δg4c bacteria possessed an OAg layer of about half of the thickness of the S. sonnei WT layer. G4C expression in S. sonnei Δg4c was restored by complementing the knockout in trans through the insertion of a functional operon with its own promoter on a low copy number vector. In these S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) bacteria, the thickness of the Phase I layer was augmented, extending from the outer membrane about 20–30 nm. The control S. sonnei -pSS OAg-deficient strain was negative for both the alcian blue and the immune labelling, confirming staining specificity.
Fig 3. Group 4 capsule forms a dense outer layer on the surface of S. sonnei.
Surface analysis of S. sonnei WT (Ss WT), S. sonnei Δg4c (Ss Δg4c), S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) (Ss Δg4c(g4c)) and S. sonnei -pSS (Ss -pSS) bacteria by electron microscopy. Left column: electron-dense material at the bacterial surface corresponding to exopolysaccharides is revealed by alcian blue staining. Scale bar: 100 nm. Arrows indicate the LPS/capsule layer. Right column: immunogold labelling of S. sonnei bacteria with anti-S. sonnei Phase I monovalent antiserum (anti-Ss Phase I).
S. sonnei entry into epithelial cells is affected by the group 4 capsule
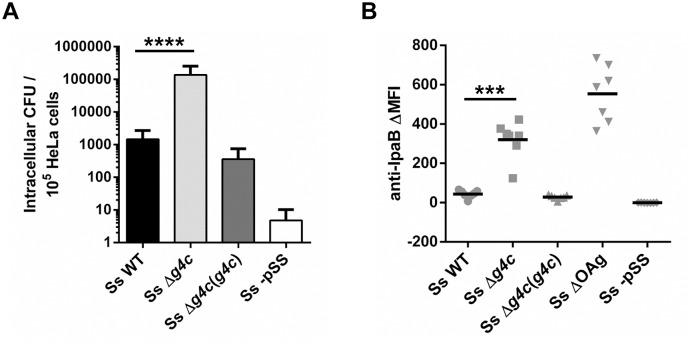
The invasiveness of S. sonnei WT and S. sonnei Δg4c was investigated in vitro by evaluating the number of intracellular bacteria after 1 h infection in HeLa cells (Fig. 4A). Uncapsulated S. sonnei Δg4c had about 100-fold more colony forming units (CFU) compared to the WT strain. Complementation of the g4c knockout in S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) reduced invasiveness of S. sonnei Δg4c by about 400-fold, resulting in 4-fold less intracellular bacteria than with S. sonnei WT. S. sonnei -pSS lacking the virulence plasmid did not invade HeLa cells, as expected [25]. These results show that the expression level of the capsule polysaccharide affects S. sonnei cell invasion in vitro. Thus, we investigated if the G4C masks critical elements of the invasion complex. Using flow cytometry (Fig. 4B) we examined the ability of a monoclonal antibody to bind to the invasion plasmid antigen B (IpaB) located at the tip of T3SS [36]. IpaB-dependent fluorescence on the surface of S. sonnei WT and S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) was only detected at a level comparable to the negative control. The anti-IpaB signal was stronger on the capsule-deficient S. sonnei Δg4c strain. By Western blot, similar amounts of IpaB protein were detected in S. sonnei WT and S. sonnei Δg4c (S5 Fig). Thus, the T3SS tip is more accessible in the absence of the capsule. IpaB was not detected by Western blot in S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) suggesting an interference of the excess of capsule material either with IpaB detection or with IpaB expression. The anti-IpaB staining on S. sonnei ΔOAg, lacking both the LPS OAg side chain and the G4C but still possessing the virulence plasmid, was further increased over the staining on uncapsulated S. sonnei Δg4c. S. sonnei -pSS was negative, as expected.
Fig 4. Group 4 capsule impacts S. sonnei HeLa cell invasion and IpaB exposure on the surface.
(A) HeLa epithelial cells were infected with S. sonnei WT (Ss WT), S. sonnei Δg4c (Ss Δg4c), S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) (Ss Δg4c(g4c)) or S. sonnei -pSS (Ss -pSS) at an MOI of 10. Columns show the average number and standard deviation (error bars) of intracellular bacteria (CFU) collected from 105 cells in three independent experiments in triplicate (****p<0.0001, Mann-Whitney test). (B) Flow cytometry analysis of IpaB exposure on the surface of live S. sonnei WT (Ss WT), S. sonnei Δg4c (Ss Δg4c), S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) (Ss Δg4c(g4c)), S. sonnei ΔOAg (Ss ΔOAg) and S. sonnei -pSS (Ss -pSS). Results are expressed as differential Mean Fluorescence Intensity (ΔMFI): the difference between the MFI of the anti-IpaB immune straining and the MFI of a control staining, using only the secondary antibody. Three independent experiments were performed, twice in triplicate and once as single assay. Individual results are shown as scatter plot, the mean ΔMFI is shown as line (***p = 0.0006, Mann-Whitney test).
Uncapsulated S. sonnei Δg4c triggers increased inflammation in the rabbit intestine but has decreased spreading ability and complement resistance
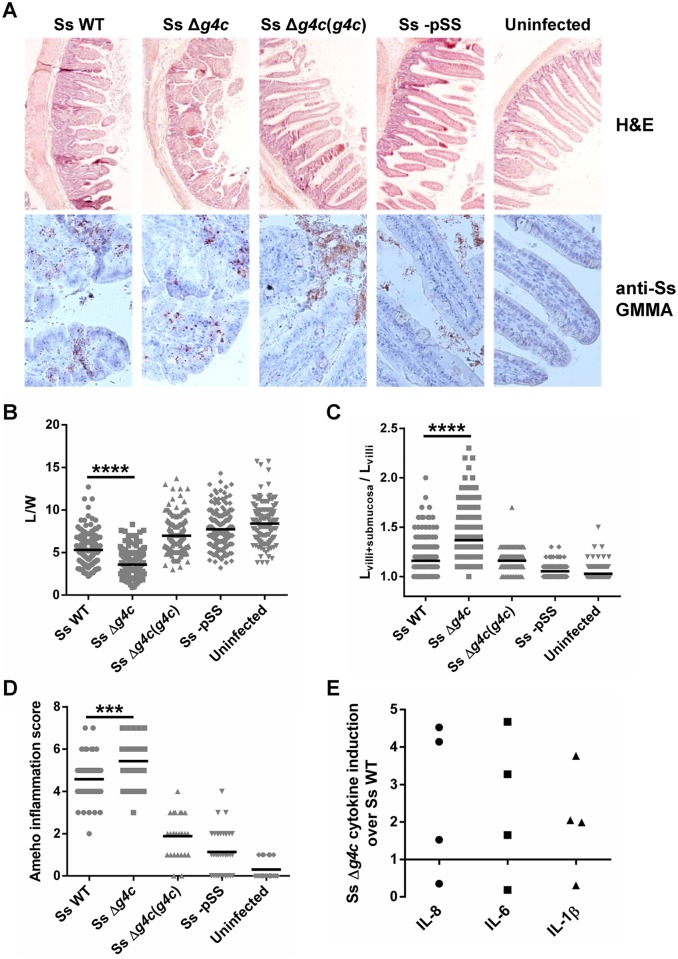
The impact of the capsule on S. sonnei virulence was tested in the rabbit ligated ileal loop model. Separate intestinal loops were infected with equal numbers (3x109) of S. sonnei WT, capsule-deficient S. sonnei Δg4c, complemented S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c), or S. sonnei -pSS per loop (3 replicate loops per animal for each strain). Eight hours after infection, local sites were examined for Shigella-dependent pathology, while peripheral sites were examined for the relative presence of the different S. sonnei strains. In the intestine, fluids and blood were present in the S. sonnei WT-infected loops. S. sonnei Δg4c caused more fluid and blood accumulation, with loops having pale outer surface and intense inflammation. The pathology observed with the complemented S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) strain was less severe than that with the WT, whereas the non-invasive S. sonnei -pSS barely caused fluid production and tissue alteration. Histopathology supported the qualitative data (Fig. 5A). Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stained slices showed alterations of villi from infected tissues and bacteria were detected by immunostaining with a polyclonal anti-S. sonnei GMMA serum. After infection by S. sonnei WT, villi were shortened and enlarged, with an average length to width ratio (L/W) of 5.3 (Fig. 5B), with several indentations. Numerous regions of tissue disruption were observed and infiltration of inflammatory cells was detected within the lamina propria and in the edematous submucosal tissues (Fig. 5C). These observations resulted in an inflammation score of 4.6, according to the Ameho criteria with grading scores from 0–6 [37] (Fig. 5D). Infection by S. sonnei Δg4c led to dramatic alterations of mucosal tissues with extensive zones of rupture and destruction of the intestinal epithelium, including epithelial detachment and loss of villi with tissue necrosis. Remaining villi had a lower L/W ratio (3.6) than villi in S. sonnei WT-infected loops (Fig. 5B). Submucosal tissues were strongly edematous (Fig. 5C), with a large area infiltrated by inflammatory cells between the residual mucosa and the muscular layer. These observations were graded as a very high 5.4 Ameho score (Fig. 5D). In accordance with the profound epithelial changes, following infection with both S. sonnei WT and S. sonnei Δg4c, most bacteria were associated with the lamina propria and the epithelium of the villi, particularly in areas of abscesses, rupture/destruction of the epithelial lining and of villi indentation (Fig. 5A). In contrast, slices from S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c)-infected tissues showed a lower level of pathology (Ameho score of 1.9), with villi with a length to width ratio (L/W of 7.0) similar to those following infection with S. sonnei -pSS or uninfected (L/W of 7.7 and 8.4, respectively), limited edema with few cells infiltrating the lamina propria, and few tissue lesions. The reduced severity of tissue damage in H&E-stained slices correlated with most of the S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) bacteria being present in the lumen instead of in the epithelium. Villi of loops infected with the avirulent S. sonnei -pSS strain were long and narrow, similar to the normal rabbit epithelial architecture of uninfected tissue, with no evidence of mucosal alteration, a low inflammation score of 1.1, and no invasive bacteria detected within the epithelium.
Fig 5. Group 4 capsule affects the pattern of S. sonnei pathology in the rabbit intestine.
(A) Representative results of histopathological analysis of S. sonnei WT (Ss WT), S. sonnei Δg4c (Ss Δg4c), S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) (Ss Δg4c(g4c)) and S. sonnei -pSS (Ss -pSS) infected loops after 8 h of single strain challenge. Control sample is the uninfected tissue. Upper row: Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining of 7 μm slices of rabbit ileal loops. Lower row: immunostaining of 7 μm slices of rabbit loops with a polyclonal S. sonnei GMMA antisera (anti-Ss GMMA) to demonstrate bacteria localization (red dots) and counterstaining with Hematoxylin. (B) Histological alteration observed in the rabbit model following 8 h infection by S. sonnei strains. Severity of villi atrophy is measured according to the ratio between the length and width (L/W) of 120 villi counted on each among at least 4 different loops in 2 different animals (****p<0.0001, Mann-Whitney test). (C) Severity of submucosal edema is measured according to the ratio between the length of the entire mucosal and submucosal layer and the length of the villi (Lvilli+submucosa/Lvilli). 120 measurements were performed on each among at least 4 different loops in 2 different animals (****p<0.0001, Mann-Whitney test). (D) Evaluation of the Shigella-induced pathology for each strain according to the Ameho histopathological grading scale was performed on at least 4 image fields of 4 different loops in 2 different animals (***p = 0.0001, Mann-Whitney test). (E) Induction of IL-8, IL-6 and IL-1β in rabbit loops by S. sonnei Δg4c (Ss Δg4c) relative to S. sonnei WT (Ss WT). Expression levels were measured by RT-qPCR in the set up experiment using an infectious dose of 5x109/loop (the other experiments used 3x109 bacteria/loop). Two loops per strain were inoculated in 2 different animals. The scatter plot shows induction of gene expression in S. sonnei Δg4c loops relative to the adjacent S. sonnei WT loop.
Pro-inflammatory cytokines were measured to further analyze the inflammatory response of the tissue in the infected loops. In an initial experiment to establish the infectious dose of S. sonnei in the rabbit ligated loop model, 5x109 bacteria per loop were used. At this dose, the S. sonnei Δg4c capsule-deficient strain induced, on average, higher levels of Interleukin 8 (IL-8), IL-6, and IL-1β compared to S. sonnei WT (Fig. 5E) but the number of replicate loops tested (2 each in 2 rabbits) was too small to reach statistical significance. The high induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines was accompanied by severe tissue destruction. Thus, for the main experiment a slightly lower infectious dose (3x109/loop) was chosen. At this dose, in general lower inflammation was observed. While the histology assessment showed a difference in the inflammatory potential of S. sonnei WT and Δg4c as described above, no difference was detected in the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, possibly since, at the lower dose, lesions are more dispersed and the analysis is performed on whole loops so that the results from the infected tissue are hidden by the results from the normal tissue.
In the same model used for assessing the Shigella-induced histopathology, we then investigated how the G4C contributes to S. sonnei dissemination by evaluating the bacterial load in mesenteric lymph nodes, spleen, liver, or blood. Eight hours after infection of separate intestinal loops in the same animal with S. sonnei WT, S. sonnei Δg4c, S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c), or S. sonnei-pSS the number of bacteria from these strains in the systemic organs was determined (Fig. 6A). In each organ S. sonnei WT bacteria predominated (on average 70% of the bacteria recovered in the specific organ). S. sonnei Δg4c bacteria accounted for 26% of bacteria per organ, and only a negligible number of S. sonnei -pSS and S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) bacteria was found peripherally.
Fig 6. Group 4 capsule affects S. sonnei peripheral spreading and sensitivity to direct complement lysis.
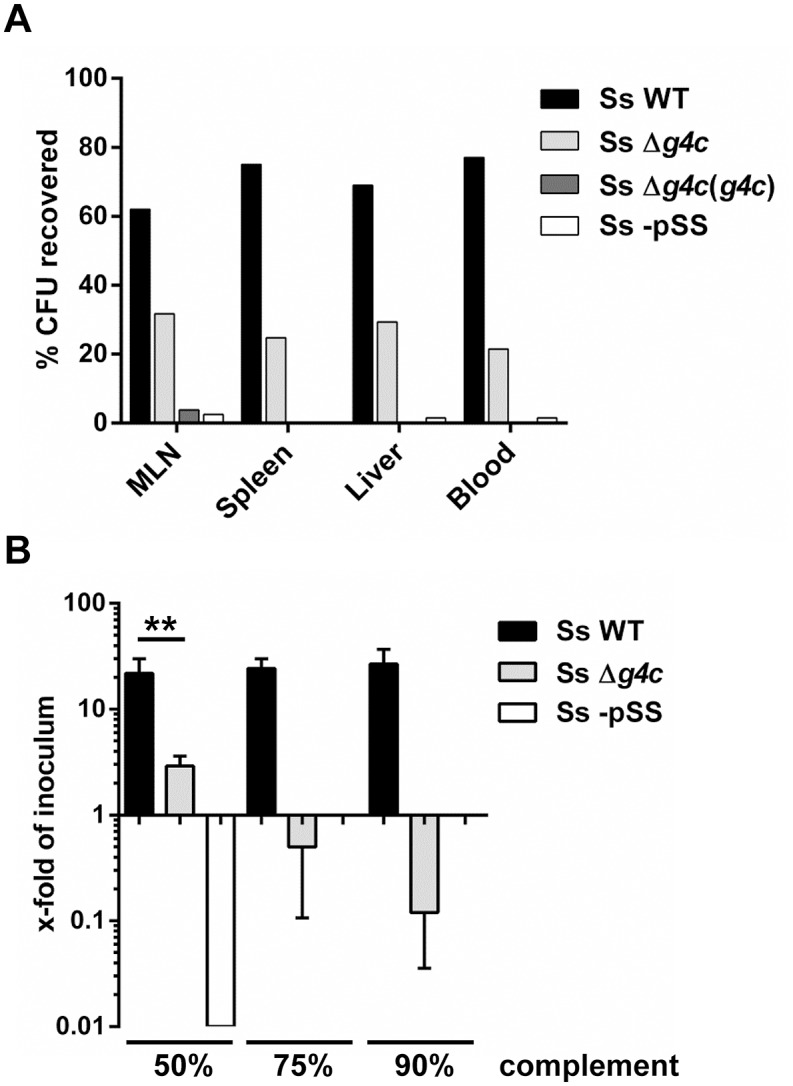
(A) Systemic load of S. sonnei WT (Ss WT), S. sonnei Δg4c (Ss Δg4c), S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) (Ss Δg4c(g4c)) and S. sonnei -pSS (Ss -pSS) bacteria following 8 h of single strain infection in separate loops (3 loops per strain) in the same animal. The different strains were enumerated by plating on solid media using the distinct antibiotic resistance profiles of the strains for their differentiation. The prevalence of individual strains in mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN), spleen, liver, or blood is reported as percent of CFU recovered from the specific organ. Results present the average counts of 2 animals. (B) Sensitivity of S. sonnei WT (Ss WT), S. sonnei Δg4c (Ss Δg4c) and S. sonnei -pSS (Ss -pSS) strains to increasing concentrations of baby rabbit complement (50, 75, and 90%). Assays with 3 h incubation were performed in triplicate in three independent experiments and the results are expressed as x-fold increase/decrease compared to the number of the bacteria in the inoculum. No colonies were retrieved after incubation of S. sonnei -pSS with 75% and 90% of complement. (**p = 0.0022, Mann-Whitney test).
Sensitivity to complement was assessed (Fig. 6B) as a measure for the ability of S. sonnei WT and uncapsulated S. sonnei Δg4c to survive in the systemic environment. S. sonnei WT was highly resistant to complement: even in 90% baby rabbit complement, the number of cells increased to 22-fold of the inoculum size during 3 h incubation (approximately 4.5 generations). In contrast, in 50% baby rabbit complement the number of cells of the capsule-deficient strain increased to only 3-fold of inoculum size and 90% baby rabbit complement resulted in killing of the mutant to a viable cell count of 10% of the inoculum. S. sonnei -pSS and S. flexneri 2a served as controls. As previously reported [38,39], S. sonnei -pSS was not able to survive in 50% complement (Fig. 6B), and S. flexneri 2a was more sensitive to complement than S. sonnei WT (S6 Fig). Thus, while the OAg is essential for resistance to serum lysis [38] the capsule strongly augments S. sonnei resistance to direct complement-mediated killing.
Collectively, these data show that the lack of capsule increases S. sonnei local pathogenicity but reduces peripheral dissemination, likely due to reduced complement resistance. Conversely, overexpression of capsule (S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c)) decreased dissemination, presumably because these bacteria failed to invade epithelial cells effectively.
Discussion
The presence of a group 4 capsule in S. sonnei was uncovered by the immunological characterization of the S. sonnei galU knockout deep rough mutant that does not possess an acceptor for the OAg polysaccharide on the LPS molecule. We demonstrated that this mutant still has the ability to assemble OAg units on the surface through an alternative pathway to form an OAg capsule, in accordance with the presence of an intact wbg OAg (Wzy-dependent [29]) synthesis cluster on the S. sonnei virulence plasmid, essential for both LPS OAg and OAg capsule. A low mobility material, not linked to the LPS, was extracted from S. sonnei WT and ΔgalU bacteria and was visualized in immunoblot analyses with a Phase I-specific antiserum. This observation was similar to the identification of a slowly migrating Phase I-reactive material in S. sonnei and in a Phase I-transformed Salmonella Typhi live vector vaccine candidate [18]. Although an OAg capsule-like material in S. sonnei has been suggested [40], no further studies have clarified this hypothesis. We found that SDS-PAGE analyses could not differentiate between LPS alone and LPS plus capsule, with both running with a smearing component. Thus, in the present study the identity of the S. sonnei G4C was confirmed by genetic and structural analyses. Genes homologous to those identified in E. coli for the G4C were found in different Shigella genomes [30]. In agreement with this finding, S. sonnei strains 53G and 046 were confirmed to have an intact g4c operon and its functionality in S. sonnei 53G was demonstrated. In contrast, our genomic analysis revealed that S. flexneri 2a strains 2457T and 301 carry an inactivated operon due to a deletion in the etk locus. Consequently, in S. flexneri 2a the ΔgalU mutation resulted in OAg deficiency as previously reported [21], as the strain lacks the capsule assembly system that would provide an alternative pathway for OAg surface expression to LPS.
We studied the biochemical characteristics of the S. sonnei G4C extracted from GMMA since these outer membrane preparations contain very low amounts of DNA and cytoplasmic components. We used G4C positive and negative isogenic mutants from hyperblebbing S. sonnei strains with stabilized virulence plasmid-driven expression of the OAg to obtain highly purified exopolysaccharide and demonstrated that the g4c cluster encodes for the formation of a high molecular weight polysaccharide with about 10 times higher molecular weight than the main medium molecular weight LPS population. Phase I antigen comprising both, LPS OAg and OAg capsule, is likely to be a common feature in the S. sonnei serogroup. For instance, a similar exopolysaccharide profile to S. sonnei 53G was found in a different S. sonnei isolate (25931, S2 Table). The LPS OAg and the capsular OAg share the same biosynthesis cluster. Accordingly, mutants in the wbg OAg operon (S. sonnei -pSS and S. sonnei ΔOAg) were both rough and uncapsulated. LPS core residues were found in the LPS-derived medium and low molecular weight polysaccharides, but not in the capsular polysaccharide, suggesting again that this population is not a high molecular weight LPS species, but is linked to the bacteria independently of the LPS. The S. sonnei Phase I polysaccharide has an uncommon zwitterionic structure [41] of sugars carrying a carboxylic group (C-4 of the FucNAc4N) and an amino group (C-6 of the L-AltNAcA) [9]. Given the presence of amino groups in the OAg units, fixation with formaldehyde is likely to cross-link the capsule and to bind it to LPS OAg and to surface proteins, making its detachment from the bacteria more difficult, as it was shown in EM and flow cytometry analyses. However, we found G4C bound to unfixed bacteria and on GMMA indicating that S. sonnei G4C is not completely released by bacteria. Therefore, the presence of a linker molecule could be envisaged. Structural analyses of G4C from Salmonella Enteritidis have shown that purified capsule has fatty acids at levels consistent with a lipid anchor [42]. Further studies are needed to test if the S. sonnei capsule is linked to the surface through such an anchor.
The current model of Shigella pathogenesis is mainly derived from studies of S. flexneri [1]. S. flexneri has a bimodal LPS OAg distribution including the so-called very long OAg that contributes to virulence in S. flexneri 2a [23] and is absent in S. sonnei [18]. Instead, as S. sonnei but not S. flexneri 2a was found to be encapsulated, we investigated the role of G4C as a S. sonnei specific virulence factor. We demonstrated that S. sonnei G4C, together with the LPS OAg, constitutes a dense outer layer that impacts on S. sonnei surface accessibility and invasive potential. For example, the exopolysaccharide layer masked antibodies raised against OAg-lacking outer membrane GMMA particles from recognizing their target epitopes in vitro. Bacterial capsules have been characterized to modulate the functionality of other virulence factors, such as adhesins in E. coli [43], fimbriae in Klebsiella [44] and pili in Neisseria [45]. G4C, in particular, have been shown to play critical roles in interactions between bacteria and their immediate environments [32] and hosts [31]. In pathogenic E. coli, G4C appeared to mask surface structures, inhibit the attachment of bacteria to tissue-cultured epithelial cells, diminish their capacity to induce the formation of actin pedestals, and attenuate T3SS-mediated protein translocation into host cells [31]. Similarly, in S. sonnei the presence of the capsule polysaccharide accounted for changes in cell invasion ability in vitro. Uncapsulated S. sonnei Δg4c were significantly more invasive than S. sonnei WT, while capsule overexpressing S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) strain displayed reduced cell entry. Thus, the in vitro studies indicated a role of the G4C in negatively affecting the invasive abilities of S. sonnei. The virulence of Shigella is mainly mediated by the activity of an array of plasmid-encoded virulence factors among which the T3SS is one of the most important [1]. We evaluated the possibility of capsule-mediated shielding of T3SS in S. sonnei. We observed that the accessibility of the IpaB protein at the tip of the T3SS was increased in vitro in S. sonnei Δg4c compared to the WT strain. As similar amounts of IpaB were detected by Western blot this showed that the G4C at least partially covers the tip of the T3SS. The importance of a balance between surface LPS OAg length and T3SS exposure in Shigella has been demonstrated for S. flexneri 5a M90T, which has evolutionarily acquired a phage-encoded OAg glucosylation, reported to have optimized the length of the OAg for T3SS function without compromising the protective properties of the LPS [24]. Shielding of T3SS by a G4C has also been found in EPEC and EHEC [31]. Still, expression of G4C has been shown to be required for efficient host colonization by EHEC in vivo, and to be inversely regulated to T3SS expression during different stages of pathogenesis [31]. Therefore, we used the rabbit model of experimental shigellosis to investigate G4C contribution to pathogenicity of S. sonnei in vivo and to the induction of inflammatory host responses during the infection. Analysis of infected rabbit tissues indicated that the lack of the capsule in S. sonnei Δg4c caused a dramatic increase of pathogenicity and inflammatory potential in the gut, particularly characterized by the augmentation of mucus and blood production in the infected loop, rupture and destruction of the epithelial lining, and tissue inflammatory manifestations as determined by villi atrophy, submucosal edema, and Ameho grading. In addition, induction of cytokine production of the infected epithelium was higher in S. sonnei Δg4c-infected loops than in S. sonnei WT-infected loops at the infectious dose of 5x109 bacteria/loop. We hypothesize that in uncapsulated bacteria, virulence factors are not shielded by the capsule polysaccharide and this facilitates bacterial adhesion and entry in the host cells. Concomitantly, the recognition of invasive bacteria by the innate immune system of the host could be enhanced in the absence of the capsule, as demonstrated for Neisseria [46], further augmenting the inflammatory response. In contrast, hyper-encapsulated S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) strain showed an attenuated phenotype, with less bacteria invading the epithelium and less tissue inflammation compared to WT. We cannot exclude that in addition to the larger amount of capsule other factors contribute to the attenuated phenotype as we could not detect IpaB by Western blot; and it is not clear if this is a technical artefact due to interference of the capsule material with the immunodetection or a true lack of IpaB in S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c). Moreover, the reduced pathogenicity of G4C-overexpressing S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) could be related not only to reduced invasiveness but also to higher host tolerance to encapsulated bacteria, as was shown for Salmonella serovars expressing Vi capsule [47].
In contrast to the stronger pathogenicity in the gut, lack of G4C reduced the ability of S. sonnei to spread to systemic infection sites. This was in accordance with enhanced complement sensitivity of S. sonnei Δg4c compared to the WT. Similarly, the presence of the very long OAg was shown to be important for resistance to direct complement-mediated serum killing in S. flexneri 2a [48]. Complement resistance could play a role at the stage of inflammation in epithelial lesions involving complement recruitment [48] and at the stage of systemic disease which is increasing in children and immunocompromised patients [7,8]. Therefore, the capsule could be an important virulence factor for S. sonnei to survive host killing, both locally and systemically, and might play a similar role in infection as the very long OAg in S. flexneri 2a. Capsule deficiency could be beneficial in the early stages of the infection for proficiently invading the intestinal epithelium, but with a disadvantage in translocation. If G4C expression in S. sonnei is regulated during pathogenesis as the G4C in EHEC [31], or in a growth-dependent manner as the very long OAg in S. flexneri [22] remains to be addressed.
In conclusion, in S. sonnei expression of the capsule modulates virulence and results in a successful phenotype in vivo, with balanced capabilities to invade and persist in the host environment. Based on the substantial changes in pathogenesis observed upon deletion or overexpression of the S. sonnei capsule, we hypothesize that its level of expression may be under significant evolutionary pressure.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial strains, mutant construction, and growth conditions
Shigella strains used in this work are listed and described in Table 1. All S. sonnei strains are derivatives of S. sonnei 53G [49] (S. sonnei WT), all S. flexneri 2a strains are derivatives of S. flexneri 2a 2457T [50]. The S. sonnei Phase II colony (S. sonnei -pSS) was isolated during in vitro cultivation of S. sonnei WT bacteria on TSB Congo red agar plates by screening for spontaneous loss of pSS [33]. The experimentally induced S. sonnei -pSS nalidixic acid resistant (NAR) strain was isolated by serial passages of S. sonnei -pSS on LB agar plates supplemented with increasing concentrations of nalidixic acid (from 10 to 50 μg/mL). S. sonnei ΔgalU was obtained using the same 3-step PCR method and materials as for generation of S. sonnei ΔtolRΔgalU [33]. OAg deletion in S. flexneri 2a was performed as previously described [51].
Table 1. Shigella strains used in this study, their abbreviation and a brief description of their phenotype.
| Strain Nomenclature and Genetic Background | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| S. sonnei WT S. sonnei 53G, +pSS | Phase I, carrying OAg-encoding virulence plasmid (pSS) | [49] |
| S. sonnei ΔgalU ΔgalU::cat, +pSS | LPS deep rough mutant. Knockout of galU blocks the synthesis of uridine diphosphoglucose (UDP-glucose), resulting in an incomplete LPS core with no OAg attached | This study |
| S. sonnei—pSS S. sonnei 53G, -pSS | Phase II, LPS OAg-deficient rough mutant. Avirulent | This study |
| S. sonnei -pSS NA R S. sonnei 53G, -pSS | S. sonnei -pSS, resistant to nalidixic acid. Used in in vivo experiments | This study |
| S. sonnei ΔOAg Δwbg::cat, +pSS | LPS OAg-deficient rough mutant. Knockout of wbg OAg biosynthesis cluster (genes wzz to wbgZ) on pSS. Growth on Cm selects for the presence of pSS | This study |
| S. sonnei Δg4c Δg4c::erm, +pSS | Group 4 capsule-deficient mutant. Knockout of g4c cluster coding sequence (genes ymcD to etk) | This study |
| S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) Δg4c::erm +pACYC(g4c), +pSS | Complementation of Δg4c null mutation using pACYC184 carrying functional g4c gene cluster. Growth on Cm selects for pACYC(g4c) | This study |
| S. sonnei ΔvirG ΔvirG::cat, +pSS | Gene virG in pSS replaced by chloramphenicol resistance gene. Growth on Cm selects for the presence of pSS and thus avoids loss of the wbg OAg cluster in vitro. WT LPS and capsule. Attenuated | This study |
| S. sonnei ΔtolR ΔtolR::kan, +pSS | Hyperblebbing S. sonnei WT. WT LPS and capsule | [33] |
| S. sonnei ΔtolRΔgalU ΔtolR::kan, ΔgalU::cat, +pSS | Hyperblebbing S. sonnei ΔgalU. LPS deep rough mutant | [33] |
| S. sonnei ΔtolR -pSS ΔtolR::kan, -pSS | Hyperblebbing S. sonnei -pSS. LPS OAg-deficient rough mutant | [33] |
| S. sonnei ΔtolRΔOAg ΔtolR::kan, Δwbg::cat, +pSS | Hyperblebbing S. sonnei ΔOAg. LPS OAg-deficient rough mutant | This study |
| S. sonnei ΔtolRΔvirG ΔtolR::kan, ΔvirG::cat, +pSS | Hyperblebbing S. sonnei ΔvirG. WT LPS and capsule | This study |
| S. sonnei ΔtolRΔvirGΔg4c ΔtolR::kan, ΔvirG::cat, Δg4c::erm, | Hyperblebbing S. sonnei Δg4c, with stabilized pSS-driven OAg expression. WT LPS, capsule-deficient | This study |
| S. flexneri 2a WT S. flexneri 2a 2457T, +pINV | WT LPS, carrying virulence plasmid (pINV) | [50] |
| S. flexneri 2a ΔgalU ΔgalU::Tn10, +pINV | LPS deep rough mutant. Knockout of galU results in an incomplete LPS core with no OAg attached | [21] |
| S. flexneri 2a ΔOAg ΔrfbG::erm, +pINV | LPS OAg-deficient rough mutant. Knockout of rfbG and partial deletion of flanking genes rfbF and rfc in OAg biosynthesis cluster on the chromosome | [51] |
For generating the other knockout mutants, the chloramphenicol resistance gene (cat) from pKOBEG [52] was used to replace S. sonnei virG [53], galU [21], and the wbg cluster, encoding the biosynthesis of the O repeating units, from gene wzz to wbgZ on pSS [20]. Erythromycin resistance gene (erm) from pAT110 [54] was used to replace the S. sonnei g4c operon coding sequence, from gene ymcD to gene etk [30]. Upstream and downstream flanking regions of the locus to be deleted and the antibiotic resistance gene chosen for replacement were amplified using the primers described in Table 2 and inserted into pBluescript (Stratagene), so that the antibiotic resistance cassette interposed the flanking regions. A linear replacement construct (upstream region—resistance cassette—downstream region) was amplified by PCR and transformed into recombination-prone Shigella cells, produced by using the highly proficient homologous recombination system (red operon) [55] encoded on pAJD434 [56]. The deletion of the g4c operon in S. sonnei Δg4c was complemented in trans as follows. The g4c gene cluster with the 280 bp upstream region was amplified by PCR (LongRange PCR Kit, QIAGEN) and cloned in pACYC184 (New England BioLabs) yield pACYC(g4c). g4c complementation in S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) was checked by exopolysaccharide expression.
Table 2. Primers used in this study.
| DELETION | PRIMERS | SEQUENCE |
|---|---|---|
| ΔOAg (S. sonnei) | wzz-5 Sac | ACTCGAGCTCGGCAGACTCAGCGCAAG |
| wzz-3 Sma | CTAACCCGGGCATTGACACAACAATACGTAACCCAG | |
| wgbZ-5 Sma | CTAACCCGGGTGCGATTTGGTAATGTACTCGG | |
| wgbZ-3 SalI | ACGCGTCGACATTGCTCGCTTGTGATAACAGC | |
| Δg4c | EcoRV.cps.3’.F | AGCTTGATATCcgcatggacaatacgtacgc |
| XhoI.cps.3’.R | CCGCTCGAGacgtgtggaattttgccgcg | |
| XbaI.cps.5’.F | CTAGTCTAGAgatcaagacagcgttgacgc | |
| EcoRV.cps.5’.R | AGCTTGATATCaactgaaagtggccggatgc | |
| ΔvirG | virGup-5 Sac | ACTCGAGCTCTGTAGTTGATTTGACAGTTGACATCC |
| virGup-3 Sma | CTAACCCGGGCACTATATTATCAGTAAGTGGTTGATAAACC | |
| virGdown-5 Sma | CTAACCCGGGCGTGTTGATGTCCTGC | |
| virGdown-3 Sal | ACGCGTCGACAGTTCAGTTCAGGCTGTACGC | |
| INSERTION | PRIMER | SEQUENCE |
| erm | EcoRV.Ery.F | AGCTTGATATCAGAGTGTGTTGATAGTGCAGTATC |
| EcoRV.Ery.R | AGCTTGATATCACCTCTTTAGCTTCTTGGAAGCT | |
| cat | EcoRV.Cm.F | AGCTTGATATCTGTGACGGAAGATCACTTCG |
| EcoRV.Cm.R | AGCTTGATATCGGGCACCAATAACTGCCTTA | |
| g4c [pACYC(g4c)] | XbaI.COMPLcps.5’.F | CTAGTCTAGACATCCGGCCACTTTCAGTTTTAC |
| SalI.COMPLcps.3’.R | ACGCGTCGACCAGCCAGTTATAGTACCACTTG |
E. coli and Shigella strains were routinely cultured in LB or in TSB medium. When needed, growth media were supplemented with 30 μg/mL kanamycin, 20 μg/mL chloramphenicol, 100 μg/mL erythromycin, 50 μg/mL nalidixic acid, 100 μg/mL trimethoprim, 100 μg/mL ampicillin.
GMMA preparation
GMMA were prepared as previously described [33] or from flask cultures as follows. Bacteria were grown in TSB medium in 1 L flasks to an OD600 of 5. Culture supernatants were collected by 10 min centrifugation at 4000 g and 0.22 μm filtered, concentrated using a 100 KDa regenerated cellulose membrane (Millipore) in a Stirred Ultrafiltration Cells (Amicon), separated from soluble proteins by 2 h ultracentrifugation at 186000 g at 4°C (Optima L‐series, 45Ti rotor, Beckman Instruments) and resuspended in phosphate buffer saline (PBS). All preparations were 0.22 μm filtered. GMMA protein concentration was quantified by Bradford Assay (Bio-Rad Protein Assay) using Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA, Thermo Scientific Pierce) as standard.
Mice immunization
Groups of 8 CD1 female mice of 4 to 6 weeks of age were immunized subcutaneously on days 0, 21 and 35 with 2 μg of GMMA of S. sonnei ΔtolR, S. sonnei ΔtolRΔgalU, and S. sonnei ΔtolR -pSS strains in 100 μL PBS, or with PBS alone. Blood samples were collected before the first immunization (preimmune sera) and 14 days after the third injection.
Bacterial surface staining coupled with flow cytometry analysis
Overnight (ON) Shigella cultures were diluted in TSB medium to OD600 = 0.05 and grown to OD600 = 0.5 (2.5x108 CFU/mL). Cells were collected and diluted to 2x107 CFU/mL. For formalin fixation, bacteria were diluted in 0.5% formalin solution in PBS and fixed with agitation ON at room temperature. Live or fixed bacteria were washed and resuspended in TSB. Primary staining was performed with mouse sera, the IpaB mouse monoclonal antibody (H16) [57], the S. sonnei Phase I monovalent rabbit antiserum (Denka Seiken, cat.# 295316), or the S. flexneri type II monovalent rabbit antiserum (Denka Seiken, cat.# 295019) at the desired dilution for 1 h at 4°C. For competitive staining experiments, 1:1000 diluted anti-S. sonnei ΔgalU GMMA sera were incubated with 11.25 μg of LPS (as quantified by phenol-sulfuric assay) [58] extracted from S. sonnei WT or S. sonnei -pSS bacteria, for 1 h at 4°C in PBS, prior to bacterial staining. After washing with 1% BSA in PBS, bacteria were incubated with Allophycocyanin-conjugated AffiniPure F(ab')2 fragment Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (Jackson ImmunoResearch) or with Alexa Fluor 488 F(ab′)2 fragment of Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) (Invitrogen) antibodies for 1 h on ice. Bacteria were washed, fixed with 4% formalin in PBS for 20 min on ice and analyzed for cell-bound fluorescence using a FACSCanto II flow cytometer (BD Biosciences). To evaluate IpaB exposure on the surface of S. sonnei WT, S. sonnei Δg4c, S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c), S. sonnei ΔOAg and S. sonnei -pSS bacteria were stained with the 1:50 dilution of the IpaB monoclonal antibody. For quantitative analyses, the differential Mean Fluorescence Intensity (ΔMFI) was measured as the difference between the MFI of the immune staining and the MFI of the control staining using the secondary antibody alone. Flow cytometry data were processed using FlowJo software (Tree Star).
LPS and capsule isolation
LPS and G4C crude extracts were prepared by the phenol-water method [59], with modifications. For total cellular extraction, ON Shigella cultures were diluted in 50 mL LB supplemented with antibiotics, if needed, to OD600 = 0.1 and grown until OD600 = 1. Bacteria were collected by centrifugation and resuspended in 500 μL PBS. After 5 min boiling, the mixture was treated with 0.5 μg/μL of Proteinase K (Thermo Scientific Pierce) at 60°C ON. An equal volume of saturated phenol solution (pH 8.0) (Sigma-Aldrich) was added and incubated for 1 h at 70°C with occasional mixing. After 1 h centrifugation at 10000 g, the upper aqueous phase was mixed with 2 volumes of absolute ethanol and incubated for 1 h at -70°C. Samples were centrifuged at 12000 g for 30 min and the pellet containing LPS and capsule polysaccharides was dried in a rotary vacuum drier (SpeedVac) and dissolved in distilled water. To obtain LPS and capsule material with minimal protein and nucleic acids contaminants, GMMA were used as starting outer membrane preparations. After Proteinase K incubation step, samples were treated as described above. The lipid A moiety of LPS was subsequently removed from phenol-water extracts by mild acid hydrolysis treatment with 1% acetic acid for 1.5 h at 100°C and adjusted to pH 6.5 with ammonium hydroxide. Samples were centrifuged at 15000 g ON and the supernatant, containing exopolysaccharide, was collected and dialyzed against distilled water.
Silver stained SDS-PAGE and western blot
Phenol-water extracts and total cell lysates were analyzed by 12% Bis‐Tris Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and silver stained using the SilverQuest Silver Staining Kit (Invitrogen). Samples were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and incubated with a 1:1000 dilution of the primary antibody, washed and then incubated with a 1:5000 dilution of the appropriate secondary antibody (Goat anti-Mouse IgG-Alkaline Phosphatase antibody, Sigma-Aldrich, or Goat anti-Rabbit IgG-Alkaline Phosphatase conjugate, Invitrogen). Immunoblots were developed using the SIGMAFAST BCIP/NBT tablet (Sigma-Aldrich) solution. At least two independent experiments were performed. Representative blots are shown.
Polysaccharide molecular weight distribution analysis
High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Size Exclusion Chromatography (HPLC-SEC) analysis was used to analyze the size distribution of exopolysaccharide populations and to isolate fractions of different molecular weight. Acid-cleaved exopolysaccharide samples were run on a TSK gel G3000 PWXL column (30 cm X 7.8 mm; particle size 7 μm; cat.# 808021) with a TSK gel PWXL guard column (4.0 cm X 6.0 mm; particle size 12 μm; cat.# 808033) (Tosoh Bioscience). The mobile phase was 0.1 M NaCl, 0.1 M NaH2PO4, 5% CH3CN, pH 7.2 at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min (isocratic method for 30 min). Void and bed volumes were calibrated with λ-DNA (λ-DNA Molecular Weight Marker III 0.12–21.2 Kbp, Roche) and sodium azide (Merck), respectively. Column void volume (T0): 10.58 min; total volume (Ttot): 23.03 min. Distribution coefficient, Kd = (Tretention—T0)/(Ttot—T0). Polysaccharide peaks were detected by differential refractive index (dRI) or at 214 nm, when run with a dextran standard curve (270–12 kDa range) to calculate the apparent average molecular weight. Exopolysaccharide was fractionated and collected as follow: HMW-PS, from 11.5 min to 13 min; MMW-PS, from 14 min to 16 min; LMW-PS, from 17 min to 18 min.
H1-NMR
1D proton NMR analysis was performed to confirm the identity of the polysaccharide samples. NMR spectra of isolated Phase I exopolysaccharide fractions were collected using a standard one-pulse experiment after solubilization of polysaccharide samples in deuterated water. Experiments were recorded at 25°C on Varian VNMRS-500 spectrometer, equipped with a Pentaprobe. Chemical shifts were referenced to hydrogen deuterium oxide (HDO) at 4.79 ppm. For data acquisition and processing VNMRJ ver. 2.2 rev. C and Mestrenova 6.1 (Mestrelab Research) were used respectively.
Electron microscopy of bacterial ultrathin sections
For alcian blue staining, single colonies were looped directly from the plate into fixative containing 2.5% glutaraldehyde, 2% paraformaldehyde, 0.075% alcian blue 8 GX and 50 mM L-lysine monohydrochloride in 0.025 M sodium acetate buffer at pH 5.7 for 2 hours at room temperature. Samples were then rinsed 3 times in buffer and post-fixed in 1% osmium tetroxide in 0.1 M sodium cacodylate buffer, rinsed again, dehydrated through an ethanol series, en bloc stained with 2% uranyl acetate at the 30% stage and embedded in TAAB 812 resin. Ultrathin 60 nm sections were cut on a Leica EM UC6 ultramicrotome, contrasted with uranyl acetate and lead citrate, examined on a 120 kV FEI Spirit Biotwin and imaged with a Tietz F4.15 CCD camera.
For immunogold-labelling, single colonies were looped into 2% paraformaldehyde and 0.25% glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (PB) at pH 7.4 for 1 hour at room temperature, rinsed 3 times in buffer, infiltrated with 1% and then 10% gelatin before immersing in 2.3 M sucrose in PB ON at 4°C for cryoprotection. Frozen samples were prepared by mounting onto aluminum pins and rapidly immersing in liquid nitrogen in preparation for ultrathin 80 nm sectioning on a Leica EM FC6 ultramicrotome. Ultrathin sections were labelled as per Tokuyasu [60], with the S. sonnei Phase I monovalent rabbit antiserum (dil. 1:25) and detected with 10 nm protein A gold. Imaging was performed as above. Thickness of Phase I material extending beyond the outer membrane was evaluated on different micrographs fields, as average of 20 measurements along the bacterial surface.
HeLa cells invasion assay
Invasiveness of the different S. sonnei strains was evaluated in vitro by using a gentamicin protection assay conducted on HeLa semiconfluent monolayers. Each condition was tested in triplicate in three independent experiments. Briefly, 5x105 HeLa cells/well (HeLa ATCC, CCL-2) were seeded ON in 6 well cell culture plates (Corning Costar) in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) high Glucose (Invitrogen), supplemented with 10% FBS (New Zealand, Invitrogen). The following day, Shigella ON cultures were diluted in TSB medium (supplemented with antibiotics, if needed) and grown to OD600 = 0.5. Bacteria were collected, diluted in DMEM and used to infect HeLa cells with a Multiplicity of Infection (MOI) of 10 bacteria/cell. After the addition of the bacteria, the cells were centrifuged at 1100 g for 18 min at 37°C and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. Subsequently, the monolayers were washed with PBS and the medium was replaced with DMEM containing 80 μg/mL gentamicin, to kill extracellular bacteria. After 2 h cells were washed and lysed by the addition of cold 0.5% sodium deoxycholate (Sigma-Aldrich) in water. Suitable dilutions were plated in triplicates on Congo red agar plates to determine the number of recovered viable intracellular bacteria.
Complement sensitivity assay
Shigella ON cultures were diluted in TSB medium and grown to OD600 = 0.5, equivalent to 2.5x108 Shigella bacteria/mL. Bacteria were collected, diluted to 10,000/mL in PBS and used as 10x suspension for the assay. Lyophilized baby rabbit complement (Cedarlane, CL3441) was reconstituted with 1 mL of sterile MilliQ water. The bacteria were mixed with reconstituted complement and PBS to yield 50%, 75%, 90% final complement concentration and an inoculum of 1000 bacteria/mL. Heat-inactivated complement was used as control. Bacterial counts were determined by plating on Congo Rod agar at time zero and after 3 h incubation at 37°C. To determine complement sensitivity of S. sonnei WT and S. sonnei Δg4c only red colonies possessing the OAg-encoding pSS virulence plasmid were counted at time zero as white colonies lacking pSS and thus the OAg are highly complement sensitive [38]. The results are expressed as x-fold increase/decrease of the cell count after incubation compared to the count at time zero (inoculum).
Rabbit ligated ileal loop model
Virulence of the different S. sonnei strains was evaluated in vivo by testing their ability to induce a Shigella-dependent gut pathology and to spread to systemic sites in the rabbit model of ligated ileal loops in New Zealand White rabbits weighing 2.5–3 kg (Charles River Breeding Laboratories, Wilmington, MA). In the main experiment, each loop was infected with 3x109 bacteria of a single strain in 500 μL of physiological saline buffer (0.9% NaCl). 12 loops per animal of 5 cm segments of ileum starting at the ileum-cecum transition were ligated, avoiding all Peyer’s patches, while maintaining the existing vasculature. Each strain was tested in 2 rabbits, in 3 replicate loops per rabbit, with a randomized order for each rabbit. Surgery was performed as described [61]. In a preliminary experiment, 5x109 bacteria/loop infectious dose was tested in 2 loops for each strain in 2 rabbits. After euthanasia, loops were dissected and processed for RNA extraction and histology. Uninfected tissues were collected as control. Mesenteric lymph nodes, spleen, liver and blood were collected and processed for bacterial counting. Appropriate dilutions of the different tissue samples were plated on selective and non-selective TSB-agar: S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) was identified by growth on chloramphenicol; S. sonnei Δg4c was enumerated by growth on erythromycin minus the counts of S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) determined on chloramphenicol as S. sonnei Δg4c(g4c) is resistant to both; S. sonnei -pSS was selected on nalidixic acid; S. sonnei WT does not carry any resistance markers and thus was counted by plating on non-selective medium and subtracting the number of the other strains determined on the selective media from the total number of CFU obtained on non-selective medium.
Tissue pathology analysis
For histopathological analysis of Shigella infected ileal loops and bacterial immune-localization, intestinal biopsies were fixed at 4°C in 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS, embedded in paraffin and sectioned into 7 μm slices using a microtome. Sections were deparaffinated, rehydrated and used for H&E staining, or for anti-Shigella immune staining.
Immune staining was performed as follows. Sections were permeabilized for 15 min with antigen unmasking solution (10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA, 0.05% Tween20, pH 9), treated with 3.3% H2O2 for 10 min and washed. Samples were blocked for 15 min with Ultra V block (Lab Vision Corp; Thermo Scientific, cat.# TA-125UB) and incubated ON with the in-house mouse polyclonal anti-S. sonnei serum raised against S. sonnei ΔtolR GMMA. Samples were then incubated with a peroxidase labelled polymer conjugated to goat anti-mouse immunoglobulins (DAKO, cat.# K4000) for 1 h, revealed with the 3-amino-9-ethylcarbzole AEC+ Substrate-Chromogen (DAKO, cat.# K3461), counterstained with hematoxylin and mounted with aqueous mounting medium (Merck). Histology images were taken using light microscopy, at 4X magnification for H&E staining, and at 20X magnification for immune staining.
Shigella-dependent intestinal inflammation and the degree of tissue alteration were assessed by evaluating the extent of villi atrophy and submucosal edema and by determining scores of inflammation according to the generally used criteria of the Ameho gradation scale [37], in slices from rabbit loops after 8 hours infection with 3x109 bacteria/loop of a single strain.
Pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β) gene expression was measured by RT-qPCR in rabbit loops after 8 hours infection with 5x109 bacteria/loop of a single strain. Primers and methods were previously described [61]. The expression levels of the cytokine genes were determined as fold induction over the housekeeping gene GAPDH in each loop. To compare expression levels elicited by S. sonnei Δg4c and S. sonnei WT the ratio of the fold induction (over GAPDH) in S. sonnei Δg4c infected loops and the fold induction in the adjacent S. sonnei WT infected loop was calculated.
List of Gene ID numbers
S. sonnei genes (S. sonnei 046): tolR: 3669577; virG: 3670887; galU: 3667724; wzz: 3670967; wzx: 3670970; wzy: 3670971; wbgZ: 3670977; ymcD: 3666464; ymcC: 3666463; ymcB: 3666462; ymcA: 3666461; yccZ: 3669961; etp (yccY): 3669960; etk (yccC): 3669959. S. flexneri genes (S. flexneri 2a 2457T): tolR: 1077009; galU: 1077674; rfbG: 1078499; rfbF: 1078523; rfc: 1078521.
Ethics statement
The mouse immunization experiments performed at the Novartis Animal Facility in Siena, Italy, complied with the relevant guidelines of Italy (Italian Legislative Decree n. 116/1992) and the institutional policies of Novartis. The animal protocol was approved by the Animal Welfare Body of Novartis Vaccines, Siena, Italy, and by the Italian Ministry of Health (Approval number AEC 2009–05). The experiments using the rabbit ileal loop model performed at Institut Pasteur, Paris, France, complied with the EU Directive 2010/63 and the French Decree 2013–118. The respective protocol was approved by the Comité Regional d’Éthique pour l’Expérimentation Animale in Paris 1 (protocol no.20070004) and reviewed by the Global Animal Welfare Board of Novartis.
Supporting Information
Flow cytometry analysis of surface staining of live S. sonnei WT (left column) and S. flexneri 2a WT (right column) with mouse sera raised against 109 formalin-fixed CFU of the corresponding WT (anti-WT), ΔOAg mutant with rough LPS (anti-ΔOAg), and ΔgalU mutant with deep rough LPS (anti-ΔgalU). Left column: S. sonnei WT was stained with sera raised against S. sonnei WT, S. sonnei ΔOAg generated by deletion of the S. sonnei wgb OAg biosynthesis cluster encoded on the virulence plasmid, or S. sonnei ΔgalU. Right column: S. flexneri 2a WT (S. flexneri WT) was stained with sera raised against S. flexneri 2a WT, S. flexneri 2a ΔOAg generated by deletion of the S. flexneri 2a rfb OAg biosynthesis cluster encoded on the chromosome, or S. flexneri 2a ΔgalU. Gray profiles: staining with preimmune sera; black profiles: staining with formalin-fixed bacteria antisera (S. sonnei (Ss) antisera binding and S. flexneri 2a (Sf) antisera binding). Sera dilution was 1:500. Representative results of three experiments are shown.
(TIFF)
Schematic representation of the S. sonnei g4c gene cluster (ymcDCBA, yccZ, etp, etk) in its genomic context with flanking genes (cspH, appA), built utilizing the Artemis browser (https://www.sanger.ac.uk/resources/software/artemis/) and the S. sonnei 046 genome sequence (NC_007384.1). In the S. sonnei Δg4c mutant the complete cluster from the start of ymcD to the end of etk has been removed. An alignment of Etk amino acid sequences of E. coli (Ec) 0127:H6 E2348/69, S. sonnei (Ss) 046, Ss 53G, S. flexneri (Sf) 2a 2457T and Sf 2a 301 is shown. A deletion of 14 bases (from position 135 to 148) in the etk locus causes a frame-shift mutation (effective at amino acid K47) affecting Sf 2a 2457T and Sf 2a 301. Asterisks indicate the presence of a stop codon in the corresponding DNA sequence.
(TIFF)
HPLC-SEC (dRI) analysis of acid-cleaved exopolysaccharide (EPS) purified from GMMA of hyperblebbing S. sonnei ΔgalU (ΔgalU EPS, dashed-dotted line) without stabilized virulence plasmid-driven expression of the OAg, in comparison to the trimodal Phase I EPS from S. sonnei GMMA (solid line). High molecular weight polysaccharides (HMW-PS) are present at similar retention time in both ΔgalU and Phase I EPS. Samples were run on TosoHaas TSK gel G3000 PWXL-CP column.
(TIFF)
Presence of 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO) at the reducing end of isolated S. sonnei Phase I polysaccharide populations after acid cleavage was estimated by semicarbazide assay for α-ketoacids determination by HPLC-SEC analysis, as described [62] (reaction in the square box). Derivatized polysaccharide fractions (high, medium, low molecular weight polysaccharides, respectively HMW, MMW, LMW-PS) were run on TosoHaas TSK gel G3000 PWXL-CP column. Detection was at 252 nm. Solid line: HMW-PS; dashed line: MMW-PS; dotted line: LMW-PS.
(TIFF)
IpaB-specific immunoblot analysis of total cell lysates of S. sonnei WT, S. sonnei Δg4c, S. sonnei ΔOAg and S. sonnei -pSS. 108 bacteria/lane were run on 12% Bis-Tris SDS-PAGE, blotted, and membranes were incubated with the IpaB monoclonal antibody (anti-IpaB) at a dilution of 1:1000.
(TIFF)
Sensitivity of S. sonnei WT (Ss WT) and S. flexneri 2a WT (Sf WT) to increasing concentrations of baby rabbit complement (50, 75, and 90%) in 3 h incubation. Assays were performed in triplicate in three independent experiments and the results are expressed as x-fold increase/decrease compared to the number of the bacteria in the inoculum (**p = 0.0087).
(TIF)
Average values and standard deviations (SD) of the differential Mean Fluorescence Intensity (ΔMFI) of three independent surface staining experiments of live or formalin-fixed S. sonnei strains with S. sonnei Phase I monovalent antiserum (anti-Ss Phase I).
(PDF)
Distribution coefficients (Kd) of high, medium and low molecular weight polysaccharides (HMW, MMW and LMW-PS) of acid-cleaved exopolysaccharide (EPS) purified from S. sonnei 53G and S. sonnei 25931 bacteria and analyzed by HPLC-SEC (dRI).
(PDF)
Acknowledgments
We thank Céline Mulet (Institut Pasteur) for help with histology, and Francesco Berlanda Scorza (NVGH), Giuseppe Stefanetti (NVGH), and Thomas Connor (WTSI) for discussion. We are grateful to Armelle Phalipon (Institut Pasteur) for providing the monoclonal IpaB antibody H16 and Shigella sonnei 25931 and to Maria Lina Bernardini (Università La Sapienza, Rome, Italy) for providing Shigella flexneri 2a ΔgalU.
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
The research was supported in part by the European Union Seventh Framework Programme [FP7/2007-2013] under Grant Agreement 261472 ‘STOPENTERICS’. http://ec.europa.eu/research/health/infectious-diseases/neglected-diseases/projects/016_en.html. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Schroeder GN, Hilbi H. Molecular pathogenesis of Shigella spp.: controlling host cell signaling, invasion, and death by type III secretion. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2008;21: 134–156. 10.1128/CMR.00032-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380: 2095–2128. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Kotloff KL, Nataro JP, Blackwelder WC, Nasrin D, Farag TH, Panchalingam S, et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): a prospective, case-control study. Lancet. 2013;382: 209–222. 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60844-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Bennish ML. Potentially lethal complications of shigellosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13 Suppl 4: S319–S324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Struelens MJ, Patte D, Kabir I, Salam A, Nath SK, Butler T. Shigella septicemia: prevalence, presentation, risk factors, and outcome. J Infect Dis. 1985;152: 784–790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Duncan B, Fulginiti VA, Sieber OF Jr, Ryan KJ. Shigella sepsis. Am J Dis Child. 1981;135: 151–154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Keddy KH, Sooka A, Crowther-Gibson P, Quan V, Meiring S, Cohen C, et al. Systemic shigellosis in South Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54: 1448–1454. 10.1093/cid/cis224 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Kligler RM, Hoeprich PD. Shigellemia. West J Med. 1984;141: 375–378. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Liu B, Knirel YA, Feng L, Perepelov AV, Senchenkova SN, Wang Q, et al. Structure and genetics of Shigella O antigens. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008;32: 627–653. 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00114.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Levine MM, Kotloff KL, Barry EM, Pasetti MF, Sztein MB. Clinical trials of Shigella vaccines: two steps forward and one step back on a long, hard road. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5: 540–553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Bennish ML, Harris JR, Wojtyniak BJ, Struelens M. Death in shigellosis: incidence and risk factors in hospitalized patients. J Infect Dis. 1990;161: 500–506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Vinh H, Nhu NT, Nga TV, Duy PT, Campbell JI, Hoang NV, et al. A changing picture of shigellosis in southern Vietnam: shifting species dominance, antimicrobial susceptibility and clinical presentation. BMC Infect Dis. 2009;9: 204 10.1186/1471-2334-9-204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Ud-Din AI, Wahid SU, Latif HA, Shahnaij M, Akter M, Azmi IJ, et al. Changing trends in the prevalence of Shigella species: emergence of multi-drug resistant Shigella sonnei biotype g in Bangladesh. PLoS One. 2013;8: e82601 10.1371/journal.pone.0082601 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Karaolis DK, Lan R, Reeves PR. Sequence variation in Shigella sonnei (Sonnei), a pathogenic clone of Escherichia coli, over four continents and 41 years. J Clin Microbiol. 1994;32: 796–802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Holt KE, Baker S, Weill FX, Holmes EC, Kitchen A, Yu J, et al. Shigella sonnei genome sequencing and phylogenetic analysis indicate recent global dissemination from Europe. Nat Genet. 2012;44: 1056–1059. 10.1038/ng.2369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Robin G, Cohen D, Orr N, Markus I, Slepon R, Ashkenazi S, et al. Characterization and quantitative analysis of serum IgG class and subclass response to Shigella sonnei and Shigella flexneri 2a lipopolysaccharide following natural Shigella infection. J Infect Dis. 1997;175: 1128–1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Kenne L, Lindberg B, Petersson K, Katzenellenbogen E, Romanowska E. Structural studies of the O-specific side-chains of the Shigella sonnei Phase I lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr Res. 1980;78: 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- 18. Xu DQ, Cisar JO, Ambulos JN Jr., Burr DH, Kopecko DJ. Molecular cloning and characterization of genes for Shigella sonnei form I O polysaccharide: proposed biosynthetic pathway and stable expression in a live Salmonella vaccine vector. Infect Immun. 2002;70: 4414–4423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Morona R, van den Bosch L, Manning PA. Molecular, genetic, and topological characterization of O-antigen chain length regulation in Shigella flexneri . J Bacteriol. 1995;177: 1059–1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Jiang Y, Yang F, Zhang X, Yang J, Chen L, Yan Y, et al. The complete sequence and analysis of the large virulence plasmid pSS of Shigella sonnei . Plasmid. 2005;54: 149–159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Sandlin RC, Lampel KA, Keasler SP, Goldberg MB, Stolzer AL, Maurelli AT. Avirulence of rough mutants of Shigella flexneri: requirement of O antigen for correct unipolar localization of IcsA in the bacterial outer membrane. Infect Immun. 1995;63: 229–237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Carter JA, Blondel CJ, Zaldívar M, Álvarez SA, Marolda CL, Valvano MA, et al. O-antigen modal chain length in Shigella flexneri 2a is growth-regulated through RfaH-mediated transcriptional control of the wzy gene. Microbiology. 2007;153: 3499–3507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Morona R, Daniels C, van den Bosch L. Genetic modulation of Shigella flexneri 2a lipopolysaccharide O antigen modal chain length reveals that it has been optimized for virulence. Microbiology. 2003;149: 925–939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. West NP, Sansonetti P, Mounier J, Exley RM, Parsot C, Guadagnini S, et al. Optimization of virulence functions through glucosylation of Shigella LPS. Science. 2005;307: 1313–1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Kopecko DJ, Washington O, Formal SB. Genetic and physical evidence for plasmid control of Shigella sonnei form I cell surface antigen. Infect Immun. 1980;29: 207–214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Sansonetti PJ, Kopecko DJ, Formal SB. Shigella sonnei plasmids: evidence that a large plasmid is necessary for virulence. Infect Immun. 1981;34: 75–83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Roberts IS. The biochemistry and genetics of capsular polysaccharide production in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1996;50: 285–315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Whitfield C. Biosynthesis and assembly of capsular polysaccharides in Escherichia coli . Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75: 39–68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Cuthbertson L, Mainprize IL, Naismith JH, Whitfield C. Pivotal roles of the outer membrane polysaccharide export and polysaccharide copolymerase protein families in export of extracellular polysaccharides in gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009;73: 155–177. 10.1128/MMBR.00024-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Peleg A, Shifrin Y, Ilan O, Nadler-Yona C, Nov S, Koby S, et al. Identification of an Escherichia coli operon required for formation of the O-antigen capsule. J Bacteriol. 2005;187: 5259–5266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Shifrin Y, Peleg A, Ilan O, Nadler C, Kobi S, Baruch K, et al. Transient shielding of intimin and the type III secretion system of enterohemorrhagic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by a group 4 capsule. J Bacteriol. 2008;190: 5063–5074. 10.1128/JB.00440-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Gibson DL, White AP, Snyder SD, Martin S, Heiss C, Azadi P, et al. Salmonella produces an O-antigen capsule regulated by AgfD and important for environmental persistence. J Bacteriol. 2006;188: 7722–7730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Berlanda Scorza F, Colucci AM, Maggiore L, Sanzone S, Rossi O, Ferlenghi I, et al. High yield production process for Shigella outer membrane particles. PLoS One. 2012;7: e35616 10.1371/journal.pone.0035616 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Robbins JB, Kubler-Kielb J, Vinogradov E, Mocca C, Pozsgay V, Shiloach J, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and immunogenicity in mice of Shigella sonnei O-specific oligosaccharide-core-protein conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106: 7974–7978. 10.1073/pnas.0900891106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Droge W, Lehmann V, Luderitz O, Westphal O. Structural investigations on the 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate region of lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1970;14: 175–184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Marteyn B, Gazi A, Sansonetti P. Shigella: a model of virulence regulation in vivo . Gut Microbes. 2012;3: 104–120. 10.4161/gmic.19325 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Ameho CK, Adjei AA, Harrison EK, Takeshita K, Morioka T, Arakaki Y, et al. Prophylactic effect of dietary glutamine supplementation on interleukin 8 and tumour necrosis factor alpha production in trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid induced colitis. Gut. 1997;41: 487–493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Madonna GS, Allen RC. Shigella sonnei phase I and phase II: susceptibility to direct serum lysis and opsonic requirements necessary for stimulation of leukocyte redox metabolism and killing. Infect Immun. 1981;32: 153–159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Okamura N, Nakaya R, Suzuki K, Kondo S, Hisatsune K, Imagawa Y, et al. Differences among Shigella spp. in susceptibility to the bactericidal activity of human serum. J Gen Microbiol. 1988;134: 2057–2065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Dharmasena MN, Hanisch BW, Wai TT, Kopecko DJ. Stable expression of Shigella sonnei form I O-polysaccharide genes recombineered into the chromosome of live Salmonella oral vaccine vector Ty21a. Int J Med Microbiol. 2013;303: 105–113. 10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Batta G, Liptak A, Schneerson R, Pozsgay V. Conformational stabilization of the altruronic acid residue in the O-specific polysaccharide of Shigella sonnei/Plesiomonas shigelloides . Carbohydr Res. 1997;305: 93–99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Snyder DS, Gibson D, Heiss C, Kay W, Azadi P. Structure of a capsular polysaccharide isolated from Salmonella Enteritidis. Carbohydr Res. 2006;341: 2388–2397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Schembri MA, Dalsgaard D, Klemm P. Capsule shields the function of short bacterial adhesins. J Bacteriol. 2004;186: 1249–1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Schembri MA, Blom J, Krogfelt KA, Klemm P. Capsule and fimbria interaction in Klebsiella pneumoniae . Infect Immun. 2005;73: 4626–4633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Virji M, Makepeace K, Peak IR, Ferguson DJ, Jennings MP, Moxon ER. Opc- and pilus-dependent interactions of meningococci with human endothelial cells: molecular mechanisms and modulation by surface polysaccharides. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18: 741–754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Lo H, Tang CM, Exley RM. Mechanisms of avoidance of host immunity by Neisseria meningitidis and its effect on vaccine development. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009;9: 418–427. 10.1016/S1473-3099(09)70132-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Raffatellu M, Santos RL, Chessa D, Wilson RP, Winter SE, Rossetti CA, et al. The capsule encoding the viaB locus reduces interleukin-17 expression and mucosal innate responses in the bovine intestinal mucosa during infection with Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi. Infect Immun. 2007;75: 4342–4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Hong M, Payne SM. Effect of mutations in Shigella flexneri chromosomal and plasmid-encoded lipopolysaccharide genes on invasion and serum resistance. Mol Microbiol. 1997;24: 779–791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Formal SB, Kent TH, May HC, Palmer A, Falkow S, LaBrec EH. Protection of monkeys against experimental shigellosis with a living attenuated oral polyvalent dysentery vaccine. J Bacteriol. 1966;92: 17–22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Formal SB, Dammin GJ, LaBrec EH, Schneider H. Experimental Shigella infections: characteristics of a fatal infection produced in guinea pigs. J Bacteriol. 1958;75: 604–610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Rossi O, Pesce I, Giannelli C, Aprea S, Caboni M, Citiulo F, et al. Modulation of Endotoxicity of Shigella Generalized Modules for Membrane Antigens (GMMA) by Genetic Lipid A Modifications: Relative Activation of TLR4 and TLR2 Pathways in Different Mutants. J Biol Chem. 2014;289: 24922–24935. 10.1074/jbc.M114.566570 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Chaveroche MK, Ghigo JM, d'Enfert C. A rapid method for efficient gene replacement in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans . Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28: E97 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Makino S, Sasakawa C, Yoshikawa M. Genetic relatedness of the basic replicon of the virulence plasmid in shigellae and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli . Microb Pathog. 1988;5: 267–274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Trieu-Cuot P, Poyart-Salmeron C, Carlier C, Courvalin P. Nucleotide sequence of the erythromycin resistance gene of the conjugative transposon Tn1545. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990;18: 3660 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Datsenko KA, Wanner BL. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97: 6640–6645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Maxson ME, Darwin AJ. Identification of inducers of the Yersinia enterocolitica phage shock protein system and comparison to the regulation of the RpoE and Cpx extracytoplasmic stress responses. J Bacteriol. 2004;186: 4199–4208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Barzu S, Nato F, Rouyre S, Mazie JC, Sansonetti P, Phalipon A. Characterization of B-cell epitopes on IpaB, an invasion-associated antigen of Shigella flexneri: identification of an immunodominant domain recognized during natural infection. Infect Immun. 1993;61: 3825–3831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. 1956;28: 350–356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Westphal O, Jann K. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides: extraction with phenol-water and further application of the procedure. 1965;5: 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- 60. Tokuyasu KT. Immunocytochemistry on ultrathin cryosections In: Specer DL, Goodman RD, Leinwand, editors. Cells, a laboratory manual. Subcellular localization of genes and their products. Cold Spring Harbour: Laboratory Press; 1997. pp. 131.1–131.27. [Google Scholar]
- 61. Schnupf P, Sansonetti PJ. Quantitative RT-PCR profiling of the rabbit immune response: assessment of acute Shigella flexneri infection. PLoS One. 2012;7: e36446 10.1371/journal.pone.0036446 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Micoli F, Rondini S, Gavini M, Pisoni I, Lanzilao L, Colucci AM, et al. A scalable method for O-antigen purification applied to various Salmonella serovars. Anal Biochem. 2013;434: 136–145. 10.1016/j.ab.2012.10.038 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Flow cytometry analysis of surface staining of live S. sonnei WT (left column) and S. flexneri 2a WT (right column) with mouse sera raised against 109 formalin-fixed CFU of the corresponding WT (anti-WT), ΔOAg mutant with rough LPS (anti-ΔOAg), and ΔgalU mutant with deep rough LPS (anti-ΔgalU). Left column: S. sonnei WT was stained with sera raised against S. sonnei WT, S. sonnei ΔOAg generated by deletion of the S. sonnei wgb OAg biosynthesis cluster encoded on the virulence plasmid, or S. sonnei ΔgalU. Right column: S. flexneri 2a WT (S. flexneri WT) was stained with sera raised against S. flexneri 2a WT, S. flexneri 2a ΔOAg generated by deletion of the S. flexneri 2a rfb OAg biosynthesis cluster encoded on the chromosome, or S. flexneri 2a ΔgalU. Gray profiles: staining with preimmune sera; black profiles: staining with formalin-fixed bacteria antisera (S. sonnei (Ss) antisera binding and S. flexneri 2a (Sf) antisera binding). Sera dilution was 1:500. Representative results of three experiments are shown.
(TIFF)
Schematic representation of the S. sonnei g4c gene cluster (ymcDCBA, yccZ, etp, etk) in its genomic context with flanking genes (cspH, appA), built utilizing the Artemis browser (https://www.sanger.ac.uk/resources/software/artemis/) and the S. sonnei 046 genome sequence (NC_007384.1). In the S. sonnei Δg4c mutant the complete cluster from the start of ymcD to the end of etk has been removed. An alignment of Etk amino acid sequences of E. coli (Ec) 0127:H6 E2348/69, S. sonnei (Ss) 046, Ss 53G, S. flexneri (Sf) 2a 2457T and Sf 2a 301 is shown. A deletion of 14 bases (from position 135 to 148) in the etk locus causes a frame-shift mutation (effective at amino acid K47) affecting Sf 2a 2457T and Sf 2a 301. Asterisks indicate the presence of a stop codon in the corresponding DNA sequence.
(TIFF)
HPLC-SEC (dRI) analysis of acid-cleaved exopolysaccharide (EPS) purified from GMMA of hyperblebbing S. sonnei ΔgalU (ΔgalU EPS, dashed-dotted line) without stabilized virulence plasmid-driven expression of the OAg, in comparison to the trimodal Phase I EPS from S. sonnei GMMA (solid line). High molecular weight polysaccharides (HMW-PS) are present at similar retention time in both ΔgalU and Phase I EPS. Samples were run on TosoHaas TSK gel G3000 PWXL-CP column.
(TIFF)
Presence of 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO) at the reducing end of isolated S. sonnei Phase I polysaccharide populations after acid cleavage was estimated by semicarbazide assay for α-ketoacids determination by HPLC-SEC analysis, as described [62] (reaction in the square box). Derivatized polysaccharide fractions (high, medium, low molecular weight polysaccharides, respectively HMW, MMW, LMW-PS) were run on TosoHaas TSK gel G3000 PWXL-CP column. Detection was at 252 nm. Solid line: HMW-PS; dashed line: MMW-PS; dotted line: LMW-PS.
(TIFF)
IpaB-specific immunoblot analysis of total cell lysates of S. sonnei WT, S. sonnei Δg4c, S. sonnei ΔOAg and S. sonnei -pSS. 108 bacteria/lane were run on 12% Bis-Tris SDS-PAGE, blotted, and membranes were incubated with the IpaB monoclonal antibody (anti-IpaB) at a dilution of 1:1000.
(TIFF)
Sensitivity of S. sonnei WT (Ss WT) and S. flexneri 2a WT (Sf WT) to increasing concentrations of baby rabbit complement (50, 75, and 90%) in 3 h incubation. Assays were performed in triplicate in three independent experiments and the results are expressed as x-fold increase/decrease compared to the number of the bacteria in the inoculum (**p = 0.0087).
(TIF)
Average values and standard deviations (SD) of the differential Mean Fluorescence Intensity (ΔMFI) of three independent surface staining experiments of live or formalin-fixed S. sonnei strains with S. sonnei Phase I monovalent antiserum (anti-Ss Phase I).
(PDF)
Distribution coefficients (Kd) of high, medium and low molecular weight polysaccharides (HMW, MMW and LMW-PS) of acid-cleaved exopolysaccharide (EPS) purified from S. sonnei 53G and S. sonnei 25931 bacteria and analyzed by HPLC-SEC (dRI).
(PDF)
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.