Abstract
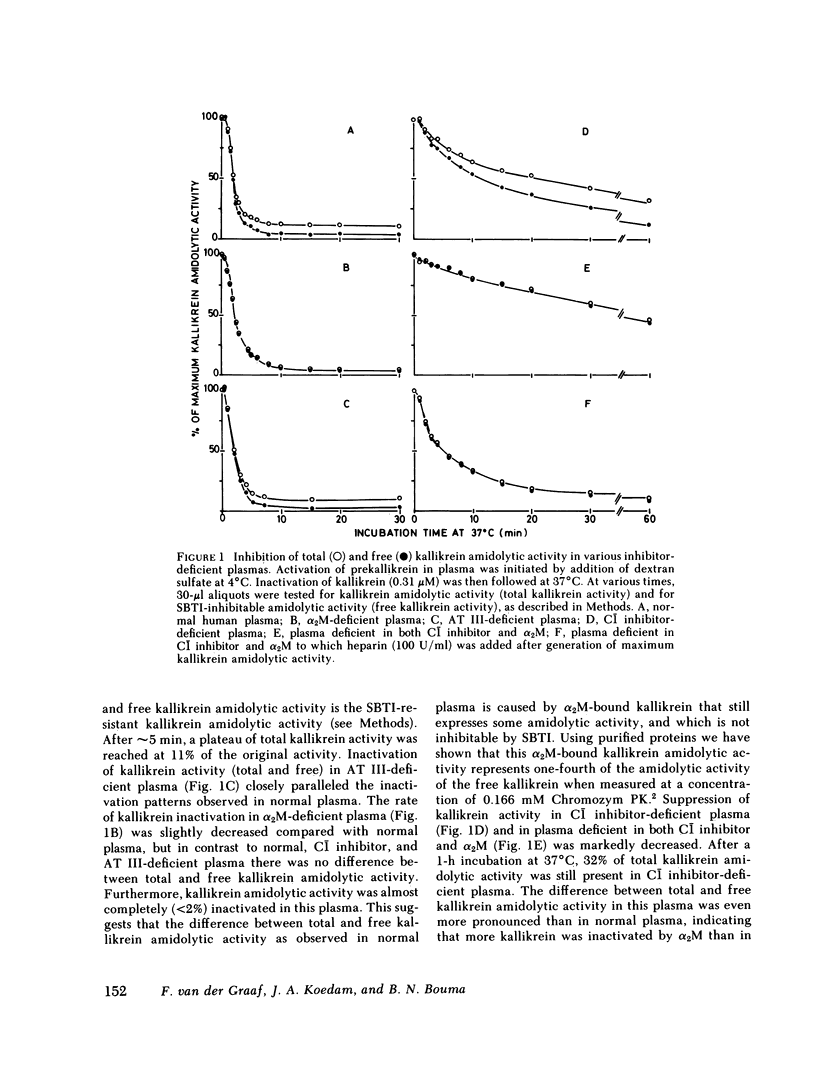
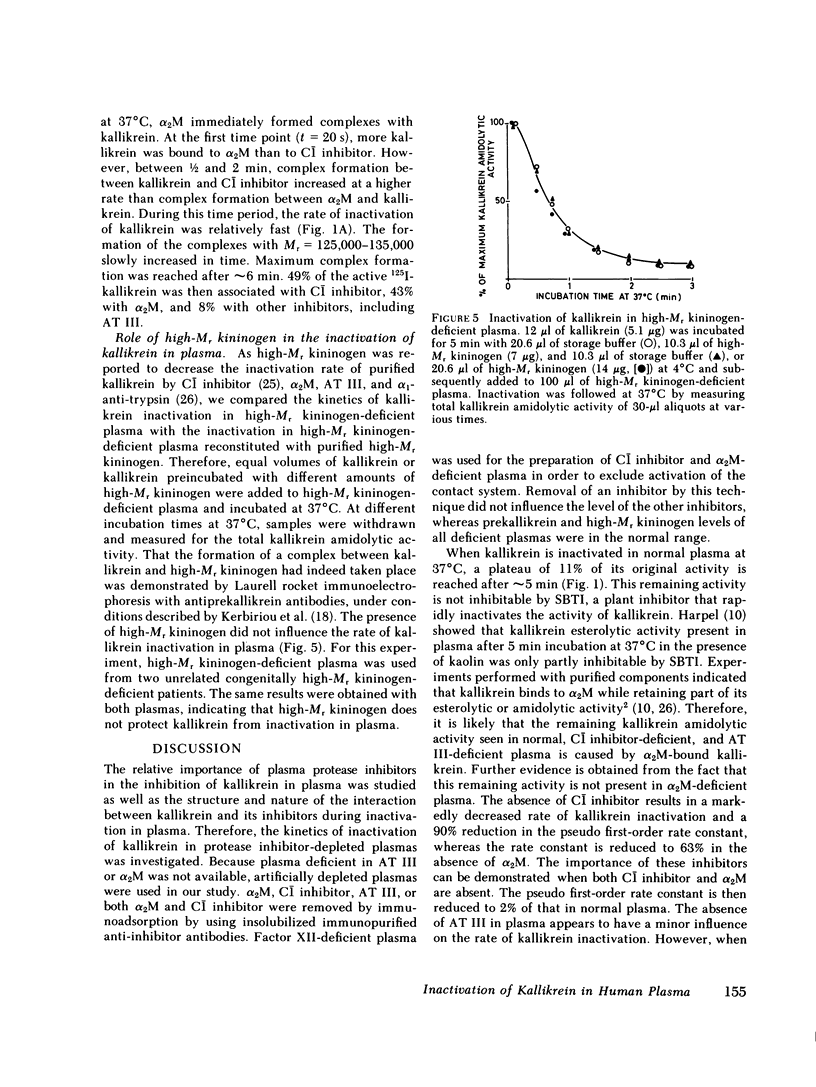
Human plasma kallikrein is inactivated by plasma protease inhibitors. This study was designed to determine the nature of these protease inhibitors and to assess their relative importance in the inactivation of kallikrein. Therefore, the kinetics of kallikrein inactivation and the formation of kallikrein inhibitor complexes were studied in normal plasma and in plasma depleted of either alpha 2-macroglobulin (alpha 2M), C1 inhibitor, or antithrombin (AT III). Prekallikrein was activated by incubation of plasma with dextran sulfate at 4 degrees C. After maximal activation, kallikrein was inactivated at 37 degrees C. Inhibition of kallikrein amidolytic activity in AT III-deficient plasma closely paralleled the inactivation rate of kallikrein in normal plasma. The inactivation rate of kallikrein in alpha 2M-deficient plasma was slightly decreased compared with normal plasma, but in contrast to normal, C1 inhibitor-deficient, and AT III-deficient plasma, no kallikrein amidolytic activity remained after inactivation that was resistant to inhibition by soybean trypsin inhibitor. Suppression of kallikrein activity in C1 inhibitor-deficient plasma was markedly decreased, and this was even more pronounced in plasma deficient in both C1 inhibitor and alpha 2M. The pseudo first-order rate constants for kallikrein inactivation in normal, AT III-deficient, alpha 2M-deficient, C1 inhibitor-deficient plasma, and plasma deficient in both alpha 2M and C1 inhibitor, were 0.68, 0.60, 0.43, 0.07, and 0.016 min-1, respectively. Sodium dodecyl sulfate gradient polyacrylamide slab gel electrophoresis showed that during inactivation of kallikrein in plasma, high-Mr complexes were formed with Mr at 400,000-1,000,000, 185,000, and 125,000-135,000, which were identified as complexes of 125I-kallikrein with alpha 2M, C1 inhibitor, and AT III, respectively. In addition, the presence of an unidentified kallikrein-inhibitor complex was observed in AT III-deficient plasma. 52% of the 125I-kallikrein was associated with C1-inhibitor, 35% with alpha 2M, and 13% with AT III and another protease inhibitor. A similar distribution of 125I-kallikrein was observed when the 125I-kallikrein inhibitor complexes were removed from plasma by immunoadsorption with insolubilized anti-C1 inhibitor, anti-alpha 2M, or anti-AT III antibodies. These results suggest that only covalent complexes are formed between kallikrein and its inhibitors in plasma. As a function of time, 125I-kallikrein formed complexes with C1 inhibitor at a higher rate than with alpha 2M. No difference was observed between the inactivation rate of kallikrein in high-Mr kininogen-deficient plasma and that in high-Mr kininogen-deficient plasma reconstituted with high-Mr kininogen; this suggests that high-Mr kininogen does not protect kallikrein from inactivation in the plasma milieu. These results have quantitatively demonstrated the major roles of C1 inhibitor and alpha 2M in the inactivation of kallikrein in plasma.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouma B. N., Miles L. A., Beretta G., Griffin J. H. Human plasma prekallikrein. Studies of its activation by activated factor XII and of its inactivation by diisopropyl phosphofluoridate. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1151–1160. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrowes C. E., Habal F. M., Movat H. Z. The inhibition of human plasma kallikrein by antithrombin III. Thromb Res. 1975 Jul;7(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. Activation of plasminogen by human plasma kallikrein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 29;35(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curd J. G., Prograis L. J., Jr, Cochrane C. G. Detection of active kallikrein in induced blister fluids of hereditary angioedema patients. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):742–747. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes C. D., Pensky J., Ratnoff O. D. Inhibition of activated Hageman factor and activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent by purified serum C1 inactivator. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Nov;76(5):809–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz H., Wunderer G., Kummer K., Heimburger N., Werle E. -Antitrypsin und c 1-inaktivator: progressiv-inhibitoren für serumkallikreine von mensch und schwein. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Jun;353(6):906–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore M. J., Amundsen E., Larsbraaten M., Lyngaas K., Fareid E. Studies on plasma inhibitors of plasma kallikrein using chromogenic peptide substrate assays. Thromb Res. 1979;16(5-6):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Mason J. W., Colman R. W., Austen K. F. Interaction of plasma kallikrein with the C1 inhibitor. J Immunol. 1970 Mar;104(3):574–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin. An inhibitor of plasma kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):329–352. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbiriou D. M., Bouma B. N., Griffin J. H. Immunochemical studies of human high molecular weight kininogen and of its complexes with plasma prekallikrein or kallikrein. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3952–3958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbiriou D. M., Griffin J. H. Human high molecular weight kininogen. Studies of structure-function relationships and of proteolysis of the molecule occurring during contact activation of plasma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12020–12027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri B., Bagdasarian A., Mitchell B., Talamo R. C., Colman R. W. Antithrombin-heparin cofactor: an inhibitor of plasma kallikrein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Aug;175(2):737–747. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90567-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIS J. Activation of plasma by contact with glass: evidence for a common reaction which releases plasma kinin and initiates coagulation. J Physiol. 1958 Nov 10;144(1):1–22. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandle R. J., Colman R. W., Kaplan A. P. Identification of prekallikrein and high-molecular-weight kininogen as a complex in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4179–4183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandle R., Jr, Kaplan A. P. Hageman factor substrates. Human plasma prekallikrein: mechanism of activation by Hageman factor and participation in hageman factor-dependent fibrinolysis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):6097–6104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell D. J. Inhibitors of kallikrein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1611–1623. doi: 10.1172/JCI106962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Pensky J., Ogston D., Naff G. B. The inhibition of plasmin, plasma kallikrein, plasma permeability factor, and the C'1r subcomponent of the first component of complement by serum C'1 esterase inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1969 Feb 1;129(2):315–331. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Goldsmith G. H., Moroi M., Aoki N. Inhibitory spectrum of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2013–2017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Contribution of plasma protease inhibitors to the inactivation of kallikrein in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):462–468. doi: 10.1172/JCI110470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Protection of human plasma kallikrein from inactivation by C1 inhibitor and other protease inhibitors. The role of high molecular weight kininogen. Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2738–2743. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., James A., Silver L. D., Kueppers F., James H. L., Colman R. W. High molecular weight kininogen or its light chain protects human plasma kallikrein from inactivation by plasma protease inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):567–572. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. Inhibition by C1INH of Hagemann factor fragment activation of coagulation, fibrinolysis, and kinin generation. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1402–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI107313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneröd A. M., Laake K. Inhibition of purified plasma kallikrein by antithrombin III and heparin. Thromb Res. 1975 Jul;7(1):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneröd A. M., Laake K., Solberg A. K., Strömland S. Inactivation and binding of human plasma kallikrein by antithrombin III and heparin. Thromb Res. 1976 Nov;9(5):457–466. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. S., Gallin J. I., Kaplan A. P. Fletcher factor deficiency. A diminished rate of Hageman factor activation caused by absence of prekallikrein with abnormalities of coagulation, fibrinolysis, chemotactic activity, and kinin generation. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):622–633. doi: 10.1172/JCI107597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D. Prekallikrein deficiency in man. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1345–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J. Activation of the early components of the classical complement pathway under physiologic conditions. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1769–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Graaf F., Keus F. J., Vlooswijk R. A., Bouma B. N. The contact activation mechanism in human plasma: activation induced by dextran sulfate. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1225–1233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




