Abstract
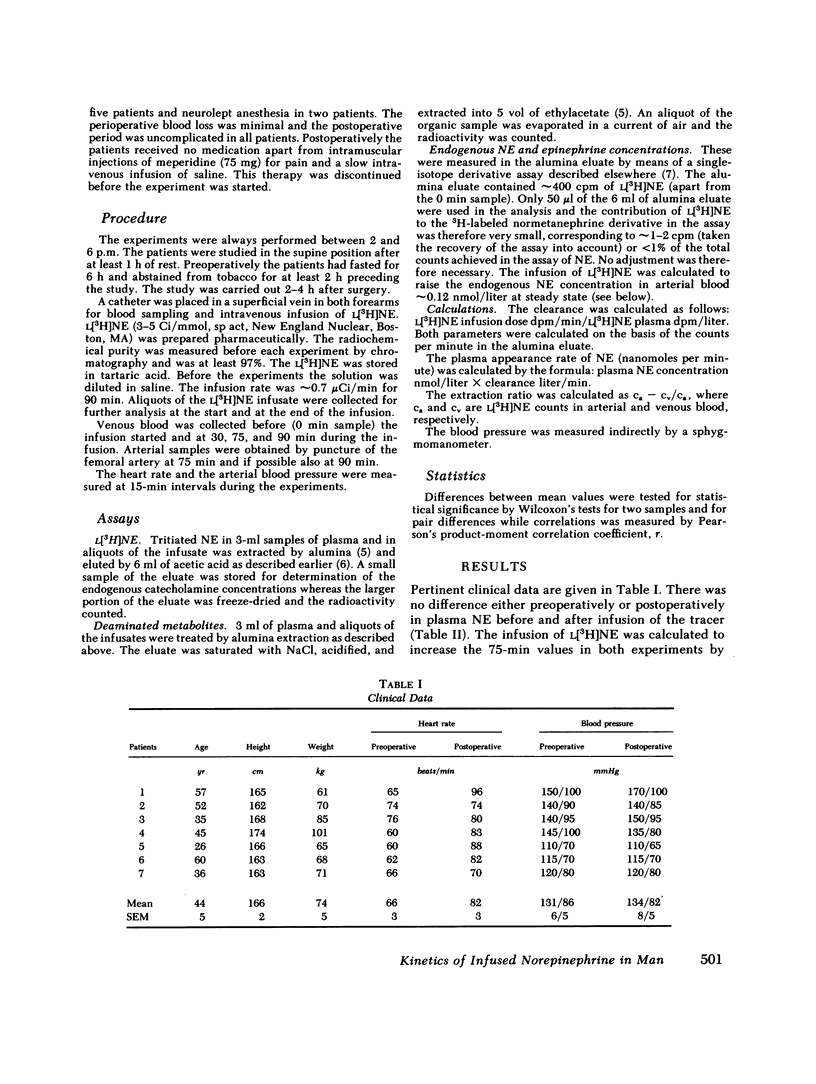
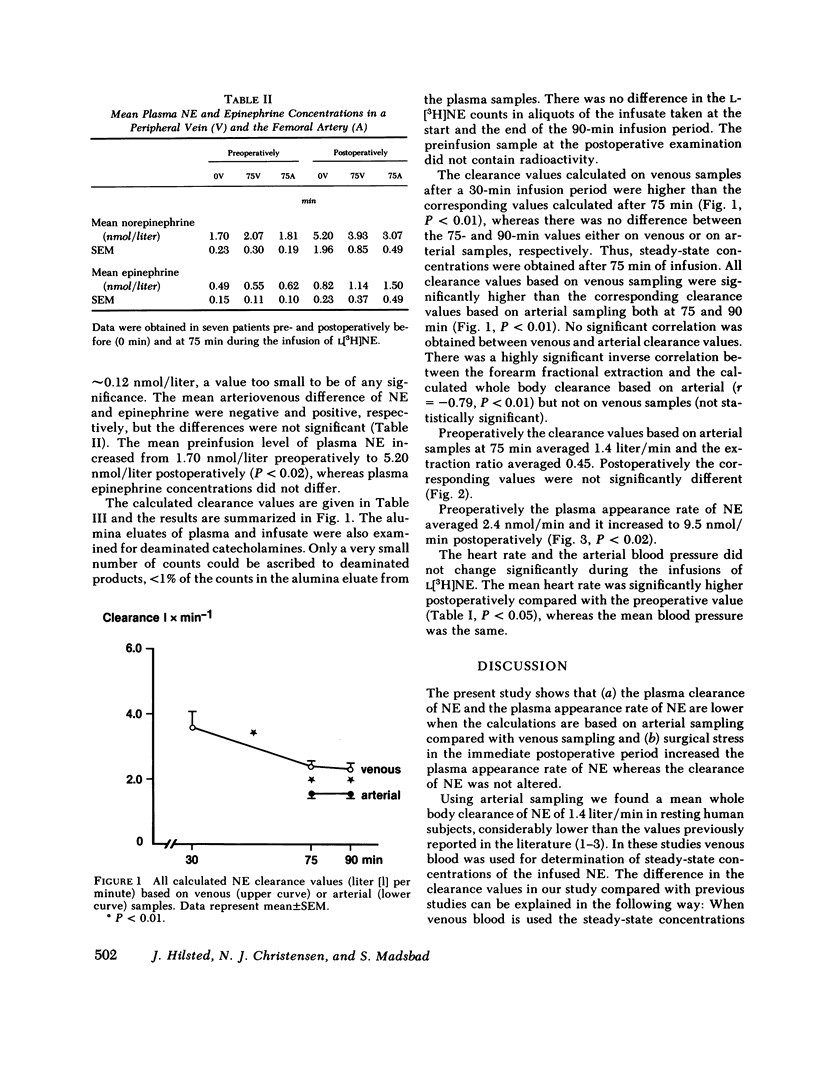
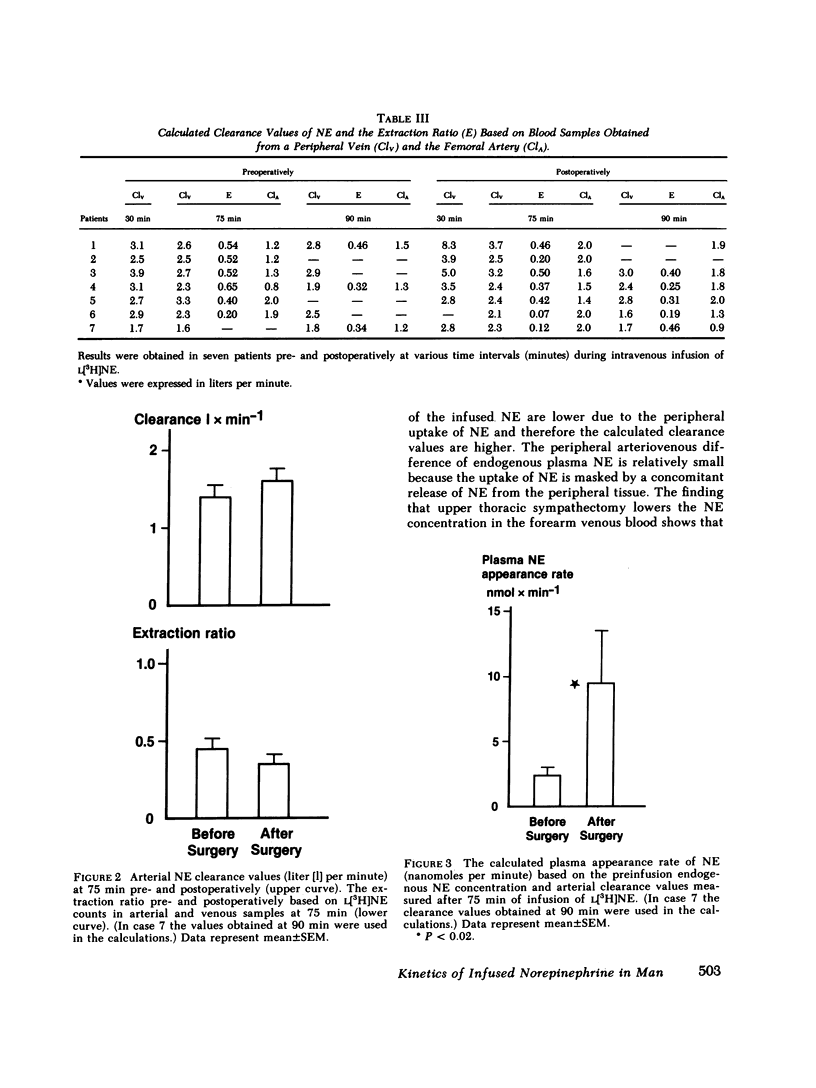
The whole body clearance of norepinephrine (NE) was measured in seven patients pre- and postoperatively. L[3H]NE was infused intravenously for 90 min and steady-state concentrations of L[3H]NE were measured at 75 and 90 min in both arterial and peripheral venous blood. Preoperatively, in the resting supine position, the clearance values based on arterial and venous sampling averaged 1.4 and 2.5 liter/min, respectively (P < 0.02). The difference in clearance values was due to a peripheral uptake of NE averaging 45%.
The mean plasma NE increased from 1.70 nmol/liter preoperatively to 5.20 nmol/liter postoperatively (P < 0.02). The plasma appearance rate of NE averaged 2.4 nmol/min before surgery and it increased to 9.5 nmol/min postoperatively (P < 0.02). The plasma clearance of NE averaged 1.4 and 1.6 liter/min pre- and postoperatively, respectively (not significantly different).
Our study demonstrates that the calculation of plasma NE clearance based on venous sampling results in values that are too high. Furthermore, such values may be influenced by individual variations in the peripheral uptake of NE, since we found no correlation between clearance values based on venous and arterial sampling. The increase in plasma NE postoperatively was due to an increase in the plasma appearance rate of NE because the clearance rate did not change.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Best J. D., Halter J. B. Release and clearance rates of epinephrine in man: importance of arterial measurements. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Aug;55(2):263–268. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J. Plasma noradrenaline and adrenaline in patients with thyrotoxicosis and myxoedema. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Aug;45(2):163–171. doi: 10.1042/cs0450163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J. Sympathetic nervous activity and age. Eur J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;12(2):91–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J., Vestergaard P., Sørensen T., Rafaelsen O. J. Cerebrospinal fluid adrenaline and noradrenaline in depressed patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1980 Feb;61(2):178–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1980.tb00577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubocovich M. L., Langer S. Z. Influence of the frequency of nerve stimulation on the metabolism of 3H-norepinephrine released from the perfused cat spleen: differences observed during and after the period of stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jul;198(1):83–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M., Jackman G., Bobik A., Kelleher D., Jennings G., Leonard P., Skews H., Korner P. Determination of norepinephrine apparent release rate and clearance in humans. Life Sci. 1979 Oct 22;25(17):1461–1470. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90371-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald G. A., Hossmann V., Hamilton C. A., Reid J. L., Davies D. S., Dollery C. T. Interindividual variation in kinetics of infused epinephrine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Dec;26(6):669–675. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979266669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehlet H., Brandt M. R., Rem J. Role of neurogenic stimuli in mediating the endocrine-metabolic response to surgery. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1980 Mar-Apr;4(2):152–156. doi: 10.1177/014860718000400216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen S. E., Eide I., Christensen C., Westheim A., Müller O. Renal contribution to plasma catecholamines--effect of age. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1982 Sep;42(5):461–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. L., Christensen N. J., Olsen N., Lassen N. A. Raynaud's phenomenon: peripheral catecholamine concentration and effect of sympathectomy. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1980;502:57–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorie D. K., Muldoon S. M., Tyce G. M. Disposition of norepinephrine during nerve stimulation in dog saphenous vein. Am J Physiol. 1980 Aug;239(2):H238–H246. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.239.2.H238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A. Flow dependence of norepinephrine extraction by isolated perfused rat lungs. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):H844–H848. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1982.242.5.H844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg A. B., Shah S. D., Haymond M. W., Cryer P. E. Norepinephrine: hormone and neurotransmitter in man. Am J Physiol. 1978 Mar;234(3):E252–E256. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.3.E252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sole M. J., Drobac M., Schwartz L., Hussain M. N., Vaughan-Neil E. F. The extraction of circulating catecholamines by the lungs in normal man and in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 1979 Jul;60(1):160–163. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.60.1.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Kaijser L., Mathé A., Birke G. Specific and unspecific removal of circulating noradrenaline in pulmonary and systemic vascular beds in man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Sep;95(1):46–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb10023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin B. G., Sundlöf G., Eriksson B. M., Dominiak P., Grobecker H., Lindblad L. E. Plasma noradrenaline correlates to sympathetic muscle nerve activity in normotensive man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Jan;111(1):69–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



