Abstract
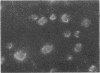
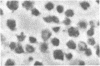
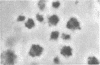
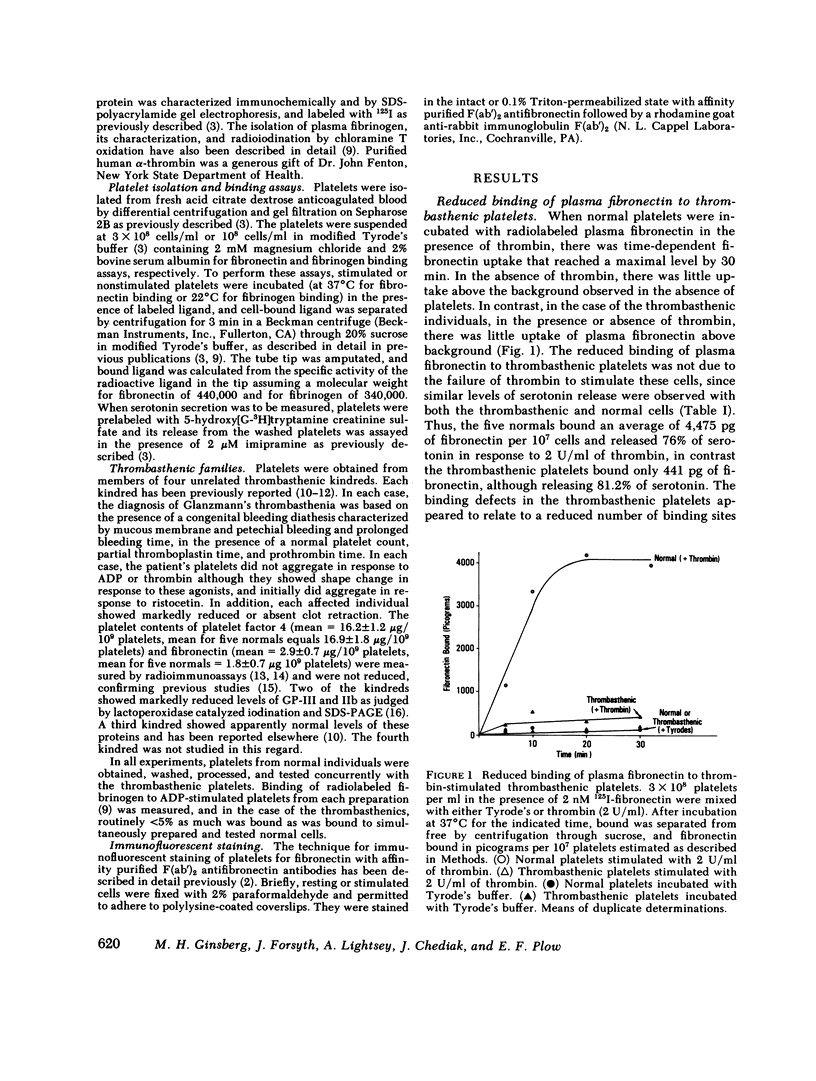
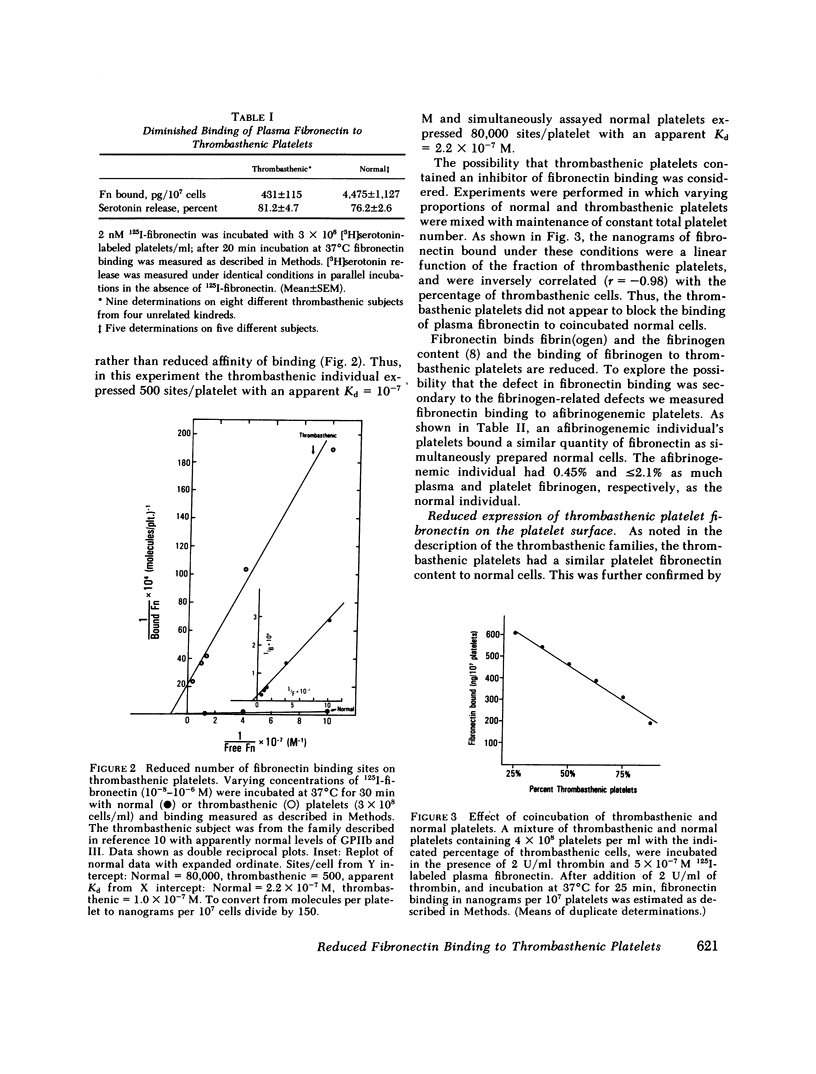
Thrombin stimulation results in increased surface expression of endogeneous fibronectin and binding of plasma fibronectin to human platelets. Platelets of patients with Glanzmann's thrombasthenia, a bleeding disorder, exhibit reduced thrombin-induced platelet aggregation, little or no clot retraction, and abnormal platelet spreading on glass surfaces. Thrombin stimulation of patient platelets from four thrombasthenic kindreds resulted in little fibronectin binding. Nevertheless, thrombin did induce serotonin secretion from these cells, indicating that stimulation was occurring. Thrombasthenic platelets did not inhibit thrombin-stimulated fibronectin binding to coincubated normal cells, suggesting that their defect was not due to the presence of a soluble inhibitor of fibronectin binding. Thrombin-stimulated afibrinogenemic platelets bound similar quantities of fibronectin to normal cells, indicating that the thrombasthenic deficit is not secondary to reduced fibrinogen content or binding. The thrombasthenic cells had an endogenous fibronectin content of 2.9 +/- 0.7 micrograms/10(9) platelets, whereas cells simultaneously prepared from five normal individuals contained 1.8 +/- 0.7 micrograms/10(9) platelets, a statistically insignificant difference. Nevertheless, thrombin stimulation did not increase expression of endogeneous fibronectin antigen on the surface of the thrombasthenic platelets as judged by immunofluorescence. These defects in platelet fibronectin binding and surface expression may account for some of the manifestations of Glanzmann's thrombasthenia.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arneson M. A., Hammerschmidt D. E., Furcht L. T., King R. A. A new form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Fibronectin corrects defective platelet function. JAMA. 1980 Jul 11;244(2):144–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. S., Vilaire G. Exposure of platelet fibrinogen receptors by ADP and epinephrine. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1393–1401. doi: 10.1172/JCI109597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chazov E. I., Alexeev A. V., Antonov A. S., Koteliansky V. E., Leytin V. L., Lyubimova E. V., Repin V. S., Sviridov D. D., Torchilin V. P., Smirnov V. N. Endothelial cell culture on fibrillar collagen: model to study platelet adhesion and liposome targeting to intercellular collagen matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5603–5607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chediak J., Telfer M. C., Vander Laan B., Maxey B., Cohen I. Cycles of agglutination-disagglutination induced by ristocetin in thrombasthenic platelets. Br J Haematol. 1979 Sep;43(1):113–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb03726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I., Potter E. V., Glaser T., Entwistle R., Davis L., Chediak J., Anderson B. Fibronectin in von Willebrand's disease and thrombasthenia: role in platelet aggregation. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Jan;97(1):134–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donati M. B., Balconi G., Remuzzi G., Borgia R., Morasca L., de Gaetano G. Skin fibroblasts from a patient with Glanzmann's thrombasthenia do not induce fibrin clot retraction. Thromb Res. 1977 Jan;10(1):173–174. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90092-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Hoskins R., Sigrist P., Painter R. G. Purification of a heparin-neutralizing protein from rabbit platelets and its homology with human platelet Factor 4. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12365–12371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Painter R. G., Forsyth J., Birdwell C., Plow E. F. Thrombin increases expression of fibronectin antigen on the platelet surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1049–1053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Plow E. F., Forsyth J. Fibronectin expression on the platelet surface occurs in concert with secretion. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;17(1):91–98. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.380170111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell F., Hays D. G. Cell adhesion and spreading factor. Similarity to cold insoluble globulin in human serum. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Aug;115(1):221–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90419-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Ali I. U., Destree A. T., Mautner V., Perkins M. E., Senger D. R., Wagner D. D., Smith K. K. A large glycoprotein lost from the surfaces of transformed cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:317–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marguerie G. A., Edgington T. S., Plow E. F. Interaction of fibrinogen with its platelet receptor as part of a multistep reaction in ADP-induced platelet aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):154–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEver R. P., Baenziger N. L., Majerus P. W. Isolation and quantitation of the platelet membrane glycoprotein deficient in thrombasthenia using a monoclonal hybridoma antibody. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1311–1318. doi: 10.1172/JCI109983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor J. L., Clemetson K. J., James E., Capitanio A., Greenland T., Lüscher E. F., Dechavanne M. Glycoproteins of platelet membranes from Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. A comparison with normal using carbohydrate-specific or protein-specific labelling techniques and high-resolution two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May 15;116(2):379–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Fibronectin. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1980;5:111–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Budzynski A. Z., Morinelli T. A., Brudzynski T. M., Stewart G. J. Exposure of fibrinogen receptor on human platelets by proteolytic enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):917–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Caen J. P. The different glycoprotein abnormalities in thrombasthenic and Bernard-Soulier platelets. Semin Hematol. 1979 Jul;16(3):234–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I., Zucker M. B., Grant R. A., Egan J. J., Johnson M. M. Correlation between fibrinogen binding to human platelets and platelet aggregability. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):841–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet membrane defects in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Evidence for decreased amounts of two major glycoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):535–545. doi: 10.1172/JCI108805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Birdwell C., Ginsberg M. H. Identification and quantitation of platelet-associated fibronectin antigen. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):540–543. doi: 10.1172/JCI109334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Specific and saturable binding of plasma fibronectin to thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9477–9482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remuzzi G., Marchesi E., de Gaetano G., Donati M. B. [Abnormal tissue repair in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia]. Lancet. 1977 Feb 12;1(8007):374–375. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Vaheri A. Interaction of soluble fibroblast surface antigen with fribrinogen and fibrin. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):497–501. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg B. M., Smith K., Colozzo M., Pollack R. Establishment and transformation diminish the ability of fibroblasts to contract a native collagen gel. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):304–308. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]