Abstract
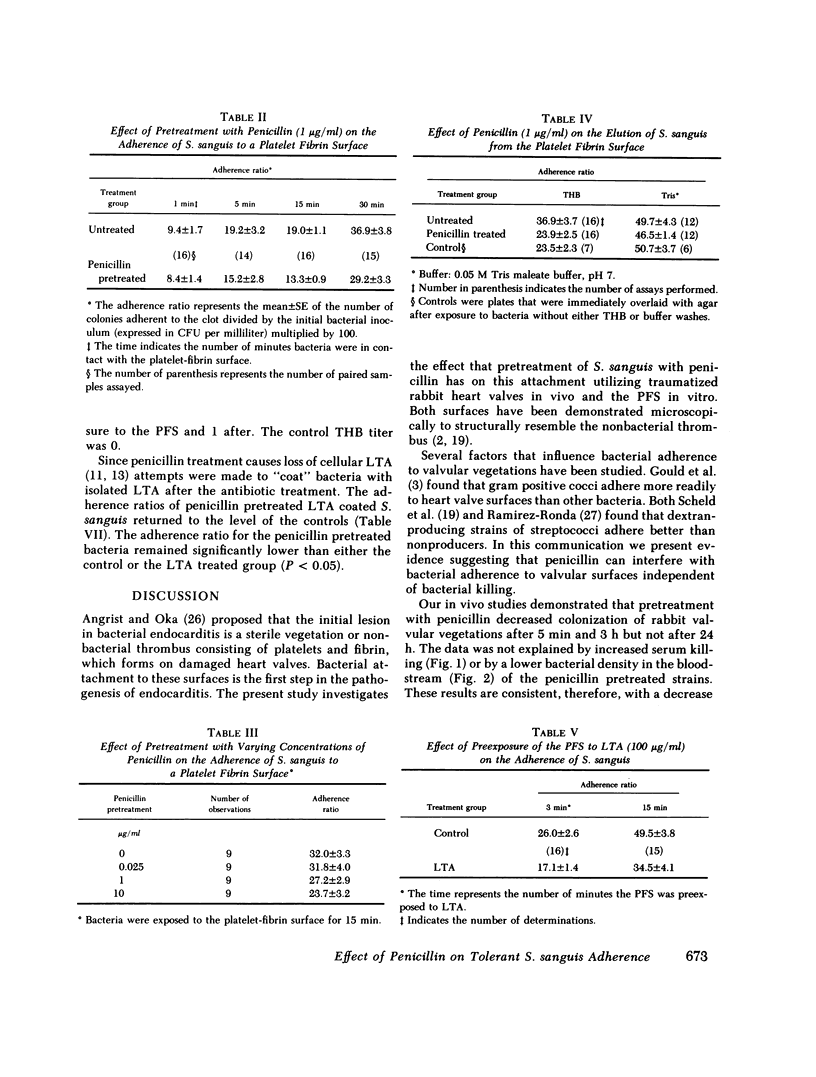
The effect of penicillin treatment of Streptococcus sanguis in vitro, on subsequent bacterial density in the bloodstream and on cardiac valves in the rabbit model of endocarditis was studied. As experimental tools for this study, isogenic pairs of S. sanguis differing in resistance to streptomycin or rifampin were prepared by genetic transformation. Rabbits with traumatized heart valves received an intravenous inoculation of penicillin treated (1 μg/ml) and untreated S. sanguis, each marked by resistance to either streptomycin or rifampin. The number of penicillin-treated and untreated bacteria attached to the valvular surfaces was determined by differential counting on streptomycin or rifampin containing media. Penicillin pretreatment reduced cardiac valve colonization 5 min after inoculation (“adherence ratio” × 108 was 4.11 for the control and 3.66 for the penicillin-treated bacteria, P < 0.001). The results were not due to differences in serum killing or bacterial densities in the bloodstream. There was no difference in valvular bacterial densities 24 h after bacterial inoculation (adherence ratio × 108, 7.26 untreated vs. 6.34 penicillin-pretreated, P > 0.10).
In vitro experiments were performed using platelet-fibrin surfaces to test the possibility that penicillin-induced loss of lipoteichoic acid was responsible for decreased streptococcal adherence. Pretreatment of S. sanguis cultures with inhibitory concentrations of penicillin or with antiserum against lipoteichoic acid and precoating of the platelet-fibrin surfaces with lipoteichoic acid, all caused reduction in bacterial adherence. The findings are interpreted as support for the role of lipoteichoic acid as an adhesin in S. sanguis interactions with particular host tissue surfaces.
Full text
PDF


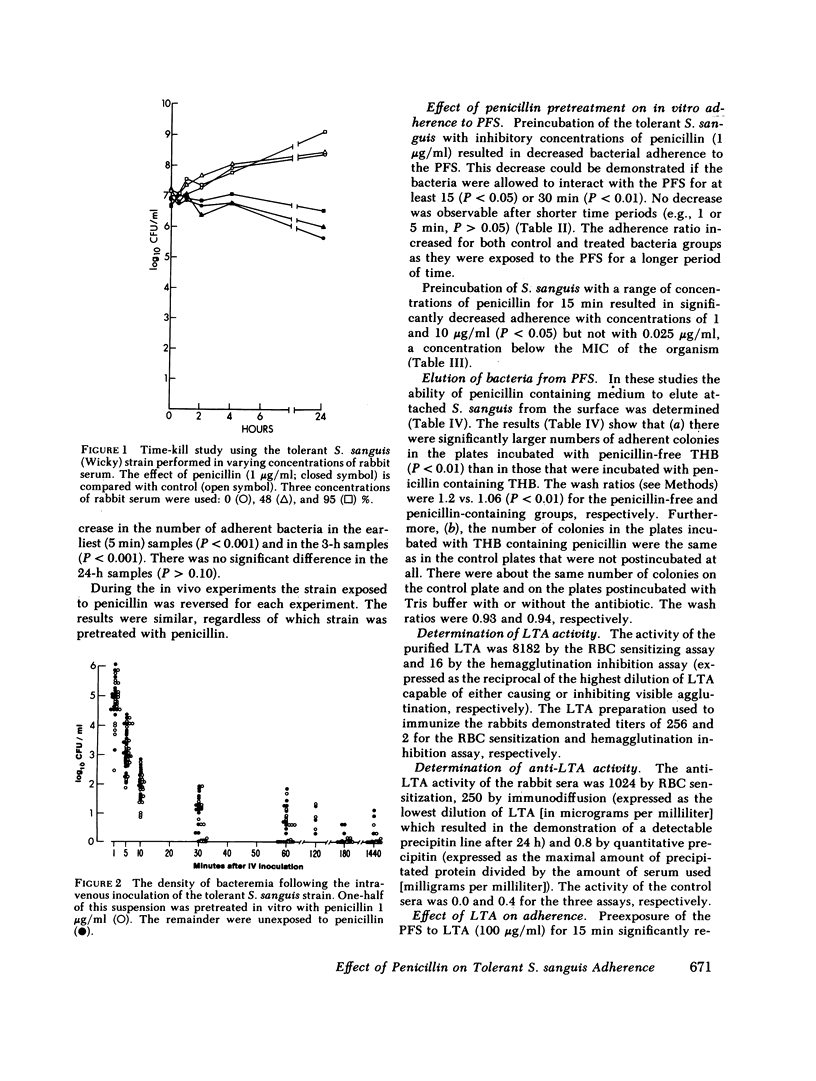
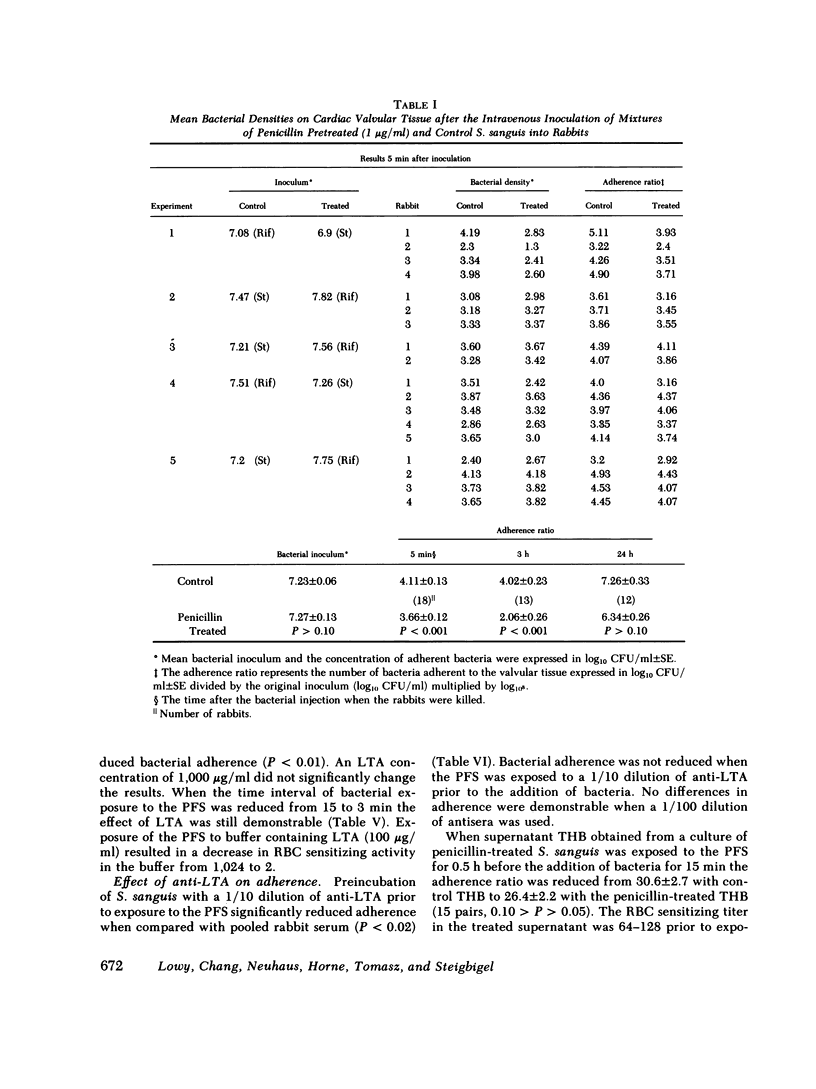


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANGRIST A. A., OKA M. Pathogenesis of bacterial endocarditis. JAMA. 1963 Jan 26;183:249–252. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.63700040009010b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkan M. L., Beachey E. H. Excretion of lipoteichoic acid by group A streptococci. Influence of penicillin on excretion and loss of ability to adhere to human oral mucosal cells. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):671–677. doi: 10.1172/JCI108979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Chiang T. M., Ofek I., Kang A. H. Interaction of lipoteichoic acid of group A streptococci with human platelets. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):649–654. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.649-654.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Ofek I. Epithelial cell binding of group A streptococci by lipoteichoic acid on fimbriae denuded of M protein. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):759–771. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M. Teichoic acids: antigenic determinants, chain separation, and their location in the cell wall. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):910–917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Beeson P. B. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. I. Colonization of a sterile vegetation. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Feb;53(1):44–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. IV. Structure and evolution of very early lesions. J Pathol. 1975 Feb;115(2):81–89. doi: 10.1002/path.1711150204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey G. J., Neu H. C. Infective endocarditis--an evolving disease. A review of endocarditis at the Columbia-Presbyterian Medical Center, 1968-1973. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 Mar;57(2):105–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K., Ramirez-Ronda C. H., Holmes R. K., Sanford J. P. Adherence of bacteria to heart valves in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1364–1370. doi: 10.1172/JCI108216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger M., Macpherson C. F. QUANTITATIVE MICRO-ESTIMATION OF ANTIBODIES IN THE SERA OF MAN AND OTHER ANIMALS. Science. 1943 Apr 30;97(2522):405–406. doi: 10.1126/science.97.2522.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Tomasz A. Lethal effect of a heterologous murein hydrolase on penicillin-treated Streptococcus sanguis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):235–246. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Tomasz A. Release of lipoteichoic acid from Streptococcus sanguis: stimulation of release during penicillin treatment. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1180–1184. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1180-1184.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Tomasz A. Tolerant response of Streptococcus sanguis to beta-lactams and other cell wall inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):888–896. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Hewett M. J., Wicken A. J. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: antigenicity and serological specificity of teichoic acid preparations. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):303–313. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCARTY M., LANCEFIELD R. C. Variation in the group-specific carbohydrate of group A streptococci. I. Immunochemical studies on the carbohydrates of variant strains. J Exp Med. 1955 Jul 1;102(1):11–28. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Gross K. C., Masur H., Roberts R. B. Serious infections caused by Streptococcus milleri. Am J Med. 1978 May;64(5):759–764. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90514-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Jefferson W., Campbell G. L. Cell membrane-binding properties of group A streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):990–1003. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakula R. Production of competence-provoking factor and development of competence of a transformable streptococcus in serum-free media. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Oct;11(5):811–822. doi: 10.1139/m65-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman B. B., Freedman L. R. Experimental endocarditis. II. Staphylococcal infection of the aortic valve following placement of a polyethylene catheter in the left side of the heart. Yale J Biol Med. 1971 Oct;44(2):206–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Ronda C. H. Adherence of glucan-positive and glucan-negative streptococcal strains to normal and damaged heart valves. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):805–814. doi: 10.1172/JCI109192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Casey J. I., Ruch P. A., Stumpf L. L., Finland M. Rapid microassay of gentamicin, kanamycin, neomycin, streptomycin, and vancomycin in serum or plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Sep;78(3):457–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Valone J. A., Sande M. A. Bacterial adherence in the pathogenesis of endocarditis. Interaction of bacterial dextran, platelets, and fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1394–1404. doi: 10.1172/JCI109057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Zak O., Vosbeck K., Sande M. A. Bacterial adhesion in the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis. Effect of subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations on streptococcal adhesion in vitro and the development of endocarditis in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1381–1384. doi: 10.1172/JCI110388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Gibbens J. W., Knox K. W. Comparative studies on the isolation of membrane lipoteichoic acid from Lactobacillus fermenti. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):365–372. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.365-372.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


