Correction to: The EMBO Journal (2015) 34: 410–424. DOI 10.15252/embj.201488947 | Published online 12 January 2015
Due to a technical error in the printing process, the colors of figure 7 are displayed incorrectly in the printed issue; the online version is unaffected by this error. Please find below the correct figure:
Figure 7.
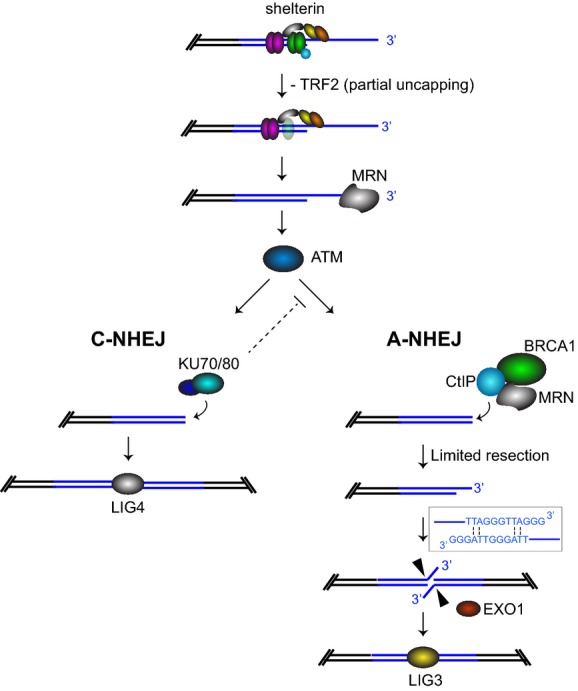
Model for the role of BRCA1-CtIP in A-NHEJ
Telomeres uncapped by TRF2 depletion undergo 3′ overhang excision in MRN-dependent manner. Most telomeres are bound by Ku heterodimer and re-joined by C-NHEJ promoted by 53BP1. A subset of the telomeres become substrates for resection reactions, which require MRN, BRCA1 and CtIP. Initiation of resection generates short 3′ telomeric overhangs, whose annealing is facilitated by the homology provided by 2 A-T base pairs per telomeric repeat. The resulting flaps are cleaved by EXO1 and telomeres re-joined through the LIG3-dependent A-NHEJ pathway.


