Abstract
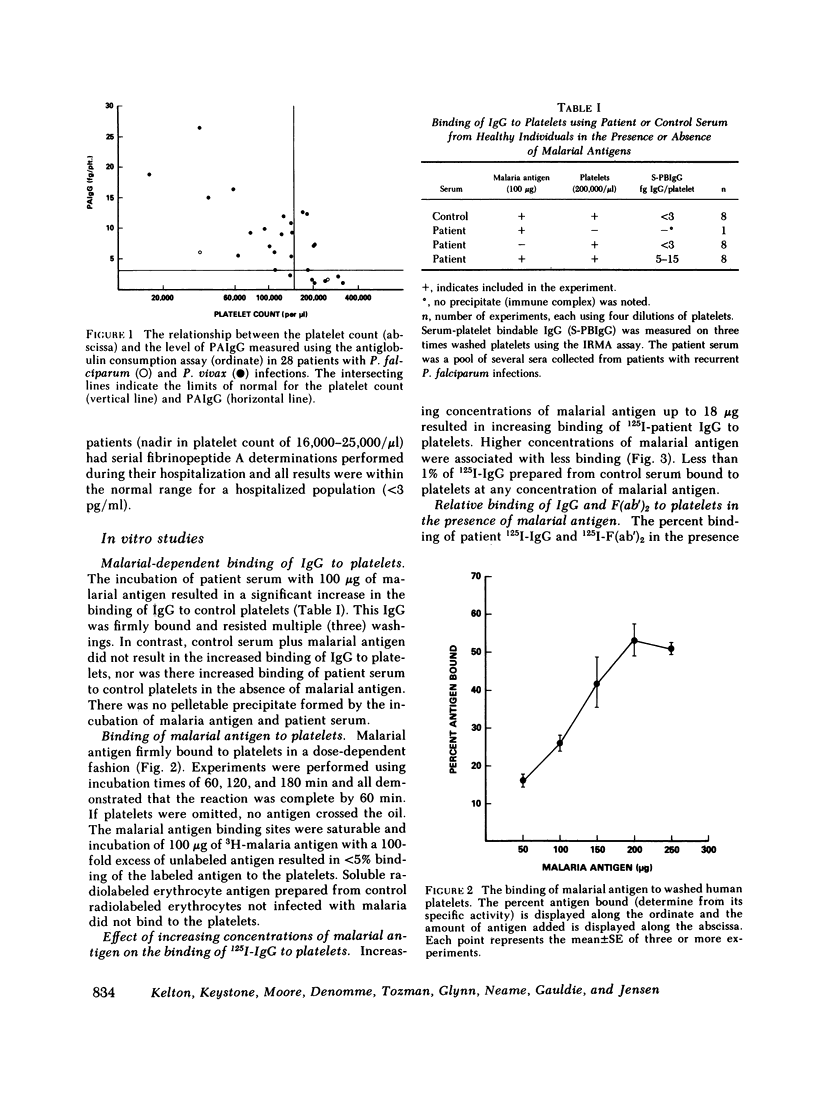
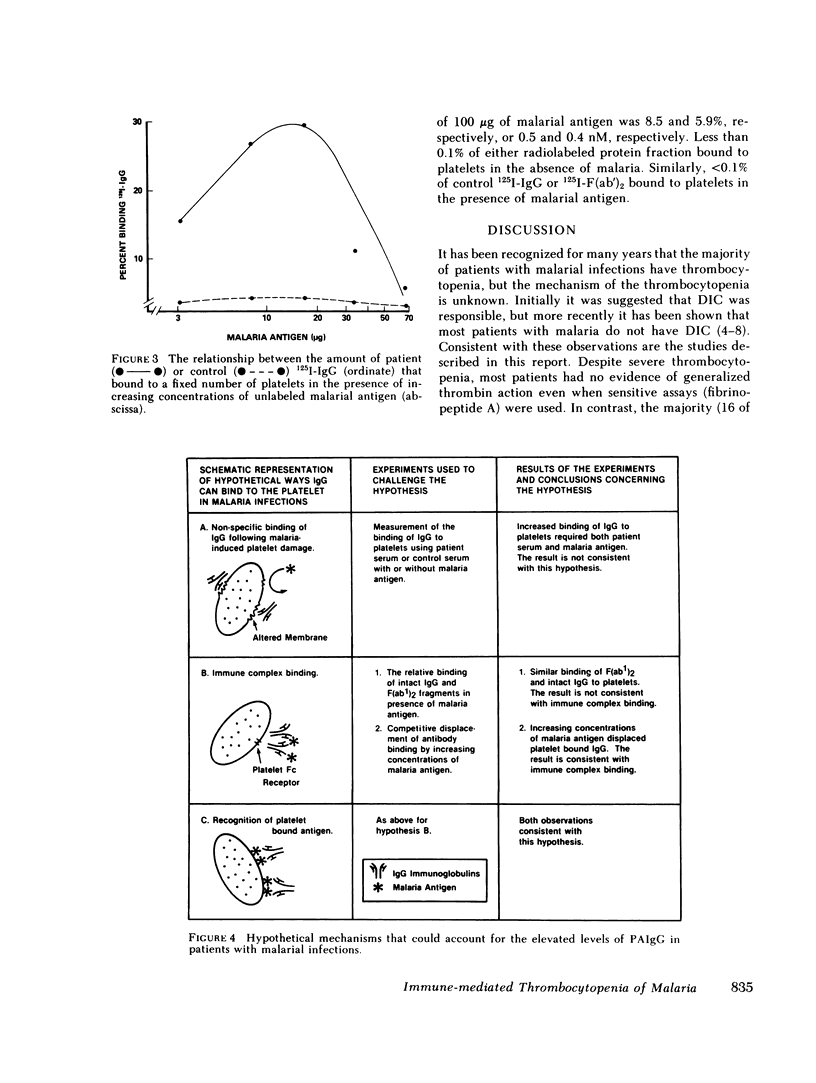
Thrombocytopenia frequently complicates malarial infections but the mechanism has not been elucidated. We studied 28 patients with malarial infections and noted that 16 of 17 thrombocytopenic patients had elevated levels of platelet-associated IgG (PAIgG). In all thrombocytopenic patients studied, the level of PAIgG returned to normal as the platelet count rose to normal levels. To study the mechanism of the elevated platelet-bound IgG, IgG and F(ab')2 from patients with recurrent Plasmodium falciparum infections was purified and radiolabeled. Labeled and unlabeled P. falciparum antigen was also prepared. IgG did not nonspecifically bind to malaria-damaged platelets. Binding studies with 3H-malarial antigen demonstrated platelets have saturable binding sites for malarial antigen. Increasing concentrations of malarial antigen displaced the 125I-IgG antimalarial antibody from the platelets. The binding of 125I-IgG and 125I-F(ab')2 was similar and this excluded significant immune complex binding. The thrombocytopenia that complicates at least some malarial infections is caused by immune mechanisms; specific IgG binds to platelet-bound malaria antigen through the Fab portion of the immunoglobulin molecule.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beale P. J., Cormack J. D., Oldrey T. B. Thrombocytopenia in malaria with immunoglobulin (IgM) changes. Br Med J. 1972 Feb 5;1(5796):345–349. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5796.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis L. H., Eichelberger J. W., Inman M. M., Conrad M. E. Depletion of coagulation factors in drug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Blood. 1967 May;29(5):713–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R., Rosse W., Ebbert L. Quantitative determination of antibody in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Correlation of serum and platelet-bound antibody with clinical response. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jan 30;292(5):230–236. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197501302920503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL G. J., 2nd, KNIGHT V., JEFFERY G. M. THROMBOCYTOPENIA IN VIVAX MALARIA. Lancet. 1964 Feb 1;1(7327):240–241. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstmann R. D., Dietrich M., Bienzle U., Rasche H. Malaria-induced thrombocytopenia. Blut. 1981 Mar;42(3):157–164. doi: 10.1007/BF01026385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. B., Trager W. Plasmodium falciparum in culture: use of outdated erthrocytes and description of the candle jar method. J Parasitol. 1977 Oct;63(5):883–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelton J. G., Denomme G. The quantitation of platelet-associated IgG on cohorts of platelets separated from healthy individuals by buoyant density centrifugation. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):136–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelton J. G., Giles A. R., Neame P. B., Powers P., Hageman N., Hirsch J. Comparison of two direct assays for platelet-associated IgG (PAIgG) in assessement of immune and nonimmune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):424–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelton J. G., Moore J., Gauldie J., Neame P. B., Hirsh J., Tozman E. The development and application of a serum assay for platelet-bindable IgG (S-PBIgG). J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Aug;98(2):272–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelton J. G., Neame P. B., Bishop J., Ali M., Gauldie J., Hirsh J. The direct assay for platelet-associated IgG (PAIgG): lack of association between antibody level and platelet size. Blood. 1979 Jan;53(1):73–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skudowitz R. B., Katz J., Lurie A., Levin J., Metz J. Mechanisms of thrombocytopenia in malignant tertian malaria. Br Med J. 1973 Jun 2;2(5865):515–518. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5865.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. J., Neame P. B., Kelton J. G. Infection-induced thrombocytopenia. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1982 Jul;8(3):217–233. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


