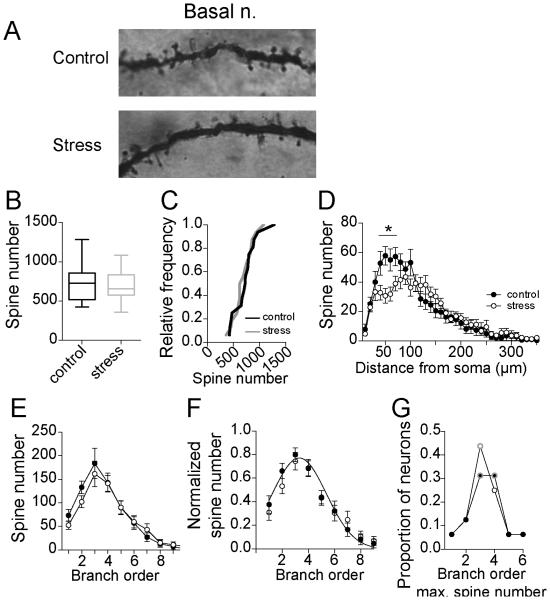
Figure 6. Repeated stress has weak effects on spine number of BA neurons.
A) Examples of Golgi stain in secondary dendrites of a BA neuron from control and stress groups. B) Repeated stress had no significant effect on the average spine number of principal neurons of the adolescent BA (box plot with 5-95th percentile). C) Overall, there were statistically similar number of BA neurons with higher average spine number after repeated stress and control, indicated by no shift in the cumulative frequency probability. D) There was a significant decrease in the spine number after stress at 40-70 μm from the soma (* indicates p<0.05 in post-hoc Holms-Sidak's tests). E) There was no significant difference in spine number across branch order after stress. F) When normalized by peak dendritic length, there was no significant shift in the distribution of spines across the entire dendritic tree. G) The branch that accounted for the most spines did not shift after repeated stress (peak order is encircled with gray).