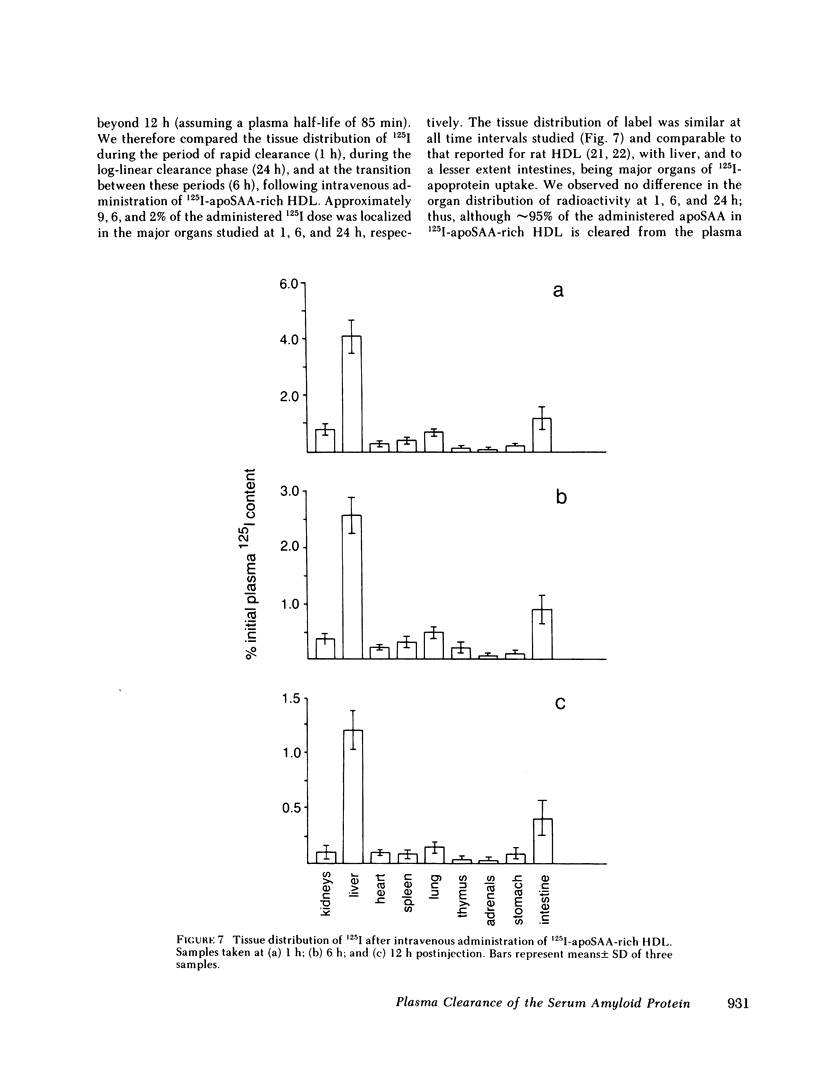
Abstract
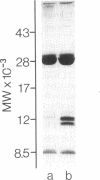
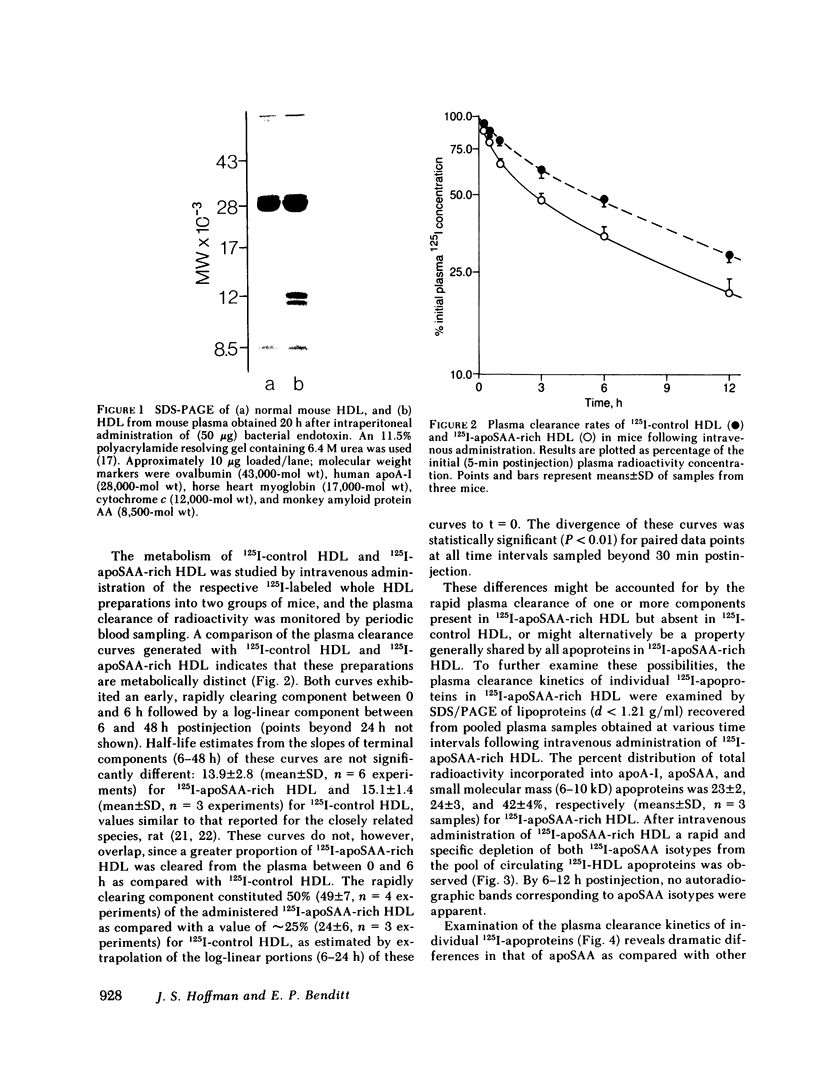
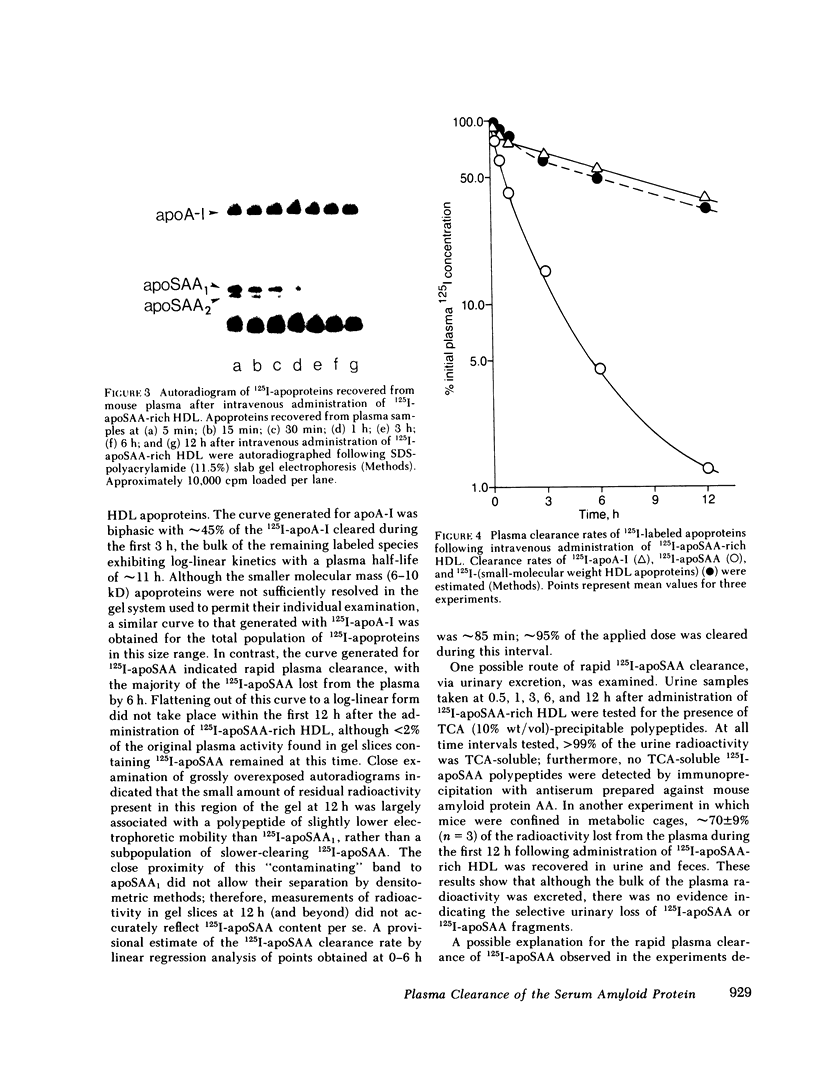
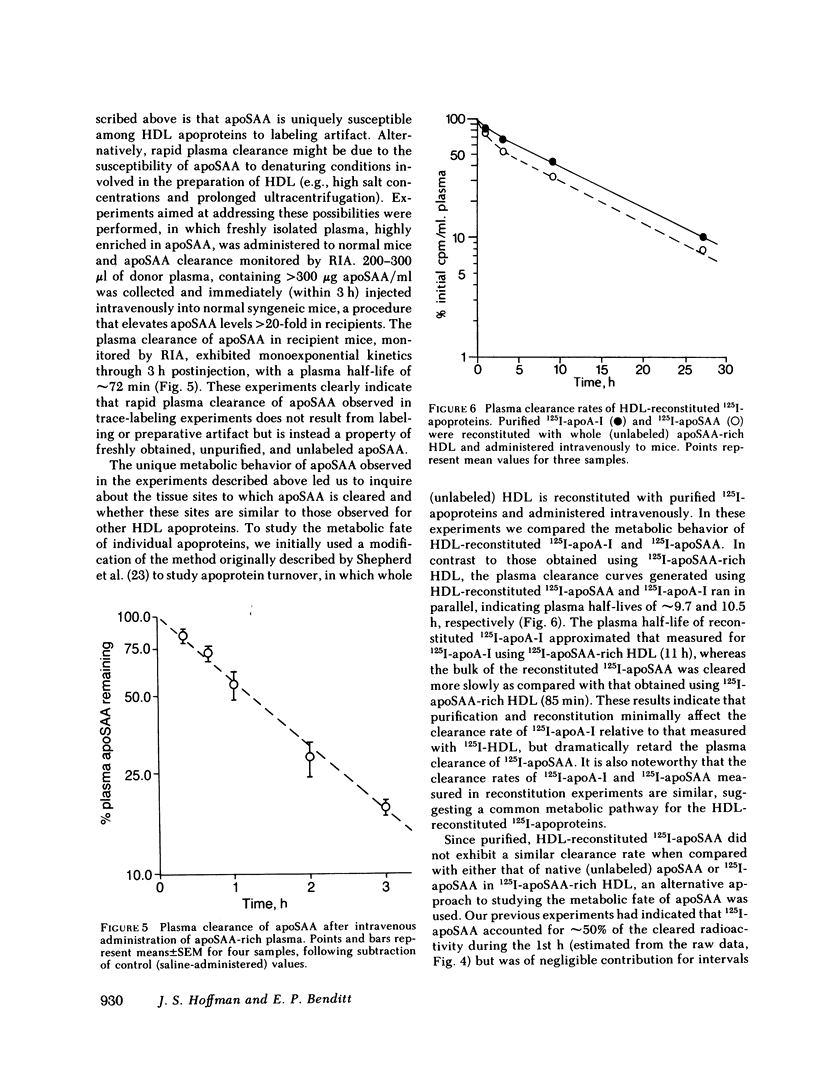
The plasma clearance kinetics of the amyloid-related high density lipoprotein (HDL) apoprotein serum amyloid protein (apoSAA) was examined in BALB/c mice by two different methods, using labeled 125I-apoSAA-rich HDL and unlabeled plasma apoSAA (clearance monitored by radioimmunoassay). The plasma half-life of apoSAA, estimated by both methods, was on the order of 75-80 min, as compared with a value of approximately 11 h for mouse apoA-I. In trace-labeling studies, the rapid plasma clearance of both major 125I-labeled apoSAA isotypes was observed; this metabolic behavior was unique to these polypeptides among HDL apoproteins. The property of rapid plasma clearance was lost upon purification and reconstitution of 125I-apoSAA with HDL, indicating that this property is labile to denaturing conditions. Studies aimed at determining the metabolic fate of 125I-apoSAA gave no evidence for either the selective excretion of 125I-apoSAA or clearance to unique tissue sites as compared with other 125I-HDL apoproteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders R. F., Natvig J. B., Michaelsen T. E., Husby G. Isolation and characterization of amyloid-related serum protein SAA as a low molecular weight protein. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(4):397–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders R. F., Natvig J. B., Sletten K., Husby G., Nordstoga K. Amyloid-related serum protein SAA from three animal species: comparison with human SAA. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):229–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N. Amyloid protein SAA is associated with high density lipoprotein from human serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4025–4028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N. Chemical similarity among amyloid substances associated with long standing inflammation. Lab Invest. 1972 Jun;26(6):615–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N., Hanson R. H. Amyloid protein SAA is an apoprotein of mouse plasma high density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4092–4096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N., Hermodson M. A., Ericsson L. H. The major proteins of human and monkey amyloid substance: Common properties including unusual N-terminal amino acid sequences. FEBS Lett. 1971 Dec 1;19(2):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80506-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D., Kleiner E. Synthesis and secretion of serum amyloid protein A (SAA) by hepatocytes in mice treated with casein. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):495–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. The metabolism of very low density lipoprotein proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Windmueller H. G., Levy R. I. Metabolic fate of rat and human lipoprotein apoproteins in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1973 Jul;14(4):446–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg M. A., Bøg-Hansen T. C., Back U., Galanos C. Interaction of lipopolysaccharides with plasma high-density lipoprotein in rats. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):373–380. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.373-380.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidez L. I., Swaney J. B., Murnane S. Analysis of rat serum apolipoproteins by isoelectric focusing. I. Studies on the middle molecular weight subunits. J Lipid Res. 1977 Jan;18(1):59–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M. R., Rattner E. C., Koehler M. M., Balikov S. R., Bock S. C. Two-dimensional electrophoresis of small-molecular-weight proteins. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;99(1):33–40. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. S., Benditt E. P. Changes in high density lipoprotein content following endotoxin administration in the mouse. Formation of serum amyloid protein-rich subfractions. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10510–10517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. S., Benditt E. P. Secretion of serum amyloid protein and assembly of serum amyloid protein-rich high density lipoprotein in primary mouse hepatocyte culture. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10518–10522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. F., Stearman R. S., Peltzman C. G., Potter D. A. Induction of hepatic synthesis of serum amyloid A protein and actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4718–4722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne J. C., Jr, Brewer H. B., Jr The plasma lipoproteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:253–337. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks J. S., Rudel L. L. Isolation and characterization of high density lipoprotein apoproteins in the non-human primate (vervet). J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6716–6723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roheim P. S., Rachmilewitz D., Stein O., Stein Y. Metabolism of iodinated high density lipoproteins in the rat. I. Half-life in the circulation and uptake by organs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 5;248(2):315–329. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Franklin E. C. Variation with age and disease of an amyloid A protein-related serum component. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):746–753. doi: 10.1172/JCI107985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Edelstein C. Solubility in aqueous solutions of ethanol of the small molecular weight peptides of the serum very low density and high density lipoproteins: relevance to the recovery problem during delipidation of serum lipoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1971 Dec;44(2):576–588. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90247-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Feldmann R. J. Amphipathic helixes and plasma lipoproteins: a computer study. Biopolymers. 1977 Sep;16(9):2053–2065. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger M. J., McAdam K. P., Kaplan M. M., Sipe J. D., Vogel S. N., Rosenstreich D. L. Monokine-induced synthesis of serum amyloid A protein by hepatocytes. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):498–500. doi: 10.1038/285498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J., Packard C. J., Gotto A. M., Jr, Taunton O. D. A comparison of two methods to investigate the metabolism of human apolipoproteins A-I and and A-II. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jul;19(5):656–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogen B., Børresen A. L., Natvig J. B., Berg K., Michaelsen T. E. High-density lipoprotein as carrier for amyloid-related protein SAA in rabbit serum. Scand J Immunol. 1979;10(1):39–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb01332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztein M. B., Vogel S. N., Sipe J. D., Murphy P. A., Mizel S. B., Oppenheim J. J., Rosenstreich D. L. The role of macrophages in the acute-phase response: SAA inducer is closely related to lymphocyte activating factor and endogenous pyrogen. Cell Immunol. 1981 Sep 1;63(1):164–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Johnston A. R., Weinstein D. B. New function for high density lipoproteins. Their participation in intravascular reactions of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1516–1524. doi: 10.1172/JCI109610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van't Hooft F., Havel R. J. Metabolism of chromatographically separated rat serum lipoproteins specifically labeled with 125I-apolipoprotein E. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3963–3968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]