Abstract
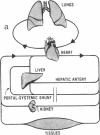
A multicompartmental pharmacokinetic model based on physiological principles, experimental data, and the standard mathematical principles of compartmental analysis has been constructed that fully describes the metabolism and enterohepatic cycling in man of cholic acid, a major bile acid. The model features compartments and linear transfer coefficients. The compartments are aggregated into nine spaces based on physiological considerations (liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, jejunum, ileum, colon, portal blood sinusoidal blood, and general circulation). The transfer coefficients are also categorized according to function: flow, i.e., emptying of gallbladder or intestinal spaces, and circulation of the blood; biotransformation, i.e., conjugation, deconjugation, or dehydroxylation; and transport, i.e., active or passive transport. The model is made time dependent by introducing meals, which trigger discrete increases in gallbladder emptying and intestinal flow. Each space contains three compartments. For cholic acid, these are unconjugated cholic acid, cholylglycine, and cholyltaurine. The model was then used with all existing experimental data to simulate cholic acid metabolism in healthy man over a 24-h period. Satisfactory agreement was obtained between simulated and experimental results for serum bile acid levels, hepatic bile acid secretion, and bile acid secretion into the intestine. The model was also used to classify 16 clinical instances in which the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids is altered by drugs or disease. The model can be extended to describe completely the metabolism and enterohepatic circulation of any bile acids in man in health and digestive disease. The model should also be broadly applicable to the description of the pharmacokinetics of all other drugs whose metabolism is similar to that of bile acids, i.e., drugs for which there are tissue and bacterial biotransformations, enterohepatic cycling, and appreciable first-pass clearance.
Full text
PDF



















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlberg J., Angelin B., Björkhem I., Einarsson K. Individual bile acids in portal venous and systemic blood serum of fasting man. Gastroenterology. 1977 Dec;73(6):1377–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach W. H., Hofmann A. F. Ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of cholesterol cholelithiasis. Part II. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Sep;27(9):833–856. doi: 10.1007/BF01391378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balistreri W. F., Suchy F. J., Heubi J. E. Serum bile acid response to a test meal stimulus: a sensitive test of ileal function. J Pediatr. 1980 Mar;96(3 Pt 2):582–589. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80870-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff K. B., Dedrick R. L. Thiopental pharmacokinetics. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Aug;57(8):1346–1351. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600570814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff K. B., Dedrick R. L., Zaharko D. S., Longstreth J. A. Methotrexate pharmacokinetics. J Pharm Sci. 1971 Aug;60(8):1128–1133. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600600803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bungay P. M., Dedrick R. L., Guarino A. M. Pharmacokinetic modeling of the dogfish shark (Squalus acanthias): distribution and urinary and biliary excretion of phenol red and its glucuronide. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1976 Oct;4(5):377–388. doi: 10.1007/BF01062827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bungay P. M., Dedrick R. L., Matthews H. B. Enteric transport of chlordecone (Kepone) in the rat. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1981 Jun;9(3):309–341. doi: 10.1007/BF01059269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C., Small D. M. The physical chemistry of cholesterol solubility in bile. Relationship to gallstone formation and dissolution in man. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):998–1026. doi: 10.1172/JCI109025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier F., Lutton C. Cinétiques journalière et horaire de la transformation du cholestérol-26-14C en acides biliaires. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1966;48(2):295–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., Bates J. H., Maslowski A. H., McKinnon A. E., Campbell C. B. The extent of reflux of unconjugated 14C-cholic acid from the liver in subjects with normal liver function. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1981 Dec;59(Pt 6):779–790. doi: 10.1038/icb.1981.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowen A. E., Korman M. G., Hofmann A. F., Cass O. W. Metabolism of lethocholate in healthy man. I. Biotransformation and biliary excretion of intravenously administered lithocholate, lithocholylglycine, and their sulfates. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jul;69(1):59–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowen A. E., Korman M. G., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Plasma disappearance of radioactivity after intravenous injection of labeled bile acids in man. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jun;68(6):1567–1573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedrick R. L., Forrester D. D., Cannon J. N., el-Dareer S. M., Mellett L. B. Pharmacokinetics of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (ARA-C) deamination in several species. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Oct 1;22(19):2405–2417. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90342-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devroede G. J., Phillips S. F. Studies of the perfusion technique for colonic absorption. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jan;56(1):92–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Hellström K. The formation of bile acids in patients with three types of hyperlipoproteinaemia. Eur J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;2(4):225–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1972.tb00648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Hellström K. The formation of deoxycholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid in man. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Feb;46(2):183–190. doi: 10.1042/cs0460183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everson G. T., Braverman D. Z., Johnson M. L., Kern F., Jr A critical evaluation of real-time ultrasonography for the study of gallbladder volume and contraction. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jul;79(1):40–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forker E. L., Luxon B. Hepatic transport kinetics and plasma disappearance curves: distributed modeling versus conventional approach. Am J Physiol. 1978 Dec;235(6):E648–E660. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.6.E648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Carlson G. L., Hofmann A. F., Farivar S., Amin P. Metabolism in man of 7-ketolithocholic acid: precursor of cheno- and ursodeoxycholic acids. Am J Physiol. 1980 Sep;239(3):G161–G166. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.239.3.G161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORESKY C. A. A linear method for determining liver sinusoidal and extravascular volumes. Am J Physiol. 1963 Apr;204:626–640. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore I. T., Hofmann A. F. Altered drug metabolism and elevated serum bile acids in liver disease: a unified pharmacokinetic explanation. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jan;78(1):177–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore I. T., Thompson R. P. Kinetics of 14C-glycocholic acid clearance in normal man and in patients with liver disease. Gut. 1978 Dec;19(12):1110–1115. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.12.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore I. T., Thompson R. P. Plasma clearance of oral and intravenous cholic acid in subjects with and without chronic liver disease. Gut. 1980 Feb;21(2):123–127. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.2.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go V. L., Poley J. R., Hofmann A. F., Summerskill W. H. Disturbances in fat digestion induced by acidic jejunal pH due to gastric hypersecretion in man. Gastroenterology. 1970 May;58(5):638–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greim H., Czygan P., Schaffner F., Popper H. Determination of bile acids in needle biopsies of human liver. Biochem Med. 1973 Oct;8(2):280–286. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(73)90032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Metzger A. L. A physiological method for estimation of hepatic secretion of biliary lipids in man. Gastroenterology. 1972 Jun;62(6):1200–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison W. G. Hepatic taurine concentration and dietary taurine as regulators of bile acid conjugation with taurine. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jul;75(1):71–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepner G. W., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Metabolism of steroid and amino acid moieties of conjugated bile acids in man. I. Cholylglycine. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1889–1897. doi: 10.1172/JCI106991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepner G. W., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Metabolism of steroid and amino acid moieties of conjugated bile acids in man. II. Glycine-conjugated dihydroxy bile acids. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1898–1905. doi: 10.1172/JCI106992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepner G. W., Sturman J. A., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Metabolism of steroid and amino acid moieties of conjugated bile acids in man. 3. Cholyltaurine (taurocholic acid). J Clin Invest. 1973 Feb;52(2):433–440. doi: 10.1172/JCI107200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman N. E., Hofmann A. F. Metabolism of steroid and amino acid moieties of conjugated bile acids in man. V. Equations for the perturbed enterohepatic circulation and their application. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jan;72(1):141–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman N. E., Hormann A. F. Metabolsim of steroid and amino acid moieties of conjugated bile acids in man. Gastroenterology. 1974 Nov;67(5):887–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F. The enterohepatic circulation of conjugated bile acids in healthy man: quantitative description and functions. Expos Annu Biochim Med. 1977;33:69–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F. The medical treatment of gallstones: a clinical application of the new biology of bile acids. Harvey Lect. 1980;74:23–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzbach R. T., Marsh M., Olszewski M., Holan K. Cholesterol solubility in bile. Evidence that supersaturated bile is frequent in healthy man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1467–1479. doi: 10.1172/JCI107321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak W., Waldram R., Murray-Lyon I. M., Schuster E., Williams R. Kinetics of [14C]cholic acid in fulminant hepatic failure: a prognostic test. Gastroenterology. 1976 Nov;71(5):809–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlin P., Zinsmeister A., Phillips S. Relationship of motility to flow of contents in the human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1982 Apr;82(4):701–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDSTEDT S. The turnover of cholic acid in man: bile acids and steroids. Acta Physiol Scand. 1957 Sep 17;40(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1957.tb01473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Hoffman N. E., Korman M. G., Hofmann A. F., Cowen A. E. Determinants of fasting and postprandial serum bile acid levels in healthy man. Am J Dig Dis. 1978 May;23(5):385–391. doi: 10.1007/BF01072919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Korman M. G., Hoffman N. E., Hofmann A. F. Dynamics of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. Postprandial serum concentrations of conjugates of cholic acid in health, cholecystectomized patients, and patients with bile acid malabsorption. N Engl J Med. 1974 Oct 3;291(14):689–692. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197410032911401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Heaton K. W., Heaton S. T., Read A. E. Gallbladder inertia and sluggish enterohepatic circulation of bile-salts in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1971 May 15;1(7707):991–994. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91387-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luecke R. H., Wosilait W. D. Drug elimination interactions: analysis using a mathematical model. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1979 Dec;7(6):629–641. doi: 10.1007/BF01061211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz R. J., Dedrick R. L., Zaharko D. S. Physiological pharmacokinetics: an in vivo approach to membrane transport. Pharmacol Ther. 1980;11(3):559–592. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino I., Hashimoto H., Shinozaki K., Yoshino K., Nakagawa S. Sulfated and nonsulfated bile acids in urine, serum, and bile of patients with hepatobiliary diseases. Gastroenterology. 1975 Mar;68(3):545–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallory A., Kern F., Jr, Smith J., Savage D. Patterns of bile acids and microflora in the human small intestine. I. Bile acids. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jan;64(1):26–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McJunkin B., Fromm H., Sarva R. P., Amin P. Factors in the mechanism of diarrhea in bile acid malabsorption: fecal pH--a key determinant. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jun;80(6):1454–1464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekhjian H. S., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Colonic absorption of unconjugated bile acids: perfusion studies in man. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Jul;24(7):545–550. doi: 10.1007/BF01489324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milanese M., Molino G., Cappelletti F. New results on saturation phenomena in BSP metabolism: the role of free and conjugated BSP. Med Biol Eng Comput. 1981 Nov;19(6):707–716. doi: 10.1007/BF02441332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molino G., Milanese M. Structural analysis of compartmental models for the hepatic kinetics of drugs. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 May;85(5):865–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. M., Edkins S. M., Williams J. W., Catty D. The preparation and properties of an antiserum for the radioimmunoassay of serum conjugated cholic acid. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Jul 15;54(1):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northfield T. C., Hofmann A. F. Biliary lipid output during three meals and an overnight fast. I. Relationship to bile acid pool size and cholesterol saturation of bile in gallstone and control subjects. Gut. 1975 Jan;16(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northfield T. C., McColl I. Postprandial concentrations of free and conjugated bile acids down the length of the normal human small intestine. Gut. 1973 Jul;14(7):513–518. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.7.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo H., Okuda K., Iida S., Makino I. Ursodeoxycholic acid oral tolerance test in patients with constitutional hyperbilirubinemias and effect of phenobarbital. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jul;81(1):126–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters T. L., Vantrappen G., Janssens J. Bile acid output and the interdigestive migrating motor complex in normals and in cholecystectomy patients. Gastroenterology. 1980 Oct;79(4):678–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. F., Giller J. The contribution of the colon to electrolyte and water conservation in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 May;81(5):733–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponz De Leon M., Murphy G. M., Dowling R. H. Physiological factors influencing serum bile acid levels. Gut. 1978 Jan;19(1):32–39. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pries J. M., Sherman C. A., Williams G. C., Hanson R. F. Hepatic extraction of bile salts in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol. 1979 Feb;236(2):E191–E197. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.2.E191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pries J. M., Staples A. B., Hanson R. F. The effect of hepatic blood flow on taurocholate extraction by the isolated perfused rat liver. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Mar;97(3):412–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roda A., Roda E., Aldini R., Festi D., Mazzella G., Sama C., Barbara L. Development, validation, and application of a single-tube radioimmunoassay for cholic and chenodeoxycholic conjugated bile acids in human serum. Clin Chem. 1977 Nov;23(11):2107–2113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalm S. W., LaRusso N. F., Hofmann A. F., Hoffman N. E., van Berge-Henegouwen G. P., Korman M. G. Diurnal serum levels of primary conjugated bile acids. Assessment by specific radioimmunoassays for conjugates of cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid. Gut. 1978 Nov;19(11):1006–1014. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.11.1006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalm S. W., van Berge-Henegouwen G. P., Hofmann A. F., Cowen A. E., Turcotte J. Radioimmunoassay of bile acids: development, validation, and preliminary application of an assay for conjugates of chenodeoxycholic acid. Gastroenterology. 1977 Aug;73(2):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfield L. J., Lachin J. M. Chenodiol (chenodeoxycholic acid) for dissolution of gallstones: the National Cooperative Gallstone Study. A controlled trial of efficacy and safety. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Sep;95(3):257–282. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-3-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Lawson A. M., Blackstock E. J., Murphy G. M. Diurnal changes in serum unconjugated bile acids in normal man. Gut. 1982 Aug;23(8):637–642. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.8.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds W. J., Korman M. G., Go V. L., Hofmann A. F. Radioimmunoassay of conjugated cholyl bile acids in serum. Gastroenterology. 1973 Nov;65(5):705–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skrede S., Solberg H. E., Blomhoff J. P., Gjone E. Bile acids measured in serum during fasting as a test for liver disease. Clin Chem. 1978 Jul;24(7):1095–1099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehl A., Earnest D. L., Admirant W. H. Sulfation and renal excretion of bile salts in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Gastroenterology. 1975 Mar;68(3):534–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ståhl E., Arnesjö B. Taurocholate metabolism in man. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1972;7(6):559–566. doi: 10.3109/00365527209180957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanida N., Hikasa Y., Hosomi M., Satomi M., Oohama I., Shimoyama T. Fecal bile acid analysis in healthy Japanese subjects using a lipophilic anion exchanger, capillary column gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1981;16(4):363–371. doi: 10.1007/BF02774469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahcevic Z. R., Miller J. R., Farrar J. T., Swell L. Kinetics and pool size of primary bile acids in man. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jul;61(1):85–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Berge Henegouwen G. P., Brandt K. H., Eyssen H., Parmentier G. Sulphated and unsulphated bile acids in serum, bile, and urine of patients with cholestasis. Gut. 1976 Nov;17(11):861–869. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.11.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Berge Henegouwen G. P., Hofmann A. F. Nocturnal gallbladder storage and emptying in gallstone patients and healthy subjects. Gastroenterology. 1978 Nov;75(5):879–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]