Abstract
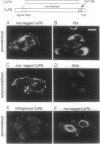
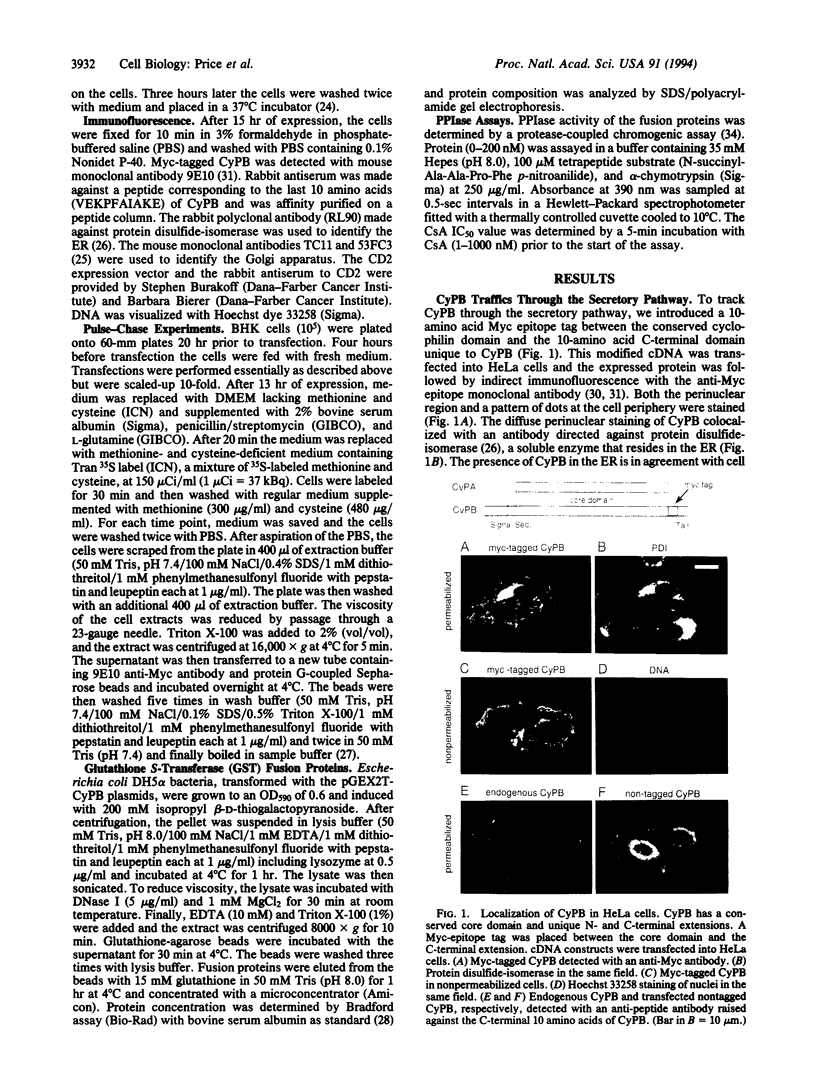
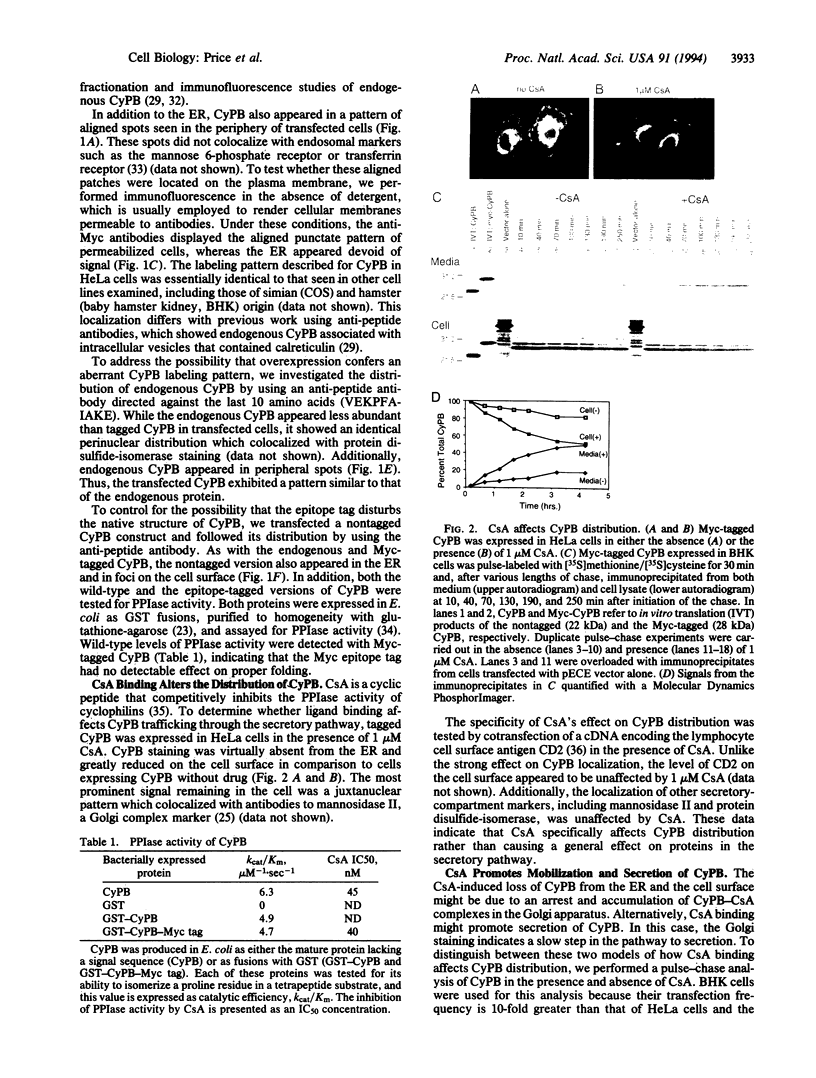
Cyclophilin B is targeted to the secretory pathway via an endoplasmic reticulum signal sequence. We analyzed the localization and trafficking of endogenous and transfected cyclophilin B in mammalian cells. Cyclophilin B accumulates both in the endoplasmic reticulum and in complexes on the plasma membrane. The immunosuppressant cyclosporin A specifically mobilizes cyclophilin B from the endoplasmic reticulum, and promotes the secretion of cyclophilin B into the medium. We suggest that cyclosporin A competes with endogenous plasma membrane proteins for association with cyclophilin B in the secretory pathway. These findings argue in favor of a role for cyclophilin B as a chaperone to proteins destined for the plasma membrane, rather than solely as a proline isomerase functioning within the endoplasmic reticulum.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agard D. A. To fold or not to fold.... Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1903–1904. doi: 10.1126/science.8100365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. K., Gallinger S., Roder J., Frey J., Young H. A., Ortaldo J. R. A cyclophilin-related protein involved in the function of natural killer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):542–546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arber S., Krause K. H., Caroni P. s-cyclophilin is retained intracellularly via a unique COOH-terminal sequence and colocalizes with the calcium storage protein calreticulin. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):113–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Eder C., Gross M., Kersten H., Sylvester D., Appelbaum E., Cusimano D., Livi G. P., McLaughlin M. M., Kasyan K. The cyclophilin multigene family of peptidyl-prolyl isomerases. Characterization of three separate human isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23204–23214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Schreiber S. L., Burakoff S. J. The effect of the immunosuppressant FK-506 on alternate pathways of T cell activation. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Feb;21(2):439–445. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bole D. G., Hendershot L. M., Kearney J. F. Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1558–1566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacino J. S., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Chen C., Antusch D., Samelson L. E., Klausner R. D. Association and dissociation of the murine T cell receptor associated protein (TRAP). Early events in the biosynthesis of a multisubunit receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8965–8971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B., Griffiths G., Reggio H., Louvard D., Warren G. A monoclonal antibody against a 135-K Golgi membrane protein. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1621–1628. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cacalano N. A., Chen B. X., Cleveland W. L., Erlanger B. F. Evidence for a functional receptor for cyclosporin A on the surface of lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4353–4357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Rothenfluh A., McGlynn E., Schneider C. S-cyclophilin. New member of the cyclophilin family associated with the secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10739–10742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley N. J., Baker E. K., Stamnes M. A., Zuker C. S. The cyclophilin homolog ninaA is required in the secretory pathway. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90177-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland C. S., Doms R. W., Bolzau E. M., Webster R. G., Helenius A. Assembly of influenza hemagglutinin trimers and its role in intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1179–1191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A. Chaperones: helpers along the pathways to protein folding. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1902–1903. doi: 10.1126/science.8100364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Bang H., Berger E., Schellenberger A. Conformational specificity of chymotrypsin toward proline-containing substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 23;791(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90285-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Wittmann-Liebold B., Lang K., Kiefhaber T., Schmid F. X. Cyclophilin and peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase are probably identical proteins. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):476–478. doi: 10.1038/337476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freskgård P. O., Bergenhem N., Jonsson B. H., Svensson M., Carlsson U. Isomerase and chaperone activity of prolyl isomerase in the folding of carbonic anhydrase. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):466–468. doi: 10.1126/science.1357751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J., Weissman I. Two cytoplasmic candidates for immunophilin action are revealed by affinity for a new cyclophilin: one in the presence and one in the absence of CsA. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):799–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90123-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galat A. Peptidylproline cis-trans-isomerases: immunophilins. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Sep 15;216(3):689–707. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasel K. W., Glass J. R., Godbout M., Sutcliffe J. G. An endoplasmic reticulum-specific cyclophilin. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3484–3491. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heald R., McKeon F. Mutations of phosphorylation sites in lamin A that prevent nuclear lamina disassembly in mitosis. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):579–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90470-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendershot L., Bole D., Köhler G., Kearney J. F. Assembly and secretion of heavy chains that do not associate posttranslationally with immunoglobulin heavy chain-binding protein. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):761–767. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai N., Inagami T. Molecular cloning of a complementary DNA to rat cyclophilin-like protein mRNA. Kidney Int. 1990 Jun;37(6):1460–1465. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaetzel C. S., Rao C. K., Lamm M. E. Protein disulphide-isomerase from human placenta and rat liver. Purification and immunological characterization with monoclonal antibodies. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):39–47. doi: 10.1042/bj2410039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefhaber T., Quaas R., Hahn U., Schmid F. X. Folding of ribonuclease T1. 1. Existence of multiple unfolded states created by proline isomerization. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 27;29(12):3053–3061. doi: 10.1021/bi00464a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofron J. L., Kuzmic P., Kishore V., Colón-Bonilla E., Rich D. H. Determination of kinetic constants for peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerases by an improved spectrophotometric assay. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 25;30(25):6127–6134. doi: 10.1021/bi00239a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Lodish H. F. Oligomerization is essential for transport of vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein to the cell surface. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90075-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. Ligand-induced redistribution of a human KDEL receptor from the Golgi complex to the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):353–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90476-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Farmer J. D., Jr, Lane W. S., Friedman J., Weissman I., Schreiber S. L. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Kong N. Cyclosporin A inhibits an initial step in folding of transferrin within the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14835–14838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luban J., Alin K. B., Bossolt K. L., Humaran T., Goff S. P. Genetic assay for multimerization of retroviral gag polyproteins. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5157–5160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5157-5160.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luban J., Bossolt K. L., Franke E. K., Kalpana G. V., Goff S. P. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag protein binds to cyclophilins A and B. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1067–1078. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90637-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):899–907. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narula N., McMorrow I., Plopper G., Doherty J., Matlin K. S., Burke B., Stow J. L. Identification of a 200-kD, brefeldin-sensitive protein on Golgi membranes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):27–38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettey C. L., Alarcon B., Malin R., Weinberg K., Terhorst C. T3-p28 is a protein associated with the delta and epsilon chains of the T cell receptor-T3 antigen complex during biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4854–4859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price E. R., Zydowsky L. D., Jin M. J., Baker C. H., McKeon F. D., Walsh C. T. Human cyclophilin B: a second cyclophilin gene encodes a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase with a signal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1903–1907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L., Crabtree G. R. The mechanism of action of cyclosporin A and FK506. Immunol Today. 1992 Apr;13(4):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90111-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönbrunner E. R., Mayer S., Tropschug M., Fischer G., Takahashi N., Schmid F. X. Catalysis of protein folding by cyclophilins from different species. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3630–3635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spik G., Haendler B., Delmas O., Mariller C., Chamoux M., Maes P., Tartar A., Montreuil J., Stedman K., Kocher H. P. A novel secreted cyclophilin-like protein (SCYLP). J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10735–10738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamnes M. A., Shieh B. H., Chuman L., Harris G. L., Zuker C. S. The cyclophilin homolog ninaA is a tissue-specific integral membrane protein required for the proper synthesis of a subset of Drosophila rhodopsins. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90156-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann B., Bruckner P., Superti-Furga A. Cyclosporin A slows collagen triple-helix formation in vivo: indirect evidence for a physiologic role of peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans-isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1299–1303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoorvogel W., Geuze H. J., Griffith J. M., Schwartz A. L., Strous G. J. Relations between the intracellular pathways of the receptors for transferrin, asialoglycoprotein, and mannose 6-phosphate in human hepatoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2137–2148. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Hayano T., Suzuki M. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase is the cyclosporin A-binding protein cyclophilin. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):473–475. doi: 10.1038/337473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A., Ohlén C., Bastin J., Ljunggren H. G., Foster L., Kärre K. Association of class I major histocompatibility heavy and light chains induced by viral peptides. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):443–448. doi: 10.1038/340443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. T., Zydowsky L. D., McKeon F. D. Cyclosporin A, the cyclophilin class of peptidylprolyl isomerases, and blockade of T cell signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13115–13118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Mechanism of protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:499–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]