Abstract
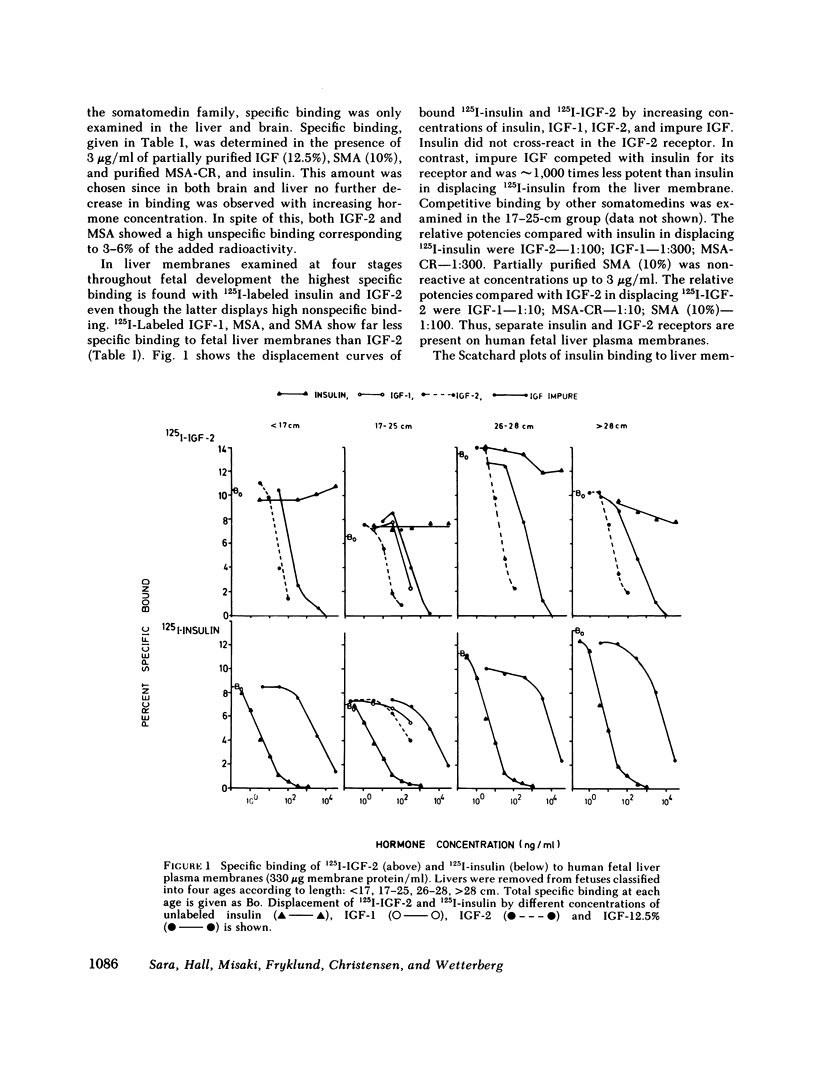
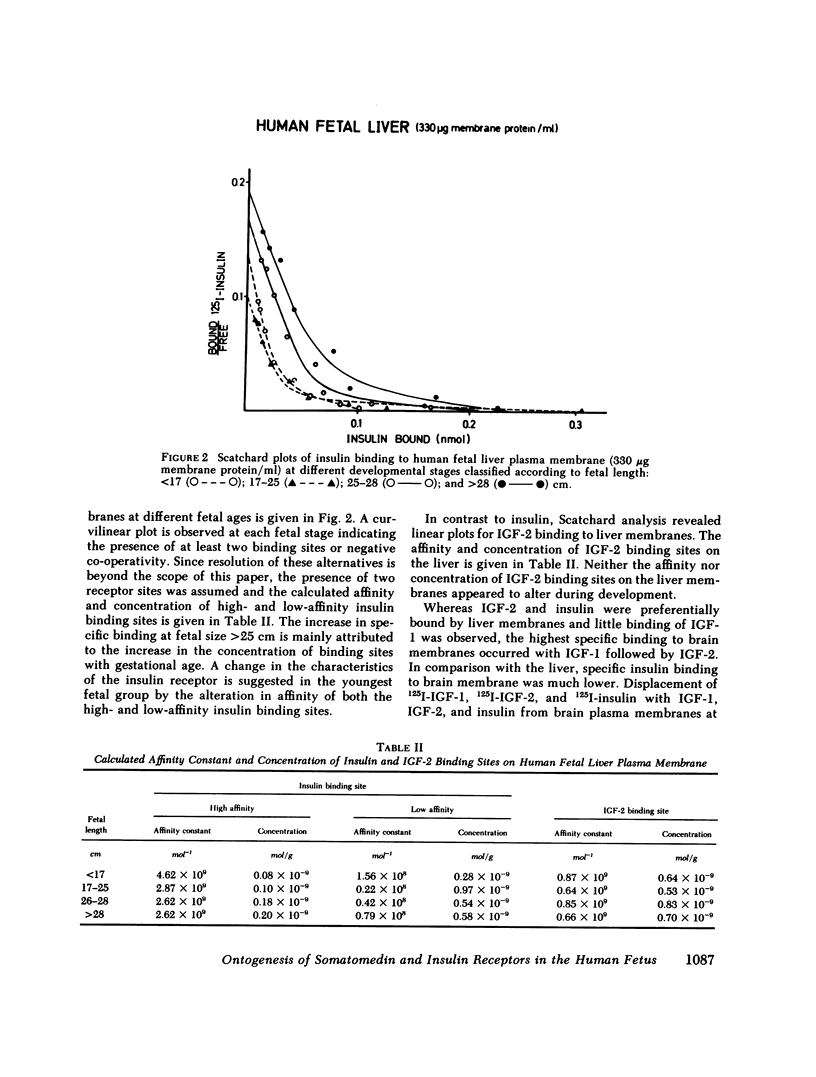
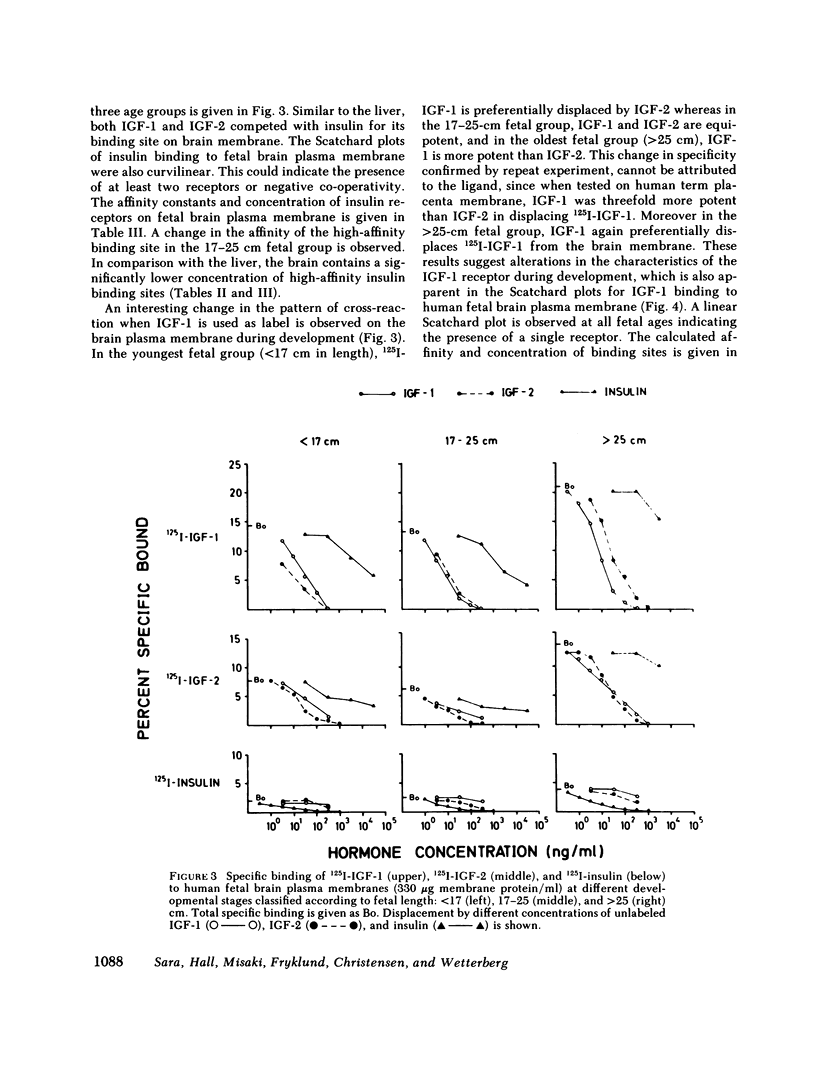
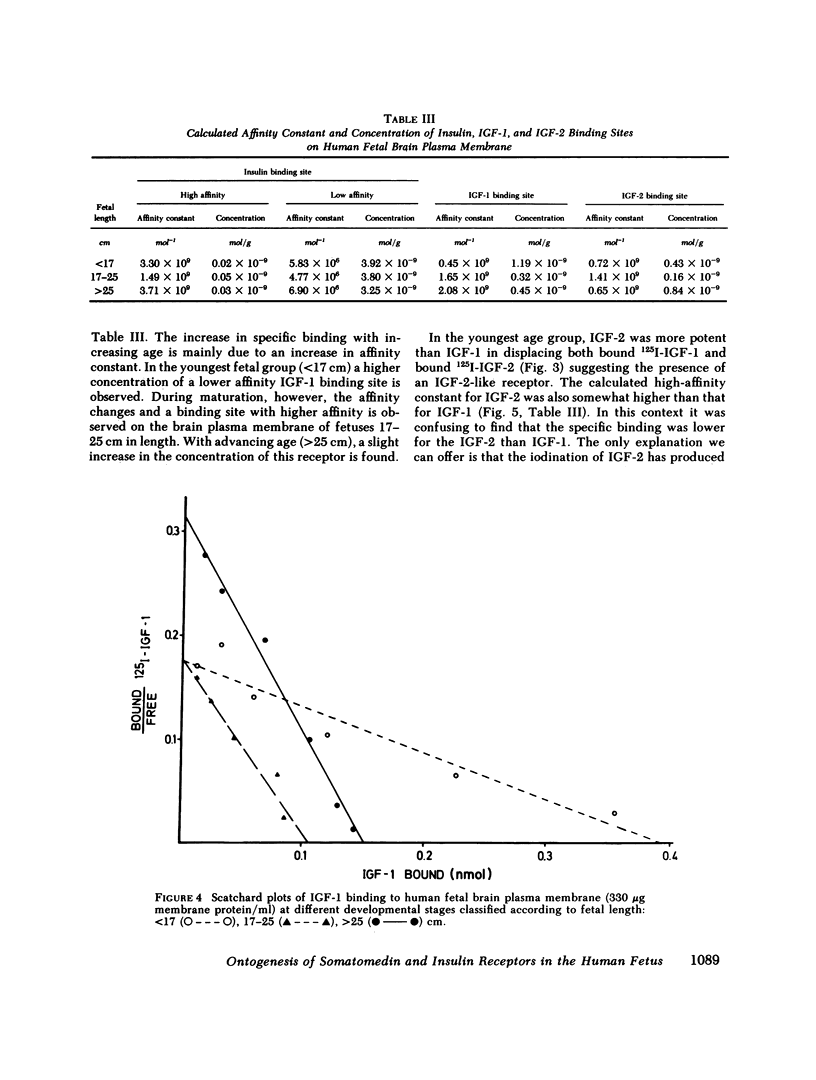
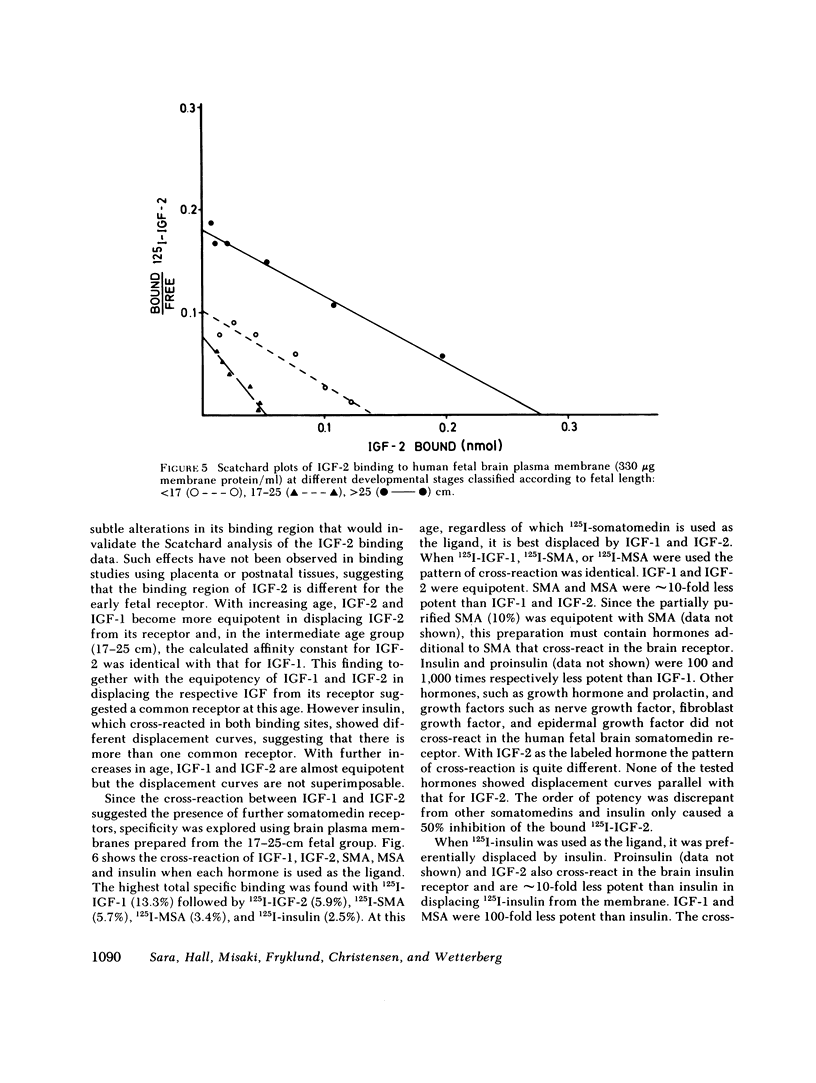
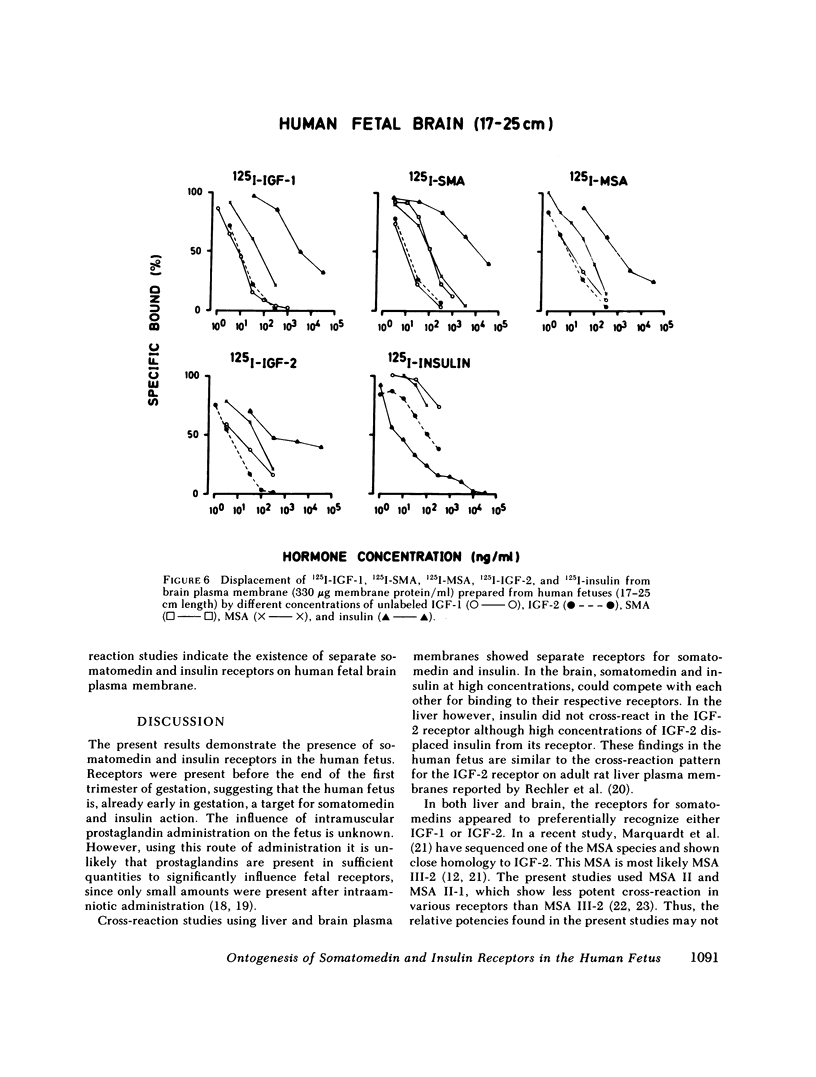
This study examines the ontogenesis of somatomedin and insulin receptors in man. Particulate plasma membranes were prepared by ultracentrifugation from various tissues removed from fetuses after abortion and classified as less than 17, 17-25, and greater than 25 cm in length. The binding of iodinated insulinlike growth factors 1 (IGF-1) and 2 (IGF-2), somatomedin A (SMA), multiplication-stimulating activity (MSA), and insulin was examined at the different ages. In the liver, cross-reaction studies revealed separate insulin and IGF-2 receptors. The Scatchard plots of insulin binding to liver membranes were curvilinear and showed an increase in the concentration of insulin receptors with advancing age. A single IGF-2 receptor was found on liver and no alteration was observed during development. The brain contained a lower concentration of insulin receptors. A change in the brain receptors for somatomedins occurred during development. Early in gestation, a high concentration of a low-affinity IGF-1 receptor was found. After approximately the 17th wk of gestation a higher affinity IGF-1 receptor appeared, which then increased in concentration. Cross-reaction studies also revealed changes in the specificity of these receptors during development. In the youngest fetal group IGF-2 was preferentially bound. Around midgestation a separate IGF-1 receptor, indicated by the preferential displacement of iodinated IGF-1 by IGF-1, appeared. In contrast, iodinated IGF-2 bound to a receptor where IGF-1 and IGF-2 were equipotent.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard B., Preston B., Beaupre P., Elliott K., Sadava D. Multiple forms of thymidine kinase during human development. Biol Neonate. 1977;31(3-4):225–228. doi: 10.1159/000240964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazquez E., Rubalcava B., Montesano R., Orci L., Unger R. H. Development of insulin and glucagon binding and the adenylate cyclase response in liver membranes of the prenatal, postnatal, and adult rat: evidence of glucagon "resistance". Endocrinology. 1976 Apr;98(4):1014–1023. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-4-1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARDELL B. S. The infants of diabetic mothers; a morphological study. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1953 Dec;60(6):834–853. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1953.tb07282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Underwood L. E., Groelke J., Plet A. Leprechaunism: studies of the relationship among hyperinsulinism, insulin resistance, and growth retardation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Mar;48(3):495–502. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-3-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'ercole A. J., Foushee D. B., Underwood L. E. Somatomedin-C receptor ontogeny and levels in porcine fetal and human cord serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Nov;43(5):1069–1077. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-5-1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbing J., Sands J. Quantitative growth and development of human brain. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Oct;48(10):757–767. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.10.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gréen K., Bygdeman M., Wiqvist N. Kinetic and metabolic studies of Prostaglandin F2-alpha administered intra-amniotically for induction of abortion. Life Sci. 1974 Jun 1;14(11):2285–2297. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gréen K., Granström E., Bygdeman M., Wiqvist N. Kinetic and metabolic studies of 15-methyl-prostaglandin F2alpha administered intra-amniotically for induction of abortion. Prostaglandins. 1976 Apr;11(4):699–711. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K., Brandt J., Enberg G., Fryklund L. Immunoreactive somatomedin A in human serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Feb;48(2):271–278. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-2-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg V. L., Boughter J. M., Carlisle S. K., Ahmad F., Hill D. E. 125I-insulin receptor binding to cord blood erythrocytes of varying gestational age and comparison with adult values. Pediatr Res. 1980 Jan;14(1):4–7. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198001000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Van Obberghen E., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Demonstration of two subtypes of insulin-like growth factor receptors by affinity cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5305–5308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. A., Posner B. I., Tsushima T., Friesen H. G. Studies of insulin, growth hormone and prolactin binding: ontogenesis, effects of sex and pregnancy. Endocrinology. 1974 Aug;95(2):532–539. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-2-532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Olefsky J. M., Elders J., Mako M. E., Given B. D., Schedwie H. K., Fiser R. H., Hintz R. L., Horner J. A., Rubenstein A. H. Insulin resistance due to a defect distal to the insulin receptor: demonstration in a patient with leprechaunism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3469–3473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Todaro G. J., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S. Purification and primary structure of a polypeptide with multiplication-stimulating activity from rat liver cell cultures. Homology with human insulin-like growth factor II. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6859–6865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. N., Underwood L. E., Voina S. J., Foushee D. B., Van Wyk J. J. Characterization of the insulin and somatomedin-C receptors in human placental cell membranes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Aug;39(2):283–292. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nissley S. P., Short P. A., Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M. Purification and characterization of multiplication-stimulating activity. Insulin-like growth factors purified from rat-liver-cell-conditioned medium. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(2):387–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens P. C., Brinsmead M. W., Waters M. J., Thorburn G. D. Ontogenic changes in multiplication-stimulating activity binding to tissues and serum somatomedin-like receptor activity in the ovine fetus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Oct 31;96(4):1812–1820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Zapf J., Nissley S. P., Froesch E. R., Moses A. C., Podskalny J. M., Schilling E. E., Humbel R. E. Interactions of insulin-like growth factors I and II and multiplication-stimulating activity with receptors and serum carrier proteins. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1451–1459. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R., Thorsson A. V., Hintz R. L. Increased somatomedin receptor sites in newborn circulating mononuclear cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Mar;48(3):456–461. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-3-456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sara V. R., Hall K., Rodeck C. H., Wetterberg L. Human embryonic somatomedin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3175–3179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sara V. R., Hall K. Somatomedins and the fetus. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Sep;23(3):765–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sara V. R., Hall K., Von Holtz H., Humbel R., Sjögren B., Wetterberg L. Evidence for the presence of specific receptors for insulin-like growth factors 1 (IGE-1) and 2 (IGF-2) and insulin throughout the adult human brain. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Dec 23;34(1):39–44. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsson A. V., Hintz R. L. Insulin receptors in the newborn. Increase in receptor affinity and number. N Engl J Med. 1977 Oct 27;297(17):908–912. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197710272971704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E. E., Rechler M. M., Romanus J. A., Knight A. B., Nissley S. P., Humbel R. E. Receptors for insulinlike growth factor I are defective in fibroblasts cultured from a patient with leprechaunism. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1356–1365. doi: 10.1172/JCI110383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk J. J., Svoboda M. E., Underwood L. E. Evidence from radioligand assays that somatomedin-C and insulin-like growth factor-I are similar to each other and different from other somatomedins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jan;50(1):206–208. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-1-206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson E. M., Crabb D. E., Milner R. D. Cellular development of some human organs before birth. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Aug;47(254):652–655. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.254.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


