Abstract
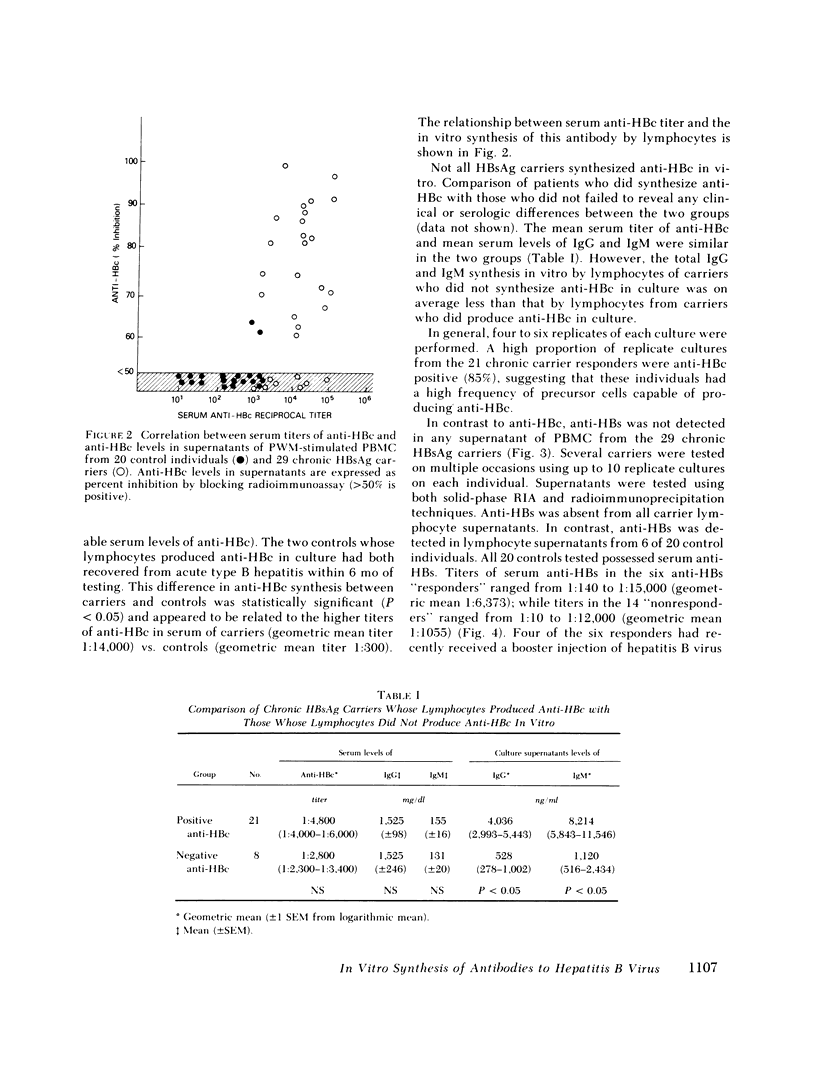
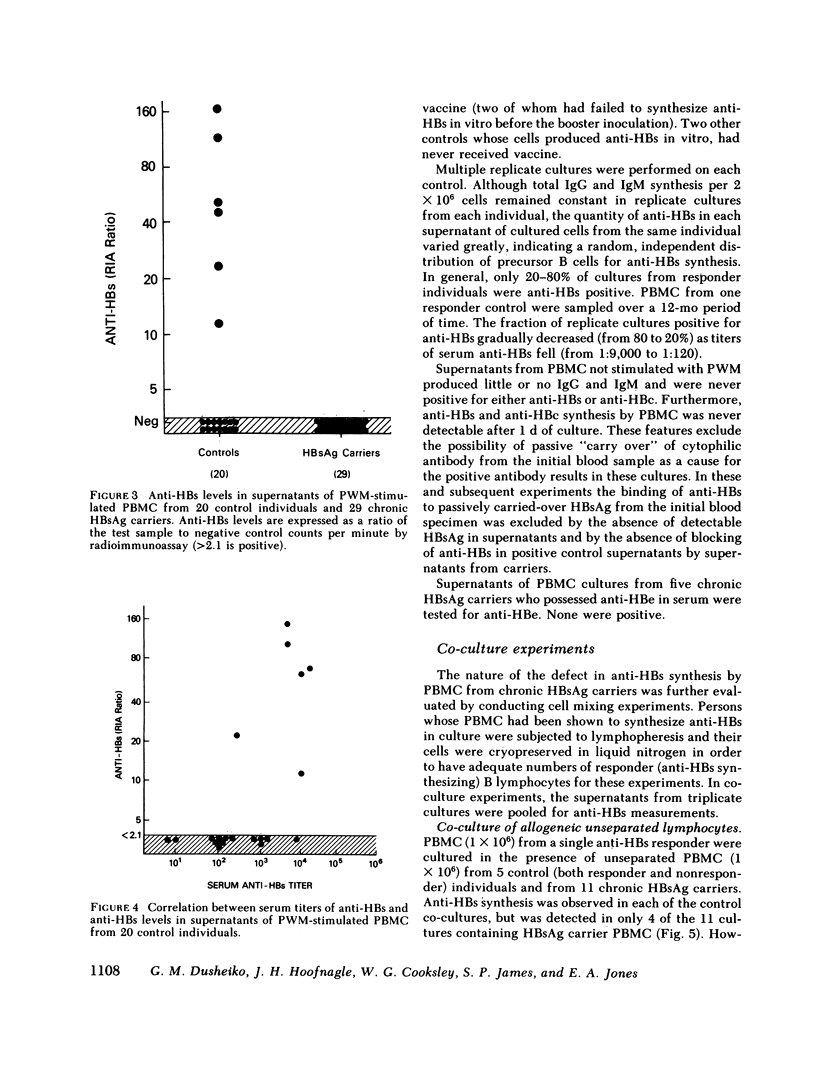
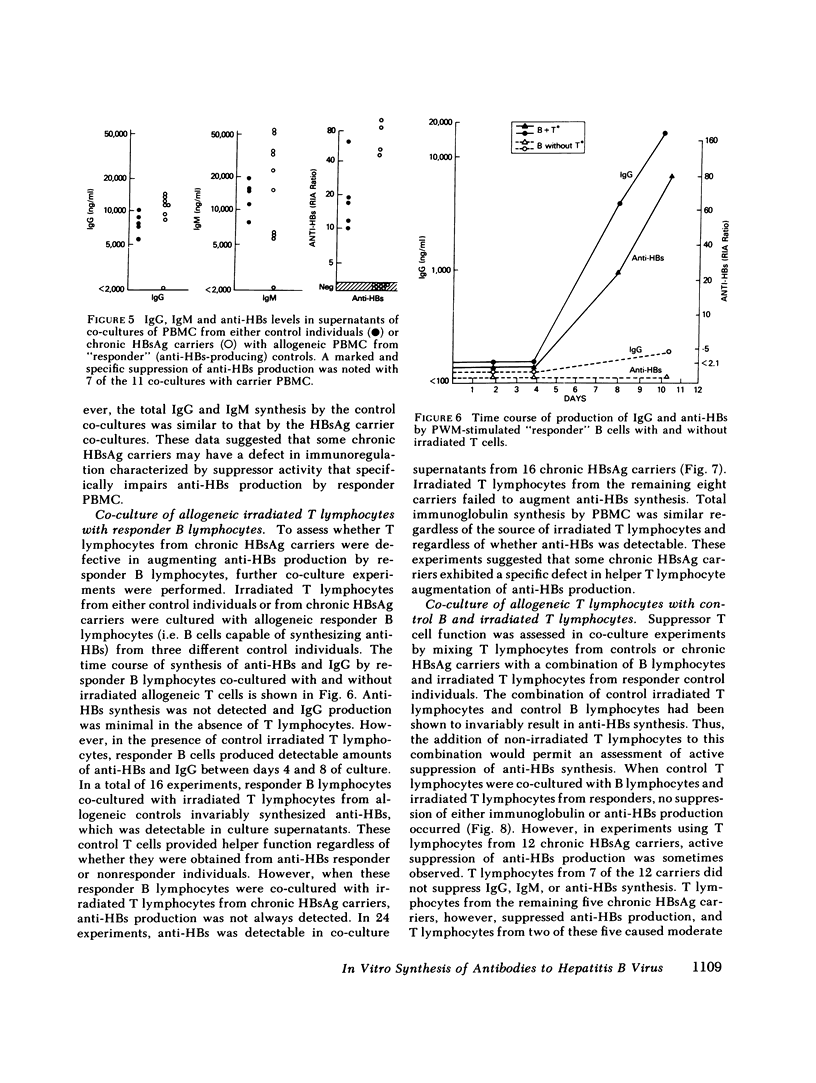
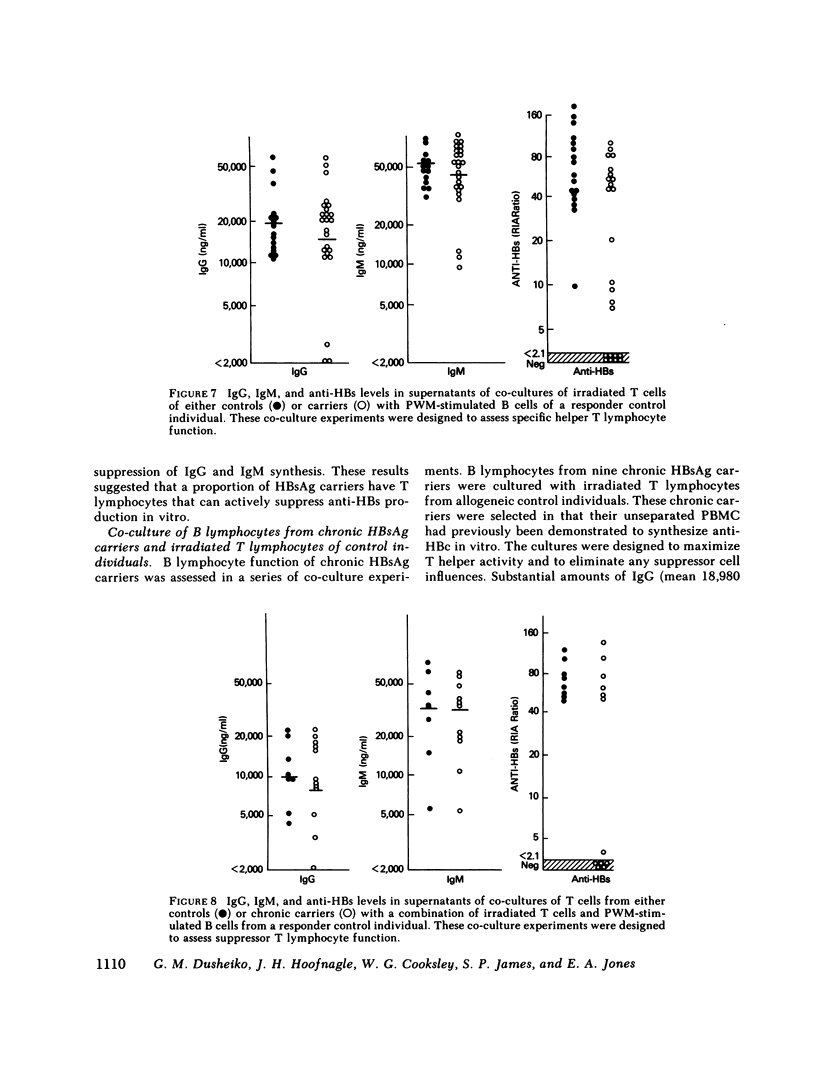
It has been postulated that host immune defects are responsible for the development and persistence of the hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) carrier state. The nature of these defects is unknown, but the absence of a readily detectable antibody response to HBsAg (anti-HBs) may be important. The synthesis of both anti-HBs and antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HBc) in cultures containing peripheral blood mononuclear cells from chronic HBsAg carriers and from control (antibody-positive) patients was measured in the presence of pokeweed mitogen. Similar amounts of polyclonal IgG and IgM were synthesized by cultures containing lymphocytes from chronic carriers and controls. Anti-HBc was detectable in lymphocyte supernatants from 2 of 20 controls and from 21 of 29 carriers. The presence of anti-HBc synthesis in vitro correlated with high serum titers of anti-HBc. In contrast, anti-HBs was detected in lymphocyte supernatants from 6 of 20 controls (predominantly in those who had high serum titers of anti-HBs) but in none of the supernatants from 29 HBsAg carriers. In order to identify the mechanisms for the lack of detectable anti-HBs synthesis by chronic HBsAg carrier lymphocytes, co-culture experiments were performed using T and B lymphocyte fractions that had been purified by affinity chromatography. B lymphocytes from carriers co-cultured with allogeneic irradiated ("helper") T lymphocytes from controls synthesized normal amounts of IgG, IgM, and anti-HBc but still did not synthesize detectable amounts of anti-HBs. In the converse experiments, B lymphocytes from controls were co-cultured with irradiated T lymphocytes from carriers. The T lymphocytes from 16 of 24 carriers augmented anti-HBs production by control B cells normally, the remaining eight did not. Finally, mixtures of control B cells and control irradiated T lymphocytes were co-cultured with T lymphocytes from chronic HBsAg carriers. 5 of 12 carriers demonstrated active suppression of anti-HBs production, and in three this suppression was specific, as IgG and IgM production remained normal. We conclude that chronic HBsAg carriers have a specific B lymphocyte defect in anti-HBs production. In addition, defects in the function of regulatory T lymphocytes may contribute to the absence of anti-HBs synthesis in some HBsAg carriers.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldershvile J., Dietrichson O., Hardt F., Nielsen J. O., Skinhöj P. Humoral and cell-mediated immunity to hepatitis B virus antigens in acute and chronic liver disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(8):917–922. doi: 10.3109/00365527709181350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P. Immune complexes in hepatitis. Lancet. 1969 Nov 8;2(7628):983–986. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90540-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. S., Sutnick A. I., London W. T. Australia antigen as a hepatitis virus. Variation in host response. Am J Med. 1970 Jan;48(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(70)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolin T. D., Davis A. E., Liddelow A. G. Liver disease and cell-mediated immunity in hepatitis-associated antigen (HAA) carriers. Gut. 1973 May;14(5):365–368. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.5.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøyum A. Isolation of lymphocytes, granulocytes and macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess L., MacDermott R. P., Schlossman S. F. Immunologic functions of isolated human lymphocyte subpopulations. I. Quantitative isolation of human T and B cells and response to mitogens. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1113–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desaules M., Frei P. C., Libanska J., Wuilleret B. Lack of leukocyte migration inhibition by hepatitis B antigen and normal nonspecific immunoreactivity in asymptomatic carriers. J Infect Dis. 1976 Nov;134(5):505–509. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.5.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener E., Feldmann M. Mechanisms at the cellular level during induction of high zone tolerance in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1972 Sep;5(1):130–136. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90090-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley F. J., Fox R. A., Sherlock S. Cellular immunity and hepatitis-associated, Australia antigen liver disease. Lancet. 1972 Apr 1;1(7753):723–726. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feighery C., Greally J. F., Weir D. G. Mitogen responsiveness in viral hepatitis and chronic active hepatitis: the role of reversible suppressive influences. Gut. 1980 Sep;21(9):738–744. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.9.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Elson C. O., Jones E. A., Strober W. Abnormal regulation of immunoglobulin synthesis in vitro in primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1980 Aug;79(2):242–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. M., Greenman R. L., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Robinson W. S. DNA polymerase associated with human hepatitis B antigen. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):995–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.995-1005.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Fauci A. S. Inhibition of polyclonal B-cell activation by suppressor monocytes in patients with sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Jun;32(3):554–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander J. J., Alter H. J., Purcell R. H. Frequency of antibody to hepatitis-associated antigen as measured by a new radioimmunoassay technique. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1166–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughter A. H., Lidsky M. D., Twomey J. J. Suppression of immunoglobulin synthesis by monocytes in health and in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Dec;14(4):435–440. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levo Y., Shouval D., Tur-Kaspa R., Wollner S., Penchas S., Zlotnick A., Eliakim M. Immunological evaluation of asymptomatic carriers of hepatitis B virus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Apr;44(1):63–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaliński K., Sztachelska-Budkowska A., Brzosko W. J. DEAE-cellulose chromatography: a method for dissociation of soluble immune complexes of hepatitis B antigen. J Infect Dis. 1974 Apr;129(4):371–375. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.4.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudawwar F. B., Yunis E. J., Geha R. S. Antigen-specific helper factor in man. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1032–1043. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutchnick M. G., Lederman H. M., Missirian A., Johnson A. G. In vitro synthesis of IgG by peripheral blood lymphocytes in chronic liver disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Feb;43(2):370–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. O., Reinicke V., Dietrichson O., Andersen V., Thomsen M., Andersen E. Immunological studies of Australia antigen carriers with and without liver diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Sep;15(1):9–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L. Hepatitis B vaccines. On the threshold. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jul;70(1 Suppl):159–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rümke H. C., Terpstra F. G., Huis B., Out T. A., Zeijlemaker W. P. Immunoglobulin production in human mixed lymphocyte cultures: implications for co-cultures of cells from patients and healthy donors. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):696–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serjeantson S., Woodfield D. G. Immune response of leprosy patients to hepatitis B virus. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Apr;107(4):321–327. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman N. R., Barker L. F. Virus-like antigen, antibody, and antigen-antibody complexes in hepatitis measured by complement fixation. Science. 1969 Jul 18;165(3890):304–306. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3890.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Siegal M. Enhancement by irradiated T cells of human plasma cell production: dissection of helper and suppressor functions in vitro. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):642–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. H. Immunoglobulin-bearing cells are a target for the antigen-induced inhibition of pokeweed mitogen-stimulated antibody production. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):968–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. H., Saxon A. Immunoregulation in humans: control of antitetanus toxoid antibody production after booster immunization. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1154–1160. doi: 10.1172/JCI109234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutnick A. I., Bugbee S. J., London W. T., Loeb L. A., Peyretti F., Litwin S., Blumberg B. S. Lymphocyte function in normal people with persistent Australia antigen. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Jul;82(1):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Trefts P. E., Tse H. Y., Dutton R. W. The significance of T-B collaboration across haplotype barriers. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):597–609. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor E., Gerety R. J., Smallwood L. A., Barker L. F. Coincident hepatitis B surface antigen and antibodies of different subtypes in human serum. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):369–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong M. J., Wallace A. M., Peters R. L., Reynolds T. B. Lymphocyte stimulation in hepatitis B infections. N Engl J Med. 1975 Aug 14;293(7):318–322. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197508142930702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman D. J., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Antigen-induced in vitro antibody production in humans: a model for B cell activation and immunoregulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2528–2531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Mann E., Alpert E., Isselbacher K. J. The pathogenesis of arthritis associated with acute hepatitis-B surface antigen-positive hepatitis. Complement activation and characterization of circulating immune complexes. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):930–936. doi: 10.1172/JCI108022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



