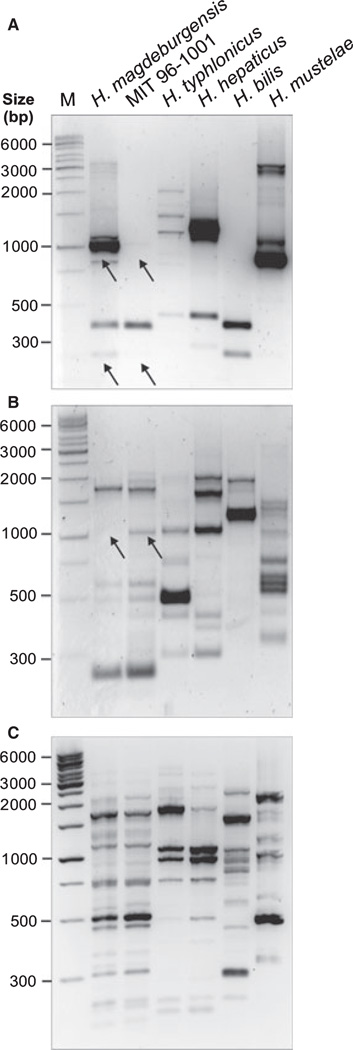
Figure 5.
PCR-based randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) fingerprinting of Helicobacter species. To investigate the genetic relatedness between H. magdeburgensis and the closest known relative (MIT 96-1001) and other strains, we performed RAPD analysis as described [37]. (A–C) This method uses a set of single primers (D14307, D9355 or D8635), which arbitrarily anneal and amplify genomic DNA resulting in strain-specific fingerprinting patterns [39]. Typical RAPD fingerprinting profiles with each of the three primers are shown. Arrows indicate some bands either present or missing in H. magdeburgensis and MIT 96-1001, respectively.