Abstract
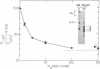
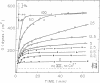
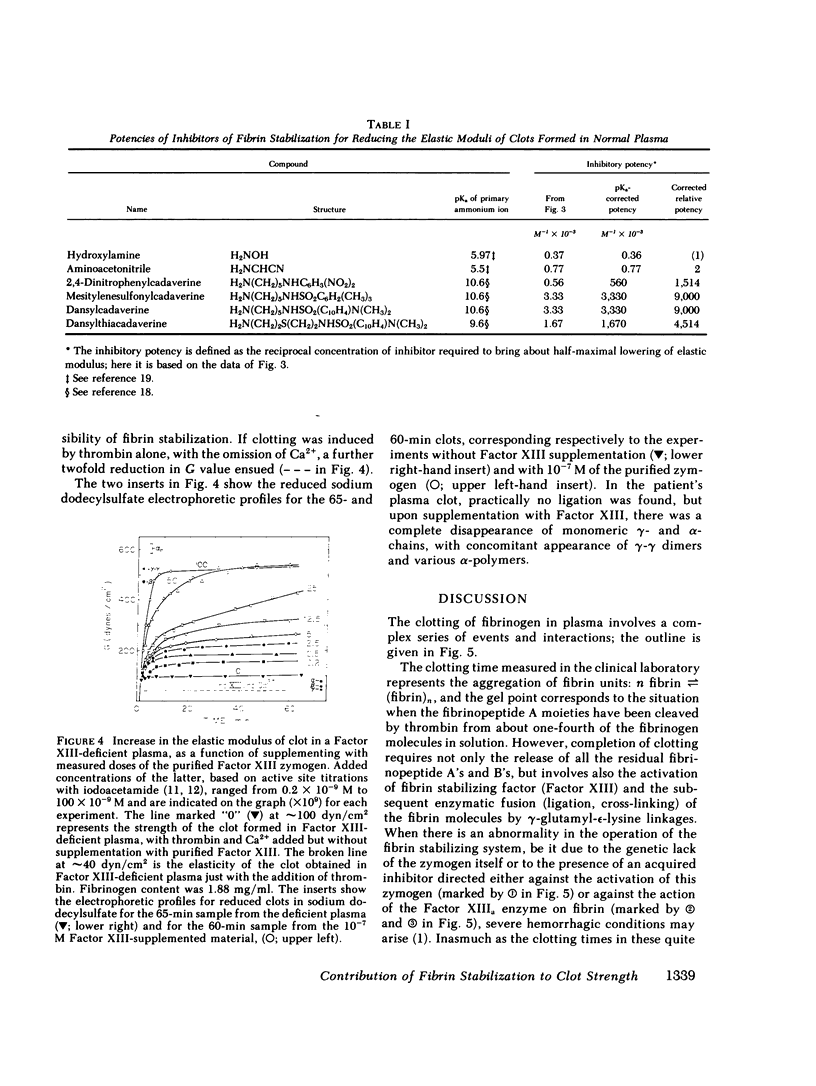
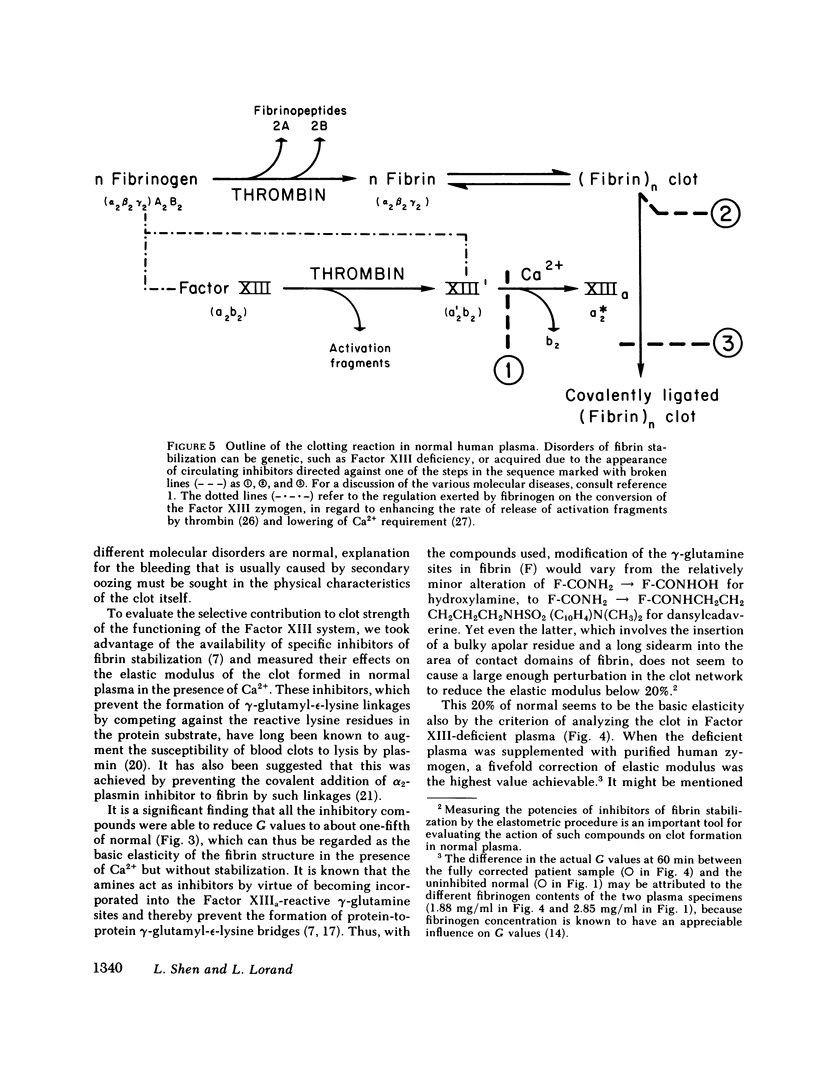
The contribution of fibrin stabilization to clot strength, measured as the static elastic modulus, was evaluated in human plasma by two independent procedures. In the first approach, amine inhibitors of fibrin stabilization were examined for their effects on the rigidity of normal plasma clots. It is a unique property of these inhibitors that they do not interfere with the reversible aggregation of fibrin molecules, i.e., do not delay clotting time, but selectively prevent only the formation of gamma-glutamyl-epsilon-lysine protein-to-protein linkages. Though the compounds tested were of different chemical structures and potencies, a fivefold reduction in clot strength was obtained in each instance. This value of 20% of normal seems to correspond to the rigidity of the Factor XIII-deficient plasma clot because, as demonstrated by the second approach, when a plasma specimen that genetically lacked the fibrin stabilizing factor was supplemented by the addition of measured amounts of the purified zymogen, a fivefold increase in clot strength could be achieved. The described procedure of evaluating Factor XIII in terms of correcting the elastic modulus of a deficient plasma clot is considered an important assay for the functional competence of purified preparations of the zymogen for the purpose of therapeutic application.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTRUP T., BRAKMAN P., NISSEN U. THE ESTIMATION OF FIBRINOGEN. A REVISION. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1965;17:57–65. doi: 10.3109/00365516509077284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. E., Shen L. L., Hermans J. A physical standard of fibrinogen: measurement of the elastic modulus of dilute fibrin gels with a new elastometer. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90522-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Credo R. B., Curtis C. G., Lorand L. Alpha-chain domain of fibrinogen controls generation of fibrinoligase (coagulation factor XIIIa). Calcium ion regulatory aspects. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3770–3778. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis C. G., Brown K. L., Credo R. B., Domanik R. A., Gray A., Stenberg P., Lorand L. Calcium-dependent unmasking of active center cysteine during activation of fibrin stabilizing factor. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3774–3780. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis C. G., Lorand L. Fibrin-stabilizing factor (factor XIII). Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:177–191. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerth C., Roberts W. W., Ferry J. D. Rheology of fibrin clots. II. Linear viscoelastic behavior in shear creep. Biophys Chem. 1974 Oct;2(3):208–217. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(74)80046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. J., McIntire L. V., Brown C. H., 3rd, Natelson E. A. Rheological properties of fibrin clots. Effects of fibrinogen concentration, Factor XIII deficiency, and Factor XIII inhibition. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Oct;86(4):644–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand J. B., Pilkington T. R., Lorand L. Inhibitors of fibrin cross-linking: relevance for thrombolysis. Nature. 1966 Jun 18;210(5042):1273–1274. doi: 10.1038/2101273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Campbell-Wilkes L. K., Cooperstein L. A filter paper assay for transamidating enzymes using radioactive amine substrates. Anal Biochem. 1972 Dec;50(2):623–631. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Lockridge O. M., Campbell L. K., Myhrman R., Bruner-Lorand J. Transamidating enzymes. II. A continuous fluorescent method suited for automating measurements of factor XIII in plasma. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):221–231. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90363-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Losowsky M. S., Miloszewski K. J. Human factor XIII: fibrin-stabilizing factor. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1980;5:245–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Ong H. H. Labeling of amine-acceptor cross-linking sites of fibrin by transpeptidation. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1747–1753. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Parameswaran K. N., Stenberg P., Tong Y. S., Velasco P. T., Jönsson N. A., Mikiver L., Moses P. Specificity of guinea pig liver transglutaminase for amine substrates. Biochemistry. 1979 May 1;18(9):1756–1765. doi: 10.1021/bi00576a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Rule N. G., Ong H. H., Furlanetto R., Jacobsen A., Downey J., Oner N., Bruner-Lorand J. Amine specificity in transpeptidation. Inhibition of fibrin cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1968 Mar;7(3):1214–1223. doi: 10.1021/bi00843a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Urayama T., De Kiewiet J. W., Nossel H. L. Diagnostic and genetic studies on fibrin-stabilizing factor with a new assay based on amine incorporation. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jun;48(6):1054–1064. doi: 10.1172/JCI106061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mockros L. F., Roberts W. W., Lorand L. Viscoelastic properties of ligation-inhibited fibrin clots. Biophys Chem. 1974 Aug;2(2):164–169. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(74)80037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelb G. W., Gerth C., Ferry J. D. Rheology of fibrin clots. III. Shear creep and creep recovery of fine ligated and coarse unligated closts. Biophys Chem. 1976 Sep;5(3):377–387. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(76)80050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. W., Lorand L., Mockros L. F. Viscoelastic properties of fibrin clots. Biorheology. 1973 Mar;10(1):29–42. doi: 10.3233/bir-1973-10105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata Y., Aoki N. Cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin by fibrin-stabilizing factor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):290–297. doi: 10.1172/JCI109671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Pizzo S. V., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. Human Factor XIII from plasma and platelets. Molecular weights, subunit structures, proteolytic activation, and cross-linking of fibrinogen and fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1395–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Hermans J., McDonagh J., McDonagh R. P., Carr M. Effects of calcium ion and covalent crosslinking on formation and elasticity of fibrin cells. Thromb Res. 1975 Mar;6(3):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., McDonagh R. P., McDonagh J., Hermans J., Jr Fibrin gel structure: influence of calcium and covalent cross-linking on the elasticity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 4;56(3):793–798. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90675-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]