Abstract
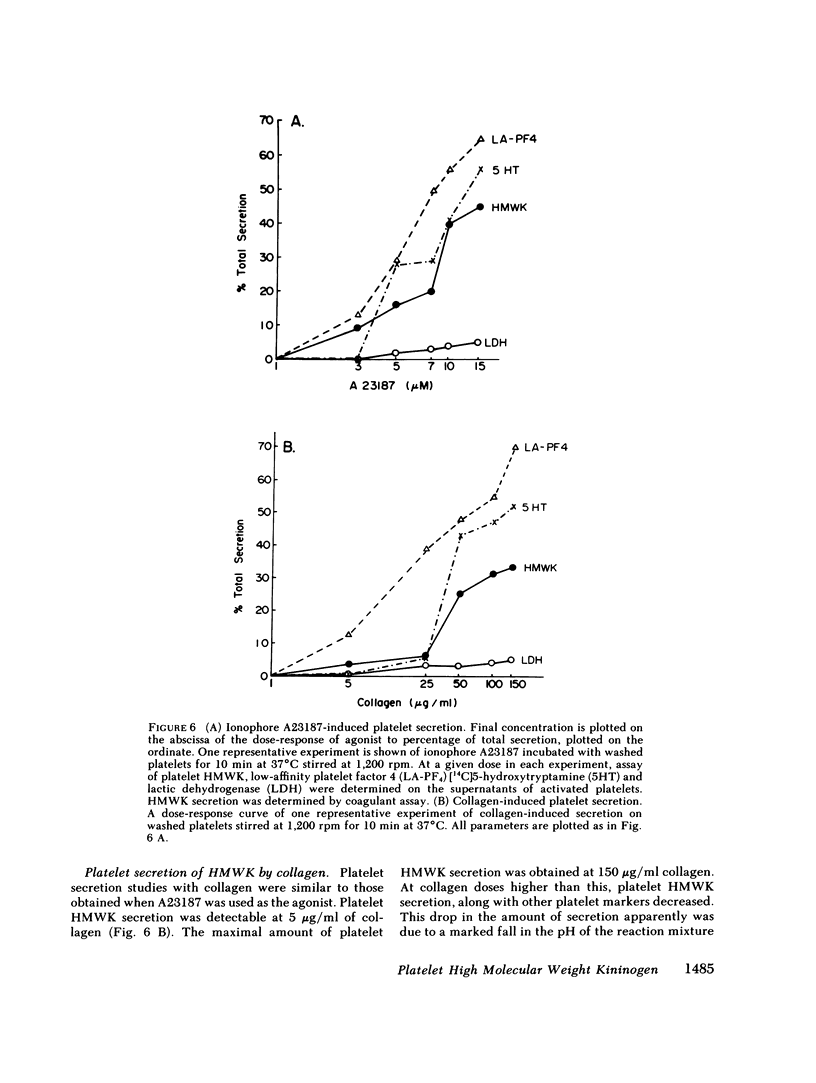
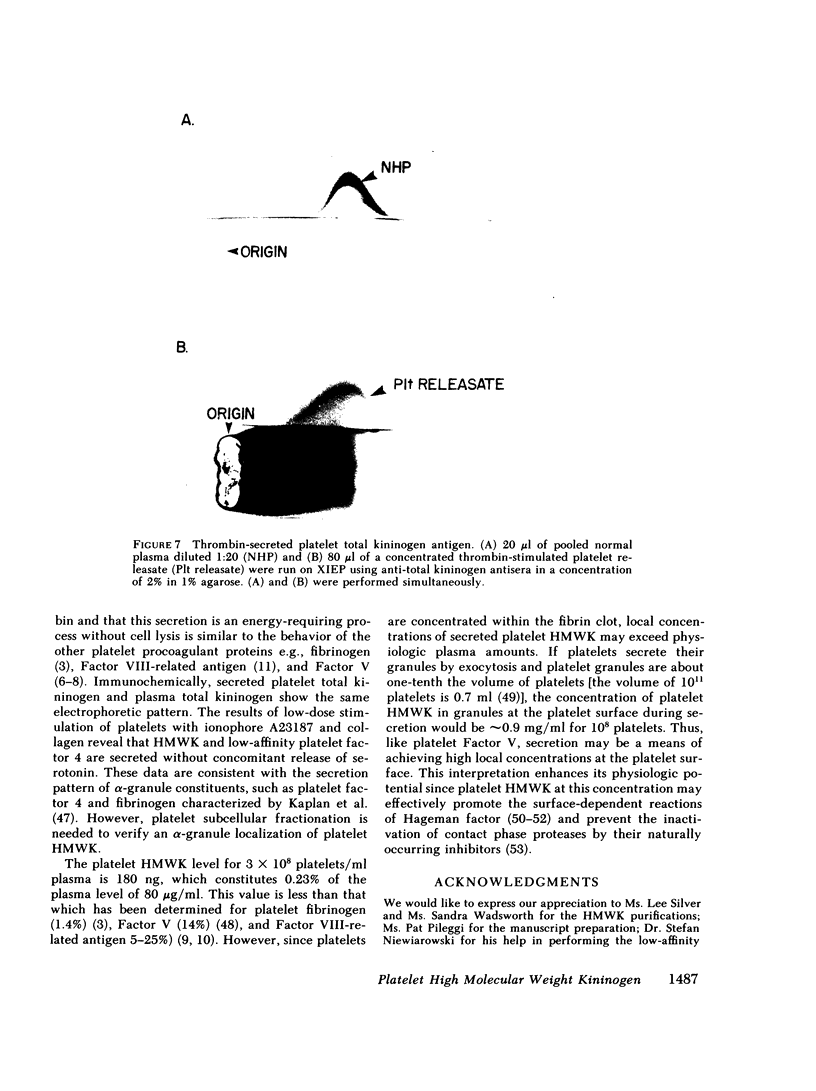
Human platelets were studied immunochemically to determine if they contain high-molecular weight kininogen. On crossed immunoelectrophoresis with total kininogen antisera (antisera that recognizes both high- and low-molecular weight kininogen) extracts of platelets contained total kininogen antigen. Platelet total kininogen antigen showed complete antigenic identity with plasma total kininogen and displayed the same electrophoretic migration as plasma total kininogen. Using antisera monospecific to high molecular weight kininogen, a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (CELISA) was developed to directly measure platelet high-molecular weight kininogen. By CELISA, 27-101 ng of high molecular weight kininogen antigen per 10(8) platelets was quantitated in detergent-soluble lysates of washed human platelets from nine normal donors with a mean level of 60 ng +/- 24/10(8) platelets. Plasma high-molecular weight kininogen, either in the platelet suspending medium or on the surface of the platelets, could only account for 5% of antigen measured in the solubilized platelets. On the CELISA, platelet high-molecular weight kininogen was immunochemically identical to plasma and purified high-molecular weight kininogen. Platelet high-molecular weight kininogen was secreted from platelets after exposure to ionophore A23187 (3-15 microM), collagen (5-150 micrograms/ml), and thrombin (1.6 U/ml). Secreted platelet high-molecular weight kininogen did not become a part of the platelet Triton-insoluble cytoskeleton. On cross immunoelectrophoresis secreted platelet total kininogen antigen had a similar electrophoretic migration to plasma total kininogen. Thus, human platelets contain high-molecular weight kininogen that can be secreted from platelets and that may participate in plasma coagulation reactions.
Full text
PDF



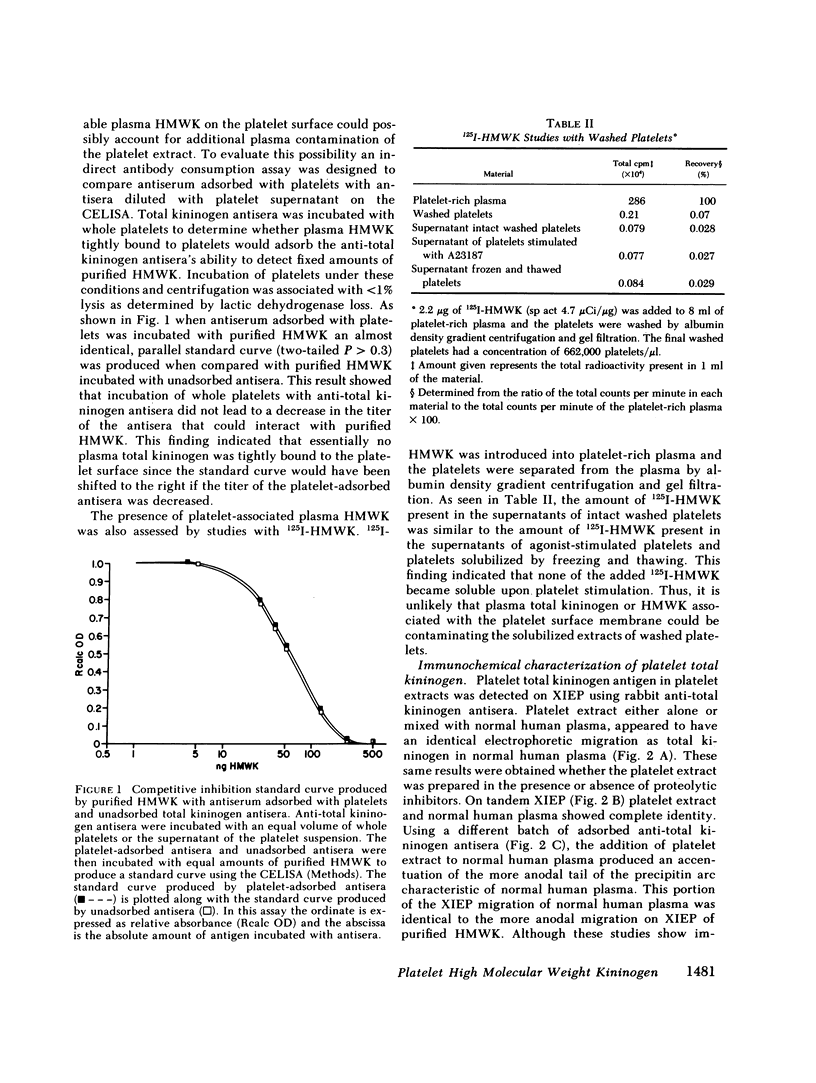
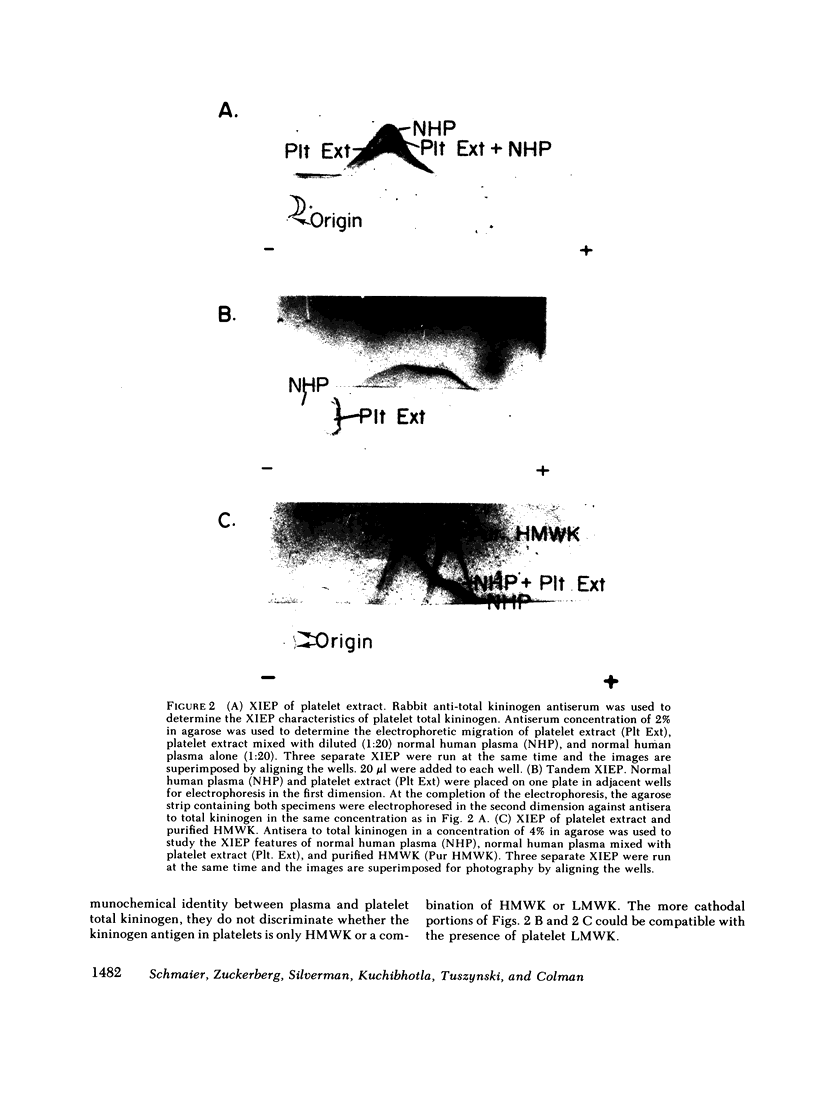
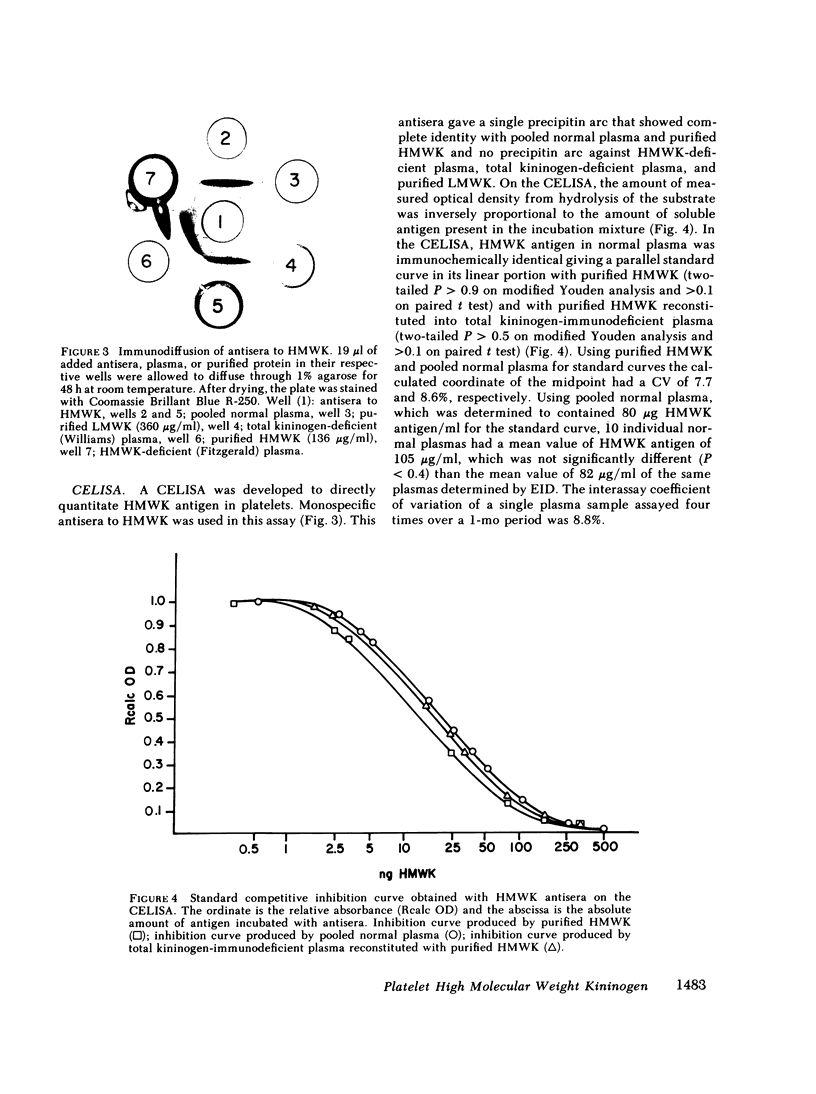
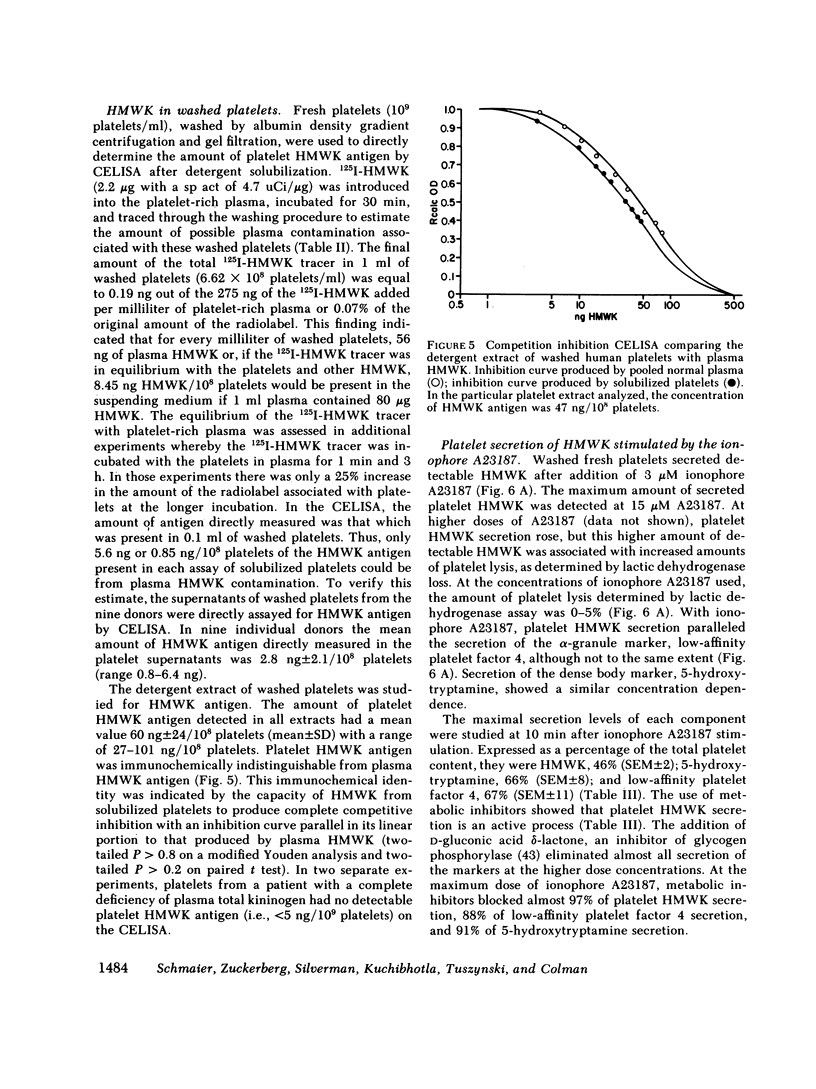



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breederveld K., Giddings J. C., ten Cate J. W., Bloom A. L. The localization of factor V within normal human platelets and the demonstration of a platelet-factor V antigen in congenital factor V deficiency. Br J Haematol. 1975 Mar;29(3):405–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb01838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekman M. J., Handin R. I., Cohen P. Distribution of fibrinogen, and platelet factors 4 and XIII in subcellular fractions of human platelets. Br J Haematol. 1975 Sep;31(1):51–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canellas P. F., Karu A. E. Statistical package for analysis of competition ELISA results. J Immunol Methods. 1981;47(3):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney C. M., Pifer D., Colman R. W. Subcellular localization and secretion of factor V from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5180–5184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Bagdasarian A., Talamo R. C., Scott C. F., Seavey M., Guimaraes J. A., Pierce J. V., Kaplan A. P. Williams trait. Human kininogen deficiency with diminished levels of plasminogen proactivator and prekallikrein associated with abnormalities of the Hageman factor-dependent pathways. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1650–1662. doi: 10.1172/JCI108247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Edelman R., Scott C. F., Gilman R. H. Plasma kallikrein activation and inhibition during typhoid fever. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):287–296. doi: 10.1172/JCI108938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Schreiber A. D. Effect of heterologous antibody on human platelets. Blood. 1976 Jul;48(1):119–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E. Enzyme immunoassay ELISA and EMIT. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):419–439. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Cochrane C. G. Mechanisms for the involvement of high molecular weight kininogen in surface-dependent reactions of Hageman factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habal F. M., Movat H. Z., Burrowes C. E. Isolation of two functionally different kininogens from human plasma--separation from proteinase inhibitors and interaction with plasma kallikrein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Aug 15;23(16):2291–2303. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90558-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habal F. M., Movat H. Z. Rapid purification of human high molecular weight kininogen. Agents Actions. 1976 Sep;6(5):565–568. doi: 10.1007/BF01971570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Robkin L. Effects of antimycin A and 2-deoxyglucose on energy metabolism in washed human platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Feb 29;42(5):1460–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerushalmy Z., Zucker M. B. Some effects of fibrinogen degradation products (FDP) on blood platelets. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 May 15;15(3):413–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Lindhout M. J., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Factor Va-dependent binding of factor Xa to human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1170–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K. L., Broekman M. J., Chernoff A., Lesznik G. R., Drillings M. Platelet alpha-granule proteins: studies on release and subcellular localization. Blood. 1979 Apr;53(4):604–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keenan J. P., Solum N. O. Quantitative studies on the release of platelet fibrinogen by thrombin. Br J Haematol. 1972 Oct;23(4):461–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb07080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koutts J., Walsh P. N., Plow E. F., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Bouma B. N., Zimmerman T. S. Active release of human platelet factor VIII-related antigen by adenosine diphosphate, collagen, and thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1255–1263. doi: 10.1172/JCI109246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb M. S., Walsh P. N. Human platelets and factor XI. Localization in platelet membranes of factor XI-like activity and its functional distinction from plasma factor XI. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):1006–1014. doi: 10.1172/JCI109368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier H. L., Pierce J. V., Colman R. W., Kaplan A. P. Activation and function of human Hageman factor. The role of high molecular weight kininogen and prekallikrein. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):18–31. doi: 10.1172/JCI108754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Jaffe E. A. Subcellular platelet factor VIII antigen and von Willebrand factor. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):1101–1113. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Marcus A. J., Zucker-Franklin D. Immunologic studies of proteins associated with subcellular fractions of normal human platelets. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Apr;69(4):651–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I., Lavine K. K. Factor V activity of platelets: evidence for an activated factor V molecule and for a platelet activator. Blood. 1977 May;49(5):819–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCTOR R. R., RAPAPORT S. I. The partial thromboplastin time with kaolin. A simple screening test for first stage plasma clotting factor deficiencies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961 Sep;36:212–219. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/36.3.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rucinski B., Niewiarowski S., James P., Walz D. A., Budzynski A. Z. Antiheparin proteins secreted by human platelets. purification, characterization, and radioimmunoassay. Blood. 1979 Jan;53(1):47–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., James A., Silver L. D., Kueppers F., James H. L., Colman R. W. High molecular weight kininogen or its light chain protects human plasma kallikrein from inactivation by plasma protease inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):567–572. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Claypool W., Colman R. W. Crotalocytin: recognition and purification of a timber rattlesnake platelet aggregating protein. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):1013–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Colman R. W. Crotalocytin: characterization of the timber rattlesnake platelet activating protein. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):1020–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Function and immunochemistry of prekallikrein-high molecular weight kininogen complex in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):413–421. doi: 10.1172/JCI109684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg M., Nicoll J. E., Kaplan A. P. The mechanism by which the light chain of cleaved HMW-kininogen augments the activation of prekallikrein, factor XI and Hageman factor. Thromb Res. 1980 Oct 15;20(2):173–189. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90383-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. E., Mandle R., Jr, Kaplan A. P. Characterization of human high molecular weight kininogen. Procoagulant activity associated with the light chain of kinin-free high molecular weight kininogen. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):488–499. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmons S., Hawiger J. Separation of human platelets from plasma proteins including factor VIII VWF by a combined albumin gradient-gel filtration method using HEPES buffer. Thromb Res. 1978 Feb;12(2):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90300-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Eide L. L., Bowie E. J., Mann K. G. Radioimmunoassay of factor V in human plasma and platelets. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):59–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuszynski G. P., Bevacqua S. J., Schmaier A. H., Colman R. W., Walsh P. N. Factor XI antigen and activity in human platelets. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1148–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuszynski G. P., Walsh P. N., Piperno J. R., Koshy A. Association of coagulation factor V with the platelet cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4557–4563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicic W. J., Lages B., Weiss H. J. Release of human platelet factor V activity is induced by both collagen and ADP and is inhibited by aspirin. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):448–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N., Gagnatelli G. Platelet antiheparin activity: storage site and release mechanism. Blood. 1974 Aug;44(2):157–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N., Mills D. C., White J. G. Metabolism and function of human platelets washed by albumin density gradient separation. Br J Haematol. 1977 Jun;36(2):287–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N. The effects of collagen and kaolin on the intrinsic coagulant activity of platelets. Evidence for an alternative pathway in intrinsic coagulation not requiring factor XII. Br J Haematol. 1972 Apr;22(4):393–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb05687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N. The role of platelets in the contact phase of blood coagulation. Br J Haematol. 1972 Feb;22(2):237–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Broekman M. J., Kaplan K. L. Factor VIII-related antigen in human blood platelets: localization and release by thrombin and collagen. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Nov;94(5):675–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









