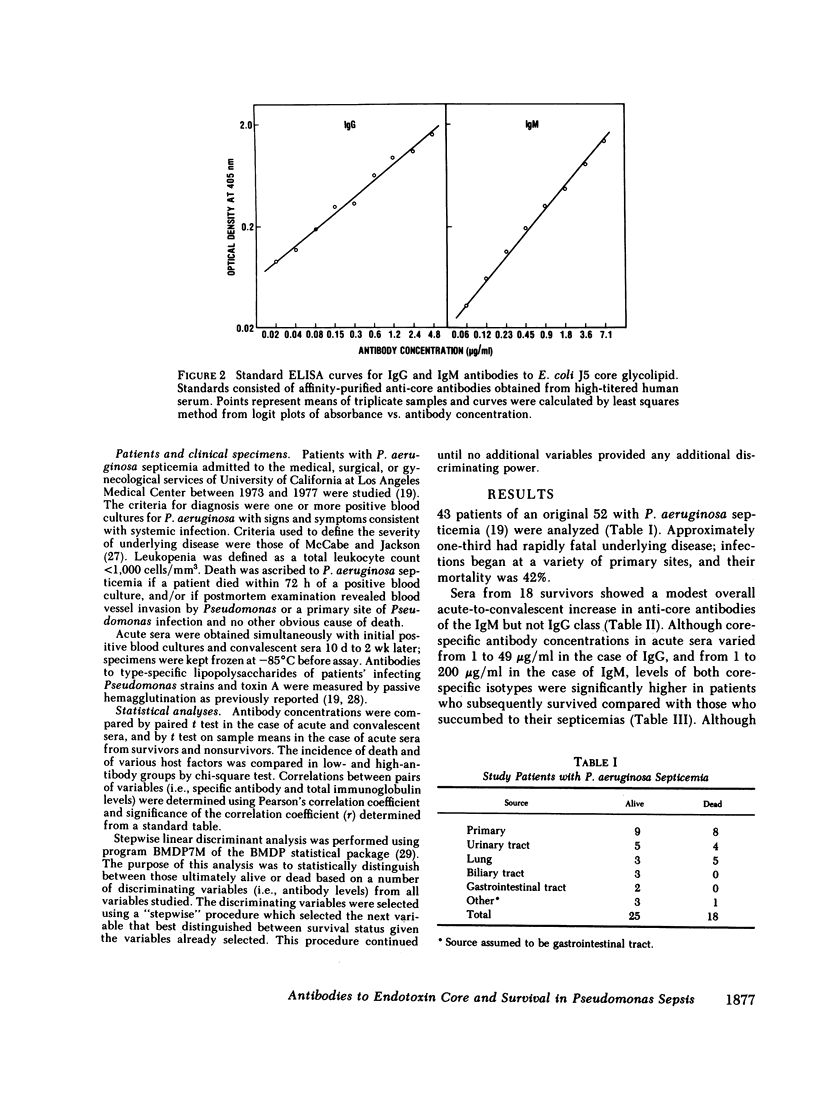
Abstract
We studied the relationship between serum antibodies to the cross-reactive endotoxin core of Escherichia coli and survival following Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicemia. Core glycolipid was purified from the outer cell membrane of a uridine diphosphate galactose 4-epimerase-deficient rough mutant E. coli (J5 strain), characterized, and used as the antigen in a quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to measure core-specific IgG and IgM antibodies. 43 patients with Pseudomonas septicemia, among whom there was a mortality of 42%, were evaluated. Core-specific antibody concentrations in acute sera ranged from 1 to 49 micrograms/ml in the case of IgG and from 1 to 200 micrograms/ml for IgM. Core-specific antibodies of both isotypes were higher in patients who survived compared with those who succumbed to their septicemias (mean, microgram/ml +/- SEM, 26 +/- 3 vs. 14 +/- 4, P = 0.005 for IgG, and 55 +/- 12 vs. 18 +/- 5, P = 0.009 for IgM). Although total IgG levels were also higher in acute sera from survivors compared with nonsurvivors (mean, mg/dl +/- SEM, 1,120 +/- 99 vs. 694 +/- 119, P = 0.004), total IgM levels were virtually identical in the two groups (146 +/- 23 vs. 148 +/- 48, P = 0.52). Conversely, patients with core-specific IgG levels greater than 10 micrograms/ml at the onset of septicemia had better survival than those with levels less than 10 micrograms/ml (79 vs. 14%, P less than 0.001), and patients with core-specific IgM levels greater than 30 micrograms/ml had better survival than those with levels less than 30 micrograms/ml (81 vs. 44%, P = 0.01). In comparison, patients with total IgG levels greater than 1,000 mg/dl also had better survival than those with levels less than 1,000 mg/dl (82 vs. 42%, P = 0.01), while those with total IgM levels greater than 150 mg/dl showed somewhat less improvement in survival compared with those with levels less than 150 mg/dl (71 vs. 50%, P = 0.12). Core-specific IgM was highly correlated with core-specific IgG (r = 0.52), but not with type-specific anti-lipopolysaccharide (r = 0.13) or anti-toxin A (r = 0.12) antibodies, or with total IgG (r = 0.28) or IgM (r = 0.31). In contrast, core-specific IgG correlated somewhat more closely with type-specific antibodies (r = 0.36), and with total IgG (r = 0.51) and IgM (r = 0.52). Stepwise linear discriminant analysis indicated that type-specific antibody levels were the best predictor of outcome, among those antibodies examined, followed by anti-core IgM. Although anti-core IgG, anti-toxin A, and total IgG levels all correlated individually with survival, none augmented the prognostic power of type-specific antibodies in combination with anti-core IgM, which together predicted outcome accurately 73.5% of the time. Host factors not significantly associated with anti-core antibody levels included rapidly fatal underlying disease, age, sex, leukopenia, and prior treatment with cytotoxic drugs. In contrast, prior steroid therapy was associated with low levels of both core-specific IgG and IgM (P < 0.05). These data suggest cross-protective activity against P. aeruginosa septicemia of naturally occurring antibodies to the endotoxin core of E. coli. Anti-core antibodies, particularly of the IgM isotype appear to augment the more specific protective immunity engendered by antibodies to the O-specific side chains of Pseudomonas lipopolysaccharides. This cross-protective immunity likely applies to other Gram-negative pathogens as well.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braude A. I., Ziegler E. J., Douglas H., McCutchan J. A. Antibody to cell wall glycolipid of Gram-negative bacteria: induction of immunity to bacteremia and endotoxemia. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S167–S173. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. T., Rossen R. D. Effects of corticosteroids on immunity in man. I. Decreased serum IgG concentration caused by 3 or 5 days of high doses of methylprednisolone. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2629–2640. doi: 10.1172/JCI107455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Parant F., Boyer F. A proposed mechanism for natural immunity to enterobacterial pathogens. J Immunol. 1968 Feb;100(2):292–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELBEIN A. D., HEATH E. C. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF CELL WALL LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. THE BIOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF A URIDINE DIPHOSPHATE GALACTOSE 4-EPIMERASELESS MUTANT. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:1919–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller N. A., Wu M., Wilkinson R. G., Heath E. C. The biosynthesis of cell wall lipopolysaccharide in Escherichia coli. VII. Characterization of heterogeneous "core" oligosaccharide structures. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7938–7950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath E. C., Mayer R. M., Edstrom R. D., Beaudreau C. A. Structure and biosynthesis of the cell wall lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):315–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns M. A., Bruins S. C., McCabe W. R. Immunization with R mutants of Salmonella minnesota. II. Serological response to lipid A and the lipopolysaccharide of Re mutants. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):9–15. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.9-15.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns M., Skehill A., McCabe W. R. Immunization with rough mutants of Salmonella minnesota. IV. Protection by antisera to O and rough antigens against endotoxin. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):57–67. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R. Immunization with R mutants of S. Minnesota. I. Protection against challenge with heterologous gram-negative bacilli. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):601–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R., Kreger B. E., Johns M. Type-specific and cross-reactive antibodies in gram-negative bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 1972 Aug 10;287(6):261–267. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197208102870601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng A. K., Chen C. L., Chang C. M., Nowotny A. Relationship of structure to function in bacterial endotoxins: serologically cross-reactive components and their effect on protection of mice against some gram-negative infections. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):107–116. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Taylor N. S. Serum antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin measured by a passive hemagglutination assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):58–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.58-61.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Young L. S. Protective activity of antibodies to exotoxin A and lipopolysaccharide at the onset of Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):276–286. doi: 10.1172/JCI109300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore B. J., Morrison D. C., Chiller J. M., Weigle W. O. Immunologic properties of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). II. The unresponsiveness of C3H/HeJ Mouse spleen cells to LPS-induced mitogenesis is dependent on the method used to extract LPS. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1488–1508. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Johnston A. R., Weinstein D. B. New function for high density lipoproteins. Isolation and characterization of a bacterial lipopolysaccharide-high density lipoprotein complex formed in rabbit plasma. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):827–837. doi: 10.1172/JCI110100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Hoffman K. R., Stevens P. "Core" glycolipid of enterobacteriaceae: immunofluorescent detection of antigen and antibody. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jun;149(2):389–396. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. Human immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Relationship between heat-stable opsonins and type-specific lipopolysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):277–287. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Stevens P., Ingram J. Functional role of antibody against "core" glycolipid of Enterobacteriaceae. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):850–861. doi: 10.1172/JCI108164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., Douglas H., Sherman J. E., Davis C. E., Braude A. I. Treatment of E. coli and klebsiella bacteremia in agranulocytic animals with antiserum to a UDP-gal epimerase-deficient mutant. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):433–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., McCutchan J. A., Douglas H., Braude A. I. Prevention of lethal pseudomonas bacteremia with epimerase-deficient E. coli antiserum. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1975;88:101–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., McCutchan J. A., Fierer J., Glauser M. P., Sadoff J. C., Douglas H., Braude A. I. Treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and shock with human antiserum to a mutant Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1982 Nov 11;307(20):1225–1230. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198211113072001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]