Abstract
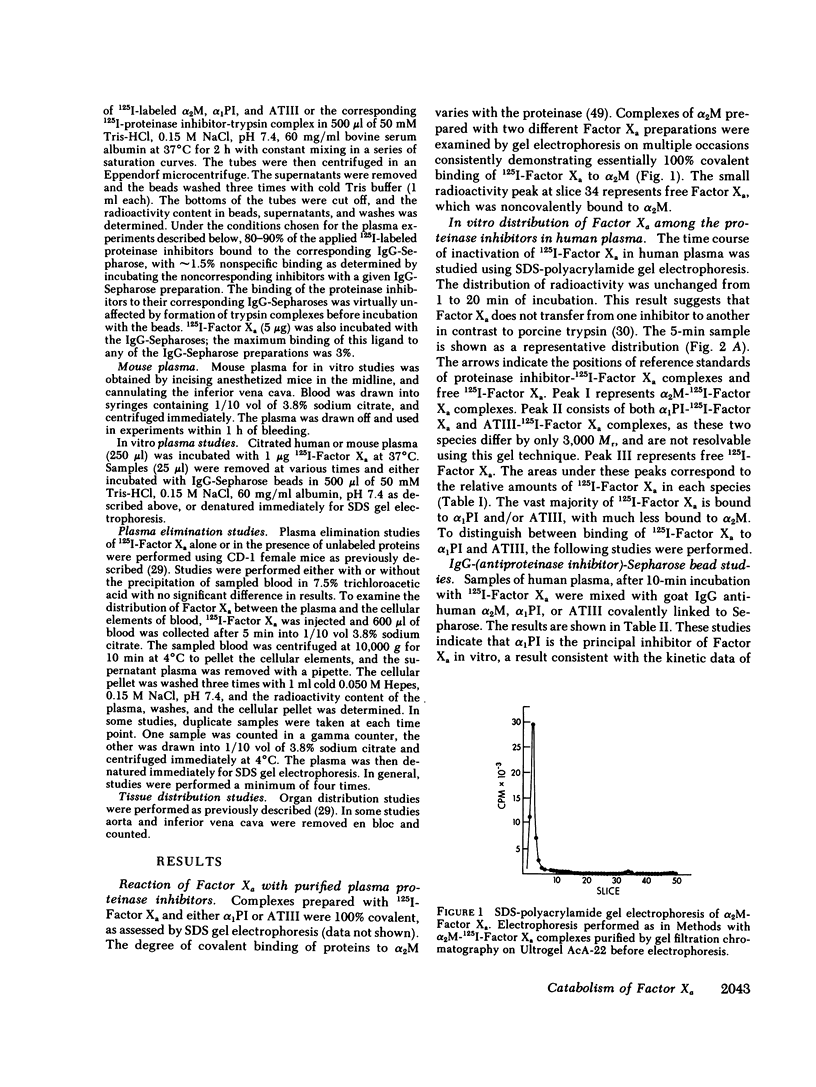
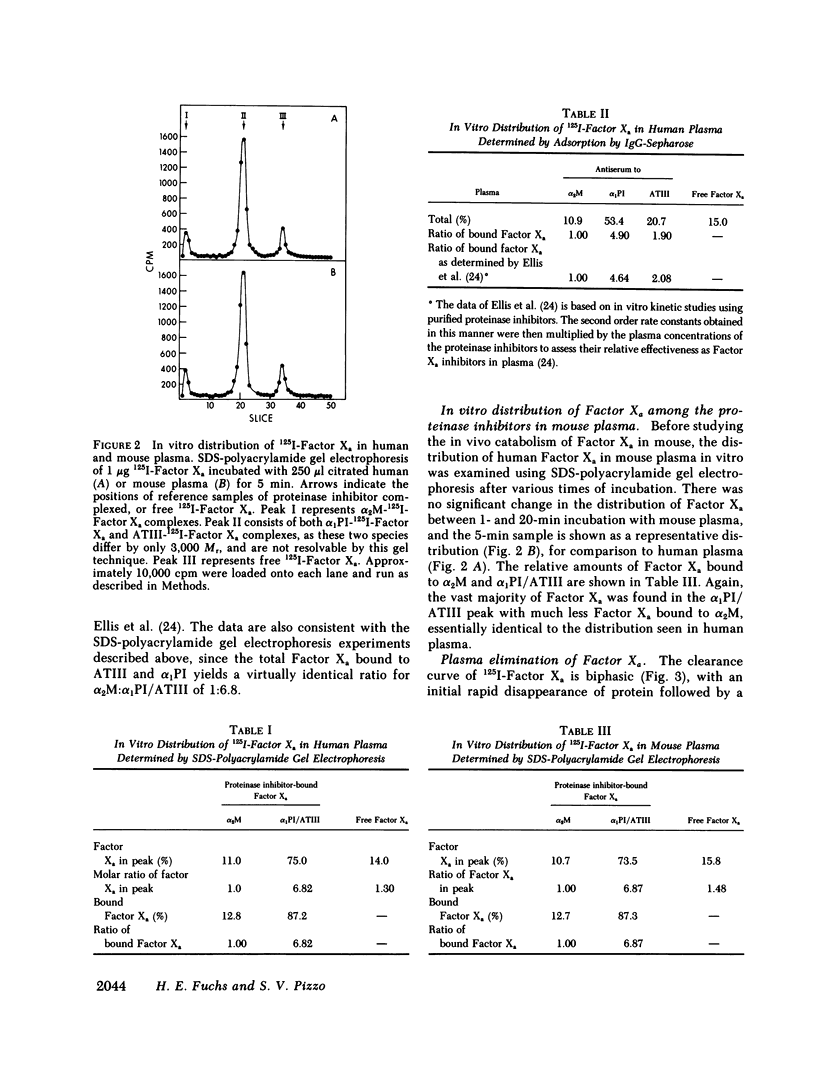
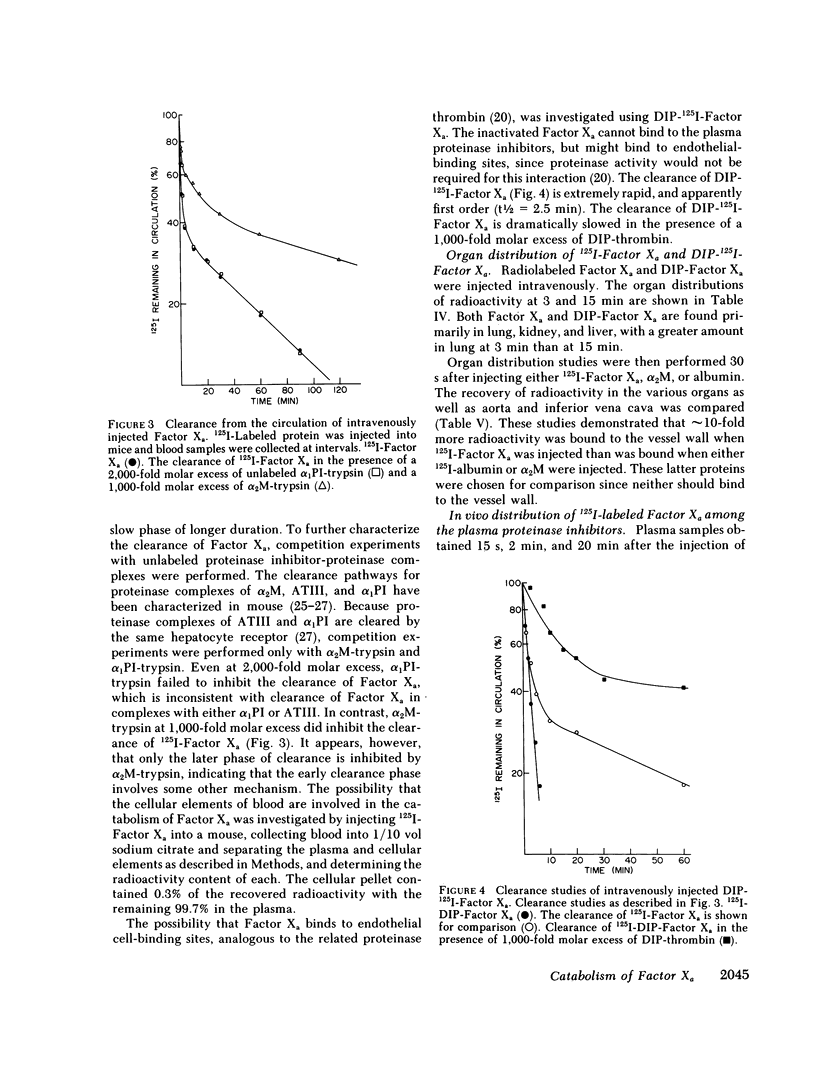
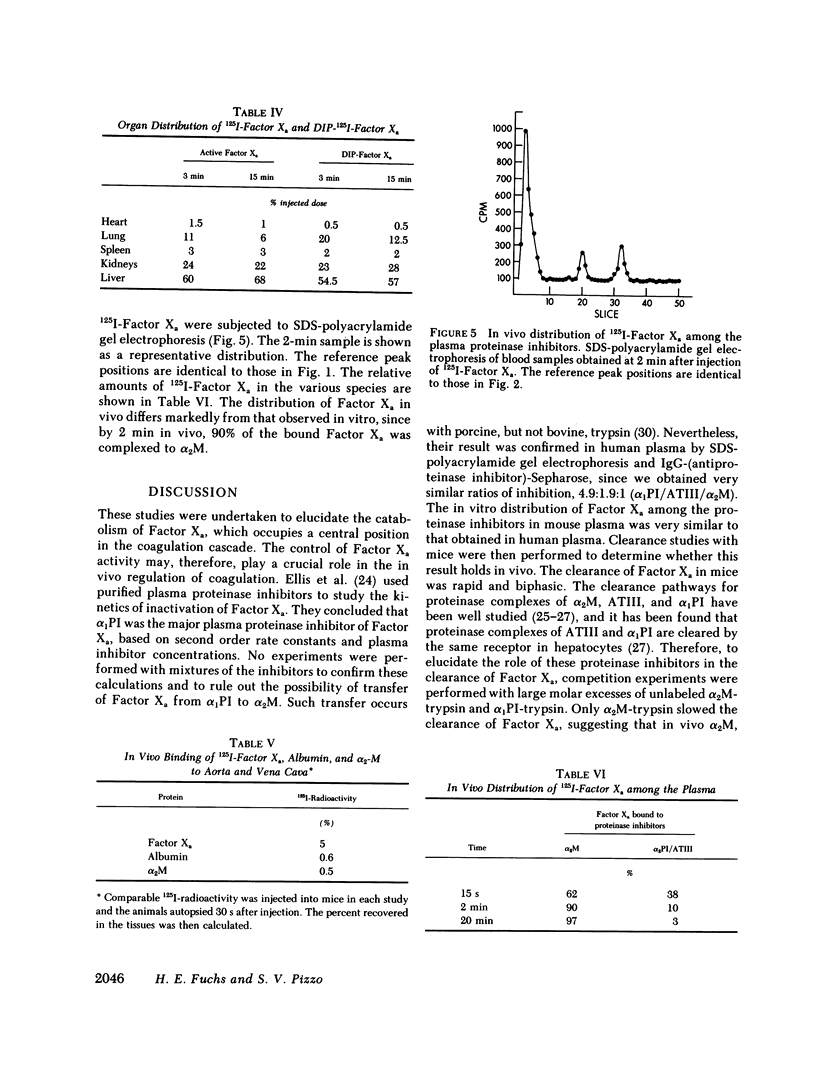
The regulation of human Factor Xa was studied in vitro in human and mouse plasma, and in vivo in mouse. In human plasma, 125I-Factor Xa bound to alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor, antithrombin III, and alpha 2-macroglobulin in a ratio of 4.9:1.9:1 as determined by gel electrophoresis and by adsorption to IgG-(antiproteinase inhibitor)-Sepharose beads. The distribution of Factor Xa in mouse plasma was similar. The clearance of Factor Xa in mice was rapid (50% clearance in 3 min) and biphasic. alpha 1-Proteinase inhibitor-trypsin, even at a 2,000-fold molar excess, failed to inhibit the clearance of Factor Xa, while alpha 2-macroglobulin-trypsin inhibited only the later phase of clearance. The plasma clearance of diisopropylphosphoryl-Factor Xa was more rapid than native Factor Xa (50% clearance in 2.5 min), and the clearance was blocked by diisopropylphosphoryl-thrombin. Electrophoresis experiments confirmed that by 2 min after injection into the murine circulation, 90% of the bound Factor Xa was on alpha 2-macroglobulin, in marked contrast to the in vitro results. Organ distribution studies at 3 and 15 min with 125I-Factor Xa demonstrated that the majority of radioactivity was in the liver, with significant radioactivity also present in lung and kidney. Autopsies performed 30 s after injection of 125I-Factor Xa also demonstrated significant binding to the aorta and vena cava. These studies indicate that Factor Xa binds to specific thrombin-binding sites on endothelial cells, and that this binding alters its proteinase inhibitor specificity. Factor Xa binds to alpha 2-macroglobulin in vivo, whereas the predominant in vitro inhibitor of Factor Xa is alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abildgaard U., Lie M., Odegård O. R. Antithrombin (heparin cofactor) assay with "new" chromogenic substrates (S-2238 and Chromozym TH). Thromb Res. 1977 Oct;11(4):549–553. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aurell L., Friberger P., Karlsson G., Claeson G. A new sensitive and highly specific chromogenic peptide substrate for factor Xa. Thromb Res. 1977 Nov;11(5):595–609. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awbrey B. J., Hoak J. C., Owen W. G. Binding of human thrombin to cultured human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4092–4095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Starkey P. M. The interaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin with proteinases. Characteristics and specificity of the reaction, and a hypothesis concerning its molecular mechanism. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):709–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1330709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beatty K., Travis J., Bieth J. The effect of alpha 2-macroglobulin on the interaction of alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor with porcine trypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 4;704(2):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsodi A. D., Bradshaw R. A. Isolation of antithrombin III from normal and alpha1-antitrypsin-deficient human plasma. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Aug 31;38(2):475–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase T., Jr, Shaw E. p-Nitrophenyl-p'-guanidinobenzoate HCl: a new active site titrant for trypsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 30;29(4):508–514. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90513-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Jacocks R. M., Ferrell G. L., Esmon C. T. Activation of protein C in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jul;70(1):127–134. doi: 10.1172/JCI110584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David G. S., Reisfeld R. A. Protein iodination with solid state lactoperoxidase. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 26;13(5):1014–1021. doi: 10.1021/bi00702a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio R. G., Hermodson M. A., Davie E. W. Activation of human factor X (Stuart factor) by a protease from Russell's viper venom. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 29;16(24):5253–5260. doi: 10.1021/bi00643a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing M. R., Bloom J. W., Mann K. G. Comparison of the inhibition of thrombin by three plasma protease inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2649–2653. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Scully M., MacGregor I., Kakkar V. Inhibition of human factor Xa by various plasma protease inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 4;701(1):24–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Esmon N. L., Harris K. W. Complex formation between thrombin and thrombomodulin inhibits both thrombin-catalyzed fibrin formation and factor V activation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7944–7947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs H. E., Shifman M. A., Pizzo S. V. In vivo catabolism of alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor-trypsin, antithrombin III-thrombin and alpha 2-macroglobulin-methylamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 27;716(2):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90263-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O. Determination of alpha-2-macroglobulin as trypsin-protein esterase. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Oct;14(4):493–501. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O. Inhibition of plasmin activity by alpha-2-macroglobulin. Clin Chim Acta. 1967 May;16(2):328–329. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(67)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Balber A. E., Hubbard W. J., Pizzo S. V. Ligand binding, conformational change and plasma elimination of human, mouse and rat alpha-macroglobulin proteinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):99–105. doi: 10.1042/bj2090099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Einarsson M., Pizzo S. V. Catabolic pathways for streptokinase, plasmin, and streptokinase activator complex in mice. In vivo reaction of plasminogen activator with alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):412–423. doi: 10.1172/JCI110631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. K., Roberts R. C. Physical and chemical properties of human plasma alpha2-macroglobulin. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 1;173(1):27–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1730027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin. An inhibitor of plasma kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):329–352. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Rosenberg R. D. Alpha 2-macroglobulin and antithrombin-heparin cofactor: modulators of hemostatic and inflammatory reactions. Alpha 2-macroglobulin. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:145–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imber M. J., Pizzo S. V. Clearance and binding of two electrophoretic "fast" forms of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8134–8139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Nemerson Y. Blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:765–811. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan R. E., Oosta G. M., Gardner W. T., Rosenberg R. D. The binding of low molecular weight heparin to hemostatic enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10073–10080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Activation of human factor XI (plasma thromboplastin antecedent) by factor XIIa (activated Hageman factor). Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5831–5839. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Fujikawa K., Schmer G., Davie E. W. Inhibition of bovine factor IXa and factor Xabeta by antithrombin III. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):373–377. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Schmer G., Hermodson M. A., Teller D. C., Davie E. W. Characterization of human, bovine, and horse antithrombin III. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):368–373. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanchantin G. F., Plesset M. L., Friedmann J. A., Hart D. W. Dissociation of esterolytic and clotting activities of thrombin by trypsin-binding macroglobulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Feb;121(2):444–449. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Owen W. G. Clearance of thrombin from circulation in rabbits by high-affinity binding sites on endothelium. Possible role in the inactivation of thrombin by antithrombin III. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1222–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI109973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr, Majerus P. W. The synthesis of sulfated dextran beads for isolation of human plasma coagulation factors II, IX, and X. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):304–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannell R., Johnson D., Travis J. Isolation and properties of human plasma alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5439–5445. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peake I. R., Bloom A. L. The dissociation of factor VIII by reducing agents, high salt concentration and affinity chromatography. Thromb Haemost. 1976 Feb 29;35(1):191–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Damus P. S. The purification and mechanism of action of human antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6490–6505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Oosta G. M., Jordan R. E., Gardner W. T. The interaction of heparin with thrombin and antithrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Oct 16;96(3):1200–1208. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvesen G. S., Barrett A. J. Covalent binding of proteinases in their reaction with alpha 2-macroglobulin. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):695–701. doi: 10.1042/bj1870695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman S., Theodor I., Rapaport S. I. Separation from Russell's viper venom of one fraction reacting with factor X and another reacting with factor V. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1397–1405. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. Inhibition by C1INH of Hagemann factor fragment activation of coagulation, fibrinolysis, and kinin generation. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1402–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI107313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. F., Schapira M., James H. L., Cohen A. B., Colman R. W. Inactivation of factor XIa by plasma protease inhibitors: predominant role of alpha 1-protease inhibitor and protective effect of high molecular weight kininogen. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):844–852. doi: 10.1172/JCI110524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shifman M. A., Pizzo S. V. In vivo metabolism of reversibly inhibited alpha-thrombin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Feb 15;32(4):739–741. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shifman M. A., Pizzo S. V. The in vivo metabolism of antithrombin III and antithrombin III complexes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3243–3248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahara H., Sinohara H. Mouse plasma trypsin inhibitors. Isolation and characterization of alpha-1-antitrypsin and contrapsin, a novel trypsin inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2438–2446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. R. High affinity binding of human and bovine thrombins to p-chlorobenzylamido-epsilon-aminocaproyl agarose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 23;422(1):200–209. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff M., Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing buffers using multiphasic buffer systems: properties of the stack, valid Rf- measurement, and optimized procedure. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):459–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin E. T., Wessler S., Stoll P. J. Rabbit plasma inhibitor of the activated species of blood coagulation factor X. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3694–3702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



