Abstract
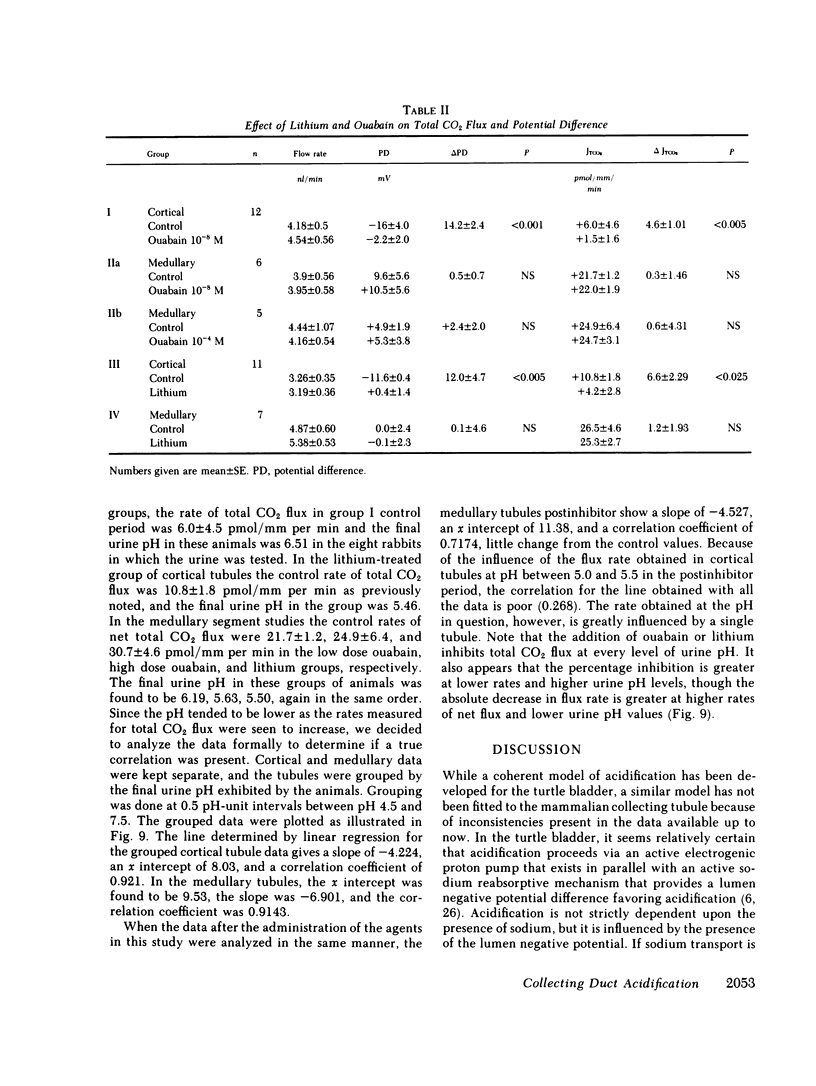
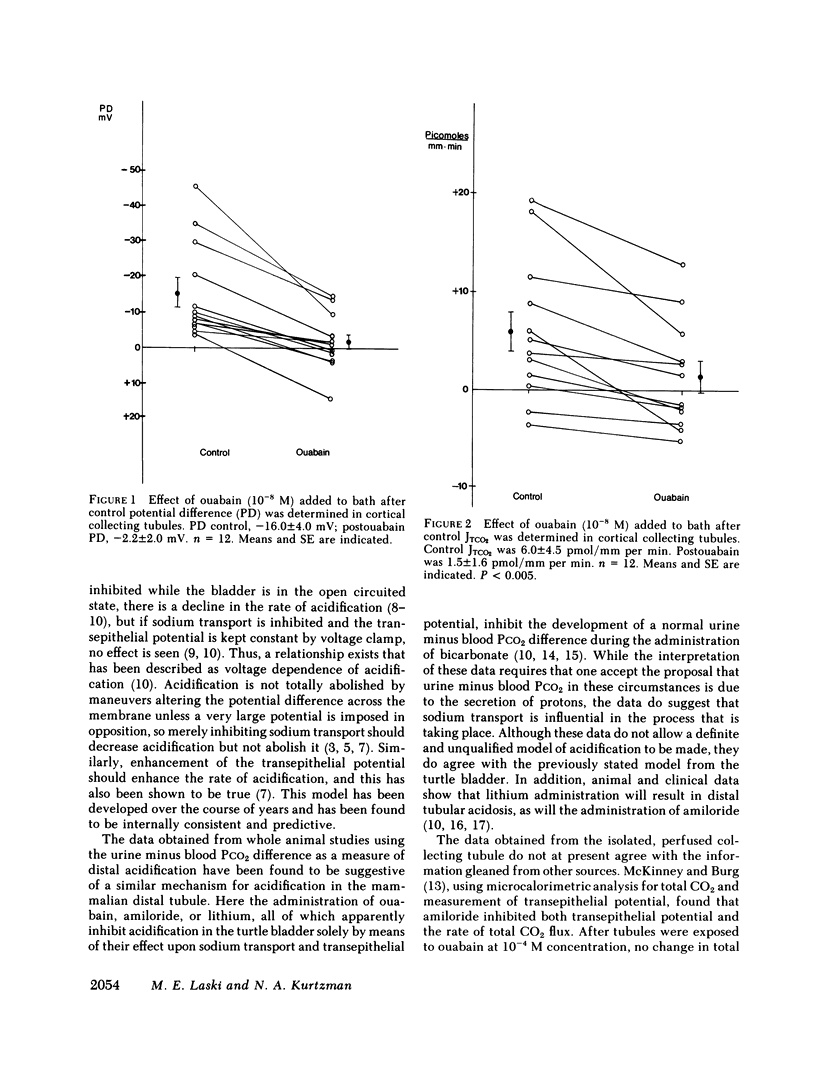
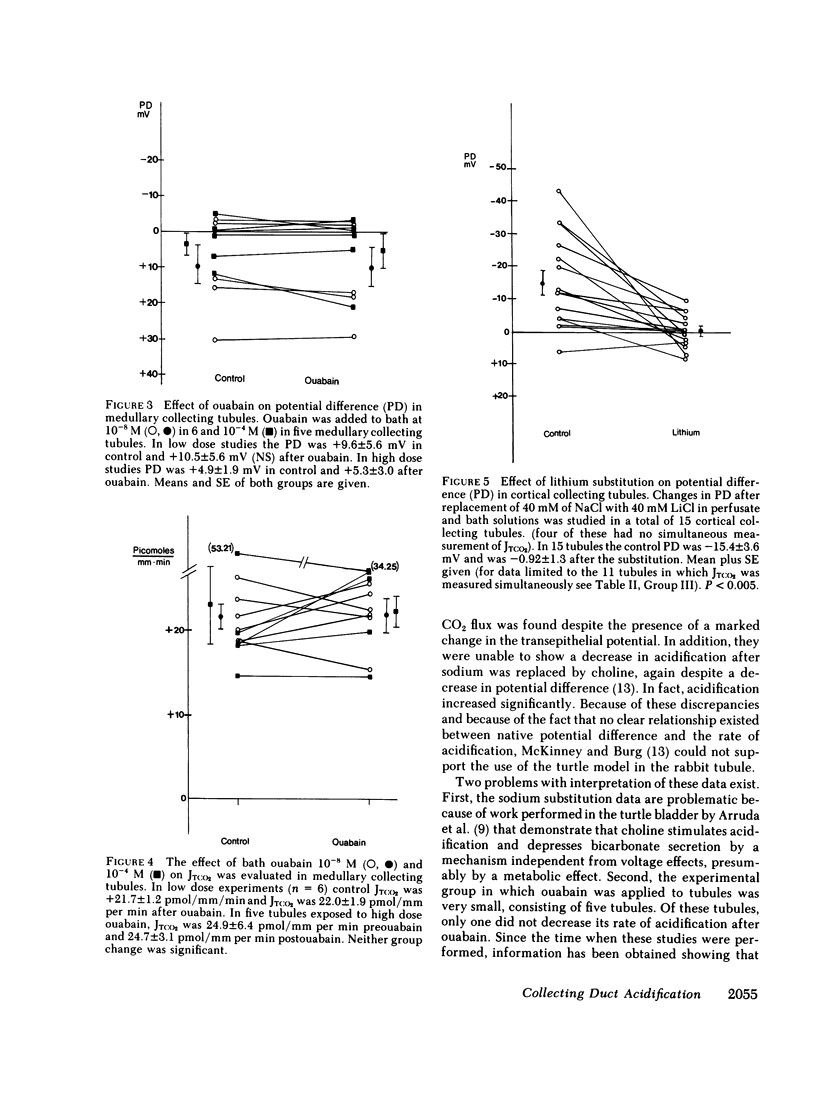
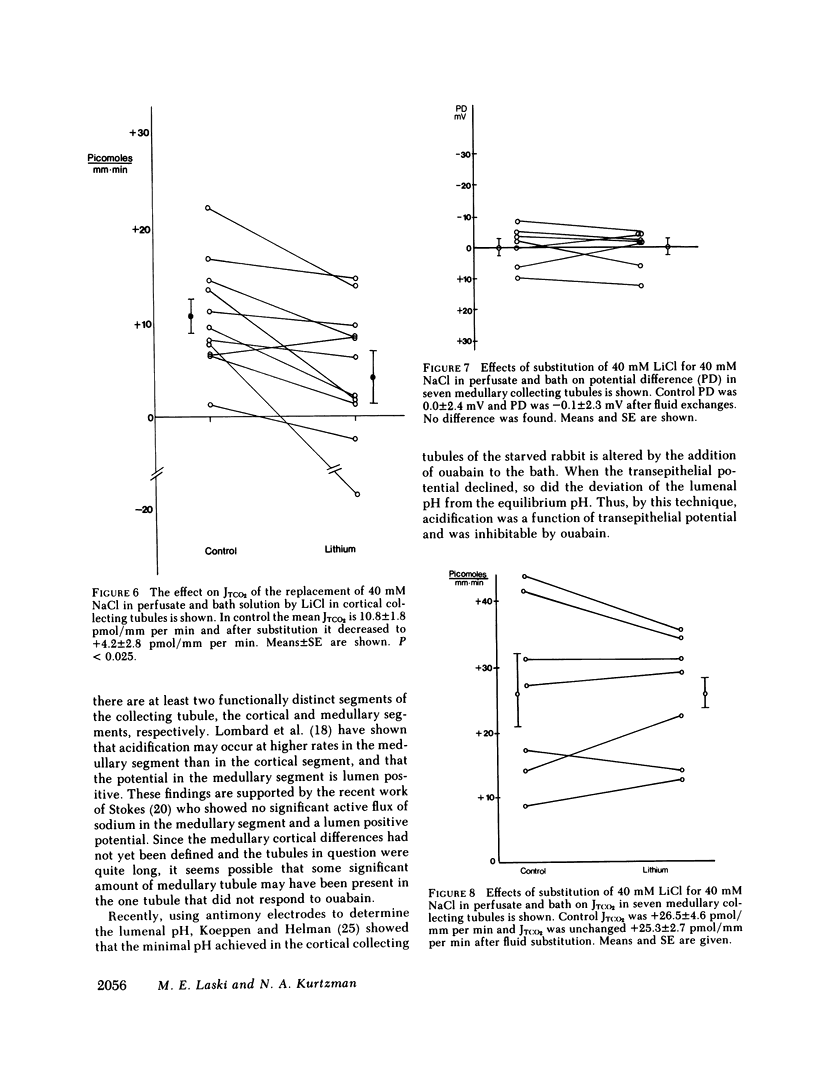
Ouabain and lithium decrease acidification in open-circuited bladders by eliminating the electrical gradient favoring acidification. The effect of ouabain and lithium on acidification in cortical and medullary collecting tubules derived from starved New Zealand white rabbits was studied by using the techniques of isolated nephron microperfusion and microcalorimetric determination of total CO2 flux. Bath and perfusion solutions were symmetric throughout all studies, and solutions contained 25 meq of bicarbonate and were bubbled with 93.3% O2/6.7% CO2 gas mixtures. In cortical collecting tubules, ouabain (10(-8) M) addition to bath resulted in a decrease in both potential difference (PD), from -16.4 to -2.2 mV (P less than 0.001), and total CO2 flux (JTCO2), from +6.0 to 1.5 pmol/mm per min (P less than 0.005). In medullary collecting tubules neither PD nor JTCO2 changed with the addition of ouabain in either 10(-8) or 10(-4) M concentration. Replacement of 40 mM NaCl with 40 mM LiCl in both perfusate and bath in cortical collecting tubules resulted in decreases in both PD, from -11.6 to 0.4 mV (P less than 0.005), and JTCO2, from +10.8 to +4.2 pmol/mm per min (P less than 0.025). This substitution had no effect on medullary collecting tubules. When control flux rates were plotted against animal bladder urine pH, both medullary and cortical tubules showed good inverse correlation between these variables, with higher values of flux rate for the medullary tubules. The data support a role for transepithelial PD in acidification in the cortical collecting tubule and also suggest that both cortical and medullary segments of the collecting tubule participate when urinary acidification is increased during starvation in the rabbit.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-awqati Q., Mueller A., Steinmetz P. R. Transport of H+ against electrochemical gradients in turtle urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):F502–F508. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.6.F502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arruda J. A., Dytko G., Mola R., Kurtzman N. A. On the mechanism of lithium-induced renal tubular acidosis: studies in the turtle bladder. Kidney Int. 1980 Feb;17(2):196–204. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arruda J. A., Subbarayudu K., Dytko G., Mola R., Kurtzman N. A. Voltage-dependent distal acidification defect induced by amiloride. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Mar;95(3):407–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batlle D., Gaviria M., Grupp M., Arruda J. A., Wynn J., Kurtzman N. A. Distal nephron function in patients receiving chronic lithium therapy. Kidney Int. 1982 Mar;21(3):477–485. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauwens R., Al-Awqati Q. Active H+ transport in the turtle urinary bladder. Coupling of transport to glucose oxidation. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Oct;68(4):421–439. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.4.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B. Perfusion of isolated renal tubules. Yale J Biol Med. 1972 Jun-Aug;45(3-4):321–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Grantham J., Abramow M., Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frindt G., Burg M. B. Effect of vasopressin on sodium transport in renal cortical collecting tubules. Kidney Int. 1972 Apr;1(4):224–231. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husted R. F., Steinmetz P. R. The effects of amiloride and ouabain on urinary acidification by turtle bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Aug;210(2):264–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen B. M., Helman S. I. Acidification of luminal fluid by the rabbit cortical collecting tubule perfused in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):F521–F531. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.5.F521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombard W. E., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Bicarbonate transport in cortical and outer medullary collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1983 Mar;244(3):F289–F296. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.3.F289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludens J. H., Fanestil D. D. Acidification of urine by the isolated urinary bladder of the toad. Am J Physiol. 1972 Dec;223(6):1338–1344. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.6.1338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney T. D., Burg M. B. Bicarbonate absorption by rabbit cortical collecting tubules in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1978 Feb;234(2):F141–F145. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.2.F141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento L., Rademacher D. R., Hamburger R., Arruda J. A., Kurtzman A. On the mechanism of lithium-induced renal tubular acidosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Mar;89(3):455–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ W. B., JENSON R. L., RELMAN A. S. Acidification of the urine and increased ammonium excretion without change in acid-base equilibrium: sodium reabsorption as a stimulus to the acidifying process. J Clin Invest. 1955 May;34(5):673–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI103117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. J., Kokko J. P. Urinary concentrating defect of adrenal insufficiency. Permissive role of adrenal steroids on the hydroosmotic response across the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):234–242. doi: 10.1172/JCI109849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz P. R., Andersen O. S. Electrogenic proton transport in epithelial membranes. J Membr Biol. 1982;65(3):155–174. doi: 10.1007/BF01869960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz P. R. Cellular mechanisms of urinary acidification. Physiol Rev. 1974 Oct;54(4):890–956. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.4.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz P. R. Characteristics of hydrogen ion transport in urinary bladder of water turtle. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1531–1540. doi: 10.1172/JCI105644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B. Na and K transport across the cortical and outer medullary collecting tubule of the rabbit: evidence for diffusion across the outer medullary portion. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):F514–F520. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.5.F514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B., Tisher C. C., Kokko J. P. Structural-functional heterogeneity along the rabbit collecting tubule. Kidney Int. 1978 Dec;14(6):585–593. doi: 10.1038/ki.1978.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone D. K., Seldin D. W., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Mineralocorticoid modulation of rabbit medullary collecting duct acidification. A sodium-independent effect. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):77–83. doi: 10.1172/JCI110986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner L. C., Burg M. B., Orloff J. Ion transport in cortical collecting tubule; effect of amiloride. Am J Physiol. 1974 Aug;227(2):453–459. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.2.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vurek G. G., Warnock D. G., Corsey R. Measurement of picomole amounts of carbon dioxide by calorimetry. Anal Chem. 1975 Apr;47(4):765–767. doi: 10.1021/ac60354a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westenfelder C., Birch F. M., Baranowski R. L., Wheeler C., Earnest W. R., Kurtzman N. A. Effect of Na-K-ATPase inhibition on hydrogen ion and potassium secretion. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Jul;386(2):161–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00584204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler T. W., Fanestil D. D., Ludens J. H. Influence of transepithelial potential difference on acidification in the toad urinary bladder. Kidney Int. 1976 Oct;10(4):279–286. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


