Abstract
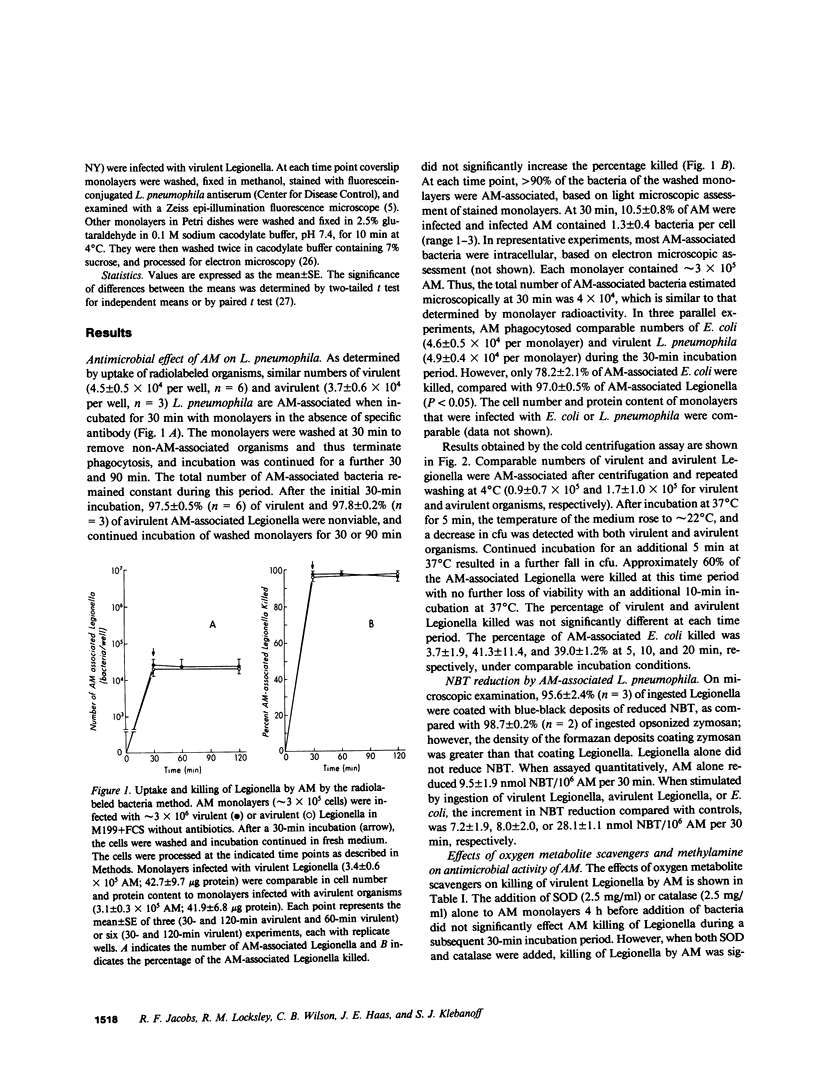
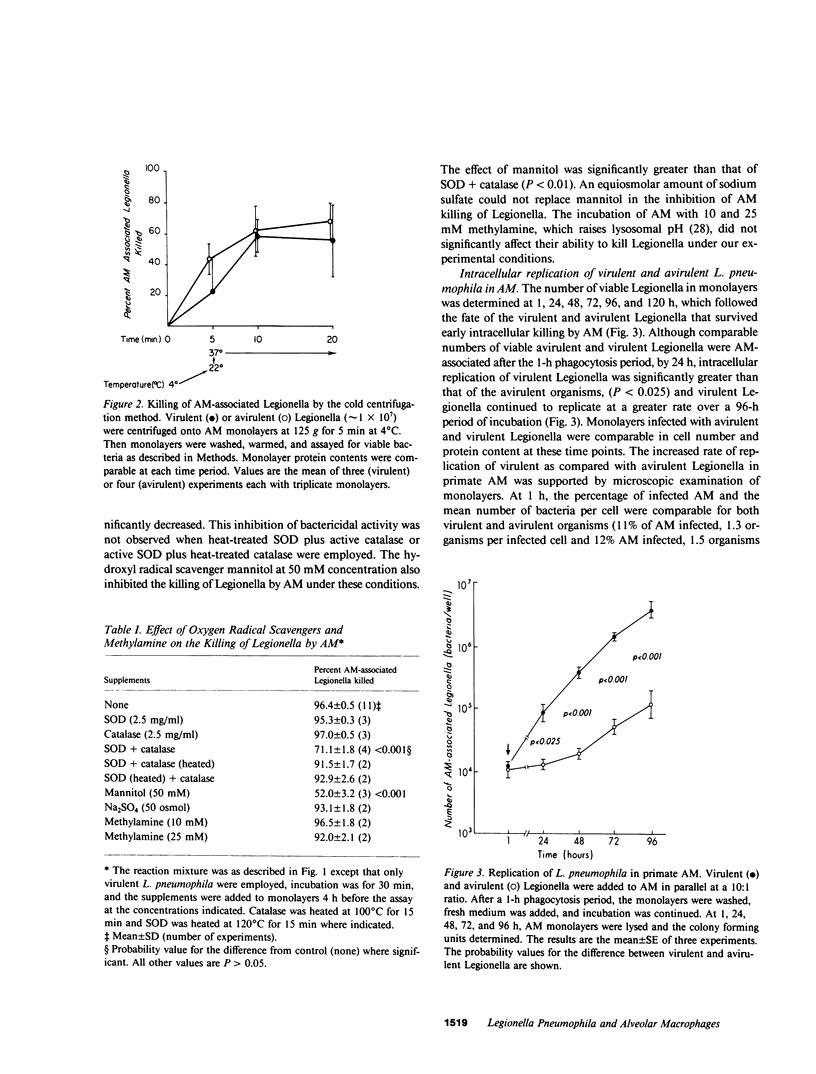
We studied the interaction between Legionella pneumophila, which is principally a pulmonary pathogen, with primate alveolar macrophages (AM), which are the primary pulmonary cellular defense mechanism. For these studies we used L. pneumophila, type I, which were grown in albumin-yeast extract broth, were greater than 80% viable, and were comparable in virulence for guinea pigs to organisms from guinea pig spleen homogenates. For comparison, avirulent agar-passed L. pneumophila, type I, and a strain of Escherichia coli were also used. In the absence of detectable antibody, AM phagocytosed similar numbers of virulent and avirulent Legionella and killed the majority of ingested Legionella in 15-30 min, as determined by two different assays. The virulent and avirulent Legionella appeared to be equally susceptible to the cidal systems of the AM and both were killed more readily than were E. coli under both assay conditions. Phagocytosis of Legionella by AM was associated with a localized respiratory burst, as indicated by nitroblue tetrazolium reduction around ingested organisms. Killing of AM-associated Legionella was inhibited by the hydroxyl radical (OH.) scavenger mannitol (but not by an equiosmolar concentration of sodium sulfate), and by a combination of superoxide dismutase and catalase (but not by either enzyme alone). These findings suggest a contribution by OH., one generated by the metal-catalyzed interaction of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide (Haber-Weiss reaction) in the anti-Legionella activity of AM. The virulent Legionella that survived intracellularly increased in number from 4 X 10(4) at 1 h to 6 X 10(6) at 96 h after infection. In contrast, avirulent Legionella replicated more slowly, increasing in number from 4 X 10(4) to 1 X 10(5) over the same period. Replication of virulent Legionella destroyed the AM monolayers by 120 h, whereas monolayers containing avirulent organisms remained intact. Thus, virulence of Legionella appears not to correlate with its ability to survive early killing by AM, but rather with the ability of the small fraction of surviving organisms to replicate within these cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baskerville A., Dowsett A. B., Fitzgeorge R. B., Hambleton P., Broster M. Ultrastructure of pulmonary alveoli and macrophages in experimental Legionnaires' disease. J Pathol. 1983 Jun;140(2):77–90. doi: 10.1002/path.1711400202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmon J. A., Chandler F. W., Cherry W. B., England A. C., 3rd, Feeley J. C., Hicklin M. D., McKinney R. M., Wilkinson H. W. Legionellosis. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jun;103(3):429–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodel P. T., Nichols B. A., Bainton D. F. Appearance of peroxidase reactivity within the rough endoplasmic reticulum of blood monocytes after surface adherence. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):264–274. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Nutritional profiles of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Neisseria lactamica in chemically defined media and the use of growth requirements for gonococcal typing. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):178–194. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulley J. R., Grieve P. A. A simple technique for eliminating interference by detergents in the Lowry method of protein determination. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):136–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Weaver R. E., Mackel D. C., Smith H. W. Primary isolation media for Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.320-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., McDade J. E. Legionellosis. Sci Am. 1979 Oct;241(4):82–99. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1079-82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Orenstein W., Parkin W. E., Beecham H. J., Sharrar R. G., Harris J., Mallison G. F., Martin S. M., McDade J. E. Legionnaires' disease: description of an epidemic of pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1189–1197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmke R. J., Kalter S. S., Heberling R. L. Distribution of Legionella pneumophilia antibody among primate species. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Mar;13(3):508–512. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.3.508-512.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Formation of a novel phagosome by the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1319–1331. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Activated human monocytes inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionnaires' disease bacteria. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1618–1635. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Interaction of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) with human phagocytes. I. L. pneumophila resists killing by polymorphonuclear leukocytes, antibody, and complement. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):386–397. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Interaction of the legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) with human phagocytes. II. Antibody promotes binding of L. pneumophila to monocytes but does not inhibit intracellular multiplication. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):398–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) multiples intracellularly in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):441–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI109874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W., Pesanti E., Elliott J. Serospecificity and opsonic activity of antisera to Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):698–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.698-704.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLOW L. S. SIMPLIFIED MYELOPEROXIDASE STAIN USING BENZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby B. D., Snyder K. M., Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Legionnaires' disease: clinical features of 24 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Sep;89(3):297–309. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto R. A., Kastello M. D., White J. D., Shirey F. G., McGann V. G., Larson E. W., Hedlund K. W. In vitro interaction between normal cynolmolgus monkey alveolar macrophages and Legionnaires disease bacteria. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):761–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.761-763.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto R. A., White J. D., Shirey F. G., McGann V. G., Berendt R. F., Larson E. W., Hedlund K. W. In vitro responses of guinea pig peritoneal macrophages to Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1209–1213. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1209-1213.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locksley R. M., Jacobs R. F., Wilson C. B., Weaver W. M., Klebanoff S. J. Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to oxygen-dependent microbicidal systems. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2192–2197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. The biology and pathology of oxygen radicals. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jul;89(1):122–127. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-1-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. III. Enhanced oxidative metabolism as an expression of macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1596–1609. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Interaction of Leishmania with a macrophage cell line. Correlation between intracellular killing and the generation of oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1690–1695. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Juangbhanich C. W., Nathan C. F., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. II. The role of oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):950–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Nathan C. F., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. IV. Role of endogenous scavengers of oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1610–1624. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Susceptibility of Leishmania to oxygen intermediates and killing by normal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1302–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Nogueira N., Juangbhanich C., Ellis J., Cohn Z. Activation of macrophages in vivo and in vitro. Correlation between hydrogen peroxide release and killing of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1056–1068. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehm S. R., Gross G. N., Pierce A. K. Early bacterial clearance from murine lungs. Species-dependent phagocyte response. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):194–199. doi: 10.1172/JCI109844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Cohen M. S. The microbicidal mechanisms of human neutrophils and eosinophils. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):565–598. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Bactericidal activity of a superoxide anion-generating system. A model for the polymorphonuclear leukocyte. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):27–39. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Role of iron and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid in the bactericidal activity of a superoxide anion-generating system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 May;208(2):512–519. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Kiyotaki C., Tanowitz H., Bloom B. R. Reconstitution of a variant macrophage cell line defective in oxygen metabolism with a H2O2-generating system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2584–2588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Remington J. S. Activity of human blood leukocytes against Toxoplasma gondii. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):890–895. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Tsai V., Remington J. S. Failure to trigger the oxidative metabolic burst by normal macrophages: possible mechanism for survival of intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):328–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr, Myerowitz R. L. The pathology of the Legionella pneumonias. A review of 74 cases and the literature. Hum Pathol. 1981 May;12(5):401–422. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. C., Ewing E. P., Jr, Callaway C. S., Peacock W. L., Jr Intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila in cultured human embryonic lung fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1014–1018. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1014-1018.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]