Abstract
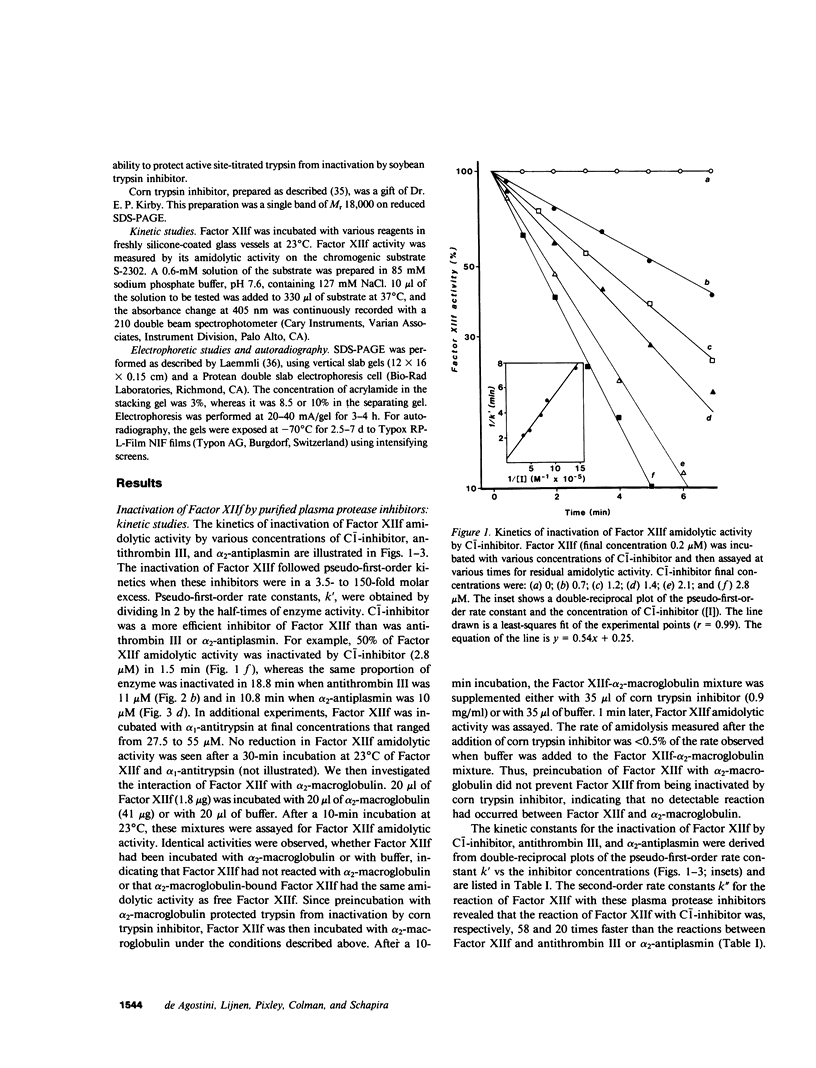
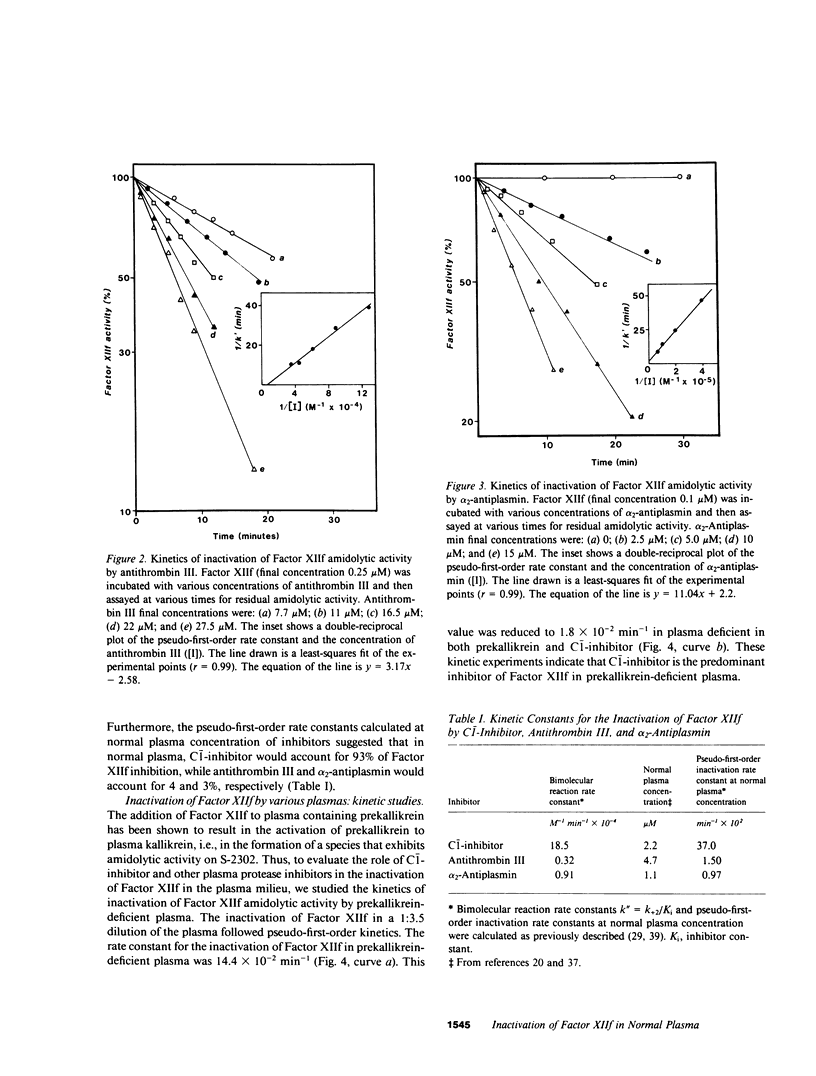
To define the factors responsible for the inactivation of the active fragment derived from Factor XII (Factor XIIf ) in plasma, we studied the inactivation kinetics of Factor XIIf in various purified and plasma mixtures. We also analyzed the formation of 125I-Factor XIIf -inhibitor complexes by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). In purified systems, the bimolecular rate constants for the reactions of Factor XIIf with C-1-inhibitor, alpha 2-antiplasmin, and antithrombin III were 18.5, 0.91, and 0.32 X 10(4) M-1 min-1, respectively. Furthermore, SDS-PAGE analysis revealed that 1:1 stoichiometric complexes were formed between 125I-Factor XIIf and each of these three inhibitors. In contrast, kinetic and SDS-PAGE studies indicated that Factor XIIf did not react with alpha 1-antitrypsin or alpha 2-macroglobulin. The inactivation rate constant of Factor XIIf by prekallikrein-deficient plasma was 14.4 X 10(-2) min-1, a value that was essentially identical to the value predicted from the studies in purified systems (15.5 X 10(-2) min-1). This constant was reduced to 1.8 X 10(-2) min-1 when Factor XIIf was inactivated by prekallikrein-deficient plasma that had been immunodepleted (less than 5%) of C-1-inhibitor. In addition, after inactivation in normal plasma, 74% of the active 125I-Factor XIIf was found to form a complex with C-1-inhibitor, whereas 26% of the enzyme formed complexes with alpha 2-antiplasmin and antithrombin III. Furthermore, 42% of the labeled enzyme was still complexed with C-1-inhibitor when 125I-Factor XII was inactivated in hereditary angioedema plasma that contained 32% of functional C-1-inhibitor. This study quantitatively demonstrates the dominant role of C-1-inhibitor in the inactivation of Factor XIIf in the plasma milieu.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alving B. M., Hojima Y., Pisano J. J., Mason B. L., Buckingham R. E., Jr, Mozen M. M., Finlayson J. S. Hypotension associated with prekallikrein activator (Hageman-factor fragments) in plasma protein fraction. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jul 13;299(2):66–70. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197807132990203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. Identification and some properties of a new fast-reacting plasmin inhibitor in human plasma. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):209–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H., EVANS R. R. A BIOCHEMICAL ABNORMALITY IN HEREDIATRY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: ABSENCE OF SERUM INHIBITOR OF C' 1-ESTERASE. Am J Med. 1963 Jul;35:37–44. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H., ROSEN F. S. ACTION OF COMPLEMENT IN HEREDITARY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: THE ROLE OF C'1-ESTERASE. J Clin Invest. 1964 Nov;43:2204–2213. doi: 10.1172/JCI105094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H. Mechanisms of activation of C'1 esterase in hereditary angioneurotic edema plasma in vitro. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):411–429. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. T., Kaplan A. P. Formation and structure of human Hageman factor fragments. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):627–631. doi: 10.1172/JCI110656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. T., Silverberg M., Kaplan A. P. The cleavage and formation of activated human Hageman factor by autodigestion and by kallikrein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1779–1784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. A., Schmaier A. H., Addonizio V. P., Colman R. W. Assay of prekallikrein in human plasma: comparison of amidolytic, esterolytic, coagulation, and immunochemical assays. Blood. 1982 May;59(5):963–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet B., Silverberg M., Kaplan A. P. Activation of the classical pathway of complement by Hageman factor fragment. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):665–676. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith G. H., Jr, Saito H., Ratnoff O. S. The activation of plasminogen by Hageman factor (Factor XII) and Hageman factor fragments. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):54–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI109113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. A pre-albumin activator of prekallikrein. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):802–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. A prealbumin activator of prekallikrein. II. Derivation of activators of prekallikrein from active Hageman factor by digestion with plasmin. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):696–712. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby E. P., McDevitt P. J. The binding of bovine factor XII to kaolin. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):652–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Hoylaerts M., Collen D. Isolation and characterization of a human plasma protein with affinity for the lysine binding sites in plasminogen. Role in the regulation of fibrinolysis and identification as histidine-rich glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10214–10222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radcliffe R., Bagdasarian A., Colman R., Nemerson Y. Activation of bovine factor VII by hageman factor fragments. Blood. 1977 Oct;50(4):611–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Pensky J., Ogston D., Naff G. B. The inhibition of plasmin, plasma kallikrein, plasma permeability factor, and the C'1r subcomponent of the first component of complement by serum C'1 esterase inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1969 Feb 1;129(2):315–331. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D. Studies on the inhibition of ellagic acid-activated Hageman factor (factor XII) and Hageman factor fragments. Blood. 1981 Jan;57(1):55–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reboul A., Arlaud G. J., Sim R. B., Colomb M. G. A simplified procedure for the purification of C1-inactivator from human plasma. Interaction with complement subcomponents C1r and C1s. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G., Bouma B. N., Griffin J. H. Surface and fluid phase activities of two forms of activated Hageman factor produced during contact activation of plasma. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):719–729. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G., Griffin J. H. The binding and cleavage characteristics of human Hageman factor during contact activation. A comparison of normal plasma with plasmas deficient in factor XI, prekallikrein, or high molecular weight kininogen. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1167–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI108741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G., Johnston A. R., Hugli T. E. Structural changes accompanying enzymatic activation of human Hageman factor. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):619–627. doi: 10.1172/JCI107799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G. The relationship of structure and function in human Hageman factor. The association of enzymatic and binding activities with separate regions of the molecule. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):852–860. doi: 10.1172/JCI108361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Goldsmith G. H., Moroi M., Aoki N. Inhibitory spectrum of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2013–2017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Contribution of plasma protease inhibitors to the inactivation of kallikrein in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):462–468. doi: 10.1172/JCI110470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Protection of human plasma kallikrein from inactivation by C1 inhibitor and other protease inhibitors. The role of high molecular weight kininogen. Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2738–2743. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., James A., Silver L. D., Kueppers F., James H. L., Colman R. W. High molecular weight kininogen or its light chain protects human plasma kallikrein from inactivation by plasma protease inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):567–572. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Silver L. D., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. New and rapid functional assay for C1 inhibitor in human plasma. Blood. 1982 Apr;59(4):719–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Silver L. D., Scott C. F., Schmaier A. H., Prograis L. J., Jr, Curd J. G., Colman R. W. Prekallikrein activation and high-molecular-weight kininogen consumption in hereditary angioedema. N Engl J Med. 1983 May 5;308(18):1050–1053. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198305053081802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. Inhibition by C1INH of Hagemann factor fragment activation of coagulation, fibrinolysis, and kinin generation. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1402–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI107313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. F., Liu C. Y., Colman R. W. Human plasma prekallikrein: a rapid high-yield method for purification. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):77–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Petersen T. E., Magnusson S. A thiol-ester in alpha 2-macroglobulin cleaved during proteinase complex formation. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 1;121(2):275–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80361-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead N., Kaplan A. P., Rosenberg R. D. Inhibition of activated factor XII by antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6481–6488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tankersley D. L., Alving B. M., Finlayson J. S. Preparation of beta-XIIa (Hageman factor fragment) from human plasma. Thromb Res. 1982 Feb 15;25(4):307–317. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rosevelt R. F., Bakker J. C., Sinclair D. M., Damen J., Van Mourik J. A. Bradykinin-mediated hypotension after infusion of plasma-protein fraction. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Aug;100(2):288–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B. Affinity-chromatographic purification of human alpha 2-antiplasmin. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):229–232. doi: 10.1042/bj1910229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J. Activation of the early components of the classical complement pathway under physiologic conditions. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1769–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Graaf F., Koedam J. A., Bouma B. N. Inactivation of kallikrein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):149–158. doi: 10.1172/JCI110743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]